 |
HP COBOL
DBMS Database Programming Manual
DISCONNECT
Function
The DISCONNECT statement logically removes the current record of the
run unit from one or more sets.
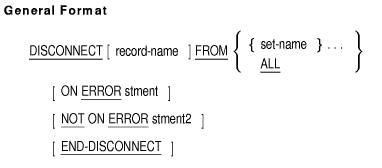
record-name
names a subschema record type.
set-name
names a subschema set type.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an on error condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not on error condition.
Syntax Rules
- The record type of record-name must be a member record
type of the set type for each set-name.
- The same set-name cannot be specified more than once in
the same DISCONNECT statement.
General Rules
- The DISCONNECT statement references the current record of the run
unit.
- The current record of the run unit must be in a realm in ready mode
and all records required by the DBCS to execute the DISCONNECT
statement must be in a realm in available mode.
- Use record-name to check that the current record of the
run unit has the same record type as record-name.
- The current record of the run unit must be an OPTIONAL member of
each set-name.
- The record type of the current record of the run unit must be a
member record type of the set type for each set-name.
- The DBCS removes the current record of the run unit from each
set-name.
- Use the ALL clause to remove the current record of the run unit
from as many sets as possible. The DBCS considers only those set types
defined in the subschema for which the record is an OPTIONAL member.
Set types not included in your subschema and set types of which the
record is not a member are ignored. The current record of the run unit
is removed from each remaining set type.
- If the set type currency indicator for a disconnected set pointed
to the current record, that currency indicator now points to the
position in the set vacated by the record. All other currency
indicators are not affected.
- If the execution of a DISCONNECT statement results in a database
exception condition, no changes are made to the membership of the
current record in the database.
- If a database exception condition occurs during the execution of a
DISCONNECT statement, the DBCS places a database exception condition
code in the special register DB-CONDITION (see Technical Notes). This
code identifies the condition.
Technical Notes
DISCONNECT statement execution can result in these DB-CONDITION
database exception condition codes:
|
DBM$_NOT_OPTNL
|
The current record of the run unit is not an OPTIONAL member of
set-name.
|
|
DBM$_CRUN_NULL
|
The currency indicator for the current record of the run unit is null.
|
|
DBM$_CRUN_POS
|
The currency indicator for the current record of the run unit specifies
the position of a vacated record in a record collection.
|
|
DBM$_WRONGRTYP
|
The record type of record-name is not the same as the current record's
type.
|
|
DBM$_NOT_MTYP
|
The current record is not a member record type of set-name.
|
|
DBM$_NOT_MBR
|
The current record is not a member of set-name.
|
|
DBM$_NOT_UPDATE
|
A realm is not in ready update usage mode.
|
Additional References
- Section 2.2 on reserved words (database special registers)
- HP COBOL Reference Manual, Chapter 6, section on scope of statements
- Section 4.8.1, on database On Error condition
- USE statement
Examples
DISCONNECT EMPLOYEE FROM CONSISTS_OF.
DISCONNECT EMPLOYEE FROM ALL.
DISCONNECT FROM ALL.
DISCONNECT FROM CONSISTS_OF.
|
ERASE
Function
The ERASE statement deletes the current record of the run unit from the
database. Additional records owned by the current record may also be
deleted and/or disconnected.
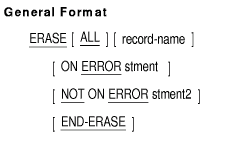
record-name
names a subschema record type.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an on error condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not on error condition.
General Rules
- The ERASE statement references the current record of the run unit.
- Use record-name to check that the current record of the
run unit has the same record type as record-name.
- The current record of the run unit must be in a realm in update
ready mode, and all records required by the Database Control System
(DBCS) to execute the ERASE statement must be in a realm in available
mode.
- The current record of the run unit is called the object
record for the remaining General Rules.
- The object record is erased from all sets in which it is a member
and deleted from the database.
- If you use the ALL phrase, the object record and all sets owned by
the object record are erased (independent of set membership retention
class).
- If you do not use the ALL phrase, these rules apply to the members
of the sets owned by the erased object record:
- Each member with FIXED membership is erased.
- Each member with OPTIONAL membership is disconnected from the set
but not deleted from the database.
- An exception occurs if any members have MANDATORY membership.
- The database key value corresponding to the erased object record is
removed from all keeplists.
- General Rules 5 to 8 apply to each erased record as if it were the
object record.
- The successful ERASE statement changes currency indicators as
follows:
- The currency indicator for the current record of the run unit
points to the position in the database vacated by the current record of
the run unit. However, you no longer have a current record.
- If an erased record is the current record of a disconnected set
type, that set type currency indicator now points to the position in
the set vacated by that record.
- If an erased record is the owner of the current set of any set
type, that set type's currency indicator becomes null.
- If an erased record is the current record of a record type, that
record type currency indicator becomes null.
- If the erased record is the current record of the realm, that realm
currency indicator now points to the position in the realm vacated by
that record.
- If the execution of an ERASE statement results in a database
exception condition, no changes are made to the database.
- If a database exception condition occurs during the execution of an
ERASE statement, the DBCS places a database exception condition code in
the special register DB-CONDITION (see Technical Notes). This code
identifies the condition.
Technical Notes
ERASE statement execution can result in these DB-CONDITION database
exception condition codes:
|
DBM$_CRUN_NULL
|
The currency indicator for the run unit is null.
|
|
DBM$_CRUN_POS
|
The currency indicator for the run unit specifies the position of a
vacated record in the record collection.
|
|
DBM$_WRONGRTYP
|
The record type of record-name is not the same as the current record's
type.
|
|
DBM$_ERASEMANDT
|
You attempted to erase a record that is the owner of a set occurrence
with a MANDATORY member record occurrence, but you did not use the ALL
option.
|
|
DBM$_NOT_UPDATE
|
A realm is not in update usage mode.
|
Additional References
- Section 2.2, on reserved words (database special registers)
- HP COBOL Reference Manual, Chapter 6, section on scope of statements
- Section 4.8.1, on database On Error condition
- USE statement
Examples
- This example erases PART record, all records owned by PART in the
PART_USES, PART_INFO, and PART_USED_ON sets. It also erases all SUPPLY
and PR_QUOTE records that it owns through the PART_INFO set. It
disconnects PART from the RESPONSIBLE_FOR set.
- This example has the same effect as in example 1 for each PART
record that the CLASS1 record owns; however, it also erases the CLASS1
record.
Note
Because CLASS1 has MANDATORY members, you cannot erase only
CLASS1.
|
|

