 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
The $LOGTYPDEF macro defines the following symbolic names for the fault
characteristic codes:
| Symbol |
Description |
|
LOGTYP$M_ARGS
|
Log system service arguments.
|
|
LOGTYP$M_FILE
|
Write log information to a file.
|
If you specify the flags argument as 0, the service
defaults to logging to a file and logging arguments.
If you specify LOGTYP$M_ARGS but lack privilege, service arguments are
not logged.
Description
The $SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW system service sets a simple value
associated with a process.
Generally, this service is used for changing process properties that
have a maximum of a single quadword. You can change only one property
at a time per call to this service.
Required Access or Privileges
To affect system service logging for another process, the calling
process might need one of the following privileges:
- GROUP privilege to affect a process in the same group, unless the
target process has the same UIC as the calling process.
- WORLD privilege to affect any process in the system.
To request logging the arguments passed to a system service, a process
needs SETPRV, CMKRNL, or CMEXEC privilege.
Required Quota
When system service logging is enabled, the log buffers are charged
against the process's paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA).
Related Services
$GETJPI
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Access violation.
|
|
SS$_WRONGSTATE
|
An attempt was made to modify system service logging characteristics of
a process when logging is disabled systemwide.
|
|
SS$_NONEXPR
|
The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process
identification was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The process does not have the privilege to affect the other process.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
Controls the association between a calling process and resource domains.
Format
SYS$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN func ,rsdm_id ,domain_number ,[nullarg]
,[access] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$set_resource_domain (unsigned int func, unsigned int *rsdm_id,
unsigned int domain_number, unsigned int nullarg, unsigned int access,
unsigned int acmode);
Arguments
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function code specifying the action that $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN is to
perform. The func argument is a longword containing
this function code. See the Function Codes section for a description of
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN function codes.
rsdm_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only to join, read only to leave |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Resource domain identification. The rsdm_id argument
is the address of a longword specifying the association of the calling
process with the resource domain.
The RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function returns a resource domain
identification. The RSDM$_LEAVE function requires the
rsdm_id argument as input to specify which resource
domain association the process is leaving.
The resource domain identification can be used as input to the $ENQ and
$ENQW system services.
domain_number
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Domain number that identifies the resource domain. The
domain_number argument is a longword value containing
the resource domain number.
The domain_number argument is required for the
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function but ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholder reserved to HP. You must specify 0.
access
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Types of access desired when using the lock management services within
the resource domain. The access argument is a longword
bit mask specifying the access types required; these can include read,
write, and lock.
The following table lists the symbols that the $RSDMDEF macro defines,
their descriptions, and the lock management system services that might
require each type of access:
| Symbol |
Access Description |
System Service |
|
RSDM$M_READ
|
Read lock value blocks
|
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
|
|
RSDM$M_WRITE
|
Write lock value blocks
|
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW,
|
|
RSDM$M_LOCK
|
Take locks
|
$ENQ, $ENQW
|
The service grants the desired access, provided your process has the
necessary access rights to the resource domain. If you do not specify
the access argument or if you specify 0,
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN attempts to access the domain in the following
order:
- Read, write, lock
- Read, lock
- Write, lock
- Lock
The access attempt terminates with the first success.
The access argument defaults to 0. It is ignored for
the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode requested for the association to the resource domain. The
most privileged access mode granted is the access mode of the caller.
Locks cannot be taken from access modes less privileged than the access
mode of the association.
The acmode argument is a longword containing the
access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the
access modes:
Symbolic
Name |
Access
Mode |
Privilege
Rank |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
High
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
--
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
--
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
Low
|
The acmode argument is optional for the
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN function. If you do not specify the
acmode argument, the access mode is set to the access
mode of the calling process. The acmode argument is
ignored for the RSDM$_LEAVE function.
Function Codes
RSDM$_JOIN_DOMAIN
A process has the option of forming multiple associations with one or
more resource domains. Each association can have different access
rights to the resource domain, such as to read lock value blocks or to
write lock value blocks. This request sets up a new association with a
resource domain.
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the desired access against the security
profile of the resource domain. If the desired access is allowed, a new
association to the resource domain is created, and a resource domain
identification for the association is returned.
This function code returns the following condition values:
SS$_NORMAL
SS$_BADPARAM
SS$_EXQUOTA
SS$_INSFMEM
SS$_NOOBJSRV
SS$_NOPRIV
RSDM$_LEAVE
This operation requests that a process end an association with a
resource domain.
A process must leave a resource domain association in the same mode as,
or in a more privileged mode than, the mode in which it joined the
resource domain.
Before a process can end its association with a resource domain, it
must release all locks taken using that association.
This function code returns the following condition values:
SS$_NORMAL
SS$_BADPARAM
SS$_IVMODE
SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
Description
The Set Resource Domain system service enables a process to use the
lock management system services $DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, and
$GETLKIW.
The lock management services enable processes with the appropriate
access rights to take and release locks on resource names and to
perform other functions related to lock management. Applications use
resource names to represent resources to which they want to synchronize
access. A resource domain is a namespace for resource names. A process
must join a resource domain to take and release locks and to read and
write value blocks associated with resources in that resource domain.
When a process requests to join a resource domain, $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN
performs an access check. After $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN verifies the
desired access to the resource domain, the service creates an
association between the resource domain and the calling process. The
association is represented by a resource domain identification. A
process can request different types of access to the same resource
domain; the type of access is a characteristic of the association with
the resource domain.
Each time a process joins a resource domain, a new association is
created.
Processes use their resource domain identifications when using $ENQ or
$ENQW to request a new lock.
The service can grant the following three types of access to resource
domains:
- The right to read lock value blocks
- The right to write lock value blocks
- The right to take and release locks
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN uses system dynamic memory, which uses BYTLM
quota, for the creation of the resource domain data structures.
Related Services
$DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The
func, the
domain_number, or the
rsdm_id argument was specified incorrectly.
|
|
SS$_EXQUOTA
|
The caller has insufficient BYTLM quota.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There is insufficient memory to join the resource domain.
|
|
SS$_IVMODE
|
An attempt was made to leave an association created by a more
privileged access mode.
|
|
SS$_NOOBJSRV
|
The audit server process, which maintains the security profile for
resource domains, is not running. The process access rights to the
domain cannot be determined, so access is denied.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Access to the resource domain was denied.
|
|
SS$_RSDM_ACTIVE
|
Unable to leave the resource domain because there are locks still
associated with this resource domain.
|
|
SS$_RSDMNOTFOU
|
The resource domain was not found.
|
$SET_RETURN_VALUE (Alpha and Integrity servers)
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, sets the return values or
condition codes in the Mechanism Array, independent of the architecture.
Format
SYS$SET_RETURN_VALUE mechanism_arg, return_type, return_value
C Prototype
int sys$set_return_value (void *mechanism_arg, unsigned int
*return_type, void *return_value);
Arguments
mechanism_arg
| OpenVMS usage: |
mechanism vector address |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The address of the location of the mechanism vector. If the
mechanism_arg argument is 0, the mechanism vector for
the currently active signal is used.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
return_type
| OpenVMS usage: |
integer |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of the location of a longword that contains one of the
function return signature codes.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
return_value
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer |
| type: |
scalar |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of the location that contains a value of the appropriate
type. The referenced value is read as a longword, quadword, or
octaword, depending on the return_type.
If the address of the return_type argument is 0, the
return_value argument is fetched by value and is
treated as return-type PSIG$K_FR_U32. This combination of arguments can
be used to set a condition code, such as SS$_ACCVIO, as a return value.
Description
The Set Return Value service allows the caller to specify return values
and condition codes in the Mechanism Array, independent of the
architecture.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
status
|
Success or failure. The given return value is placed in the appropriate
fields of the specified mechanism vector, according to the return type.
|
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
|
|
SS$_NOSIGNAL
|
No signal is currently active for an exception condition.
|
$SET_SECURITY
Modifies the security characteristics of a protected object.
Format
SYS$SET_SECURITY [clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst]
,[contxt] ,[acmode]
C Prototype
int sys$set_security (void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan,
unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int
*acmode);
Arguments
clsnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the object class. The clsnam argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to a string that contains the name of
the object class.
The following is a list of the protected object class names:
CAPABILITY
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
DEVICE
FILE
GLXGRP_GLOBAL_SECTION
GLXSYS_GLOBAL_SECTION
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
ICC_ASSOCIATION
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
QUEUE
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
SECURITY_CLASS
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
VOLUME
objnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going
to be retrieved. The objnam argument is the address of
a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the protected
object.
The format of an object name is class specific. The following table
lists object names and describes their formats:
| Object Class |
Object Name Format |
|
CAPABILITY
|
A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR.
|
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common
Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service.
|
|
DEVICE
|
Standard device specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
FILE
|
Standard file specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual.
|
|
GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
ICC_ASSOCIATION
|
ICC security object name
node::association_name. The special node name, ICC$::, refers
to entries in the clusterwide registry. For registry entries, the
Access Access Type does not apply.
|
|
LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
|
Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT)
system service.
|
|
QUEUE
|
Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller
($SNDJBC) system service.
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets.
|
|
SECURITY_CLASS
|
Any class name shown in the Object Class column of this table, or a
class name followed by a period (.) and the template name. Use the DCL
command SHOW SECURITY to display possible template names.
|
|
SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
|
Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system
service.
|
|
VOLUME
|
Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted.
|
objhan
| OpenVMS usage: |
object_handle |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Data structure identifying the object to address. The
objhan argument is an address of a longword containing
the object handle. You can use the objhan argument as
an alternative to the objnam argument; for example, a
channel number clearly specifies the file open on the channel and can
serve as an object handle.
The following table shows the format of the object classes:
| Object Class |
Object Handle Format |
|
COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
|
Event flag number
|
|
DEVICE
|
Channel number
|
|
FILE
|
Channel number
|
|
RESOURCE_DOMAIN
|
Resource domain identifier
|
|
VOLUME
|
Channel number
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
flags |
| type: |
mask_longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Mask specifying processing options. The flags argument
is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the
corresponding option. The flags argument requires the
contxt argument.
The following table describes each flag:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
OSS$M_LOCAL
|
Do not update the master profile for the specified object. This flag
allows you to call $SET_SECURITY several times to modify a local copy
of a profile; once the modifications are satisfactory, you can clear
the OSS$M_LOCAL flag, set the OSS$M_RELCTX flag, and have $SET_SECURITY
update the master profile. The flag applies only to calls made with the
contxt argument.
|
|
OSS$M_RELCTX
|
Release the context structure at the completion of this request.
|
The $OSSDEF macro defines symbolic names for the flag bits. You
construct the flags argument by specifying the
symbolic names of each desired option.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes
is to be modified. The itmlst argument is the address
of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword
of 0.
With the item list, the user modifies the protected object's
characteristics. The user defines which security characteristics to
modify. If this argument is not present, only the
flags argument is processed. Without the
itmlst argument, you can only manipulate the
security profile locks or release contxt resources.
The following data structure depicts the format of a single item
descriptor:
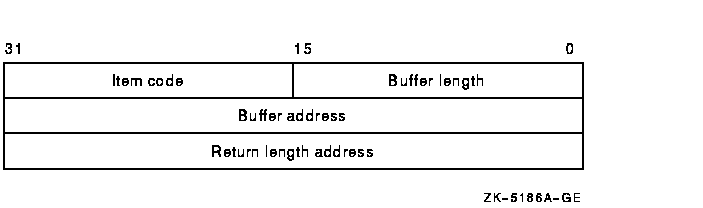
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the
buffer from which $SET_SECURITY is to read the information. The length
of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item
code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too
small, $SET_SECURITY truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information
that $SET_SECURITY is to modify. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes.
A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer from which
$SET_SECURITY is to read the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
Not used.
|
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
context |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Value used to maintain protected object processing context when dealing
with a single protected object across multiple
$GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY calls. Whenever the context value is
nonzero, the class name, object name, or object handle arguments are
disregarded. An input value of 0 indicates that a new context should be
established.
|
