HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary
HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary
This command disables the XON/XOFF flow control.
| #5 |
$ SET HOST/DTE/ERROR_ACTION=EXIT TTA2
|
This command sets the error action to EXIT.
| #6 |
$ SET HOST/DTE/MAX_BUFFERS=150 TTA2
|
This command sets the maximum number of receive buffers to 150.
| #7 |
$ SET HOST/DTE/ESCAPE=E TTA2
|
This command defines the letter E as the escape character. Note that
DTEPAD is not case sensitive.
| #8 |
$ SET HOST/DTE/LOG TTA2
|
This command enables logging of the session. Since no log file is
specified, the log is written to the default log file, DTEPAD.LOG.
| #9 |
$ SET HOST/DTE/INIT=MYFILE.INI TTA2
|
This command uses the initialization file MYFILE.INI.
This example shows you how to access DTE command mode by pressing
Ctrl/@, where @ is the command character.
| #11 |
DTEPAD> SAVE MYFILE.INI
|
This command saves the information on the current configuration in the
file MYFILE.INI.
| #12 |
DTEPAD> SET DTE/BREAK=G
|
This command defines the letter G as the break character.
This command sets the terminal port so that echoing is performed by the
local system.
| #14 |
DTEPAD> SET DTE/SPEED=4800
|
This command sets the input and output baud rates to 4800.
| #15 |
DTEPAD> SET DTE/LOG=myfile.log
|
This command directs logging to the file MYFILE.LOG.
| #16 |
DTEPAD> SHOW DTE
Port TXA0 EIGHT_BIT ECHO
Flow control XON/XOFF
Parity NONE
Transmit Speed 4800
Receive Speed 4800
Error action CONTINUE
Break character B
Escape character \
Command character @
Maximum buffers 100
Read delay 50 milliseconds
Log file MYFILE.INI
Number dialed 12345678
Modem type DF03
Bytes transmitted 75
Bytes received 132
Errors 0
|
This command displays all the current settings of the configurable
characteristics, the number of bytes transmitted and received, and the
number of errors detected.
SET HOST/DUP
Connects your terminal to a storage controller through the appropriate
bus for that controller. The /SERVER and /TASK qualifiers are required.
For use only with storage controllers. Requires the DIAGNOSE
privilege.
Format
SET HOST/DUP/SERVER=server-name
/TASK=task-name node-name
Parameter
node-name
Specifies the node name of the storage controller.
Description
The SET HOST/DUP command creates a virtual terminal connection and
executes a utility or diagnostic program on a storage controller that
uses the Diagnostic and Utilities Protocol (DUP) Standard Dialogue.
Once the connection is established, operations are performed under the
control of the utility or diagnostic program.
When the utility or diagnostic program terminates, control is returned
to the local system.
To abort or prematurely terminate the connection and return control to
the local system, press Ctrl/\.
Further information regarding the operation of the utility and
diagnostic programs available on a particular controller may be
obtained from the appropriate documentation set for that controller.
Preparing for Use
To use the SET HOST/DUP facility, you must first install FYDRIVER, the
DUP class driver. To load FYDRIVER, add the following commands to the
SYSTARTUP.COM command procedure in the SYS$MANAGER directory.
On Alpha, specify the following commands:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN
SYSMAN> IO CONNECT FYA0/NOADAPTER/DRIVER=SYS$FYDRIVER
|
On VAX, specify the following commands:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGEN
SYSGEN> CONNECT FYA0/NOADAPTER
|
This operation requires CMKRNL (change mode to kernel) privilege.
Qualifiers
/LOG[=filespec]
/NOLOG (default)
Controls whether a log file of the entire session is kept. If you use
the /LOG qualifier without the file specification, the log information
is stored in the file HSCPAD.LOG.
/SERVER=server-name
Specifies the server name for the target storage controller.
This qualifier is required.
/TASK=task-name
Specifies the utility or diagnostic name to be executed on the target
storage controller under direction of the server.
This qualifier is required.
Example
|
$ SET HOST/DUP/SERVER=MSCP$DUP/TASK=DIRECT R2DH5Y
%HSCPAD-I-LOCPROGEXE, Local program executing - type ^\ to exit utility
|
The SET HOST/DUP command in this example connects the user terminal to
the utility program called DIRECT executing on a storage controller
named R2DH5Y under direction of the MSCP$DUP server.
SET HOST/HSC
Connects your terminal to an HSC disk and tape controller through the
computer interconnect (CI) bus.
Used only with HSC controllers. Requires the DIAGNOSE
privilege.
Format
SET HOST/HSC node-name
Parameter
node-name
Specifies the node name of the HSC.
Description
The SET HOST/HSC command establishes a connection to an HSC disk and
tape controller by way of the CI bus. (The SHOW CLUSTER command lists
the names of HSC controllers that are accessible to your node.) No
password is required to access the HSC; however, only SHOW commands are
accepted when the HSC Secure/Enable switch is in the Secure position.
Once the connection is made to the HSC, operations can be performed as
if you were attached to the local terminal of the HSC; however, access
to ODT (Octal Debugging Tool) and offline diagnostics are not permitted.
Press Ctrl/C to obtain a prompt from the HSC before entering commands.
To exit from the HSC and return to the local system, press Ctrl/\.
A description of HSC commands and utilities can be obtained from the
HSC documentation.
Preparing for Use
To use the SET HOST/HSC facility, you must first install FYDRIVER,
which is the Diagnostic and Utilities Protocol (DUP) driver associated
with the CI. To load FYDRIVER, add the following commands to the
SYSTARTUP.COM command procedure in the SYS$MANAGER directory:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGEN
CONNECT FYA0/NOADAPTER
|
This operation requires CMKRNL (change mode to kernel) privilege.
Qualifier
/LOG[=filespec]
/NOLOG (default)
Controls whether a log file of the entire session is kept. If you use
the /LOG qualifier without the file specification, the log information
is stored in the file HSCPAD.LOG.
Example
|
$ SET HOST/HSC HSC001
%HSCPAD-I-LOCPROGEXE, Local program executing - type ^\ to exit, ^Y for prompt
HSC>
|
This SET HOST/HSC command connects the user terminal to the HSC named
HSC001.
SET HOST/LAT
Connects your terminal to a specified service available on the local
area network (LAN), establishing one session for communication between
your terminal and that service.
The service node that provides the service must be on a remote
node, must be on the same extended LAN, and must be running at least
Version 5.0 of the LAT protocol.
Format
SET HOST/LAT service-name
Parameter
service-name
Specifies the name of the service to which you want your terminal
connected. A service is a resource on the LAN. A service often consists
of all of the resources of a computer system. Other examples of
services are a file storage system and an application program running
on a computer system. A computer system that offers one or more
services is called a service node.
If several service nodes offer the same service, and you do not specify
the /NODE=node-name qualifier, your terminal connects to the service
node that is the least busy.
To display a list of services on your LAN, use the LAT Control Program
(LATCP) SHOW SERVICES command. Refer to the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Description
The SET HOST/LAT command allows you to connect your terminal to a
specified service, establishing one LAT session for communication
between your terminal and that service. (For an overview of the LAT
protocol and its advantages, see the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.)
The service node that provides the service must be on a remote node,
must be on the same extended LAN, and must be running at least Version
5.0 of the LAT protocol.
Some services are password protected. You are prompted for a password
unless you specify the password with the /PASSWORD qualifier.
Once the connection to the service is made, you can interact with the
service as if your terminal is directly connected to it. Some services
will prompt you. For example, if the service is an OpenVMS system, it
prompts you for a user name and password. You must have an account on
the service node to log in.
Press the disconnect character to end the LAT session and return to DCL
command level on your local system. With some services, such as general
timesharing services like OpenVMS, you can end the LAT session by
logging out of the service. The default disconnect character is Ctrl/\.
Use the /DISCONNECT qualifier to change the default disconnect
character.
You cannot use SET HOST/LAT to connect to the local node.
Qualifiers
/AUTOCONNECT
/NOAUTOCONNECT
Specifies whether connection attempts should be retried automatically
when a connection fails because a service is unknown or unavailable, or
because a node is unknown or unreachable. Also specifies that
reconnects should be attempted automatically if a service has
disconnected abnormally. The default is /NOAUTOCONNECT.
/AUTOPROMPT (default)
/NOAUTOPROMPT
Causes an OpenVMS Username: prompt to appear with no user action when a
SET HOST/LAT command is issued.
On a terminal server port, you can configure the port to have
AUTOPROMPT disabled (/NOAUTOPROMPT) so that you are required to press
Return when connecting to a node to get the Username: prompt; however,
when connecting to a reverse LAT service, the AUTOPROMPT characteristic
should be disabled.
/BREAK=break-character
Defines a character that generates a break on lines that expect a break
rather than a carriage return. To generate a break, press the Ctrl and
break-character keys together. The default
break-character value is the tilde (~).
You can select any ASCII character between @ and Z, except C, M, Q, S,
Y, and the left bracket ([). You cannot select a character that is
already defined as the disconnect character.
/DESTINATION_PORT=port-name
Specifies the port on a node to which you want to connect. The /NODE
qualifier is required when you specify the /DESTINATION_PORT qualifier.
The port must be available and must offer the service you specify.
OpenVMS and certain other LAT service node systems ignore the
/DESTINATION_PORT qualifier.
/DIAL=(NUMBER:number[,MODEM_TYPE:modem-type])
Allows a modem attached to the outgoing terminal line to be autodialed
using the autodial protocol of that modem. The NUMBER keyword is the
telephone number to be autodialed and is a required parameter.
The MODEM_TYPE keyword is optional. It can be used to specify any of
the following modem types:
- DMCL (any modem that uses the DEC Modem Command Language)
- DF03 (default)
- DF112
Each modem type requires a specific modem dialer code. Check with your
system manager to see which modem dialer codes are installed on your
system.
In addition, the MODEM_TYPE keyword can be used to specify a modem type
other than DF03, DF112, or DMCL. A template is provided for users
interested in supporting other modems with autodial capabilities (see
SYS$EXAMPLES:DTE_DF03.MAR).
/DISCONNECT=disconnect-character
Defines the character that you can use to disconnect from a remote
session. To generate a disconnect, press the Ctrl and
disconnect-character keys together. The default
disconnect-character is the backslash (\).
You can select any ASCII character from @ through Z, except C, M, Q, S,
Y, and the left bracket ([). For example, if you specify /DISCONNECT=A,
Ctrl/A will be the disconnect character. You cannot select a character
that is already defined as the break character.
/EIGHT_BIT (default)
/NOEIGHT_BIT
Determines whether the outgoing terminal line supports 8-bit or 7-bit
characters. By default, 8-bit characters are supported. If you specify
/NOEIGHT_BIT, then 7-bit characters are supported.
Note
To change the number of bits per character on the remote terminal
server port, that port must have the REMOTE MODIFICATION characteristic
enabled.
|
/FRAME=n
The /FRAME=n qualifier allows a user making a LAT connection
to a remote system to specify the number of data bits that the terminal
driver expects for every character that is input or output. The value
of n can be from 5 to 8. The default value depends on the
settings for the terminal established by the /PARITY and /EIGHT_BIT
qualifiers. The following example specifies a character frame size of 7
bits per character:
$ SET HOST/LAT /FRAME=7 DIAL_OUT_SVC
|
/LOG[=log-file]
Logs all data that is delivered during the LAT session. If you do not
specify a log file, the data is stored in the file SETHOST_LAT.LOG.
/NODE=node-name
Specifies the node that offers the service to which you want to
connect. The node you specify must be a remote node. Failover is not
performed if the connection fails.
/PASSWORD=password
Specifies the password required by a service that is password
protected. If you do not specify the /PASSWORD qualifier when
requesting a connection to a password-protected service, you are
prompted for a password.
/QUEUE
/NOQUEUE (default)
When connecting to a reverse LAT service that is already in use (such
as a dial out modem), you are notified that the service is in use and
the SET HOST/LAT command terminates. However, LAT can allow incoming
connections to be queued to any reverse LAT service that supports
service queueing, which enables users to be placed on a queue when
using reverse LAT services.
LAT reports your position in the queue. When the resource becomes
available, you are immediately notified. You can cancel the queued
connection by pressing Ctrl/Y and terminating the SET HOST /LAT command.
/SPEED=(output-rate,input-rate)
Sets the baud rate at which the terminal receives and transmits data.
If the input and output rates are the same, specify the qualifier as
/SPEED=rate.
Not all terminals support different input and output baud rates. For
specific information on baud rates for your terminal, consult the
manual for that terminal.
The default transmission rates are installation dependent.
The valid values for input and output baud rates are as follows:
300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600
|
If you select an invalid or unsupported speed, the terminal line speed
will remain set at its previous value.
Note
To change the speed on the terminal server port, the REMOTE
MODIFICATION characteristic must be enabled on that terminal server
port.
When initiating a connection, SET HOST/LAT may attempt to set terminal
server port characteristics, such as the speed and the default speed
for a LAT device. If the device connected to the terminal server port
has a fixed speed (such as a dial-out modem) and you do not want the
host to try to change this, disable the REMOTE MODIFICATION
characteristic on that port using the following command:
Local> DEFINE PORT x REMOTE MODIFICATION DISABLE
Local> LOGOUT PORT x
|
Use the following command for terminal servers that support the CHANGE
command:
Local> CHANGE PORT x REMOTE MODIFICATION DISABLE
|
|
Examples
| #1 |
$ SET HOST/LAT SORTER
%LAT-S-CONNECTED, session to SORTER established
%LAT-I-TODISCON, type ^\ to disconnect the session
Username: BARKER
Password:
.
.
.
$ LOGOUT
BARKER logged out at 30-DEC-2001 11:04:51.45
%LAT-I-DISCONNECTED, session disconnected from SORTER
-LAT-I-END, control returned to node HOME
$
|
This SET HOST/LAT command connects the user to the service SORTER,
which is a computer system. The first message confirms that the user
has been connected to that service. The second message informs the user
how to disconnect the session. (The user can also disconnect the
session by logging out from SORTER.) SORTER then prompts for the
username and password. Use the normal login procedure to log in to the
system. When the user logs out of the service SORTER, the terminal
displays the DCL command prompt of the user's local processor system
(HOME).
| #2 |
$ SET HOST/LAT/DESTINATION_PORT=BOSTON-
_$ /NODE=STATE/DISCONNECT=F BUDGET
|
This command connects the user's terminal to the service BUDGET that is
offered on port BOSTON, on service node STATE. The user can disconnect
the session by pressing Ctrl/F.
| #3 |
$ SET HOST/LAT PURSE
Password:
|
This command attempts to connect the user's terminal to the service
PURSE. The service PURSE is password protected, so the user is prompted
for a password. The user could have specified the password within the
SET HOST/LAT command, as shown in the next example.
| #4 |
$ SET HOST/LAT/PASSWORD=BEOR PURSE
|
This command connects the user's terminal to the password-protected
service PURSE. The password is BEOR.
SET HOST/RLOGIN
Allows you to log in to a remote host over a TCP/IP connection and
start an interactive terminal session by accessing the RLOGIN
application.
Format
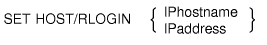
Note
You can specify the IPhostname or the IPaddress, but
not both.
|
Parameter
IPhostname
Specifies the IP host name of the remote host.
IPaddress
Specifies an IP address of the remote host.
Description
The SET HOST/RLOGIN command allows you to log in to a remote host by
invoking RLOGIN client software that runs on your system. Once you
start the terminal session, you can enter commands interactively on the
remote host. The parameter that specifies the remote host is either an
IP host name or an IP address.
Qualifiers
/AUTHENTICATE
Specifies that Kerberos authentication should be used for acquiring
access to the remote node.
/TERMINAL_TYPE=type
Sets the terminal emulator to one of the following terminal types:
VT100, VT200, VT300, VT400, VT500.
/TRUNCATE_USERNAME
Specifies that the current user name should be truncated to 8
characters before attempting to connect to the remote node. The
qualifier is required for communication with systems that limit the
size of their login names to 8 characters. The /TRUNCATE_USERNAME
qualifier is ignored if /USERNAME is specified.
/USERNAME=username
Specifies the user name for logging in to the remote node. The user
name can be enclosed in quotes to preserve the case of the user name
for case sensitive systems such as UNIX systems. If the /USERNAME
qualifier is not specified, the default is the current user's user name.
Example
|
$ SET HOST/RLOGIN remotehst1
|
This example creates an RLOGIN connection to remote host
remotehst1 over a TCP/IP connection.
|