OpenVMS Alpha Guide to 64-Bit Addressing and VLM
Features
Order Number:
AA--QSBCC--TE
January 1998
This manual describes the OpenVMS Alpha support for 64-bit virtual
addressing and Very Large Memory (VLM).
Revision/Update Information:
This manual supersedes the OpenVMS Alpha Guide to 64-Bit Addressing and VLM Features, Version 7.1.
Software Version:
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.2
Compaq Computer Corporation
Houston, Texas
January 1999
Compaq Computer Corporation makes no representations that the use of
its products in the manner described in this publication will not
infringe on existing or future patent rights, nor do the descriptions
contained in this publication imply the granting of licenses to make,
use, or sell equipment or software in accordance with the description.
Possession, use, or copying of the software described in this
publication is authorized only pursuant to a valid written license from
Compaq or an authorized sublicensor.
Compaq conducts its business in a manner that conserves the environment
and protects the safety and health of its employees, customers, and the
community.
© Compaq Computer Corporation 1999. All rights reserved.
The following are trademarks of Compaq Computer Corporation: Alpha,
Bookreader, Compaq, DEC, DECdirect, DECnet, DIGITAL, DIGITAL UNIX,
OpenVMS, VAX, VAX DOCUMENT, VAXcluster, VMS, VMScluster, and the Compaq
logo.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other
countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company, Ltd.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of
their respective holders.
ZK6467
The OpenVMS documentation set is available on CD-ROM.
This document was prepared using VAX DOCUMENT, Version V3.2n.
Preface
This guide describes the 64-bit virtual addressing and Very Large
Memory (VLM) support provided in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.2.
The information in this document applies only to applications on
OpenVMS Alpha systems; applications on OpenVMS VAX systems are not
affected.
Intended Audience
The information in this guide is intended for system and application
programmers. It presumes that its readers are familiar with the OpenVMS
Alpha programming environment and concepts.
Document Structure
Chapter 1 briefly describes OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit addressing support and
VLM features.
Chapter 2 presents an overview of the OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit virtual
memory address space.
Chapters 3 through 12 describe the OpenVMS Alpha programming tools and
languages that support 64-bit addressing and VLM.
The appendixes contain macro descriptions and programming examples.
Related Documents
This guide provides high-level descriptions of some of the topics
covered in the following manuals; refer to these books for more
detailed information:
- OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual
- OpenVMS Calling Standard
- OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual: A--GETMSG and OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual: GETQUI--Z
- OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual
- OpenVMS RTL Library (LIB$) Manual
- OpenVMS Debugger Manual
- OpenVMS Alpha System Dump Analyzer Utility Manual
- OpenVMS Alpha Guide to Upgrading Privileged-Code Applications
For additional information on the Open Systems Software Group (OSSG)
products and services, access the following OpenVMS World Wide Web
address:
http://www.openvms.digital.com
|
Reader's Comments
Compaq welcomes your comments on this manual.
Print or edit the online form SYS$HELP:OPENVMSDOC_COMMENTS.TXT and send
us your comments by:
|
Internet
|
openvmsdoc@zko.mts.dec.com
|
|
Fax
|
603 884-0120, Attention: OSSG Documentation, ZKO3-4/U08
|
|
Mail
|
Compaq Computer Corporation
OSSG Documentation Group, ZKO3-4/U08
110 Spit Brook Rd.
Nashua, NH 03062-2698
|
How to Order Additional Documentation
Use the following World Wide Web address to order additional
documentation:
http://www.openvms.digital.com:81/
|
If you need help deciding which documentation best meets your needs,
call (800-282-6672).
Conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual:
|
Ctrl/
x
|
A sequence such as Ctrl/
x indicates that you must hold down the key labeled Ctrl while
you press another key or a pointing device button.
|
|
PF1
x
|
A sequence such as PF1
x indicates that you must first press and release the key
labeled PF1 and then press and release another key or a pointing device
button.
|
|
[Return]
|
In examples, a key name enclosed in a box indicates that you press a
key on the keyboard. (In text, a key name is not enclosed in a box.)
In the HTML version of this document, this convention appears as
brackets, rather than a box.
|
|
...
|
A horizontal ellipsis in examples indicates one of the following
possibilities:
- Additional optional arguments in a statement have been omitted.
- The preceding item or items can be repeated one or more times.
- Additional parameters, values, or other information can be entered.
|
.
.
.
|
A vertical ellipsis indicates the omission of items from a code example
or command format; the items are omitted because they are not important
to the topic being discussed.
|
|
( )
|
In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate that you must
enclose the options in parentheses if you choose more than one.
|
|
[ ]
|
In command format descriptions, brackets indicate optional elements.
You can choose one, none, or all of the options. (Brackets are not
optional, however, in the syntax of a directory name in an OpenVMS file
specification or in the syntax of a substring specification in an
assignment statement.)
|
|
[|]
|
In command format descriptions, vertical bars separating items inside
brackets indicate that you choose one, none, or more than one of the
options.
|
|
{ }
|
In command format descriptions, braces indicate required elements; you
must choose one of the options listed.
|
|
bold text
|
This text style represents the introduction of a new term or the name
of an argument, an attribute, or a reason.
|
|
italic text
|
Italic text indicates important information, complete titles of
manuals, or variables. Variables include information that varies in
system output (Internal error
number), in command lines (/PRODUCER=
name), and in command parameters in text (where
dd represents the predefined code for the device type).
|
|
UPPERCASE TEXT
|
Uppercase text indicates a command, the name of a routine, the name of
a file, or the abbreviation for a system privilege.
|
|
Monospace type
|
Monospace text indicates code examples and interactive screen displays.
In the C programming language, monospace type in text identifies the
following elements: keywords, the names of independently compiled
external functions and files, syntax summaries, and references to
variables or identifiers introduced in an example.
|
|
-
|
A hyphen at the end of a command format description, command line, or
code line indicates that the command or statement continues on the
following line.
|
|
numbers
|
All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless otherwise noted.
Nondecimal radixes---binary, octal, or hexadecimal---are explicitly
indicated.
|
Chapter 1
Introduction
As of Version 7.0, the OpenVMS Alpha operating system provides support
for 64-bit virtual memory addressing. This capability makes the 64-bit
virtual address space, defined by the Alpha architecture, available to
the OpenVMS Alpha operating system and to application programs. OpenVMS
Alpha Version 7.1 provided extended, additional memory management Very
Large Memory (VLM) features.
This chapter highlights the features and benefits of OpenVMS Alpha
64-bit and VLM capabilities. The remaining chapters in this guide
describe how you can use these features to enhance application programs
to support 64-bit addresses and to efficiently harness very large
physical memory.
1.1 Using 64-Bit Addresses
Many OpenVMS Alpha tools and languages (including the Debugger,
run-time library routines, and DEC C) support 64-bit virtual
addressing. Input and output operations can be performed directly to
and from the 64-bit addressable space by means of RMS services, the
$QIO system service, and most of the device drivers supplied with
OpenVMS Alpha systems.
Underlying this are system services that allow an application to
allocate and manage the 64-bit virtual address space, which is
available for process-private use.
By using the OpenVMS Alpha tools and languages that support 64-bit
addressing, programmers can create images that map and access data
beyond the limits of 32-bit virtual addresses. The 64-bit virtual
address space design ensures upward compatibility of programs that
execute under versions of OpenVMS Alpha prior to Version 7.0, while
providing a flexible framework that allows 64-bit addresses to be used
in many different ways to solve new problems.
Nonprivileged programs can optionally be modified to take advantage of
64-bit addressing features. OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit virtual addressing
does not affect nonprivileged programs that are not explicitly modified
to exploit 64-bit support. Binary and source compatibility of existing
32-bit nonprivileged programs is guaranteed.
By using 64-bit addressing capabilities, application programs can map
large amounts of data into memory to provide high levels of performance
and make use of very large memory (VLM) systems. In addition, 64-bit
addressing allows for more efficient use of system resources, allowing
for larger user processes, as well as higher numbers of users and
client/server processes for virtually unlimited scalability.
1.2 Using VLM Features
OpenVMS Alpha VLM features for memory management provide extended
support for database, data warehouse, and other very large database
(VLDB) products. The VLM features enable database products and data
warehousing applications to realize increased capacity and performance
gains.
By using the extended VLM features, application programs can create
large in-memory global data caches that do not require an increase in
process quotas. These large memory-resident global sections can be
mapped with shared global pages to dramatically reduce the system
overhead required to map large amounts of memory.
For more information about taking advantage of these VLM features, see
Chapter 4.
Chapter 2
Overview of Virtual Address Space
This chapter describes the layout and components of the OpenVMS Alpha
64-bit virtual memory address space.
For more information about the OpenVMS Alpha programming tools and
languages that support 64-bit addressing and recommendations for
enhancing applications to support 64-bit addressing and VLM, refer to
the subsequent chapters in this guide.
2.1 Traditional OpenVMS 32-Bit Virtual Address Space Layout
In previous versions of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system, the virtual
address space layout was largely based upon the 32-bit virtual address
space defined by the VAX architecture. Figure 2-1 illustrates the
OpenVMS Alpha implementation of the OpenVMS VAX layout.
Figure 2-1 32-Bit Virtual Address Space Layout
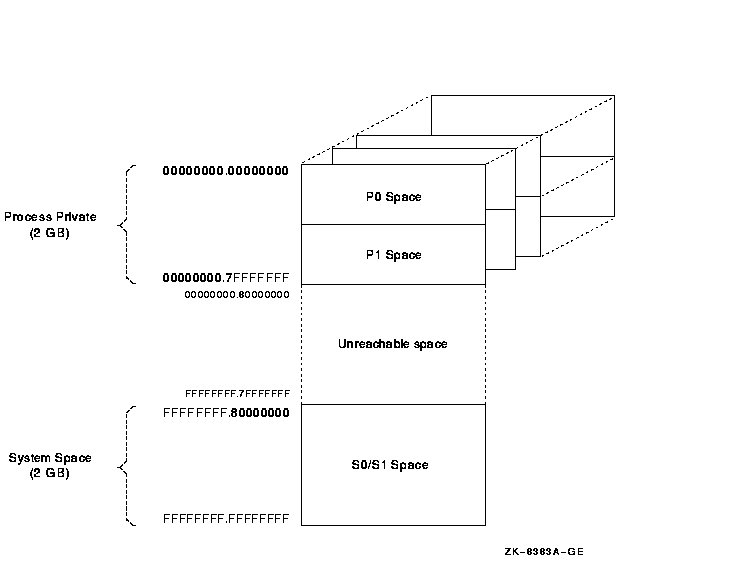
The lower half of the OpenVMS VAX virtual address space (addresses
between 0 and 7FFFFFFF16) is called process-private
space.
This space is further divided into two equal pieces called P0 space and
P1 space. Each space is 1 GB long. The P0 space range is from 0 to
3FFFFFFF16. P0 space starts at location 0 and expands toward
increasing addresses.
The P1 space range is from 4000000016 to
7FFFFFFF16. P1 space starts at location
7FFFFFFF16 and expands toward decreasing addresses.
The upper half of the VAX virtual address space is called
system space.
The lower half of system space (the addresses between
8000000016 and BFFFFFFF16) is called S0 space. S0
space begins at 8000000016 and expands toward increasing
addresses.
The VAX architecture associates a page table with each region of
virtual address space. The processor translates system space addresses
using the system page table. Each process has its own P0 and P1 page
tables. A VAX page table does not map the full virtual address space
possible; instead, it maps only the part of its region that has been
created.
2.2 OpenVMS Alpha 64-Bit Virtual Address Space Layout
The OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit address space layout is an extension of the
traditional OpenVMS 32-bit address space layout.
Figure 2-2 illustrates the 64-bit virtual address space layout design.
Figure 2-2 64-Bit Virtual Address Space Layout
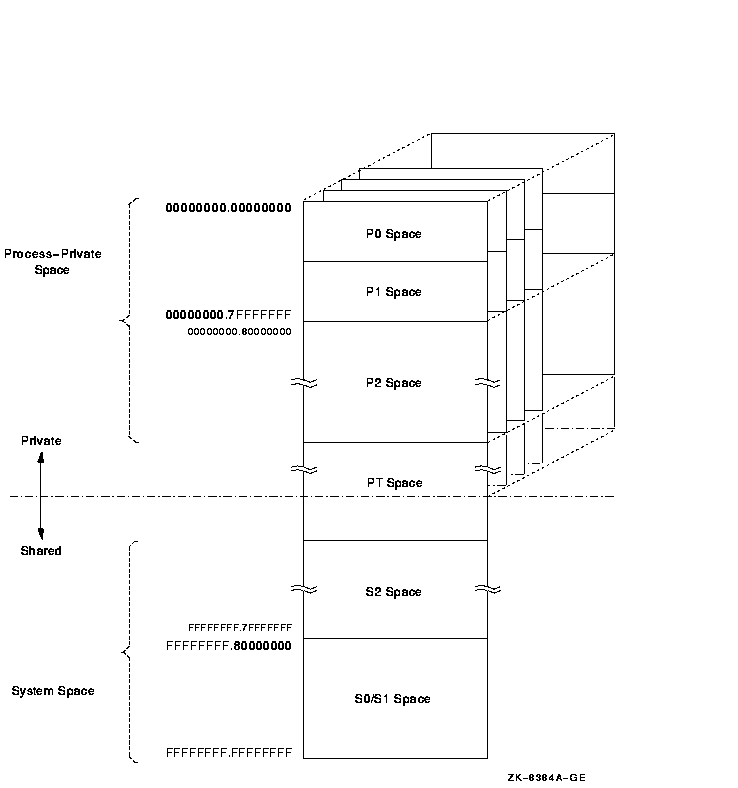
The 64-bit virtual address space layout is designed to accommodate the
current and future needs of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system and its
users. The new address space consists of the following fundamental
areas:
- Process-private space
- System space
- Page table space
2.2.1 Process-Private Space
Supporting process-private address space is a focus of much of the
memory management design within the OpenVMS operating system.
Process-private space, or process space, contains all
virtual addresses below PT space. As shown in Figure 2-2, the layout
of process space is further divided into the P0, P1, and P2 spaces. P0
space refers to the program region. P1 space refers to the control
region. P2 space refers to the 64-bit program region.
The P0 and P1 spaces are defined to
equate to the P0 and P1 regions defined by the VAX architecture.
Together, they encompass the traditional 32-bit process-private region
that ranges from 0.0000000016 to 0.7FFFFFFF16.
P2 space encompasses all remaining process space that
begins just above P1 space, 0.8000000016, and ends just
below the lowest address of PT space.
Note that P2 space addresses can be positive or negative when
interpreted as signed 64-bit integers.
2.2.2 System Space
64-bit system space refers to the portion of the
entire 64-bit virtual address range that is higher than that which
contains PT space. As shown in Figure 2-2, system space is further
divided into the S0, S1, and S2 spaces.
The S0 and S1 spaces are defined to
equate to the S0 and S1 regions defined by the VAX architecture.
Together they encompass the traditional 32-bit system space region that
ranges from FFFFFFFF.8000000016 to
FFFFFFFF.FFFFFFFF16. S2 space encompasses
all remaining system spaces between the highest address of PT space and
the lowest address of the combined S0/S1 space.
S0, S1, and S2 are fully shared by all processes. S0/S1 space expands
toward increasing virtual addresses. S2 space generally expands toward
lower virtual addresses.
Addresses within system space can be created and deleted only from code
that is executing in kernel mode. However, page protection for system
space pages can be set up to allow any less privileged access mode read
and/or write access.
System space base is controlled by the S2_SIZE system
parameter. S2_SIZE is the number of megabytes to reserve for S2 space.
The default value is based on the sizes required by expected consumers
of 64-bit (S2) system space. Consumers set up by OpenVMS at boot time
are the page frame number (PFN) database and the
global page table. (For more information about setting system
parameters with SYSGEN, see the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual: M--Z.)
The global page table, also known as the
GPT, and the PFN database reside in the
lowest-addressed portion of S2 space. By moving the GPT and PFN
database to S2 space, the size of these areas is no longer constrained
to a small portion of S0/S1 space. This allows OpenVMS to support much
larger physical memories and much larger global sections.
2.2.3 Page Table Space
In versions of OpenVMS Alpha prior to Version 7.0, page table
space (also known as PT space) was
addressable in more than one way. The PALcode translation buffer miss
handler used addresses starting at 2.0000000016 to read
PTEs, while memory management code addressed the page tables primarily
within the traditional 32-bit system space. The process page tables
were within the process header (PHD), and the system space page tables
were located in the highest virtual addresses, all within the
traditional 32-bit system space.
As of OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0, page tables are addressed primarily
within 64-bit PT space. Page tables refer to this virtual address
range; they are no longer in 32-bit shared system address space.
The dotted line in Figure 2-2 marks the boundary between
process-private space and shared space. This boundary is in PT space
and further serves as the boundary between the process-private page
table entries and the shared page table entries. Together, these sets
of entries map the entire address space available to a given process.
PT space is mapped to the same virtual address for each process,
typically a very high address such as FFFFFFFC.0000000016.
2.2.4 Virtual Address Space Size
The Alpha architecture supports 64-bit addresses. OpenVMS Alpha Version
7.0 dramatically increased the total amount of virtual address space
from 4 GB (gigabytes) to the 8 TB (terabytes) supported by the current
Alpha architecture implementations.
The Alpha architecture requires that all implementations must use or
check all 64 bits of a virtual address during the translation of a
virtual address into a physical memory address. However,
implementations of the Alpha architecture are allowed to materialize a
subset of the virtual address space. Current Alpha hardware
implementations support 43 significant bits within a 64-bit virtual
address. This results in an 8-TB address space.
On current Alpha architecture implementations, bit 42 within a virtual
address must be sign-extended or propagated through bit 63 (the least
significant bit is numbered from 0). Virtual addresses where bits 42
through 63 are not all zeros or all ones result in an access violation
when referenced. Therefore, the valid 8-TB address space is partitioned
into two disjoint 4-TB ranges separated by a no access
range in the middle.
The layout of the OpenVMS Alpha address space transparently places this
no access range within P2 space. (The OpenVMS Alpha memory management
system services always return virtually contiguous address ranges.) The
result of the OpenVMS Alpha address space layout design is that valid
addresses in P2 space can be positive or negative values when
interpreted as signed 64-bit integers.
Note that to preserve 32-bit nonprivileged code compatibility, bit 31
in a valid 32-bit virtual address can still be used to distinguish an
address in P0/P1 space from an address in S0/S1 space.
2.3 Virtual Regions
A virtual region is a reserved range of
process-private virtual addresses. It may be either a
user-defined virtual region reserved by the user
program at run time or a process-permanent virtual
region reserved by the system on behalf of the process during process
creation.
Three process-permanent virtual regions are defined by OpenVMS at the
time the process is created:
- Program region (in P0 space)
- Control region (in P1 space)
- 64-bit program region (in P2 space)
These three process-permanent virtual regions exist so that programmers
do not have to create virtual regions if their application does not
need to reserve additional ranges of address space.
Virtual regions promote modularity within applications by allowing
different components of the application to manipulate data in different
virtual regions. When a virtual region is created, the caller of the
service is returned a region ID to identify that virtual region. The
region ID is used when creating, manipulating, and deleting virtual
addresses within that region. Different components within an
application can create separate virtual regions so that their use of
virtual memory does not conflict.
Virtual regions exhibit the following characteristics.
- A virtual region is a light-weight object. That
is, it does not consume pagefile quota or working set quota for the
virtual addresses specified. Creating a user-defined virtual region by
calling a new OpenVMS system service merely defines a virtual address
range as a distinct address object within which address space can be
created, manipulated, and deleted.
- Virtual regions do not overlap. When creating address space within
a virtual region, the programmer must specify a region ID to the
OpenVMS system service. The programmer must be explicit in which
virtual region the address space is to be created.
- The programmer cannot create, manipulate, or delete address space
that does not lie entirely within the bounds of a defined virtual
region.
- Each user-defined virtual region's size is fixed at the time it is
created. Given the large range of virtual addresses in P2 space and the
light-weight nature of virtual regions, it is not costly to reserve
more address space than the application component immediately needs
within that virtual region.
Note the exception of process-permanent
regions, which have no fixed size.
The 64-bit program virtual
region is the only virtual region whose size is not fixed when it is
created. At process creation, the 64-bit program region encompasses all
of P2 space. When a user-defined virtual region is created in P2 space,
OpenVMS memory management shrinks the 64-bit program region so that no
two regions overlap. When a user-defined virtual region is deleted, the
64-bit program region expands to encompass the virtual addresses within
the deleted virtual region if no other user-defined virtual region
exists at lower virtual addresses.
- Each virtual region has an owner mode and a create mode associated
with it. Access modes that are less privileged than the owner of the
virtual region cannot delete the virtual region. Access modes that are
less privileged than the create mode set for the virtual region cannot
create virtual addresses within the virtual region. Owner and create
modes are set at the time the virtual region is created and cannot be
changed. The create mode for a virtual region cannot be more privileged
than the owner mode.
- When virtual address space is created within a virtual region,
allocation generally occurs within the virtual region in a densely
expanding manner, as is done within the program (P0 space) and control
(P1 space) regions. At the time it is created, each virtual region is
set up for the virtual addresses within that virtual region to expand
toward either increasing virtual addresses, like P0 space, or
decreasing virtual addresses, like P1 space. Users can override this
allocation algorithm by explicitly specifying starting addresses.
- All user-defined virtual regions are deleted along with the pages
created within each virtual region at image rundown.
|