OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$GETQUIW
Returns information about queues and jobs initiated from those queues.
The $SNDJBC service is the major interface to the Job Controller, which
is the queue and accounting manager. For a discussion of the different
types of job and queue, see the Description section of $SNDJBC.
The $GETQUIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to
the caller with the requested information. For asynchronous completion,
use the Get Queue Information ($GETQUI) service; $GETQUI returns to the
caller after queuing the information request, without waiting for the
information to be returned.
In all other respects, $GETQUIW is identical to $GETQUI. For more
information about $GETQUIW, refer to the description of $GETQUI in this
manual.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Format
SYS$GETQUIW [efn] ,func [,context] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getquiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned
int *context, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
$GETRMI
Returns system performance information about the local system.
Format
SYS$GETRMI [efn] [,nullarg] [,nullarg] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getrmi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int nullarg, unsigned int
nullarg, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of event flag to be set when the $GETRMI request completes. The
efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $GETRMI uses only the low order byte.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to Compaq.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Placeholding argument reserved to Compaq.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information is to be returned about the
local node. The itmlst argument is the address of a
list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. The list of descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.
The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETRMI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the
item code field. If the buffer length is too small, $GETRMI truncates
the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied code specifying the item of
information that $GETRMI is to return. The RMIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the item codes
section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a buffer in which
$GETRMI returns the requested information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which
$GETRMI writes the length in bytes of the information returned.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O
status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETRMI completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument.
Item Codes
RMI$_BLKAST
Returns the number of blocking ast's.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_BUFIO
Returns the number of buffered I/O's
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DEQ
Returns the number of DEQ operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DIRIO
Returns the number of direct I/O's
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKSRCH
Returns the number of deadlock searches.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DLCKFND
Returns the number of deadlocks found.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_DZROFLTS
Returns the number of demand zero page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQCVT
Returns the number of ENQ conversion operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNEW
Returns the number of new ENQ operations.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQNOTQD
Returns the number of ENQ operations not queued.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ENQWAIT
Returns the number of ENQ operations forced to wait.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FAULTS
Returns the number of page faults since last system initialization.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCALLS
Returns the total number of calls to the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCACHE
Returns the total number of cache hits by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPCPU
Returns the total number of CPU tics used by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPFAULT
Returns the number of FCP page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPHIT
Returns the total number of window hits tics used by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPREAD
Returns the total number of disk reads by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPSPLIT
Returns the number of split transfers performed by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FCPWRITE
Returns the total number of disk writes by the FCP.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FREFLTS
Returns the number of page faults from the free list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_FRLIST
Returns the number of pages on the freelist.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_GVALFLTS
Returns the number of global valid page faults.
Because this number is a longword the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_ISWPCNT
Returns the number of process inswaps.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_LOGNAM
Returns the number of logical name translations
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MBREADS
Returns the number of mailbox reads
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MBWRITES
Returns the number of mailbox writes
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MODLIST
Returns the number of pages on the modified page list.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_MFYFLTS
Returns the number of page faults from the modified list.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NUMLOCKS
Returns the total number of locks.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_NUMRES
Returns the total number of resources.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PREADIO
Returns physical page read I/O's.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PREADS
Returns the number of pages read.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PWRITES
Returns the number of pages written.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_PWRITIO
Returns physical page write I/O's.
This number is a longword, therefore the buffer length field in the
item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_SYSFAULTS
Returns the number of system page faults.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
RMI$_WRTINPROG
Returns the number of page faults from a write in progress.
Because this number is a longword the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Description
The Get Resource Monitor Information service returns performance
information about the local system.
Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL is required to return system performance data.
Required Quota
This service uses the process's AST limit quota (ASTLM).
Related Services
None.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The caller cannot read the item list, cannot write to the buffer
specified by the buffer address field in the item descriptor, or cannot
write to the return length address field in an item descriptor.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid item code.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process has exceeded its AST limit quota.
|
$GETSYI
Returns information about the local system or about other systems in an
OpenVMS Cluster system. The $GETSYI service completes asynchronously;
for synchronous completion, use the Get Systemwide Information and Wait
($GETSYIW) service.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to
the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$GETSYI [efn] ,[csidadr] ,[nodename] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr]
[,astprm]
C Prototype
int sys$getsyi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *csidadr, void
*nodename, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64 astprm);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when the $GETSYI request completes.
The efn argument is a longword containing this number;
however, $GETSYI uses only the low-order byte.
Upon request initiation, $GETSYI clears the specified event flag (or
event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the
request completes, the specified event flag (or event flag 0) is set.
csidadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
OpenVMS Cluster system identification of the node about which $GETSYI
is to return information. The csidadr argument is the
32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) of a longword containing this identification value.
The cluster-connection software assigns the OpenVMS Cluster system
identification of a node. You can obtain this information by using the
DCL command SHOW CLUSTER. The value of the cluster system
identification for a node is not permanent; a new value is assigned to
a node whenever it joins or rejoins the cluster.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the
nodename argument. If you specify
csidadr, you need not specify
nodename, and vice versa. If you specify both, they
must identify the same node. If you specify neither argument, $GETSYI
returns information about the local node; however, for wildcard
operations, you must use the csidadr argument.
If you specify csidadr as --1, $GETSYI assumes a
wildcard operation and returns the requested information for each node
in the cluster, one node per call. In this case, the program should
test for the condition value SS$_NOMORENODE after each call to $GETSYI
and should stop calling $GETSYI when SS$_NOMORENODE is returned.
nodename
| OpenVMS usage: |
process_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the node about which $GETSYI is to return information. The
nodename argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX
systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
The node name string must contain from 1 to 15 characters and must
correspond exactly to the node name; no trailing blanks or
abbreviations are permitted.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the
csidadr argument. See the description of
csidadr.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for
64-bit |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Item list specifying which information is to be returned about the node
or nodes. The itmlst argument is the 32-bit address
(on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a
list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of
information. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword
of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0.
All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or
64-bit.
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item
descriptor:

The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length field is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of the buffer
into which $GETSYI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of a word in
which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually
returned.
|
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
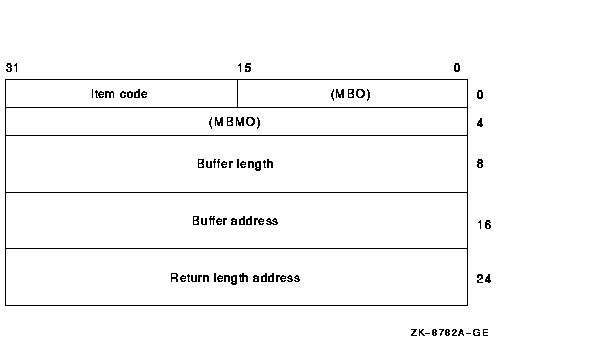
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
MBO
|
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these
codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
MBMO
|
The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Buffer length
|
A quadword containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of the buffer
into which $GETSYI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of a word in
which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually
returned.
|
See the Item Codes section for a description of the various $GETSYI
item codes.
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of the quadword I/O
status block.
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETSYI sets the
quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a
condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword
is reserved for future use.
Though this argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $GETSYI service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$GETSYI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETSYI completes. The
astadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of the $GETSYI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is the longword parameter.
Item Codes
SYI$_ACTIVECPU_CNT
Returns a count of the CPUs actively participating in the current boot
of the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ACTIVE_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a mask of the CPUs actively participating in
the current boot of the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.
SYI$_ARCHFLAG
Returns the architecture flags for the system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ARCH_NAME
Returns, as a character string, the name of the CPU architecture on
which the process is executing. Currently, either of two strings is
returned: "Alpha" for Alpha or "VAX" for VAX.
Because this name can include up to 15 characters, the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 15 (bytes).
SYI$_ARCH_TYPE
Returns the type of CPU architecture on which the process is executing.
SYI$_ARCH_TYPE returns 1 on VAX or 2 on Alpha.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_CPU_AUTOSTART
On Alpha systems, returns the array of CPU autostart states.
SYI$_AVAILCPU_CNT
Returns the number of CPUs available in the current boot of the
symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item
descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_AVAIL_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, returns a mask of the present and available CPUs
participating in the current boot of the symmetric multiprocessing
(SMP) system.
SYI$_BOOTTIME
Returns the time when the node was booted.
Because the returned time is in the standard 64-bit absolute time
format, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8
(bytes).
SYI$_CHARACTER_EMULATED
Returns the number 1 if the character string instructions are emulated
on the CPU and the value 0 if they are not.
Because this number is a Boolean value (1 or 0), the buffer length
field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
SYI$_CLUSTER_EVOTES
Returns the number of votes expected to be found in the OpenVMS Cluster
system. The cluster determines this value by selecting the highest
number from all of the following: each node's system parameter
EXPECTED_VOTES, the sum of the votes currently in the cluster, and the
previous value for the number of expected votes.
|


