| Previous | Contents | Index |
Searches for and returns information about records in the intrusion database matching the caller's specifications.
SYS$SHOW_INTRUSION user_criteria ,intruder ,intruder_len ,breakin_block ,[flags] ,[context]
int sys$show_intrusion (void *user_criteria, void *intruder, unsigned short int *intruder_len, void *breakin_block, unsigned int flags, unsigned int *context);
user_criteria
OpenVMS usage: char_string or item_list_3 type: character-coded text string or longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor or by reference
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:The user_criteria argument is the description of intruder or suspect. The user_criteria argument is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer containing the user criteria to match an intrusion record's user specification in the intrusion database.
The user_criteria argument is a character string of between 1 and 1058 bytes containing characters to match the user specification on records in the intrusion database.
A user specification is any combination of the suspect's or intruder's source node name, source user name, source DECnet for OpenVMS address, local failed user name, local terminal, or the string UNKNOWN. The user specification for an intrusion record is based on the input to the $SCAN_INTRUSION service and the settings of the LGI system parameter. For more information, see the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
Wildcards are allowed for the user_criteria argument. For more information about using wildcards to scan the intrusion database, see the Description section.
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE:
The user_criteria argument is now the address of an 32-bit item list. If the item list is used, one item, the CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL item, must be present in the item list.
The following table lists the valid item descriptions for the user_criteria argument:
Item Description CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST Address of an 8192-byte buffer into which the service writes the associated node information for the returned intrusion record. CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST Address of a list of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which the caller wants to see intrusion information about. CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL Address of a buffer, 1-1058 bytes long, containing the intruder or suspect. If a CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is provided, an intrusion record will only be returned if it originated on one of the nodes specified. If a CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is not provided, records from all nodes will be candidates for display. Multiple CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST items are permitted in the item list.
If a CIA$_OUTPUT_LIST item is provided, the item is filled with node-count records on return. The returned intrusion record will have a breakin block with a valid attempt-count field. The node-count records will have the name and attempt-count for each node represented.
intruder
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
User specification of the matched intruder or suspect record in the intrusion database. The intruder argument is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer to receive the user specification of the matched record in the intrusion database.The intruder argument is a 1058-byte string that will receive the user specification of a record in the intrusion database that matches the specifications in the user_criteria and flags arguments.
intruder_len
OpenVMS usage: string length type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Length of returned string in the intrusion buffer. The intruder_len argument is the address of a longword to receive the length of the returned intrusion buffer.The possible range of the intruder_len argument is 0 to 1058 bytes. If the longword specified by the argument contains a 0 after the call to the service, either the service did not find a record that matched the user criteria in the intrusion database, or there are no more matching items in the intrusion database.
breakin_block
OpenVMS usage: record type: block of 2 longwords (unsigned) and 1 quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Block to receive various information in the intrusion database about a record matching the user criteria. The breakin_block argument is the address of a structure with the following format:
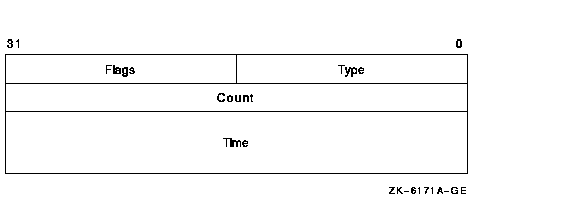
The following table defines the break-in block fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Type |
Unsigned longword containing two pieces of information: the types of
the matched record and the status of the suspect---SUSPECT or INTRUDER.
The possible values for the record type are TERM_USER, TERMINAL,
USERNAME, and NETWORK. The possible values for the status are SUSPECT
or INTRUDER. These constants are defined in $CIADEF in STARLET.
The implication is that each type will have two bits set: one bit represents the status, and the other bit represents the record type. |
| Count | Unsigned longword containing the number of login failures or break-in attempts made by the specified intruder or suspect. |
| Time | Quadword time format indicating the time when the record will expire. |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Each option has a symbolic name. The $CIADEF macro defines the following valid names:
| Symbolic Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CIA$M_ALL | All records will be shown. If the flags argument is omitted, this value is assumed. |
| CIA$M_INTRUDERS | Only intruder records matching the criteria specified by the user_criteria argument will be returned. The value of the flag field in the break-in block will always be 1. |
| CIA$M_ITEMLIST | If FALSE, the user_criteria argument is a character string. If TRUE, this argument is a 32-bit item list. |
| CIA$M_SUSPECTS | Only suspect records matching the criteria specified by the user_criteria argument will be returned. The value of the flag field in the break-in block will always be 0. |
Each of these options is mutually exclusive.
| OpenVMS usage: | context |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The initial value contained in the unsigned longword pointed to by the context argument must be 0. The contents of the unsigned longword must not be changed after the service has set its value. If the contents of the context argument are changed between calls to the service, SS$_BADCONTEXT will be returned.
Contexts become invalid after one-half hour of non-use. This means that if you call the $SHOW_INTRUSION service with a wildcard in the user_criteria argument and do not call the service to get the next matching record within one-half hour, the context becomes invalid. If the context has become invalid, you must restart your search of the intrusion database from the beginning by resetting the context to 0.
The Show Intrusion service returns information about records in the intrusion database that match the criteria you specify.You can retrieve information about multiple records in the intrusion database by specifying wildcards for the user_criteria argument. For example, specifying an asterisk (*) for the user_criteria argument and CIA$M_ALL_RECORDS for the flags argument will return information about all records in the database. Specifying TTA4* for the user_criteria argument and CIA$M_SUSPECTS_ONLY for the flags argument will return information about all suspects who have had failures on terminal TTA4.
If you specify a wildcard string for the user_criteria argument, you must also include a context argument. Because the service can only return information about one intrusion record at a time, you must call the service repeatedly to retrieve information about more than one record. The service will return SS$_NOMOREITEMS when information about all of the matching records has been returned. No intrusion information is returned from the call that returns SS$_NOMOREITEMS.
SECURITY privilege is required.
None
$DELETE_INTRUSION, $SCAN_INTRUSION
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The user_criteria or context argument cannot be read, or the intruder, intruder_len, breakin_block, or context argument cannot be written. SS$_BADBUFLEN The length of one of the specified arguments is out of range. SS$_BADCONTEXT The context argument did not contain a 0 on the first call to the service. The context argument's value changed between consecutive calls to the service. SS$_BADPARAM An invalid value was specified in the flags argument, or mutually exclusive options were specified in the flags argument. SS$_NOMOREITEMS All items matching the specified criteria have been returned. SS$_NOSECURITY The caller does not have SECURITY privilege. This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server: SECSRV$_NOSUCHINTRUDER No records matching the specified criteria were found in the intrusion database. SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later.
Returns the address of a 64-bit signal array. A 32-bit signal array and a mechanism array are passed to a condition handler when it is called. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit signal array, which might be required for programs that use 64-bit address space.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 mcharg, sigarg_64
int sys$signal_array_64 (unsigned __int64 mcharg, unsigned __int64 sigarg_64);
mcharg
OpenVMS usage: mechanism array type: vector quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference
The mechanism array. The mcharg argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of this array, which was passed to the condition handler. $SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 uses this structure to determine the 64-bit signal array address.sigarg_64
OpenVMS usage: 64-bit signal array type: vector quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference, array reference
The 32- or 64-bit address of the 64-bit signal array is returned in this argument.
$SIGNAL_ARRAY_64 provides the address of the 64-bit version of the signal array for condition handlers that need it. It is normally needed only by applications that use 64-bit address space and want to handle errors involving addresses in that region.For example, if an access violation occurs on a 64-bit address, the 32-bit signal array passed to the handler will contain only the low 32 bits of the effective address, because each entry is a longword. The 64-bit signal array, which can be obtained using this service, contains quadword entries, so the 64-bit address can be fully expressed.
None
None
$PUTMSG, which accepts either a 32-bit or 64-bit signal array as an argument.
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The sigarg_64 argument cannot be written. SS$_BADPARAM The mcharg argument is not a mechanism array in the expected format.
Writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and time.
SYS$SNDERR msgbuf
int sys$snderr (void *msgbuf);
msgbuf
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Message to be written to the error log file. The msgbuf argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the message text.
The Send Message to Error Logger service writes a user-specified message to the system error log file, preceding it with the date and time. The $SNDERR service requires system dynamic memory.To send a message to the error log file, the calling process must have BUGCHK privilege.
None
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The message buffer or buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller. SS$_INSFMEM The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service. SS$_NOPRIV The process does not have the required BUGCHK privilege.
Creates, stops, and manages queues and the batch and print jobs in those queues. The $SNDJBC service completes asynchronously; to synchronize the completion of most operations, use the Send to Job Controller and Wait ($SNDJBCW) service.
SYS$SNDJBC [efn] ,func [,nullarg] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
int sys$sndjbc (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when $SNDJBC completes. The efn argument is a longword containing this number; however, $SNDJBC uses only the low-order byte.When you queue the request, $SNDJBC clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the operation completes, $SNDJBC sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
func
OpenVMS usage: function_code type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Function code specifying the function that $SNDJBC is to perform. The func argument is a word containing this function code. The $SJCDEF macro defines the names of each function code.You can specify only one function code in a single call to $SNDJBC. Most function codes require or allow for additional information to be passed in the call. You pass this information by using the itmlst argument, which specifies a list of one or more item descriptors. Each item descriptor in turn specifies an item code, which modifies, restricts, or otherwise affects the action designated by the function code.
nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list supplying information to be used in performing the function specified by the func argument. The itmlst argument is the address of the item list. The item list consists of one or more item descriptors, each of which specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by an item code of 0 or by a longword of 0. The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item descriptor:
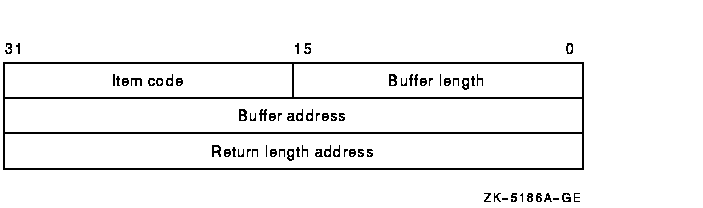
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word specifying the length of the buffer; the buffer either supplies information to be used by $SNDJBC or receives information from $SNDJBC. The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified, and is given in the description of each item code. |
| Item code | A word containing an item code, which identifies the nature of the information supplied for use by $SNDJBC or received from $SNDJBC. Each item code has a symbolic name. The $SJCDEF macro defines these symbol names. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the address of a word to receive the length (in bytes) of information returned by $SNDJBC. If you specify this address as 0, no length is returned. |
The item codes' symbolic names have the following format:
|
SJC$_code |
There are three types of item code:
Several item codes specify a queue name, form name, or characteristic name. For these item codes, the buffer must specify a string containing from 1 to 31 characters, exclusive of spaces, tabs, and null characters, which are ignored. Allowable characters in the string are uppercase alphabetic characters, lowercase alphabetic characters (which are converted to uppercase), numeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_).
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
At request initiation, $SNDJBC sets the value of the quadword I/O status block to 0. When the requested operation completes, $SNDJBC writes a condition value in the first longword of the I/O status block. It writes the value 0 into the second longword; this longword is unused and reserved for future use.
The condition values returned by $SNDJBC in the I/O status block are usually condition values from the JBC facility. These condition values are defined by the $JBCMSGDEF macro. In some cases, the condition value returned by $SNDJBC can be an error return from a system service or an OpenVMS RMS service that is used in executing the request. For the SJC$_SYNCHRONIZE_JOB request, the condition value returned is the completion status of the requested job.
The condition values returned from the JBC facility are listed in the Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block section.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you specify it, for the following reasons:
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |