 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
volume size in blocks/cluster factor + 1
Once initialized, the maximum number of files can be increased only by
reinitializing the volume.
The default maximum number of files is calculated as follows:
volume size in blocks/(cluster factor + 1) * 2
The INIT$_MAXFILES item code applies only to disks.
Note
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For
more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
|
INIT$_OVR_ACCESS
INIT$_NO_OVR_ACCESS---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether to override any character in
the accessibility field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI
magnetic tape. For more information, see the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
To specify INIT$_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume or
have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_EXP
INIT$_NO_OVR_EXP---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether the caller writes to a
magnetic tape that has not yet reached its expiration date. This item
code applies only to the magnetic tapes that were created before VAX
VMS Version 4.0 and that use the D% format in the volume owner
identifier field.
To specify INIT$_OVR_EXP, the caller must either own the volume or have
VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OVR_VOLO
INIT$_NO_OVR_VOLO---Default
A Boolean item code that allows the caller to override processing of
the owner identifier field of the ANSI volume label VOL1 on an ANSI
magnetic tape.
To specify INIT$_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either own the volume or
have VOLPRO privilege.
INIT$_OWNER
An input item code that specifies the UIC that will own the volume. The
input buffer must contain a longword value, which is the UIC. The
default is the UIC of the caller.
For magnetic tapes, no UIC is written unless protection on the magnetic
tape is specified. If the INIT$_VPROT item code is specified but the
INIT$_OWNER item code is not specified, the UIC of the caller is
assigned ownership of the volume.
INIT$_READCHECK
INIT$_NO_READCHECK---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be
performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information
about data checking, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_READCHECK item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_SIZE
An input item code that specifies the number of blocks allocated for a
RAM disk with a device type of DT$_RAM_DISK. The input buffer must
contain a longword value.
INIT$_SPECIAL_FILES--Default
INIT$_NO_SPECIAL_FILES
Boolean item codes that control whether special files are enabled on
the volume.
INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1
INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_2---Default
Symbolic item codes that specify whether the volume should be formatted
in Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 or Structure Level 2. Structure
Level 1 is incompatible with the following item codes:
- INIT$_READCHECK
- INIT$_WRITECHECK
- INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE
The default protection for a Structure Level 1 disk is full access to
system, owner, and group users, and read access to all other users.
The INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1 item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_USER_NAME
An input item code that specifies the user name that is associated with
the volume. The input buffer must contain a character string from 1 to
12 alphanumeric characters, which is the user name. The default is the
user name of the caller.
INIT$_VERIFIED
INIT$_NO_VERIFIED
A Boolean item code that indicates whether the disk contains bad block
data. INIT$_NO_VERIFIED indicates that any bad block data on the disk
should be ignored. For disks with 4096 blocks or more, the default is
INIT$_VERIFIED.
INIT$_NO_VERIFIED is the default for the following:
- Disks with fewer than 4096 blocks
- DIGITAL Storage Architecture (DSA) devices
- Disks that are not last-track devices
The INIT$_VERIFIED item codes apply only to disks.
INIT$_VOLUME_LIMIT
An input item code that specifies the maximum logical volume size. For
more information, see the DCL command INITIALIZE/LIMIT.
INIT$_VPROT
An input item code that specifies the protection assigned to the
volume. The input buffer must contain a longword protection mask that
contains four 4-bit fields. Each field grants or denies read, write,
create, and delete access to a category of users. Cleared bits grant
access; set bits deny access.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask:
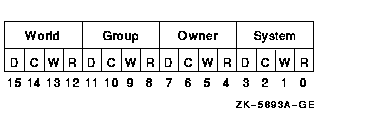
The default is the default protection of the caller.
For magnetic tape, the protection code is written to a specific volume
label. The system applies only read and write access restrictions;
execute and delete access are ignored. Moreover, the system and the
owner are always given read and write access to magnetic tapes,
regardless of the protection mask specified.
When you specify a protection mask for a disk volume, access type E
(execute) indicates create access.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 volumes, an initial security
profile is created from the VOLUME.DEFAULT profile, with the owner and
protection as currently defined for INITIALIZE.
You can use the $SET_SECURITY service to modify the security profile
after the volume is initialized and mounted.
The caller needs read, write, or control access to the device.
INIT$_WINDOW
The INIT$_WINDOW item code specifies the number of mapping pointers to
be allocated for file windows. The input buffer must contain a longword
value in the range 7 to 80. The default is 7.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to
access the data in the file.
The INIT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_WRITECHECK
INIT$_NO_WRITECHECK---Default
A Boolean item code that specifies whether data checking should be
performed for all read operations on the volume. For more information
about data checking, see the HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The INIT$_WRITECHECK item code applies only to disks.
Description
The Initialize Volume system service formats a disk or magnetic tape
volume and writes a label on the volume. At the end of initialization,
the disk is empty except for the system files containing the structure
information. All former contents of the volume are lost.
A blank magnetic tape can sometimes cause unrecoverable errors when it
is read. $INIT_VOL attempts to read the volume unless the following
three conditions are in effect:
- INIT$_OVR_ACCESS Boolean item code is specified.
- INIT$_OVR_EXP Boolean item code is specified.
- Caller has VOLPRO privilege.
If the caller has VOLPRO
privilege, $INIT_VOL initializes a disk without reading the ownership
information; otherwise, the ownership of the volume is checked.
A blank disk or a diskette with an incorrect format can sometimes cause
a fatal drive error. Such a diskette can be initialized successfully by
specifying the INIT$_DENSITY item code to format the diskette.
Required Access or Privileges
To initialize a particular volume, the caller must either have volume
protection (VOLPRO) privilege or the volume must be one of the
following:
- Blank disk or magnetic tape; that is, a volume that has never been
written
- Disk that is owned by the caller's UIC or by the UIC [0,0]
- Magnetic tape that allows write access to the caller's UIC or that
was not protected when it was initialized
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SET_SECURITY,
$SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be
accessed.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code or an
illegal item code was specified.
|
|
SS$_IVSSRQ
|
A concurrent call to SYS$INIT_VOL is already active for the process.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have sufficient privilege to initialize the volume.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist on the host system.
|
|
|
|
|
The $INIT_VOL service can also return the following condition values,
which are specific to the Initialize Volume utility:
|
|
INIT$_ALLOCFAIL
|
Index file allocation failure.
|
|
INIT$_BADACCESSED
|
Value for INIT$_ACCESSED item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADBLOCKS
|
Invalid syntax in bad block list.
|
|
INIT$_BADCLUSTER
|
Value for INIT$_CLUSTER_SIZE item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADDENS
|
Invalid value for INIT$_DENSITY item code.
|
|
INIT$_BADDIRECTORIES
|
Value for INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADEXTENSION
|
Value for INIT$_EXTENSION item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADHEADERS
|
Value for INIT$_HEADER item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADMAXFILES
|
Value for INIT$_MAXFILES item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BADOWNID
|
Invalid value for owner ID.
|
|
INIT$_BADRANGE
|
Bad block address not on volume.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOL1
|
Bad VOL1 ANSI label.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOLACC
|
Invalid value for INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS item code.
|
|
INIT$_BADVOLLBL
|
Invalid value for ANSI tape volume label.
|
|
INIT$_BADWINDOWS
|
Value for INIT$_WINDOWS item code out of range.
|
|
INIT$_BLKZERO
|
Block 0 is bad---volume not bootable.
|
|
INIT$_CLUSTER
|
Unsuitable cluster factor.
|
|
INIT$_CONFQUAL
|
Conflicting options were specified.
|
|
INIT$_DIAGPACK
|
Disk is a diagnostic pack.
|
|
INIT$_ERASEFAIL
|
Volume not completely erased.
|
|
INIT$_FACTBAD
|
Cannot read factory bad block data.
|
|
INIT$_ILLOPT
|
Item codes not appropriate for the device were specified.
|
|
INIT$_INDEX
|
Invalid index file position.
|
|
INIT$_LARGECNT
|
Disk too large to be supported.
|
|
INIT$_MAXBAD
|
Bad block table overflow.
|
|
INIT$_MTLBLLONG
|
Magnetic tape label specified is longer than 6 characters.
|
|
INIT$_MTLBLNONA
|
Magnetic tape label specified contains non-ANSI "a"
characters.
|
|
INIT$_NOBADDATA
|
Bad block data not found on volume.
|
|
INIT$_NONLOCAL
|
Device is not a local device.
|
|
INIT$_NOTRAN
|
Logical name cannot be translated.
|
|
INIT$_NOTSTRUC1
|
Options not available with Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1.
|
|
INIT$_UNKDEV
|
Unknown device type.
|
$IO_CLEANUP (Alpha and Integrity servers)
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns all resources allocated
by $IO_SETUP.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_CLEANUP fandle
C Prototype
int sys$io_cleanup (unsigned __int64 fandl);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle, passed by value, returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
Description
The Clean Up Fast I/O system service returns various internal resources
allocated by the $IO_SETUP system service. Buffer objects passed to
$IO_SETUP cannot be deleted until every $IO_SETUP call has had a
corresponding $IO_CLEANUP call.
Image rundown executes any required $IO_CLEANUP operations on behalf of
the process.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_PERFORM(W), $IO_SETUP
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADFANDLE
|
Argument was not a valid
fandle.
|
|
SS$_BUSY
|
The fandle cannot be cleaned up because an I/O is in progress. Reissue
the call to $IO_CLEANUP after the I/O has finished.
|
$IO_FASTPATH (Alpha and Integrity servers)
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, provides the ability to control
the set of Fast Path devices and their assignment to CPUs enabled for
Fast Path use.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATH efn, cpu_mask,function_code, [iosb], [astadr], [astprm]
[,[mask_length]]
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpath (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, int
function_code, struct_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params),
__int64 astprm, ...)
;)
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword bit mask (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the IO_FASTPATH(W) operation
completes. The efn argument is a longword containing
the number of the event flag.
cpu_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
bitmap |
| type: |
quadword bitmap |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The cpu_mask argument specifies a set of CPUs to be
operated upon.
function_code
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The function_code specifies the operation to be
performed. Note that there is currently only one function code:
FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS - Distribute Fast Path ports across CPUs.
mask_length
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword length |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The mask_length specifies the length of the cpu_mask
bitmap in bytes. If the mask_length is not supplied or
is specified as zero, a length of 4 bytes is used.
Description
The $IO_FASTPATH system service performs operations on the set of Fast
Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use. The $IO_FASTPATHW
system service completes synchronously. That is, it returns after the
operation is complete.
The FP$K_BALANCE_PORTS function code specifies that the system service
is to distribute the set of system assignable Fast Path ports across
the intersection of a caller-supplied set of candidate CPUs
(cpu_mask) and the current set of usable CPUs. Usable
CPUs are the intersection of the set of CPUs both enabled for Fast Path
use by IO$_PREFERRED_CPUS and whose current state is RUN.
The service does this by:
- Eliminating all CPUs not in the set of usable CPUs from the set of
candidate CPUs.
- Restoring any user assigned ports that are not currently on the
user's preferred CPU to the user's preferred CPU, if that CPU is in the
set of usable CPUs.
- Spreading the system assignable Fast Path ports, and any Fast Path
ports whose user preferred CPU is unavailable, evenly across the set of
usable candidate CPUs.
If the primary CPU is in the set of usable
candidate CPUs, the distribution will be biased against the primary CPU
in that a port will only be assigned to the primary after ports have
been assigned to each of the other usable candidate CPUs.
Required Access or Privileges
PHYS_IO
Required Quota
None.
Related Services
$GETDVI, $QIO
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
Unsupported value for cpu_mask.
|
|
SS$_ILLIOFUNC
|
Illegal function code.
|
$IO_FASTPATHW
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, performs operations on the set
of Fast Path devices and CPUs enabled for Fast Path use.
The $IO_FASTPATHW system service is functionally equivalent to the
$IO_FASTPATH service except that it completes synchronously. That is,
it returns after the operation is complete.
Format
SYS$IO_FASTPATHW efn, cpu_mask, function_code, [iosb], [astadr],
[astprm], [,[mask_length]]
C Prototype
int sys$io_fastpathw (unsigned int efn, UINT32_PQ cpu_mask, int
function_code, struct_iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(_ _unknown_params), _
_int64 astprm, ...)
;)
$IO_PERFORM (Alpha and Integrity servers)
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, starts the Fast I/O operation.
The $IO_PERFORM service completes asynchronously. For synchronous
completion, use the Perform Fast I/O and Wait ($IO_PERFORMW) service.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$IO_PERFORM fandle ,chan ,iosadr ,bufadr ,buflen ,devdata
C Prototype
int sys$io_perform (unsigned __int64 fandl, unsigned short int chan,
struct _iosa *iosadr, void *bufadr, unsigned __int64 buflen, unsigned
__int64 devdata);
Arguments
fandle
| OpenVMS usage: |
fandle |
| type: |
64-bit integer (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A fandle returned by a previous call to $IO_SETUP.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Software I/O channel number.
iosadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Address of the I/O Status Area (IOSA). This value cannot be 0; that is,
an IOSA is required. The iosadr must be aligned to a
quadword boundary.
bufadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The process buffer address. Must be aligned on a 512-byte boundary.
buflen
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
64-bit integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The byte count for the I/O. The buflen argument must
be a multiple of 512 bytes. Drivers have further limitations on the
maximum size of an I/O request.
devdata
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
pointer or integer |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A hardware integer passed unchanged to the driver. For disk devices,
this is the media address for the transfer; that is, the virtual block
number (VBN) for virtual I/O functions or the logical block number
(LBN) for logical I/O functions. This argument is ignored for tape
devices.
For drivers with complex parameters, devdata would be
the address of a descriptor or buffer specific to the device and
function and would be documented with the driver.
Description
The Perform Fast I/O system service initiates an I/O operation on the
channel number specified by the chan argument. The
bytes specified by the buflen argument are transferred
between the location (devdata) on the device driver
and the user's buffer starting at the process buffer address
(bufadr). The byte count is read or written according
to the function code previously specified in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with the fandle argument.
Upon completion, the I/O status is written to the IOSA starting at the
location specified by iosadr, and an AST is delivered
to the astadr address supplied in the $IO_SETUP call
associated with fandle. The IOSA address is passed to
the AST as the AST parameter.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$IO_CLEANUP, $IO_SETUP, $IO_PERFORMW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADBUFADR
|
The data buffer does not reside within the bounds of the data buffer
object for the fandle.
|
|
SS$_BADIOSADR
|
The IOSA does not reside within the bounds of the IOSA buffer object
for this fandle.
|
|
SS$_FANDLEBUSY
|
The operation using this fandle is already in progress.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
An invalid channel number was specified; that is, a channel number of 0
or a number larger than the number of channels available.
|
|
SS$_UNALIGNED
|
The buffer specified by
bufadr or
iosadr is not properly aligned.
|
|
SS$_WRONGACMODE
|
The request is invalid because the
fandle was created from a more privileged access mode,
or the channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode.
|
Condition Values Returned in the I/O Status Block1
The HP OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual lists these device-specific condition values for each
device.
|
