 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$CANWAK
Removes all scheduled wakeup requests for a process from the timer
queue, including those made by the caller or by other processes. The
Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service makes scheduled wakeup requests.
Format
SYS$CANWAK [pidadr] ,[prcnam]
C Prototype
int sys$canwak (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);
Arguments
pidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process for which wakeups are to be
canceled. The pidadr argument is the address of a
longword specifying the PID. The pidadr argument can
refer to a process running on the local node or a process running on
another node in the OpenVMS Cluster system.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the process for which wakeups are to be canceled. The
prcnam argument is the address of a character string
descriptor pointing to the process name string.
A process running on the local node can be identified with a 1- to
15-character string. To identify a process on a specific node in a
cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the node name as
well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23
characters.
The operating system interprets the UIC group number of the calling
process as part of the process name; the names of processes are unique
to UIC groups. Because of this, you can use the prcnam
argument only on behalf of processes in the same group as the calling
process.
Description
The Cancel Wakeup service removes from the timer queue all scheduled
wakeup requests for a process, including those made by the caller or by
other processes. The Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service makes scheduled
wakeup requests.
If the longword at address pidadr is 0, the PID of the
target process is returned.
If you specify neither the pidadr nor the
prcnam argument, scheduled wakeup requests for the
calling process are canceled.
Pending wakeup requests issued by the current image are automatically
canceled at image exit.
This service cancels only wakeup requests that have been scheduled; it
does not cancel wakeup requests made with the Wake Process from
Hibernation ($WAKE) service.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
listed privileges to use $CANWAK:
- You need GROUP privilege to cancel wakeups for processes in the
same group that do not have the same UIC.
- You need WORLD privilege to cancel wakeups for any process in the
system.
Required Quota
Canceled wakeup requests are restored to the process's AST limit
(ASTLM) quota.
Related Services
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $GETTIM, $GETTIM_PREC, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK,
$SETIME, $SETIMR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the
caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INCOMPAT
|
The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating
system.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or you specified an invalid
process identification.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to cancel wakeups for the
specified process.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as
part of the cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request.
(Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.)
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting
requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot
process.)
|
$CHECK_ACCESS
Determines on behalf of a third-party user whether a named user can
access the object specified.
Format
SYS$CHECK_ACCESS [objtyp], [objnam], [usrnam], itmlst, [contxt],
[clsnam], [objpro], [usrpro]
C Prototype
int sys$check_access (unsigned int *objtyp, void *objnam, void *usrnam,
void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, void *clsnam, void *objpro, void
*usrpro);
Arguments
objtyp
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Type of object being accessed. The objtyp argument is
the address of a longword containing a value specifying the type of
object.
The appropriate symbols are listed in the following table and are
defined in the system macro $ACLDEF library:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
ACL$C_CAPABILITY
|
Object is a restricted resource; use the reserved name VECTOR.
|
|
ACL$C_DEVICE
|
Object is a device.
|
|
ACL$C_FILE
|
Object is a Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 file.
|
|
ACL$C_GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Object is a group global section.
|
|
ACL$C_JOBCTL_QUEUE
|
Object is a batch, print, or server queue.
|
|
ACL$C_LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
Object is a logical name table.
|
|
ACL$C_SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Object is a system global section.
|
For further information about these symbols, see the description of the
clsnam argument.
objnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the object being accessed. The objnam argument
is the address of a character-string descriptor pointing to the object
name.
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the user attempting access. The usrnam
argument is the address of a descriptor that points to a character
string that contains the name of the user attempting to gain access to
the specified object. The user name string can contain a maximum of 12
alphanumeric characters.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attributes describing how the object is to be accessed and information
returned after $CHECK_ACCESS performs the protection check (for
instance, security alarm information).
For each item code, you must include a set of four elements and end the
list with a longword containing the value 0 (CHP$_END). This is shown
in the following diagram:
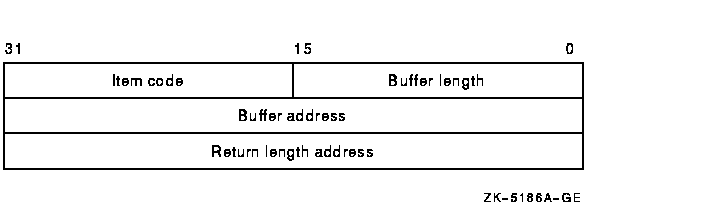
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the associated buffer. The length of the buffer needed
depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item
descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service
truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information in the associated buffer.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word in which $CHECK_ACCESS
writes the number of bytes written to the buffer pointed to by
bufadr. If the buffer pointed to by
bufadr is used to pass information to $CHECK_ACCESS,
retlenadr is ignored but must be included.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read-write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword used to maintain the user authorization file (UAF) context.
The contxt argument is the address of a longword to
receive a UAI context longword. On the initial call, this longword
should contain the value --1. On subsequent calls, the value of the
contxt argument from the previous call should be
passed back in.
Using the contxt argument keeps the UAF open across
all calls, thereby improving the performance of the system on
subsequent calls. To close the UAF, you must run down the image.
The resulting contxt value from a $CHECK_ACCESS call
can also be used as the input contxt argument to the
$GETUAI system service, and vice versa.
clsnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Object class name associated with the protected object. The
clsnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to the name of the object class associated with the object
specified by either the objnam or the
objpro argument. The clsnam and
objtyp arguments are mutually exclusive. The
clsnam argument is the preferred argument to
$CHECK_ACCESS. The following object class names are valid:
|
CAPABILITY
|
QUEUE
|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
|
DEVICE
|
SECURITY_CLASS
|
|
FILE
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
VOLUME
|
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
|
objpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream or object handle |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing an object security profile or object handle. The
objpro argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a buffer that contains an encoded object security profile
or the address of a descriptor pointing to an object handle.
Object handles vary according to the associated security object class.
Currently, the only supported object handles are for the file and
device class objects where the object handle is a word or longword
channel.
The objpro and objnam arguments are
mutually exclusive unless the objpro argument is a
simple object handle. The objpro and
usrpro arguments are also mutually exclusive unless
the objpro argument is an object handle.
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing a user security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer that
contains an encoded user security profile.
The $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service can be used to construct a user
security profile. The usrpro and
usrnam arguments are mutually exclusive. The
objpro and usrpro arguments are also
mutually exclusive unless the objpro argument is an
object handle.
The item codes used with $CHECK_ACCESS are described in the following
list and are defined in the $CHPDEF system macro library.
Item Codes
CHP$_ACCESS
A longword bit mask that represents the desired access ($ARMDEF). Only
those bits set in CHP$_ACCESS are checked against the protection of the
object to determine whether access is granted.
The default for CHP$_ACCESS is read. Symbolic representations for the
access types associated with the built-in protected classes are found
in the $ARMDEF macro.
For example, ARM$M_MANAGE specifies Manage access for the queue class
object. Access type names are object class specific and vary from class
to class. Because $CHECK_ACCESS performs only a bitwise comparison of
access desired to object protection, the original Read, Write, Execute,
and Delete names can also be used to specify the first four access
types for any object class.
The following table shows the access types available and lists their
common interpretations. These symbols are defined in the $ARMDEF system
macro library. For more information, see the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
| Access Type |
Access Permitted |
|
ARM$M_READ
|
Allows holders to read an object, perform wildcard directory lookups,
display jobs in a queue, or use an associated vector processor.
|
|
ARM$M_WRITE
|
Allows holders to alter the contents of an object, remove a directory
entry, write or extend existing files on a volume, or submit a job to a
queue.
|
|
ARM$M_EXECUTE
|
Allows holders to run an image or command procedure, perform exact
directory lookups, issue physical I/O requests to a device, create new
files on a volume, or act as operator for a queue.
|
|
ARM$M_DELETE
|
Allows holders to delete an object, perform logical I/O to a device, or
delete a job in a queue.
|
|
ARM$M_CONTROL
|
Allows holders to display or alter the security characteristics of an
object.
|
CHP$_ACMODE
A byte that defines the accessor's processor access mode ($PSLDEF). The
following access modes and their symbols are defined in the system
macro library ($PSLDEF). Objects supported by the operating system do
not consider access mode in determining object access.
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
If CHP$_ACMODE is not specified, access mode is not used to determine
access.
CHP$_ALARMNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the alarm name from any Alarm ACE
contained in the object's ACL. Currently, if a matching Alarm ACE
exists, the string SECURITY will be returned. The string returned by
CHP$_ALARMNAME can be used as input to the $AUDIT_EVENT system service,
using the NSA$_ALARM_NAME item code.
CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
A list containing information to be added to any resulting security
audit. The bufadr argument points to the beginning of
an $AUDIT_EVENT item list. See the itmlst argument of
the $AUDIT_EVENT system service for a list of valid security auditing
item codes. Note that the NSA$_EVENT_TYPE and NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE items
are ignored when auditing with $CHECK_ACCESS. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag must
be specified.
CHP$_AUDITNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the audit name from any Audit ACE
contained in the object's ACL. Currently, if a matching Audit ACE
exists, the string SECURITY will be returned. The string returned by
CHP$_AUDITNAME can be used as input to the $AUDIT_EVENT system service,
using the NSA$_AUDIT_NAME item code.
CHP$_FLAG
A longword that controls various aspects of the protection check. The
symbols in the following table are offsets to the bits within the
longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate
bit set by using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. These symbols are
defined in the system macro library ($CHPDEF).
| Symbol |
Access |
|
CHP$V_ALTER
|
Accessor desires write access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_AUDIT
|
Access audit requested.
|
|
CHP$V_CREATE
|
Perform the audit as an object creation event.
|
|
CHP$V_DELETE
|
Perform the audit as an object deletion event.
|
|
CHP$V_FLUSH
|
Force audit buffer flush.
|
|
CHP$V_INTERNAL
|
Audit on behalf of the Trusted Computing Base (TCB). Reserved to HP.
|
|
CHP$V_MANDATORY
|
Force the object access event to be audited.
|
|
CHP$V_NOFAILAUD
|
Do not perform audits for failed access.
|
|
CHP$V_NOSUCCAUD
|
Do not perform audits for successful access.
|
|
CHP$V_OBSERVE
|
Accessor desires read access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_SERVER
|
Audit on behalf of a TCB server process.
|
|
CHP$V_USEREADALL
|
Accessor is eligible for READALL privilege.
|
The default for CHP$_FLAG is CHP$V_OBSERVE.
The primary purpose of the CHP$V_OBSERVE and CHP$V_ALTER flags is as
latent support for a mandatory (lattice) security policy, such as that
provided by the Security Enhanced VMS (SEVMS) offering.
CHP$_MATCHEDACE
A variable-length data structure containing the first Identifier ACE in
the ACL that granted or denied access to the object. The $FORMAT_ACL
system service describes the format of an Identifier ACE.
CHP$_PRIVUSED
A longword mask of flags that represent the privileges used to gain
access.
You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set by
using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The symbols are defined in
the system macro library ($CHPDEF). The following symbols are offsets
to the bits within the longword:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
CHP$V_SYSPRV
|
SYSPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPPRV
|
GRPPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_BYPASS
|
BYPASS was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_READALL
|
READALL was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_OPER
|
OPER was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPNAM
|
GRPNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_SYSNAM
|
SYSNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GROUP
|
GROUP was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_WORLD
|
WORLD was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_PRMCEB
|
PRMCEB was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_UPGRADE
|
UPGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_DOWNGRADE
|
DOWNGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
Description
The Check Access service invokes the operating system control
protection check mechanism, $CHKPRO, to determine whether a named user
is allowed the described access to the named object. A file server, for
example, might check the access attributes of a user who attempts to
access a file (the object).
If the user can access the object, $CHECK_ACCESS returns the SS$_NORMAL
status code; otherwise, $CHECK_ACCESS returns SS$_NOPRIV.
The arguments accepted by this service specify the name and class of
object being accessed, the name of the user requesting access to the
object, the type of access desired, and the type of information to be
returned.
The caller can also request that an object access audit be performed if
security auditing has been enabled for the object class or if Audit
ACEs are contained in the object's ACL. Auditing ACEs include both
Alarm ACEs and Audit ACEs. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag requests an access
audit. This requires that the caller be in executive or kernel mode or
possess the AUDIT privilege.
Normally, $CHECK_ACCESS generates an object access audit when an audit
is required. The caller can specify the CHP$V_CREATE flag to force an
object creation audit instead of an object access audit. Similarly, the
CHP$V_DELETE flag forces an object deletion audit. The CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
item code can be used to specify additional information to be included
in any resulting audit records.
With certain types of devices, $CHECK_ACCESS can return a false
negative, but never a false positive. This is due to additional LOG_IO
and PHY_IO privilege checking in the $QIO system service that might
override an otherwise unsuccessful access attempt. These privilege
checks are not mirrored by the $CHECK_ACCESS system service. The
affected devices are those that are non-file-structured or mounted
foreign and also either spooled, file-oriented, or shareable. For
example, mailbox devices fall into this category because they are
non-file-structured and shareable. To accurately duplicate the result
that would be obtained if the user had issued a read or write against
these devices, it might be necessary to test for these additional
privileges using the $CHECK_PRIVILEGE system service. For more
information about access requirements for devices, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
Access to SYSUAF.DAT and RIGHTSLIST.DAT is required. AUDIT privilege is
required when requesting a user mode audit.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CHKPRO, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE, $FORMAT_ACL
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, one of the buffers
specified in the item list cannot be written by the caller, or one of
the arguments could not be read or written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Invalid or conflicting combination of parameters.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Insufficient information to identify object or user.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
Insufficient process memory to execute service.
|
|
SS$_NOAUDIT
|
Caller lacks privilege to request audit.
|
|
SS$_NOCALLPRIV
|
Caller lacks privilege to access authorization database.
|
|
SS$_NOCLASS
|
No matching object class was located.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The desired access is not granted.
|
|
SS$_UNSUPPORTED
|
Operations on remote object are not supported.
|
|
