 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$DEVICE_PATH_SCAN (Alpha and Integrity servers)
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns the displayable pathname
for a given I/O channel or device name. Can be used to return all
displayable paths to an I/O device.
Format
SYS$DEVICE_PATH_SCAN [chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,contxt] [,nullarg]
C Prototype
int sys$device_path_scan (unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void
*itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, struct_generic_64 *nullarg);
Arguments
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which
information is desired. The chan argument is a word
containing this number.
To identify a device to $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN, you can specify either the
chan or devnam parameters, but you
should not specify both. If you specify both arguments, the
chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN uses a default value of 0
for chan.
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the device about which $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN is to return path
information. The devnam argument is the address of a
character string descriptor pointing to this name string.
The device name string can be either a physical device name or a
logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore
(_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the
string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is
performed until either a physical device name is found or the system
default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the
characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN, you can specify either the
chan or devnam argument, but you
should not specify both. If both arguments are specified, the
chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN uses a default value of 0
for chan.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be
returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information.
The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0. The
following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
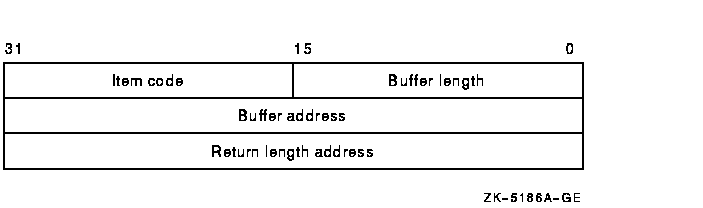
See the itmlst argument in the $GETDVI system service
description for information on the meaning of these fields in the item
list.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Value used to indicate the current position of a $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN
search. The contxt argument is the address of the
longword that receives this information. On the initial call, the
longword should contain 0.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
Item Code
DPS$_MP_PATHNAME
When you specify DPS$_MP_PATHNAME, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN returns the name
of one of the Multipath I/O paths connecting to the device named in the
devnam argument. When the value of the
contxt argument is 0, the path name for the first
established path will be returned. On subsequent calls, with a non-zero
contxt value, the path names of the remaining
available paths to the device will be returned.
In the item code, the Buffer Address field must point to the buffer
that will hold the path name to be returned by the service. The Return
Length Address field must be point to the buffer that will hold the
return length returned by the service.
Upon completion of the command, the buffer pointed to by the Buffer
Address field will hold a string identifying the requested path name.
The Return Length Address field will point to the length in bytes of
the path name being returned. The bytes in the path name buffer beyond
the end of the path string will remain in the state they were set by
the caller of the service.
The DPSDEF macro contains this item code.
Description
The Scan for Device Paths service returns I/O path information for a
given I/O channel or device name. Each call to $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN will
return information on a different I/O path connecting with the device
specified in the chan or devnam
arguments.
If the contxt argument is handled appropriately, the
service will return information on the paths in the order in which they
were established. On the first call, the contxt
argument should be set to zero. The contxt value will
be changed by the service during this call and a new value will be
written into contxt and returned to the caller. The
caller must use this same value in the next call to the service.
Following this convention will result in a different path name being
returned on each call.
Once the service has returned information on all paths to the named
device, any further calls that use the final contxt
value will result in SS$_NOMOREPATH status being returned.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$ASSIGN, $DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $SET_DEVICE
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The device name string descriptor, device name string, or
itmlst argument cannot be read; or the buffer or
return length longword cannot be written.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid item code, or the buffer length field
in an item descriptor specified insufficient space for the return
length information.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number
larger than the number of channels.
|
|
SS$_IVDEVNAM
|
The device name string contains invalid characters, or neither the
devnam nor
chan argument was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOMOREPATH
|
No more device paths exist for this device.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
$DEVICE_SCAN
Returns the names of all devices that match a specified set of search
criteria.
Format
SYS$DEVICE_SCAN return_devnam ,retlen ,[search_devnam] ,[itmlst]
,[contxt]
C Prototype
int sys$device_scan (void *return_devnam, unsigned short int *retlen,
void *search_devnam, void *itmlst, struct _generic_64 *contxt);
Arguments
return_devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Buffer to receive the device name. The return_devnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to a
buffer into which $DEVICE_SCAN writes the name of the first or next
device that matches the specified search criteria. The maximum size of
any device name is 64 bytes.
retlen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of the device name string returned by $DEVICE_SCAN. The
retlen argument is the address of a word into which
$DEVICE_SCAN writes the length of the device name string.
search_devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the device for which $DEVICE_SCAN is to search. The
search_devnam argument accepts the standard wildcard
characters, the asterisk (*), which matches any sequence of characters,
and the percent sign (%), which matches any one character. If the
search_devnam argument does not include a wildcard
character, an exact match is used for comparison. For example, to match
all unit 0 DU devices on any controller, specify
*DU%0. This string is compared to the most complete device
name (DVI$_ALLDEVNAM). Only uppercase characters are accepted.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword_unsigned |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying search criteria used to identify the device names
for return by $DEVICE_SCAN. The itmlst argument is the
address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes one
search criterion. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a
longword of 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the longword from which $DEVICE_SCAN is to read the
information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code
specified in the item code field of the item descriptor.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-specified symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $DEVICE_SCAN is to return. The $DVSDEF macro defines
these codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of a longword value that contains
item code information. Examples include DC$_DISK and DC$_MAILBOX.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the address of a word to receive the length (in
bytes) of information returned for the output value item code.
For the input value item code, this field is not used. HP recommends
the placeholder value be 0.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
quadword_unsigned |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Value used to indicate the current position of a $DEVICE_SCAN search.
The contxt argument is the address of the quadword
that receives this information. On the initial call, the quadword
should contain 0.
Item Codes
DVS$_DEVCLASS
An input value item code that specifies, as an unsigned longword, the
device class being searched. The $DCDEF macro defines these classes.
The DVS$_DEVCLASS argument is a longword containing this number;
however, DVS$_DEVCLASS uses only the low-order byte of the longword.
DVS$_DEVTYPE
An input value item code that specifies, as an unsigned longword, the
device type for which $DEVICE_SCAN is going to search. The $DCDEF macro
defines these types.
The DVS$_DEVTYPE argument is a longword containing this number;
however, DVS$_DEVTYPE uses only the low-order byte of the longword.
DVS$_DEVTYPE should be used in conjunction with DVS$_DEVCLASS to
specify the device type being searched for.
Description
The Scan for Devices system service returns the names of all devices
that match a specified set of search criteria. The names returned by
$DEVICE_SCAN can then be passed to another service; for example,
$GETDVI or $MOUNT.
The device names are returned for one process per call. A context value
is used to continue multiple calls to $DEVICE_SCAN.
$DEVICE_SCAN allows wildcard searches based on device names, device
classes, and device types. It also provides the ability to perform a
wildcard search on other device-related services.
$DEVICE_SCAN makes it possible to combine search criteria. For example,
to find only RA82 devices, use the following selection criteria:
DVS$_DEVCLASS = DC$_DISK and DVS$_DEVTYPE = DT$_RA82
|
To find all mailboxes with MB as part of the device name
(excluding mailboxes such as NLA0), use the following selection
criteria:
DVS$_DEVCLASS = DC$_MAILBOX and DEVNAM = *MB*
|
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
search_devnam,
itmlst, or
contxt argument cannot be read by the caller, or the
retlen,
return_devnam, or
contxt argument cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
contxt argument contains an invalid value, or the item
list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_NOMOREDEV
|
No more devices match the specified search criteria.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
$DGBLSC
Marks an existing permanent global section for deletion. The actual
deletion of the global section takes place when all processes that have
mapped the global section have deleted the mapped pages.
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, this service accepts 64-bit
addresses.
Format
SYS$DGBLSC [flags] ,gsdnam ,[ident]
C Prototype
int sys$dgblsc (unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, struct _secid *ident);
Arguments
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Mask indicating global section characteristics. The
flags argument is a longword value. A value of 0 (the
default) specifies a group global section; a value of SEC$M_SYSGBL
specifies a system global section; a value of SEC$M_SHMGS on an OpenVMS
Galaxy system creates a shared-memory global section.
gsdnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string
descriptor |
Name of the global section to be deleted. The gsdnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
this name string.
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the group
UIC as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global
sections are unique to UIC groups.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of the global
section to be deleted and the matching criteria to be applied. The
ident argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a
quadword structure containing three fields.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. Values for these
fields can be assigned by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If you specify no version number when
creating a section, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
The first longword specifies, in its low-order 3 bits, the matching
criteria. The valid values, the symbolic names by which they can be
specified, and their meanings are listed in the following table:
| Value |
Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify no address or specify it as 0 (the default), the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
Description
The Delete Global Section service marks an existing permanent global
section for deletion. The actual deletion of the global section takes
place when all processes that have mapped the global section have
deleted the mapped pages.
After a global section has been marked for deletion, any process that
attempts to map it receives the warning return status code
SS$_NOSUCHSEC.
Temporary global sections are automatically deleted when the count of
processes using the section goes to 0.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one or more
of the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to delete a system global section
- PRMGBL privilege to delete a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to delete a page frame section
- SHMEM privilege to delete a global section located in memory shared
by multiple processors
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,
$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
The $DGBLSC service does not unmap a global section from a process's
virtual address space. To do this, the process should call the Delete
Virtual Address Space ($DELTVA or $DELTVA_64) service, which deletes
the pages to which the section is mapped.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The global section name or name descriptor or the section
identification field cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INTERLOCK
|
The bit map lock for allocating global sections from the specified
shared memory is locked by another process.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
You set an invalid flag, reserved flag, or flag requiring a user
privilege.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The section identification match control field is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have the privilege to delete a system global
section, does not have read/write access to a group global section, or
does not have the privilege to delete a global section located in
memory that is shared by multiple processors.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHSEC
|
The specified global section does not exist, or the identifications do
not match.
|
|
SS$_NOTCREATOR
|
The section is in memory shared by multiple processors and was created
by a process on another processor.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gsdnam string exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
+VAX specific
|

