1.2 File Information Block
The file information block (FIB) contains much of the information that is exchanged between the user process and the ACP. The FIB must be writable.
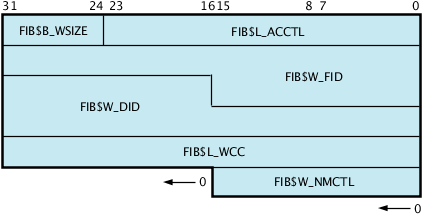
The FIB is passed by a descriptor (see Figure 1-2). A short FIB can be used in ACP calls that do not need arguments near the end of the FIB. The ACP treats the omitted portion of the FIB as if it were 0. Figure 1-3 shows the format of a typical short FIB that would be used to open an existing file.
Table 1-1 gives a brief description of the FIB fields. More detailed descriptions are provided in “ACP Subfunctions” and “Major Functions”.
Table 1-1 Contents of the FIB
Field | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
FIB$L_ACCTL | Contains flag bits that control the access to the file. “Input Parameters”, “Input Parameters”, “Input Parameters”, and “Input Parameters”, and “Delete File” describe the FIB$L_ACCTL field flag bits. | |
| FIB$L_ACL_STATUS | Status of the requested ACL attribute operation, if any. The ACL attributes are included in Table 1-7. If no ACL attributes are given, SS$_NORMAL is returned here. | |
FIB$L_ACLCTX | Maintains position context when processing ACL attributes from the attribute (P5) list. | |
FIB$B_ALALIGN | Contains the interpretation mode of the allocation (FIB$W_ALLOC) field. | |
| FIB$W_ALLOC | Contains the desired physical location of the blocks being allocated. Interpretation of the field is controlled by the FIB$B_ALALIGN field. The following subfields are defined: | |
Subfield | Meaning | |
FIB$W_LOC_FID | Three-word related file ID for RFI placement. | |
FIB$W_LOC_NUM | Related file number. | |
FIB$W_LOC_SEQ | Related file sequence number. | |
FIB$B_LOC_RVN | Related file relative volume number (RVN) or placement RVN. | |
FIB$B_LOC_NMX | Related file number extension. | |
FIB$L_LOC_ADDR | Placement logical block number (LBN), cylinder, or virtual block number (VBN). | |
FIB$B_ALOPTS | Contains option bits that control the placement of allocated blocks. “Input Parameters” describes the FIB$B_ALOPTS field flag bits. | |
FIB$L_ALT_ACCESS | A 32-bit mask that represents an access mask to check against file protection; for example, opens a file for read access and checks whether it can be deleted. The mask has the same configuration as the standard protection mask. | |
FIB$W_CNTRLFUNC | In an IO$_ACPCONTROL function, this field contains the code that specifies which ACP control function is to be performed (see “ACP Control”). This field overlays FIB$W_EXCTL. | |
FIB$L_CNTRLVAL | Contains a control function value used in an IO$_ACPCONTROL function (see “ACP Control”). The interpretation of the value depends on the control function specified in FIB$W_CNTRLFUNC. This field overlays FIB$L_EXSZ. | |
FIB$W_DID | Contains the file identifier of the directory file. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 and Level 2, the following subfields are defined: | |
Subfield | Meaning | |
FIB$W_DID_NUM | File number. | |
FIB$W_DID_SEQ | File sequence number. | |
FIB$W_DID_RVN | Relative volume number (only for magnetic tape devices). | |
FIB$B_DID_RVN | Relative volume number (only for disk devices). | |
FIB$B_DID_NMX | File number extension (only for disk devices). | |
FIB$W_EXCTL | Contains flag bits that specify extend control for disk devices. “Input Parameters” and “Input Parameters” describe the FIB$W_EXCTL field flag bits. | |
FIB$L_EXSZ | Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated in an extend operation on a disk file. | |
FIB$L_EXVBN | Specifies the starting disk file virtual block number at which a file is to be truncated. | |
FIB$W_FID | Specifies the file identification. You supply the file identifier when it is known; the ACP returns the file identifier when it becomes known; for example, as a result of a create or directory lookup. A 0 file identifier can be specified when an operation is performed on a file that is already open on a particular channel. The ACP returns the file identifier of the open file. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 and Level 2, the following subfields are defined: | |
Subfields | Meaning | |
FIB$W_FID_NUM | File number. | |
FIB$W_FID_SEQ | File sequence number. | |
FIB$W_FID_RVN | Relative volume number (only for magnetic tape devices). | |
FIB$B_FID_RVN | Relative volume number (only for disk devices). | |
FIB$B_FID_NMX | File number extension (only for disk devices). | |
FIB$W_FID_DIRNUM | Directory number of the file identifier. This is the path table record number of the directory that describes the file. | |
FIB$L_FID_RECNUM | Record number of the first directory record for the file within the current directory. | |
FIB$B_NAME_FORMAT_IN | Contains the format of the input file specification. “Input Parameters” describes the FIB$B_NAME_FORMAT_IN field flag bits. | |
FIB$B_NAME_FORMAT_OUT | Contains the format of the output file specification. “Input Parameters” describes the FIB$B_NAME_FORMAT_OUT field flag bits. | |
FIB$W_NMCTL | Contains flag bits that control the processing of a name string in a directory operation. “Input Parameters” and “Input Parameters” describe the FIB$W_NMCTL field flag bits. | |
FIB$L_STATUS | Access status. Applies to all major functions. The following bits are supported: | |
Subfields | Meaning | |
FIB$V_ALT_REQ | Set to indicate whether the alternate access bit is required for the current operation. If not set, the alternate access bit is optional. | |
FIB$V_ALT_GRANTED | If FIB$V_ALT_REQ = 0, the FIB bit returned from the file system is set if the alternate access check succeeded. Programmers can control the security information being propagated as well as the source of this information by setting the following bits (which apply only to the IO$_CREATE and IO$_MODIFY functions). | |
FIB$V_DIRACL | Propagate the ACL from the parent directory to the file, assuming the file is a directory file. | |
FIB$V_EXCLPREVIOUS | Set to indicate that propagation may not occur from a previous version of the file. | |
FIB$V_ALIAS_ENTRY | Set on any file system operation where the directory backlink in the file header is different (and nonzero) from the directory id specified in the FIB. | |
FIB$V_NOCOPYACL | Set to indicate that the ACL should not be propagated from the parent directory (or a previous version of the file) to the file. | |
FIB$V_NOCOPYOWNER | Set to indicate that the owner UIC should not be propagated from the parent directory (or a previous version of the file) to the file. | |
FIB$V_NOCOPYPROT | Set to indicate that the UIC-based protection should not be propagated from the parent directory (or a previous version of the file) to the file. | |
FIB$V_PROPAGATE | Propagate attributes from the parent directory (or previous version of the file). If you set the FIB$V_NOCOPYACL, FIB$V_NOCOPYOWNER, or FIB$V_NOCOPYPROT bits, you must also set FIB$V_PROPAGATE or a SS$_BADPARAM error results. | |
FIB$W_VERLIMIT | Contains the version limit of the directory entry. | |
FIB$L_WCC | Maintains position context when processing wildcard directory operations. | |
FIB$B_WSIZE | Controls the size of the file window used to map a disk file. If a window size of 255 is specified, the file is completely mapped by using segmented windows. | |