 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of global section to be created as well
as its characteristics. The flags argument is a
longword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The
$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_GPFILE service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_DZRO
|
Pages are demand-zero pages.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PAGFIL
|
Pages form a global page-file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies
SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group
global section.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Page File Section service allows a process
to create a permanent global page file section. Global page file
sections contain demand-zero allocation pages that are writable and
backed up by the system page file. All pages in the global page file
section are shared by all processes that map to the global section.
Required Privileges
To create a permanent global page file section, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
The systemwide number of global page file pages is limited by the
system parameter GBLPAGFIL.
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 descriptor cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages or was specified as 0.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_SECTBLFUL
|
There are no entries available in the system global section table.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_GPFN (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, creates a permanent page frame section to
which processes can map.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_GPFN gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,start_pfn ,page_count
,acmode ,flags
C Prototype
int sys$create_gpfn (void *gs_name_64, struct _secid *ident_64,
unsigned int prot, unsigned int start_pfn, unsigned int page_count,
unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
gs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is
the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.
The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three
fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the
identification value.
The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order two
bits.
The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified, and
their meanings are as follows:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign
values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a
section is created, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page frame section. The mask
contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each
field. The following diagram depicts the mask:
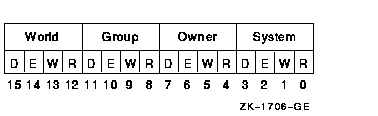
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in
that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,
write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete
access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for
those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,
read access and write access are granted to all users.
start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: |
page frame number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) on Alpha, quadword (unsigned) on
I64 |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins in memory.
page_count
| OpenVMS usage: |
CPU-specific page count |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) on Alpha, quadword (unsigned) on
I64 |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the
mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in
SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the
four access modes:
| Value |
Symbolic Name |
Access Mode |
|
0
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
1
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
2
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
3
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the page frame section to
be created. The flags argument is a longword bit
vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and
the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct
the flags argument by performing a logical OR
operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_GPFN service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
SEC$M_ARGS64
|
Indicates that all parameters, specifically
start_pfn and
page_count, are passed as 64-bit numbers.
|
|
SEC$M_GBL
|
Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PERM
|
Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in
this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_PFNMAP
|
Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always
present in this service and cannot be disabled.
|
|
SEC$M_SYSGBL
|
Pages form a system global page frame section. By default, pages form a
group global page frame section.
|
|
SEC$M_UNCACHED
|
Flag that must be set when a PFN-mapped section is created if this
section must be treated as uncached memory. Flag is ignored on Alpha
systems; it applies only to I64 systems.
|
|
SEC$M_WRT
|
Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only
section.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition value
SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegal
combination of flags is set.
Description
The Create Permanent Global Page Frame Section service allows a process
to create a global page frame section. All global page frame sections
are permanent. Pages mapped to a global page frame section are not
included in or charged against the process's working set; they are
always valid.
Do not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET_64; this
can result in a machine check if they are in I/O space.
Required Privileges
To create a permanent global page frame section, the process must have
the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag
SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_CREATED
|
The service completed successfully. The specified global section did
not previously exist and has been created.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
A global section of the same name already exists; a new global section
was not created.
|
|
SS$_GPTFULL
|
There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page
table entries for the section.
|
|
SS$_GSDFULL
|
There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control
information for global sections.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags
was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The match control field of the global section identification is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRMGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a
permanent group global section (PRMGBL).
|
|
SS$_NOSYSGBL
|
The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system
global section (SYSGBL).
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
$CREATE_RDB
Initializes a rights database.
Format
SYS$CREATE_RDB [sysid]
C Prototype
int sys$create_rdb (struct _generic_64 *sysid);
Argument
sysid
| OpenVMS usage: |
system_access_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
System identification value associated with the rights database when
$CREATE_RDB completes execution. The sysid argument is
the address of a quadword containing the system identification value.
If you omit sysid, the current system time in 64-bit
format is used.
Description
The Create Rights Database service initializes a rights database. The
database name is the file equated to the logical name RIGHTSLIST, which
must be defined as a system logical name from executive mode. If the
logical name does not exist, the database is created in
SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE] with the file name RIGHTSLIST.DAT. If the database
already exists, $CREATE_RDB fails with the error RMS$_FEX.
The rights database is created with an owner of [1,4] and a protection
of (RWED, RWED, R).
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the directory in which the file is being created is
required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER,
$FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $GRANTID, $GET_SECURITY, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID,
$SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
sysid argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
RMS$_FEX
|
A rights database already exists. To create a new one, you must
explicitly delete or rename the old one.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to SYS$SYSTEM.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$CREATE_REGION_64 (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, creates a virtual region within the process's
private address space.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$CREATE_REGION_64 length_64 ,region_prot ,flags ,return_region_id_64
,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]
C Prototype
int sys$create_region_64 ( unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int
region_prot, unsigned int flags, struct _generic_64 *return_region_id,
void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Arguments
length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Length of the virtual region to be created. The length specified must
be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. This length is fixed at the time
the region is created.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, this length is rounded up to
include an even multiple of CPU-specific pages mapped by a page table
page.
region_prot
| OpenVMS usage: |
region_protection |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Region protection to be associated with the region to be created. The
region_prot argument is a longword containing the
create and owner mode.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in
STARLET.MLB define the following symbols for valid combinations of
create and owner modes:
| Symbol |
Create and Owner Modes |
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_UOWN
|
User create mode and user owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_SOWN
|
User create mode and supervisor owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_EOWN
|
User create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_UCREATE_KOWN
|
User create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_SOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and supervisor owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_EOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_SCREATE_KOWN
|
Supervisor create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_ECREATE_EOWN
|
Executive create mode and executive owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_ECREATE_KOWN
|
Executive create mode and kernel owner mode
|
|
VA$C_REGION_KCREATE_KOWN
|
Kernel create mode and kernel owner mode
|
For both create and owner mode, the $CREATE_REGION_64 service uses
whichever of the following two access modes is least privileged:
- Access mode specified by the acmode argument
- Access mode of the caller
A subsequent call to any system service that created address space
within a region must be made from an access mode that is the same or
more privileged than the create mode associated with the region.
A subsequent call to $DELETE_REGION_64 to delete the region must be
made from an access mode that is the same or more privileged than the
owner mode associated with the region.
All regions created by $CREATE_REGION_64 are automatically deleted when
the image is run down on image exit.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the region to be created.
The flags argument is a longword bit vector in which
each bit corresponds to a flag. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB
and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each
flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a
logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.
The following table describes the flags that are valid for the
$CREATE_REGION_64 service:
| Flag |
Description |
|
VA$M_DESCEND
|
Created region is a descending region; that is, allocation occurs
toward decreasing virtual addresses. If VA$M_DESCEND is not specified,
the region allocation occurs toward increasing virtual addresses.
|
|
VA$M_SHARED_PTS
|
Created region requires the virtual address space created within it to
be capable of using shared page tables. If this flag is not specified,
the virtual address space created within the region is mapped by
process-private page tables only. By default, the region does not allow
the use of shared page tables.
|
|
VA$M_P0_SPACE
|
Create region in P0 space. This flag cannot be set if VA$M_P1_SPACE is
set.
|
|
VA$M_P1_SPACE
|
Create region in P1 space. This flag cannot be set if VA$M_P0_SPACE is
set.
|
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP. The condition value SS$_IVREGFLG is returned if any
undefined bits are set.
return_region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the created region. The
return_region_id_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the region ID.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
return address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the region. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the lowest virtual address of the region.
|
