Business employees increasingly want to be able to
work away from their offices--either from homes or from remote locations.
Sales people want to access databases while on the road, and managers want to be able
to manage groups and projects from remote locations.
With Microsoft Windows NT®
Server Remote Access Service (RAS), businesses can extend their
networks via phone lines. RAS lets mobile and work-at-home users
access corporate networks. RAS provides small businesses with
a dial-up server. Large organizations get a standards-based
dial-up server that enables client/server computing for remote users. RAS
works with different protocols, and most computers already include
software that enables end users to access RAS.
RAS LETS REMOTE USERS COMMUNICATE WITH THE OFFICE
Using
Windows NT Server RAS, remote users can securely access files and
printers as well as run applications such as Microsoft
BackOffice®. With RAS, a business can extend its network
using existing phone lines.
RAS is built-in
RAS is built into Windows NT Server so
customers don't have to buy extra software to get dial-up services. Most
operating systems include client software for RAS, so users can use
operating systems out of the box to connect to networks.
RAS supports ISDN
RAS lets users dial in across both phone lines and
ISDN.
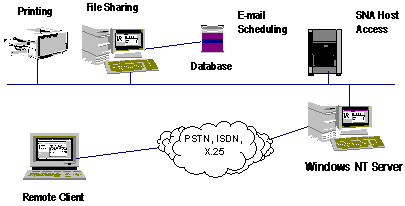
RAS extends networks to phone lines
RAS supports numerous clients
RAS supports mainstream networking clients, including:
- Windows for Workgroups-based clients
- LAN Manager-based clients
- Windows 95-based clients
- Windows NT Workstation-based clients
- Windows NT Server-based clients
- UNIX-based clients
- Macintosh-based clients
- NetWare clients
- OS/2-based clients
RAS is secure
With RAS, small business employees can connect
their PC to a phone jack at home and access the business
network. Users can enable all data to be encrypted and sent across phone
lines to a network in another location. RAS also authenticates users
securely using industry standard protocols.
RAS works with Microsoft BackOffice
With RAS, remote users
can access Microsoft BackOffice services running on computers in a
corporate network.
SMALL BUSINESSES GET A DIAL-UP SERVER
RAS is easy to use
Users click on a
graphical client application to make a connection to a business network.
RAS provides an administration tool that is easy to use. Network administrators can create RAS user accounts by using existing
Windows NT Server user accounts. Administrators can track events and
monitor performance of RAS dial-up connections using the graphical
tools--the event log and the performance monitor. RAS also automatically
assigns IP addresses to remote users and administrators do not need to
manually configure IP addresses for remote users.
RAS is available on a multipurpose platform
Windows NT Server provides file/print
services, application, and communication services one multipurpose platform. It is available on hardware from several vendors
and runs applications and services from several hundred third parties. RAS
is built-in with Windows NT Server and runs as a software service. To
use RAS as a dial-up server, businesses will need modems or modem cards
available from several modem vendors.
With RAS, users get Internet access from their workplace or homes
End-users can dial-up RAS from their homes or use RAS from
their workplace to access the Internet. For this, the business must ensure
that the systems that need Internet access have valid Internet addresses.
Internet Transfer with PPTP Technology
With Windows NT Server 4.0, RAS allows remote users to access
their network via the Internet by using Point-to-Point
Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). PPTP is a networking technology integrated with RAS
that supports multiprotocol virtual private networks (VPNs). PPTP uses the
Internet as the transfer mechanism instead of long distance telephone
lines or a toll free (1-800) service, greatly reducing transmission costs.
PPTP enables remote users to access their networks across
the Internet in two ways: by dialing into an Internet Service Provider
(ISP) or by connecting directly to the Internet. In either case, PPTP
provides one essential benefit: secure over-the-Internet data transfer.
However, using an ISP offers additional benefits:
- PPTP enables modems and ISDN cards to be separated from
the company's RAS server. They can be located at an ISP's modem bank or
a front-end processor (FEP). This greatly reduces costs because modems,
ISDN cards, etc. are loaded on the ISP's server, not the company's
server.
- PPTP means less administrative overhead because the ISP rather than
the network administrator manages the connection hardware.
- PPTP requires no changes to your existing client software.
For companies that want to manage their own networks entirely and
connect directly to the Internet through their own software and hardware,
PPTP offers the security they need.
The PPTP connection over the Internet is encrypted and secure, and
works with IP, IPX, NetBEUI, and other mainstream protocols.
LARGE ORGANIZATIONS GET A STANDARDS-BASED DIAL-UP SERVER THAT
ENABLES CLIENT/SERVER COMPUTING
RAS enables client/server computing for mobile users
With
RAS, remote users can access files, printers, as well as run applications
across long distances. RAS enables remote users to access Windows family
systems, NetWare, and UNIX systems. With RAS, large organizations thus
enable client server computing across wide area networks (WANs).
RAS is open and supports all major protocols
RAS is based on
the point-to-point protocol (PPP), which is the industry standard for
dial-up access services. RAS also supports industry standards for
authentication and encryption. Users may dial up across phone lines, ISDN,
or X.25 and access TCP/IP-, IPX-, or NetBEUI-based LANs.
RAS is a dial-up server
Large organizations can use a single Windows NT
Server-based system to provide dial-up facilities for up to 256 concurrent
users.
OTHER FEATURES IN WINDOWS NT 4.0 THAT SUPPORT RAS
- AS Multi-Link PPP --You can combine the bandwidth
of two or more physical communications links to increase your
remote access bandwidth and throughput using RAS Multilink. Based on the
IETF standard RFC 1717, RAS Multilink lets you combine analog modem paths,
ISDN paths, and mixed analog and digital communications links on both
your client and server PC. This will speed up your access to the
Internet or to your Intranet and cut down on the amount of time you have
to be remotely connected so it can reduce your costs for remote access.
- Re-startable file copy--This feature automatically begins
re-transferring a file upon re-connection whenever your RAS connection
has been lost. Nearly anyone who has used a modem can probably remember
times when they've nearly completed a file transfer across a modem only
to have their remote connection disabled before the transmission was
completed. Re-establishing the connection and starting the file transfer
process all over again can be frustrating, time-consuming, and
expensive. Restartable file copy addresses these problems by remembering
the status of your file transmission and continuing the transfer from
that point once you re-connect.
- Idle disconnect--This feature automatically terminates
your RAS connection after a certain period of time if there has been no
activity over the remote dial-up communications link. The user or
administrator can specify the amount of time before this feature is
activated. Idle disconnect reduces the cost of remote access carrier
service and can even allow a company to reduce the capacity of its
dial-in communications links, all based on the reduction of wasted
remote connect time.
- Auto-dial and Log-On Dial--Windows can map and maintain
an association between a Dial-up Networking entry and a network address
to integrate Dial-Up Networking with files and applications.
This means if you double-click an icon to open a file and that file is
only accessible over a dial-up connection, Dial-up Networking will
automatically initiate to allow you quick and easy access to the
information.
 Windows NT Server Site
Windows NT Server Site
 Microsoft Server Products Site
Microsoft Server Products Site
Last Updated: Tuesday, May 15, 2001
© 2005 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Terms of use.
