 |
OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW
Determines whether the caller has the specified privileges or
identifier. In addition to checking for a privilege or an identifier,
the Check Privilege and Wait service determines if the caller's use of
privilege needs to be audited.
$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW completes synchronously; that is, it returns the
final status to the caller only after receiving an explicit
confirmation from the audit server that the associated audit, if
enabled, has been performed.
Format
SYS$CHECK_PRIVILEGEW efn ,prvadr ,[altprv] ,[flags] ,[itmlst] ,audsts
,[astadr] ,[astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$check_privilegew (unsigned int efn, struct _generic_64 *prvadr,
struct _generic_64 *altprv, unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned
int *audsts, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$CHKPRO
Determines whether an accessor with the specified rights and privileges
can access an object with the specified attributes.
Format
SYS$CHKPRO itmlst ,[objpro] ,[usrpro]
C Prototype
int sys$chkpro (void *itmlst, void *objpro, void *usrpro);
Argument
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Protection attributes of the object and the rights and privileges of
the accessor. The itmlst argument is the address of an
item list of descriptors used to specify the protection attributes of
the object and the rights and privileges of the accessor.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the associated buffer. The length of the buffer needed
depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item
descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, the service
truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information in the associated buffer. The item codes are defined in the
$ACLDEF system macro library.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword that normally contains the user-supplied address of a word
in which the service writes the length in bytes of the information it
returned. This is not used by $CHKPRO and should contain a 0.
|
Specifying any specific protection attribute causes that protection
check to be made; any protection attribute not specified is not
checked. Rights and privileges specified are used as needed. If a
protection check requires any right or privilege not specified in the
item list, the right or privilege of the caller's process is used.
objpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing an object security profile. The
objpro argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a buffer that contains an encoded object security profile.
The objpro argument eliminates the need to supply all
of the component object protection attributes with the $CHKPRO item
list. The objpro argument is currently reserved to
Compaq.
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer containing a user security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer that
contains an encoded user security profile. The usrpro
argument eliminates the need to supply all of the component user
security attributes with the $CHKPRO item list.
The $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service can be used to construct a user
security profile. When the usrpro argument is
specified, any component user profile attributes specified in the
$CHKPRO item list replace those contained in the user security profile.
The item codes used with $CHKPRO are described in the following list
and are defined in the $CHPDEF system macro library.
Item Codes
CHP$_ACCESS
A longword bit mask representing the type of access desired ($ARMDEF).
Be aware that the $CHKPRO service does not interpret the bits in the
access mask; instead, it compares them to the object's protection mask
(CHP$_PROT). Any bits not specified by CHP$_ACCESS or CHP$_PROT are
assumed to be clear, which grants access.
CHP$_ACL
A vector that points to an object's access control list. The buffer
address, bufadr, specifies a buffer containing one or
more ACEs. The number that specifies the length of the CHP$_ACL buffer,
buflen, must be equal to the sum of all ACE lengths.
The format of the ACE structure depends on the value of the second byte
in the structure, which specifies the ACE type. The $FORMAT_ACL system
service description describes each ACE type and its format.
You can specify the CHP$_ACL item multiple times to point to multiple
segments of an access control list. You can specify a maximum of 20
segments. The segments are processed in the order specified.
CHP$_ACMODE
A byte that defines the accessor's processor access mode. The following
access modes and their symbols are defined in the $PSLDEF macro:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
If CHP$_ACMODE is not specified, access mode is not used to determine
access.
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS
A vector that points to an additional rights list segment to be
appended to the existing rights list. Each entry of the rights list is
a quadword data structure consisting of a longword containing the
identifier value, followed by a longword containing a mask identifying
the attributes of the holder. The $CHKPRO service ignores the
attributes.
A maximum of 11 rights descriptors is allowed. If you specify
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS without specifying CHP$_RIGHTS, the accessor's rights
list consists of the rights list specified by the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item
codes and the rights list of the current process.
If you specify CHP$_RIGHTS and CHP$_ADDRIGHTS, you should be aware of
the following:
- CHP$_RIGHTS must come first.
- The accessor's UIC is the identifier of the first entry in the
rights list specified by the CHP$_RIGHTS item code.
- The accessor's rights list consists of the rights list specified by
the CHP$_RIGHTS item code and the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item codes.
CHP$_ALARMNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the alarm name from any Alarm ACE
contained in the object's ACL. If the object does not have security
alarms enabled, $CHKPRO returns retlenadr as 0. If a
matching Alarm ACE exists, the string SECURITY will be returned.
CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
A security auditing item list containing additional information to be
included in any resulting security audit. The bufadr
argument points to the beginning of an $AUDIT_EVENT item list. See the
itmlst argument of the $AUDIT_EVENT system service for
a list of valid security auditing item codes. Note that the
NSA$_EVENT_TYPE and NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE items are ignored when auditing
with $CHKPRO. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag must be specified.
CHP$_AUDITNAME
Address of a buffer to receive the audit name from any Audit ACE
contained in the object's ACL. If the object does not have auditing
enabled, $CHKPRO returns retlenadr as 0. If a matching
Audit ACE exists, the string SECURITY will be returned.
CHP$_FLAGS
A longword that defines various aspects of the protection check. The
symbols in the following table are offsets to the bits within the
longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate
bit set by using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The following
symbols are defined only in the system macro library ($CHPDEF):
| Symbol |
Access |
|
CHP$V_ALTER
|
Accessor desires write access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_AUDIT
|
Access audit requested.
|
|
CHP$V_CREATE
|
Perform the audit as an object creation event.
|
|
CHP$V_DELETE
|
Perform the audit as an object deletion event.
|
|
CHP$V_FLUSH
|
Force audit buffer flush.
|
|
CHP$V_INTERNAL
|
Audit on behalf of the Trusted Computing Base (TCB). Reserved to Compaq.
|
|
CHP$V_MANDATORY
|
Force the object access event to be audited.
|
|
CHP$V_NOFAILAUD
|
Do not perform audits for failed access.
|
|
CHP$V_NOSUCCAUD
|
Do not perform audits for successful access.
|
|
CHP$V_OBSERVE
|
Accessor desires read access to object.
|
|
CHP$V_SERVER
|
Audit on behalf of a TCB server process.
|
|
CHP$V_USEREADALL
|
Accessor is eligible for READALL privilege.
|
The default for CHP$_FLAG is CHP$M_OBSERVE and CHP$M_ALTER.
The primary purpose of the CHP$V_OBSERVE and CHP$V_ALTER flags is as
latent support for a mandatory (lattice) security policy, such as that
provided by the Security Enhanced VMS (SEVMS) offering.
CHP$_MATCHEDACE
This output item is a variable-length data structure containing the
first Identifier ACE in the object's ACL that allowed or denied the
accessor to access the object. See the $FORMAT_ACL system service for a
description of an Identifier ACE format.
CHP$_MODE
A byte that defines the object's owner access mode. The following
access modes of the object's owner and their symbols are defined in the
system macro library ($PSLDEF):
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
CHP$_MODES
A quadword that defines the object's access mode protection. You
specify a 2-bit access mode as shown in CHP$_MODE for each possible
access type. The following diagram illustrates the format of an access
mode vector for bit numbers:
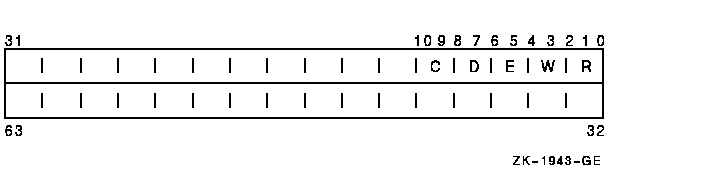
Each pair of bits in the access mode vector represents the access mode
for the specific type of access. For example, bits <6:7>
represent the access mode value used to check for delete access.
CHP$_OBJECT_CLASS
A character string containing the protected object class associated
with the object. The object class string is used to determine whether
any security auditing is enabled for the object access event. This item
code is required when the CHP$_AUDIT flag is specified.
CHP$_OBJECT_NAME
A character string containing the object name associated with the
protection check. The object name string is included in any resulting
security audit. If an object name string is not specified, the string
"<not available>" is substituted in any security audit
for all protected object classes other than FILE. For FILE class
audits, it is assumed that the caller has supplied an object name by
using the auditing item list (NSA$_OBJECT_NAME).
CHP$_OWNER
A longword describing the object's owner identifier (UIC or general
identifier). This might be either a UIC format identifier or a general
identifier.
Note
CHP$_OWNER is used in conjunction with the CHP$_PROT item code.
|
CHP$_PRIV
A quadword that defines an accessor's privilege mask. Each bit in the
mask has a symbolic name, defined by the $PRVDEF macro. You form the
bit array by specifying the symbolic name of each privilege in a
logical OR operation. See the $SETPRV system service for the symbolic
name and description of each privilege.
CHP$_PRIVUSED
A longword mask of flags representing privileges used to gain the
requested access.
You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set by
using the prefix CHP$M rather than CHP$V. The symbols are defined in
the system macro library ($CHPDEF). The following symbols are used as
offsets to the bits within the longword:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
|
CHP$V_SYSPRV
|
SYSPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPPRV
|
GRPPRV was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_BYPASS
|
BYPASS was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_READALL
|
READALL was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_OPER
|
OPER was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GRPNAM
|
GRPNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_SYSNAM
|
SYSNAM was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_GROUP
|
GROUP was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_WORLD
|
WORLD was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_PRMCEB
|
PRMCEB was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_UPGRADE
|
UPGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
|
CHP$V_DOWNGRADE
|
DOWNGRADE was used to gain the requested access.
|
CHP$_PROT
A vector describing the object's SOGW protection mask. The following
diagram depicts the format for describing the object's protection:
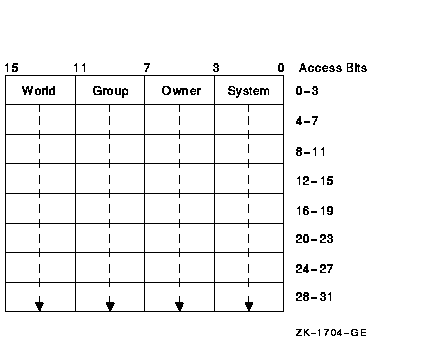
The first word contains the first four protection bits for each field,
the second word the next four protection bits, and so on. If a bit is
clear, access is granted. By convention, the first five protection bits
are (from right to left in each field of the first word) read, write,
execute, delete, and (in the low-order bit in each field of the second
word) control access. You can specify the CHP$_PROT item in increments
of words; if a short buffer is given, zeros are assumed for the
remainder.
The $CHKPRO service compares the low-order four bits of CHP$_ACCESS
against one of the 4-bit fields in the low-order word of CHP$_PROT, the
next four bits of CHP$_ACCESS against one of the 4-bit fields in the
next word of CHP$_PROT, and so on. The $CHKPRO service chooses a field
of CHP$_PROT based on the privileges specified for the accessor
(CHP$_PRIV), the UICs of the accessor (CHP$_RIGHTS or CHP$_ADDRIGHTS,
or both), and the object's owner (CHP$_OWNER).
You must also specify the identifier of the object's owner with
CHP$_OWNER when you use CHP$_PROT.
CHP$_RIGHTS
A vector that points to an accessor's rights list. The accessor's UIC
is the identifier of the first entry in the rights list. The accessor's
rights list consists of the rights list specified by CHP$_RIGHTS and,
optionally, the rights list specified by the CHP$_ADDRIGHTS item codes.
CHP$_UIC
A longword specifying the accessor's owner UIC. This item code can be
used to avoid having to pass an entire rights list segment via the
CHP$_RIGHTS item code. If CHP$_RIGHTS and then CHP$_UIC are specified,
in that order, $CHKPRO initializes the local rights list and then
replaces just the owner UIC with the value of CHP$_UIC.
Description
The Check Access Protection service determines whether an accessor with
the specified rights and privileges can access an object with the
specified attributes. The service invokes the system's access
protection check, which permits layered products and other subsystems
to build protected structures that are consistent with the protection
facilities provided by the base operating system. The service also
allows a privileged subsystem to perform protection checks on behalf of
a requester.
If the accessor can access the object, $CHKPRO returns the SS$_NORMAL
status code; otherwise, $CHKPRO returns SS$_NOPRIV.
The item list arguments accepted by this service permit you to specify
the protection of the object being accessed, the rights and privileges
of the accessor, and the type of access desired.
At minimum, the following item codes should be specified to perform a
third-party protection check:
CHP$_ACCESS
CHP$_OWNER
CHP$_PRIV
CHP$_PROT
CHP$_UIC
The default for information relating to the subject is to use the
current process information (for example, privileges). The default for
missing object information is a representation of 0.
The caller can also request that an object access audit be performed if
security auditing has been enabled for the object class or if auditing
ACEs are contained in the object's ACL. The CHP$V_AUDIT flag requests
an access audit. This requires that the caller be in executive or
kernel mode or possess the AUDIT privilege.
Normally, $CHKPRO generates an object access audit when an audit is
required. The caller can specify the CHP$V_CREATE flag to force an
object creation audit instead of an object access audit. Similarly, the
CHP$V_DELETE flag forces an object deletion audit. The CHP$_AUDIT_LIST
item code can be used to specify additional information to be included
in any resulting audit records.
Required Access or Privileges
AUDIT privilege is required when requesting an audit.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$AUDIT_EVENT, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE, $FORMAT_ACL
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or one of the buffers
specified in the item list cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_ACLFULL
|
More than 20 CHP$_ACL items were given.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The argument is invalid.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The output buffer is too small and the protection check succeeded.
|
|
SS$_IVACL
|
You supplied an invalid ACL segment with the CHP$_ACL item.
|
|
SS$_IVBUFLEN
|
The output buffer is too small and the protection check failed.
|
|
SS$_NOAUDIT
|
Caller lacks privilege to request audit.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The desired access is not granted.
|
|
SS$_RIGHTSFULL
|
More than 11 CHP$_ADDRIGHTS items were given.
|
$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT (Alpha Only)
Removes one or more notification requiests previously established by a
call to $SET_SYSTEM_EVENT.
This service does not allow you to specify a handle and an event. You
must pass a zero as one of these parameters. You can either clear by
handle or request that all events for the user be cleared.
Format
SYS$CLEAR_SYSTEM_EVENT [handle] ,[acmode] ,event
C Prototype
int sys$clear_system_event (struct _generic_64 * handle, unsigned int
acmode, unsigned int event);
Arguments
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identification of the AST request to be cleared. The
handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is
returned when the $SET_SYSTEM_EVENT service is called. The
handle argument may be omitted by specifying a zero
address.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Access mode of the system event to be cleared. The
acmode argument is a longword containing the access
mode. The value of the access mode is maximized with the access mode of
the caller.
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The event argument is a value indicating the type of
system event to be cleared. SYSEVT$C_ALL_EVENTS may be specified to
clear all event types.
Description
The Clear System Event service removes one or more event types or
notification objects previously established by a call to the
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT service.
A valid request specifies either the handle for a
specific notification request, or is a wildcard clear of all
notification objects whose is access mode is greater than or equal to
acmode.
If the handle argument is specified, caller's access
mode must be less than or equal to the access mode of the object to be
cleared.
If SYSEVT$C_ALL_EVENTS is specified, or the set of events enabled for
the object(s) becomes empty, the notification object is deleted.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$SET_SYSTEM_EVENT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the location specified by the handle.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
One of more arguments has an invalid value, such as an invalid handle.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHOBJ
|
No request was found that matches the description supplied.
|
|


