| Previous | Contents | Index |
In either case, the newly created security profile can be passed as input to the $CHKPRO and $CHECK_ACCESS system services using the usrpro argument.
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns the set of identifiers associated with the user's owner identifier. The CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item code can be used to add additional identifiers to this set.
Access to SYSUAF.DAT and RIGHTSLIST.DAT is required unless you are constructing the security profile for your own user name.
None
$CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $FIND_HELD, $FINISH_RDB, $GETUAI
SS$_NORMAL Profile created successfully. SS$_BADITMCOD Item list code is invalid. SS$_BADBUFLEN Size specified for item is invalid. SS$_ACCVIO Buffer address is invalid or inaccessible. SS$_INSFARG Insufficient call arguments. SS$_INSFMEM Insufficient memory. SS$_IVSTSFLG Invalid system service flags specified. SS$_NOPRIV Caller lacks privilege to access UAF. RMS$_RNF User name is not in UAF.
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE can also return any error returned by the $GETUAI or $FIND_HELD services.
Creates a logical name and specifies its equivalence names.On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$CRELNM [attr] ,tabnam ,lognam ,[acmode] ,[itmlst]
int sys$crelnm (unsigned int *attr, void *tabnam, void *lognam, unsigned char *acmode, void *itmlst);
attr
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Attributes to be associated with the logical name. The attr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword bit mask specifying these attributes.Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic name. These symbolic names are defined by the $LNMDEF macro. To specify an attribute, specify its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit. The longword bit mask is the logical OR of all desired attributes. All undefined bits in the longword must be 0.
If you do not specify this argument or specify it as 0 (no bits set), no attributes are associated with the logical name.
The attributes are as follows:
Attribute Description LNM$M_CONFINE If set, the logical name is not copied from the process to its spawned subprocesses. You create a subprocess with the DCL command SPAWN or the LIB$SPAWN Run-Time Library routine. If the logical name is placed into a process-private table that has the CONFINE attribute, the CONFINE attribute is automatically associated with the logical name. This applies only to process-private logical names. LNM$M_NO_ALIAS If set, the logical name cannot be duplicated in this table at an outer access mode. If another logical name with the same name already exists in the table at an outer access mode, it is deleted.
tabnam
OpenVMS usage: logical_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the table in which to create the logical name. The tabnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a descriptor that points to the name of this table. This argument is required and must be specified in uppercase.The name must be entered in uppercase letters. (This requirement differs from the $CRELNT system service, which automatically changes tabnam to uppercase.)
If tabnam is not the name of a logical name table, it is assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively until either the name of a logical name table is found or the number of translations allowed by the system has been performed. If tabnam translates to a list of logical name tables, the logical name is entered into the first table in the list.
lognam
OpenVMS usage: logical_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the logical name to be created. The lognam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a descriptor that points to the logical name string.Logical name strings of logical names created within either the system or process directory table must consist of uppercase alphanumeric characters, dollar signs ($), hyphens (-), and underscores (_); the maximum length is 31 characters. The maximum length of logical name strings created within other tables is 255 characters with no restrictions on the types of characters that can be used. This argument is required.
acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: byte (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Access mode to be associated with the logical name. The acmode argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a byte that specifies the access mode.The access mode associated with the logical name is determined by maximizing the access mode of the caller with the access mode specified by the acmode argument, which means that the less privileged of the two is used. Symbols for the four access modes are defined by the $PSLDEF macro.
You cannot specify an access mode more privileged than that of the containing table. However, if the caller has SYSNAM privilege, then the specified access mode is associated with the logical name regardless of the access mode of the caller.
If you omit this argument or specify it as 0, the access mode of the caller is associated with the logical name.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list 64b type: longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Item list describing the equivalence names to be defined for the logical name and information to be returned to the caller. The itmlst argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a list of item descriptors, each of which specifies information about an equivalence name. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or 64-bit.Note that it is possible to create a logical that has no equivalence names. This is done by either omitting the itmlst argument to $CRELNM, or by not including the LNM$_STRING item code to the itmlst data structure that is passed into $CRELNM. It is not possible to create this kind of logical using DCL.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item descriptor:
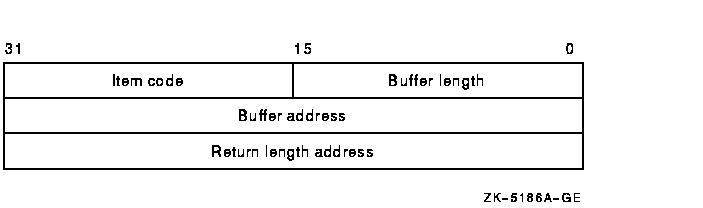
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item list entries:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service truncates the data. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the 32-bit address of the buffer that receives or passes information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the 32-bit address of a word specifying the actual length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The return length address field is used only when the item code specified is LNM$_TABLE. Although this field is ignored for all other item codes, it must nevertheless be present as a placeholder in each item descriptor. |
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item descriptor:
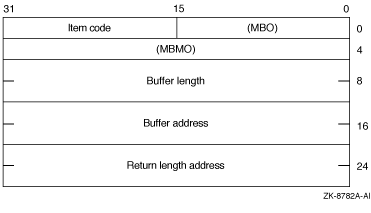
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item list entries:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| MBO | The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes section. |
| MBMO | The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Buffer length | A quadword specifying the number of bytes in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service truncates the data. |
| Buffer address | A quadword containing the 64-bit address of the buffer that receives or passes information. |
| Return length address | A quadword containing the 64-bit address of a word specifying the actual length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. The return length address field is used only when the item code specified is LNM$_TABLE. Although this field is ignored for all other item codes, it must nevertheless be present as a placeholder in each item descriptor. |
LNM$_ATTRIBUTES
When you specify LNM$_ATTRIBUTES, the buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword bit mask that specifies the current translation attributes for the logical name. The current translation attributes are applied to all subsequently specified equivalence strings until another LNM$_ATTRIBUTES item descriptor is encountered in the item list. The symbolic names for these attributes are defined by the $LNMDEF macro. The symbolic name and description of each attribute are as follows:
Attribute Description LNM$M_CONCEALED If set, OpenVMS RMS interprets the equivalence name as a device name or logical name with the LNM$M_CONCEALED attribute. LNM$M_TERMINAL If set, further iterative logical name translation on the equivalence name is not to be performed. LNM$_CHAIN
When you specify LNM$_CHAIN, the buffer address field of the item descriptor points to another item list that $CRELNM is to process immediately after it has processed the current item list.If you specify the LNM$_CHAIN item code, it must be the last item code in the current item list.
You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
LNM$_STRING
When you specify LNM$_STRING, the buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a buffer containing a user-specified equivalence name for the logical name. The maximum length of the equivalence string is 255 characters.When $CRELNM encounters an item descriptor with the item code LNM$_STRING, it creates an equivalence name entry for the logical name using the most recently specified values for LNM$_ATTRIBUTES. The equivalence name entry includes the following information:
- Name specified by LNM$_STRING.
- Next available index value. Each equivalence is assigned a unique value from 0 to 127.
- Attributes specified by the most recently encountered item descriptor with item code LNM$_ATTRIBUTES (if these are present in the item list).
Therefore, you should construct the item list so that the LNM$_ATTRIBUTES item codes immediately precede the LNM$_STRING item code or codes to which they apply.
Note that it is possible to create a logical that has no equivalence names. This is done by either omitting the itmlst argument to $CRELNM, or by not including the LNM$_STRING item code to the itmlst data structure that is passed into $CRELNM. It is not possible to create this kind of logical using DCL.
LNM$_TABLE
When you specify LNM$_TABLE, the buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a buffer in which $CRELNM writes the name of the logical name table in which it entered the logical name. The return length address field points to a word that contains a buffer that specifies the length in bytes of the information returned by $CRELNM. The maximum length of the name of a logical name table is 31 characters.This item code can appear anywhere in the item list.
The Create Logical Name service creates a logical name and specifies its equivalence name. Note that logical names are case sensitive.The calling process must have the following:
- Write access to shareable tables to create logical names in those tables
- GRPNAM or GRPPRV privilege to enter a logical name into the group logical name table
- SYSNAM or SYSPRV privilege to enter a logical name into the system logical name table
The quota for the specified logical name table must be sufficient for the creation of the logical name.
$CRELNT, $DELLNM, $TRNLNM
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully; the logical name has been created. However, if you attempted to create a new clusterwide logical name with the same access mode and identical equivalence names and attributes as an existing clusterwide logical name, this message indicates only that the service completed successfully. Because an identical clusterwide logical name already exists, and because a clusterwide update would adversely affect performance, the name is not created. SS$_SUPERSEDE The service completed successfully; the logical name has been created and a previously existing logical name with the same name has been deleted. SS$_BUFFEROVF The service completed successfully; the buffer length field in an item descriptor specified an insufficient value, so the buffer was not large enough to hold the requested data. SS$_ACCVIO The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments. SS$_BADPARAM One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table name or logical name was not specified. Or, an item list containing both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found. SS$_DUPLNAM An attempt was made to create a logical name with the same name as an already existing logical name, and the existing logical name was created at a more privileged access mode and with the LNM$M_NO_ALIAS attribute. SS$_EXLNMQUOTA The quota associated with the specified logical name table for the creation of the logical name is insufficient. SS$_INSFMEM The dynamic memory is insufficient for the creation of the logical name, or there is insufficient dynamic memory to build a message describing the creation of a clusterwide name. SS$_IVLOGNAM The tabnam argument, the lognam argument, or the equivalence string specifies a string whose length is not in the required range of 1 through 255 characters. The lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not in the required range of 1 to 31 characters for directory table entries. SS$_IVLOGTAB The tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table. SS$_NOLOGTAB Either the specified logical name table does not exist or the logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth of 10 translations. SS$_NOPRIV The caller lacks the necessary privilege to create the logical name. SS$_TOOMANYLNAM An attempt was made to create a logical name with more than 128 equivalence names.
Creates a process-private or shareable logical name table.On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$CRELNT [attr] ,[resnam] ,[reslen] ,[quota]
,[promsk] ,[tabnam] ,partab ,[acmode]
int sys$crelnt (unsigned int *attr, void *resnam, unsigned short int *reslen, unsigned int *quota, unsigned short int *promsk, void *tabnam, void *partab, unsigned char *acmode);
attr
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Attributes to affect the creation of the logical name table and to be associated with the newly created logical name table. The attr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword bit mask specifying these attributes.Each bit in the longword corresponds to an attribute and has a symbolic name. These symbolic names are defined by the $LNMDEF macro. To specify an attribute, specify its symbolic name or set its corresponding bit. The longword bit mask is the logical OR of all desired attributes. All unused bits in the longword must be 0.
If you do not specify this argument or specify it as 0 (no bits set), no attributes are associated with the logical name table or affect the creation of the new table.
The following table describes each attribute:
Attribute Description LNM$M_CONFINE If set, the logical name table is not copied from the process to its spawned subprocesses. You create a subprocess with the DCL command SPAWN or the Run-Time Library LIB$SPAWN routine. You can specify this attribute only for process-private logical name tables; it is ignored for shareable tables. The state of this bit is also propagated from the parent table to the newly created table and can be overridden only if the parent table does not have the bit set. Thus, if the parent table has the LNM$M_CONFINE attribute, the newly created table will also have it, no matter what is specified in the attr argument. On the other hand, if the parent table does not have the LNM$M_CONFINE attribute, the newly created table can be given this attribute through the attr argument. The process-private directory table LNM$PROCESS_DIRECTORY does not have the LNM$M_CONFINE attribute. LNM$M_CREATE_IF This attribute applies to all types of logical name tables except clusterwide logical name tables. If set, a new logical name table is created only if the specified table name is not already entered at the specified access mode in the appropriate directory table. If the table name exists, a new table is not created and no modification is made to the existing table name. This holds true even if the existing name has differing attributes or quota values, or even if it is not the name of a logical name table. If LNM$M_CREATE_IF is not set, the new logical name table will supersede any existing table name with the same access mode within the appropriate directory table. Setting this attribute is useful when two or more users want to create and use the same table but do not want to synchronize its creation.
Regardless of the setting of LNM$M_CREATE_IF:
- You cannot create a new clusterwide logical name table with the same name and the same mode as an existing clusterwide logical name table until you delete the existing one.
- If you specify a new clusterwide logical name table with the same name and access mode as an existing local logical name table, the new clusterwide logical name table is created, and the local table and its logical names are deleted.
LNM$M_NO_ALIAS If set, the name of the logical name table cannot be duplicated at an outer access mode within the appropriate directory table. If this name already exists at an outer access mode, it is deleted. Note that this attribute does not apply to clusterwide logical name tables. resnam
OpenVMS usage: logical_name type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the newly created logical name table, returned by $CRELNT. The resnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a descriptor pointing to this name. The name is a character string whose maximum length is 31 characters.reslen
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Length in bytes of the name of the newly created logical name table, returned by $CRELNT. The reslen argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a word to receive this length.quota
OpenVMS usage: longword_unsigned type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Maximum number of bytes of memory to be allocated for logical names contained in this logical name table. The quota argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword specifying this value.If you specify no quota value, the logical name table has an infinite quota. Note that a shareable table created with infinite quota permits users with write access to that table to consume system dynamic memory without limit.
promsk
OpenVMS usage: file_protection type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
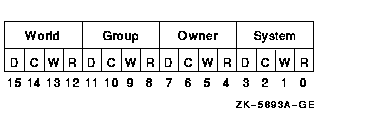
Protection mask to be associated with the newly created shareable logical name table. The promsk argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a word that contains a value that represents four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies the type of access, either delete, create, write, or read, allowed for system, owner, group, and world users.The following diagram depicts these protection bits:
Create access is required to create a shareable table within another shareable table.
Each field consists of 4 bits specifying protection for the logical name table. The remaining bits in the protection mask are as follows:
If a bit is clear, access is granted.
The initial security profile for any shared logical name table is taken from the logical name table template. The owner is then set to the process UIC and, if the promsk argument is nonzero, that value replaces the protection mask.
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |