| Previous | Contents | Index |
Allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit for a memory stack and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.
SYS$SETSTK inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
int sys$setstk (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode);
inadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Range of addresses that express the stack's new limits. The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the address of the top of the stack and the address of the base of the stack. Because stacks in P1 space expand from high to low addresses, the address of the base of the stack must be greater than the address of the top of the stack.retadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array into which $SETSTK writes, in the first longword, the previous address of the top of the stack and, in the second longword, the previous address of the base of the stack.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode of the stack to be altered. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four access modes. The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.If acmode specifies user mode, $SETSTK performs no operation and returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value.
The Set Stack Limits service allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.The calling process can adjust the size of stacks only for access modes that are equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
None
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The input address array cannot be read by the caller; the input range is invalid; or the return address array cannot be written by the caller.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit for a memory stack or a register stack and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space.
SYS$SETSTK_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode, flags, prev_start_va, prev_length
int sys$setstk_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void ** prev_start_va_64, unsigned __int64 * prev_length_64);
start_va_64
OpenVMS usage: address type: quadword address access: read only mechanism: by value
Lowest address in range of addresses that express the stack's new limits. For a memory stack, this address is the stack limit. For an Integrity servers register stack, this address is the stack base.length_64
OpenVMS usage: length type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Length of the range of addresses that express the stack's new limits.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode of the stack to be altered. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbols for the four access modes. The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.If acmode specifies user mode, $SETSTK_64 performs no operation and returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
0 for memory stack (Alpha and Integrity servers VA$M_SETSTK_REGISTER for register stack (Integrity servers only)The $VADEF macro and VADEF.H file define symbolic names for the flags argument.
prev_start_va_64
OpenVMS usage: address type: quadword address access: write only mechanism: by reference
Lowest address in the range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits. For a memory stack, this address was the stack limit. For an Integrity servers register stack, this address was the stack base.prev_length_64
OpenVMS usage: length type: quadword access: write only mechanism: by reference
Length of the range of addresses that express the stack's previous limits.
The Set Stack Limits service allows a process to change the size of its supervisor, executive, and kernel stacks by altering the values in the stack limit and base arrays held in P1 (per-process) space. For Alpha, only the memory stack limits can be changed. The address range must be within 32-bit address space. For IA64, either the memory stack or register stacklimits can be changed. The address range for the register stack can be in 64-bit address space.The calling process can adjust the size of stacks only for access modes that are equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
None
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA_64, $DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGWS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSECW_64
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The prev_start_va_64 or prev_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_LENVIO Memory stack limits were specified in 64-bit address space. Only 32-bit addresses are supported for the memory stack limits.
Allows a process to control whether it can be swapped out of the balance set.
SYS$SETSWM [swpflg]
int sys$setswm (char swpflg);
swpflg
OpenVMS usage: longword_unsigned type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Indicator specifying whether the process can be swapped. The swpflg argument is a longword value. The value 0 (the default) enables process swap mode, meaning the process can be swapped. The value 1 disables process swap mode, meaning the process cannot be swapped.
The Set Process Swap Mode service allows a process to control whether it can be swapped out of the balance set.When the process swap mode is enabled, the process can be swapped out; when disabled, the process remains in the balance set until (1) process swap mode is reenabled or (2) the process is deleted.
The $SETSWM service returns a condition value indicating whether process swap mode was enabled or disabled prior to the call to $SETSWM.
To change its process swap mode, the calling process must have PSWAPM privilege.
None
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
To lock some but not necessarily all process pages into the balance set, use the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service.
For more information, see the chapter on memory management in the HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
SS$_WASCLR The service completed successfully. The process was not previously locked in the balance set. SS$_WASSET The service completed successfully. The process was previously locked in the balance set. SS$_NOPRIV The process does not have the necessary PSWAPM privilege.
Modifies the user authorization file (UAF) record for a specified user.
SYS$SETUAI [nullarg] ,[contxt] ,usrnam ,itmlst ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg]
int sys$setuai (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *contxt, void *usrnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.contxt
OpenVMS usage: longword type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
A longword used to maintain authorization file context. The contxt argument is the address of a longword to receive a $SETUAI context value. On the initial call, this longword should contain the value --1. On subsequent calls, the value of the contxt argument from the previous call should be passed back in.usrnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the user whose UAF record is modified. The usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character text string containing the user name. The user name string can contain a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters.itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information from the specified UAF record is to be modified. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of one or more item descriptors, each of which specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by the item code 0 or by the longword 0.The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
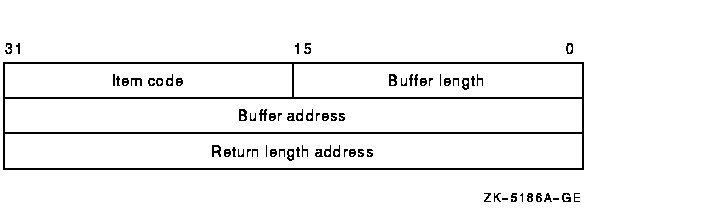
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $SETUAI is to write the information. The length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor, and is given in the description of each item code. If the value of the buffer length field is too small, $SETUAI truncates the data. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $SETUAI is to set. The $UAIDEF macro defines these codes. |
| Buffer address | A longword address of the buffer that specifies the information to be set by $SETUAI. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which $SETUAI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually set. |
The symbolic codes have the following format:
|
UAI$_code |
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
UAI$_ACCOUNT
Sets, as a blank-padded 32-character string, the account name of the user.An account name can include up to 8 characters. Because the account name is a blank-filled string, however, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_ASTLM
Sets the AST queue limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_P
Sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_S
Sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BIOLM
Sets the buffered I/O count limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BYTLM
Sets the buffered I/O byte limit.Because the buffered I/O count limit is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_CLITABLES
Sets, as a character string, the name of the user-defined CLI table for the account, if any.Because the CLI table name can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_CPUTIM
Sets the maximum CPU time limit (per session) for the process in 10-millisecond units.Because the maximum CPU time limit is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFCLI
Sets, as an OpenVMS RMS file name component, the name of the command language interpreter used to execute the specified batch job. The file specification set assumes the device name and directory SYS$SYSTEM and the file type .EXE.Because a file name can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDEV
Sets, as a 1- to 31-character string, the name of the default device.Because the device name string can include up to 31 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_DEFDIR
Sets, as a 1- to 63-character string, the name of the default directory.Because the directory name string can include up to 63 characters plus a size-byte prefix, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
UAI$_DEF_PRIV
Sets, as a quadword value, the default privileges for the user.Because the default privileges are set as a quadword value, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_DFWSCNT
Sets, in pagelets (on Alpha and Integrity server systems), the default working set size.Because the default working set size is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_P
Sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_DIALUP_ACCESS_S
Sets, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which dialup access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m., to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_DIOLM
Sets the direct I/O count limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_ENCRYPT
Sets one of the values shown in the following table to identify the encryption algorithm for the primary password:
Symbolic Name Description UAI$C_AD_II Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. It was used in VAX VMS releases prior to Version 2.0. UAI$C_PURDY Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used during VAX VMS Version 2.0 field test. UAI$C_PURDY_V Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used in VMS releases prior to Version 5.4. UAI$C_PURDY_S Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This is the current algorithm that the operating system uses for all new password changes. UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM Represents the latest encryption algorithm that the operating system uses to encrypt new passwords. Currently, it equates to UAI$C_PURDY_S. HP recommends that you use this symbol in source modules. Because the encryption algorithm is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
UAI$_ENCRYPT2
Sets one of the following values, indicating the encryption algorithm for the secondary password. For a description of the algorithms, see the UAI$_ENCRYPT item code.UAI$C_AD_II
UAI$C_PURDY
UAI$C_PURDY_V
UAI$C_PURDY_S
UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHMUAI$_ENQLM
Sets the lock queue limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_EXPIRATION
Sets, as a quadword absolute time value, the expiration date and time of the account.Because the absolute time value is a quadword in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
UAI$_FILLM
Sets the open file limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_FLAGS
Sets, as a longword bit vector, the various login flags set for the user.Each flag is represented by a bit. The $UAIDEF macro defines the following symbolic names for these flags:
Symbol Description UAI$V_AUDIT All actions are audited. UAI$V_AUTOLOGIN User can only log in to terminals defined by the Automatic Login facility (ALF). UAI$V_CAPTIVE User is restricted to captive account. UAI$V_DEFCLI User is restricted to default command interpreter. UAI$V_DISACNT User account is disabled. Same as /FLAG = DISUSER qualifier in AUTHORIZE. UAI$V_DISCTLY User cannot use Ctrl/Y. UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE User will not be forced to change expired passwords at login. UAI$V_DISIMAGE User cannot issue the RUN or MCR commands or use the foreign command mechanism in DCL. UAI$V_DISMAIL Announcement of new mail is suppressed. UAI$V_DISPWDDIC Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against the system dictionary is disabled. UAI$V_DISPWDHIS Automatic checking of user-selected passwords against previously used passwords is disabled. UAI$V_DISPWDSYNCH When set, prevents synchronizing a user's SYSUAF.DAT password using an external authentication password (when UAI$V_EXTAUTH is set). UAI$V_DISRECONNECT User cannot reconnect to existing processes. UAI$V_DISREPORT User will not receive last login messages. UAI$V_DISWELCOME User will not receive the login welcome message. UAI$V_EXTAUTH User is considered externally authenticated by an external user ID and password and not by the SYSUAF user name and password. The SYSUAF record is still used for checking login restrictions and quotas and for creating the user's OpenVMS process profile. UAI$V_GENPWD User is required to use generated passwords. UAI$V_LOCKPWD SET PASSWORD command is disabled. UAI$V_MIGRATEPWD User's SYSUAF password was set using AUTHORIZE or SYS$SETUAI and is likely to be inconsistent with the user's external user password. If password migration is enabled, the system will attempt to update the external authorization service the next time the user attempts a login. UAI$V_NOMAIL Mail delivery to user is disabled. UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED Primary password is expired. UAI$V_PWD2_EXPIRED Secondary password is expired. UAI$V_RESTRICTED User is limited to operating under a restricted account. Clear the CAPTIVE flag (UAI$V_CAPTIVE), if set, before setting the RESTRICTED flag. (For a description of restricted and captive accounts, see the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.) UAI$V_VMSAUTH When set, the user is allowed to authenticate with the SYSUAF.DAT user name and password (when UAI$V_EXTAUTH is set). UAI$_JTQUOTA
Sets the initial byte quota with which the jobwide logical name table is to be created.
Previous Next Contents Index