HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
Getting Started With the New Desktop
4.5 Registering a Third-Party ApplicationRegistering an application is the phrase used in CDE documentation for integrating and installing an application into the New Desktop. The files required for integrating an application are called a registration package. Registering an application is described in Chapter 4 of the Common Desktop Environment: Advanced User's and System Administrator's Guide. The process on UNIX systems differs from the process on OpenVMS Alpha systems. The most significant difference is that the CDE application dtappintegrate is not included with the New Desktop. However, the rest of the process on the New Desktop is similar. An application is considered fully registered into the New Desktop when it has the following components:
The registration package consists of the following components:
The installation procedure for a registration package must perform the following tasks:
Figure 4-7 CDE$USER_DEFAULTS Directory Hierarchy 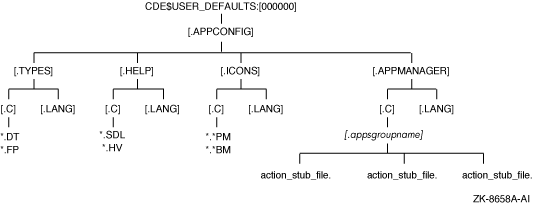
After your installation has completed and the session has restarted, you can then access the new application group and the applications in it with the following steps:
4.6 Porting UNIX Reference Pages to the New DesktopIf you have created reference pages (manpages) on a UNIX system that you would like to add to the reference pages on the New Desktop, you can do so in the following way:
After you have copied the reference page, you can view it by selecting
the Man Page Viewer from the Desktop Apps group of Application Manager.
For more detailed information about integrating applications, see the related online help, especially the Create Action help, and the following CDE manuals:
For instructions on how to access either manual on line or obtain printed copies, see Table 1-2.
Chapter 5
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contents | Description |
|---|---|
| CDE$LIBDTSVC.EXE | Desktop Services |
| Drag-and-drop convenience API | Convenience functions layered on top of the OSF/Motif R1.2 drag-and-drop services. These functions simplify the use of the OSF/Motif R1.2 drag-and-drop services, which have not changed. |
| Action invocation API | Used to initialize and load the database of action and data type definitions, query the action database, invoke an action, and register a callback to receive action status and return arguments. |
| Session Manager API (dtsession) | Services include save and restore. |
| Workspace Manager API (dtwm) 1 | Gets workspace information, sets the current workspace, and so on. |
| Header files 2 | Action.h, Dnd.h, Dts.h, Dt.h, Saver.h, Session.h, and Wsm.h. |
| For more information, see the Common Desktop Environment: Programmer's Guide. | |
| CDE$LIBDTHELP.EXE | Help Widget Support |
| DtHelpDialog | General help dialogs that include a menu bar, topic tree, and a help topic display area. |
| DtHelpQuickDialog | Quick help dialogs that include a topic display area and one or more dialog buttons at the bottom. |
| Header files 2 | Help.h, HelpQuickD.h, and HelpDialog.h. |
| For more information, see the Common Desktop Environment: Help System Author's and Programmer's Guide. | |
| CDE$LIBDTWIDGET.EXE | Custom Widgets |
| DtSpinBox | Combines a text field and arrow buttons in a control that can increment or decrement numeric or text values. |
| DtComboBox | Combines a text field and a list box in a control that displays one or more valid choices for the text field. |
| DtMenuButton | Provides menu cascading functionality outside the menu bar. |
| DtEditor | Incorporates the functionality of a simple text editor. |
| Header files 2 | SpinBox.h, ComboBox.h, MenuButton.h, and Editor.h. |
| For more information, see the Common Desktop Environment: Programmer's Guide. | |
Table 5-2 lists the CDE APIs, application integration services, and tools that are not included in the New Desktop.
| CDE Component | Name |
|---|---|
| Application Builder | dtappbuilder |
| Calendar Manager API | libcsa |
| Messaging services (ToolTalk) | libtt |
| Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) support | libdtmail |
| Terminal emulator API | libdtterm |
| Windowing Korn shell | dtksh |
For examples of how these routines are used in applications, see the
example programs, as described in Section 5.10.
5.3 Save and Restore Support
The New Desktop provides session save and restore utility functions. If these are integrated into your application, the application state is saved upon exiting Session Manager and is restored when the session is restarted.
Use the XmAddWMProtocol() function to set the WM_SAVE_YOURSELF atom on the WM_PROTOCOLS property for the top level of the application. You can view window properties by using the xprop utility program located in the DECW$UTILS directory.
Use the XmAddWMProtocolCallback() function to declare a callback procedure for when the application receives a WM_SAVE_YOURSELF client message. Session Manager sends a WM_SAVE_YOURSELF client message to your application, and the callback function is called.
The application should not interact with the user during save or restore. For example, a dialog box should not be displayed during save or restore.
An example program, DTSESSIONEXAMPLE.C, is provided as a guide. The example program creates a main window with a toggle button and saves the state of the button during execution of the save/restore routine.
The example program is available in the following location:
CDE$SYSTEM_DEFAULTS:[EXAMPLES.DTSESSION] |
For general information about the example directories, see
Section 5.10.
5.4 Create Action Application
To enable an application to be launched from the New Desktop, certain application configuration files must be created and installed. You can create and install the configuration files for most applications by using the Create Action application, which automates the process of creating these files. You can access the Create Action application from the Desktop Tools application group in Application Manager.
For more information about Create Action, see Section 4.1.
5.5 File Type Support
The New Desktop contains a set of file types with preconfigured icons and associated actions. The icons and actions can be modified with Create Action, the action database and execution management tool.
Examples of file types are executable files (with the file extension
.EXE) and data files (with the file extension .TXT). Examples of
actions include running a file if it is an executable file,
and printing and opening (in order to edit) a file if
it is a data file.
5.6 CDE Standard Fonts
CDE defines two types of standard fonts: application fonts and interface fonts. Use the application fonts for application data. Use the interface fonts with the Motif widgets.
The CDE standard application fonts supplied with the New Desktop are names of generic fonts that are available on all CDE platforms. They are mapped to different fonts on different CDE platforms, typically using the X font alias mechanism. You specify the fonts for these resources in your APP-DEFAULTS file.
The CDE standard interface fonts ensure that, for any application development that you do with Motif widgets, the application's windows look like other CDE desktop client windows, and users can change the size of these fonts using Style Manager. If you override the supplied fonts by changing the Motif font list resource specifications, then you must provide additional functionality if you want users to be able to customize the fonts in your application.
By observing these guidelines, your application will find the
appropriate fonts on all CDE platforms. For more information, see the
Common Desktop Environment: Programmer's Overview and the
Common Desktop Environment: Programmer's Guide.
5.7 Help Programming
The New Desktop help system is a complete system for developing and displaying online help for application software. This section briefly describes the process and tools that are provided for developing help. The aspects that are unique to the OpenVMS implementation are fully documented here. For more information about the process, the SGML markup language, the writing tasks, and the programming tasks that comprise this process, see the Common Desktop Environment: Help System Author's and Programmer's Guide.
The following New Desktop programming components are provided for developing help:
Online help is written in text files whose file extension is .HTG. The SGML markup language named HelpTag is used to specify how elements of the text are formatted.
HelpTag consists of a set of tags that specify the formatting of elements such as headings, paragraphs, and lists. After composing the help text and labeling the elements of the text with the appropriate tags, you process these tagged files with the DTHELPTAG.COM command procedure. DTHELPTAG.COM produces run-time help files (with the extension .SDL) that you can view with the Help Viewer.
Two styles of SGML can be used with the HelpTag markup language:
shorthand SGML or fully compliant SGML. The shorthand style is simpler
and quicker to code.
5.7.2 Help Compiler Interface
The Help compiler interface consists of three executable files that are invoked from DTHELPTAG.COM. The executable files, described in Table 5-3, are in the CDE$SYSTEM_DEFAULTS:[BIN] directory, which is referenced by the CDE$PATH logical name.
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
| DTHELP_CTAG1.EXE | Parser for fully compliant SGML-based help topics. |
| DTHELP_HTAG1.EXE | Parser for shorthand SGML-based help topics. |
| DTHELP_HTAG2.EXE | Runs after either parser for enhancement of distribution file. |
The main function of DTHELPTAG.COM is to compile a help source file. DTHELPTAG.COM can also be used for the following tasks:
DTHELPTAG.COM was ported from the UNIX version of the dthelptag shell
script. DTHELPTAG.COM supports all the functions found in the UNIX
version of this utility except file compression and decompression.
5.7.3 DTHELPTAG.COM Format and Options
The format for DTHELPTAG.COM is:
|
@CDE$PATH:DTHELPTAG [options] filename |
where filename specifies the name of the input help source file.
The DTHELPTAG.COM options, which require a leading hyphen (-), are described in Table 5-4.
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
| -formal | Specifies the parser for fully compliant SGML-based help topics. If you do not specify -formal, the parser for the shorthand SGML-based help topics is used. |
| -nooptimize | Eliminates certain optimizations that normally take place during translation of HelpTag markup to the run-time format. Using this option speeds the translation process. |
| -memo | Includes a writer's memos entered with the memo tag (<memo>) in the help file. |
| -debug | Saves the intermediate files; otherwise, they are deleted. |
| -clean | Removes all files generated by DTHELPTAG.COM for a particular help volume. |
| -files | Lists all the files associated with for a particular help file. The files include intermediate files generated during the DTHELPTAG.COM command procedure and graphics files included in the help file. |
| -help | Invokes command line help for DTHELPTAG.COM. |
For application programmers, the New Desktop provides a help API that allows the addition of help dialog boxes to any Motif application. The New Desktop help library (CDE$LIBDTHELP.EXE) provides the following two types of help dialog boxes:
For more information on the New Desktop help API, refer to the
Common Desktop Environment: Help System Author's and Programmer's
Guide.
5.7.5 HelpTag Examples
HelpTag example files are in the following directory:
CDE$SYSTEM_DEFAULTS:[EXAMPLES.DTHELP] |
The following example uses an example file to illustrate the -files HelpTag option:
$ @CDE$PATH:DTHELPTAG -files HELPDEMO.HTG |
The output from this command follows:
Workfile is --> HELPDEMO.HTG MARKUP PARSER (with non-canonical SGML enhancements) (c) Copyright 1993, 1994 Hewlett-Packard Company (c) Copyright 1993, 1994 International Business Machines Corp. (c) Copyright 1993, 1994 Sun Microsystems, Inc. (c) Copyright 1993, 1994 Unix System Labs, Inc., a subsidiary of Novell, Inc. CDE HelpTag Formatting System. - Version B.00.00 (DTD Version A.01.23) Interface generated from help.if on Thu Dec 28 09:01:10 1995 helpdemo.htg Warning: could not open locale translation database. [.graphics]AppWithHelp.xwd [.graphics]cauticon.pm [.graphics]clock.xwd [.graphics]clouds.xpm [.graphics]bee.xwd [.graphics]deadjim.xwd [.graphics]GeneralHelp.xwd [.graphics]head-down.xwd [.graphics]helpchar.ent [.graphics]helpicon.ent [.graphics]helplang.ent [.graphics]helpShelf.pm [.graphics]integral.bm [.graphics]noteicon.pm [.graphics]QuickHelp.xwd [.graphics]rooster.xpm [.graphics]Snapshot.bm [.graphics]Snapshot.xwd [.graphics]speaker.pm [.graphics]shuttle2.xwd [.graphics]sunset.xwd [.graphics]tribe.xwd [.graphics]warnicon.pm [.graphics]xload.xwd Exiting HelpTag Utility... $ |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |