 |
OpenVMS Linker Utility Manual
5.2.2 Module Relocatable Reference Synopsis (VAX Linking Only)
For VAX linking, the information contained in the Module Relocatable
Reference Synopsis section varies with the type of image being created.
For shareable images, this section lists all of the modules that
contain at least one .ADDRESS directive. For executable or system
images, this section lists the names of all object modules containing
at least one .ADDRESS reference to a shareable image. The
section lists the modules in the order in which the linker processes
them, including the number of .ADDRESS references found. The linker
formats the information as in the following example:
+---------------------------------------+
! Module Relocatable Reference Synopsis !
+---------------------------------------+
Module Name (1) Number (2) Module Name Number Module Name Number
----------- ------ ----------- ------ ----------- ------
MAIN1 1
|
- Module Name. The name of each object module
included in the link operation. The modules are listed in the order in
which the linker processed them.
- Number. The number of .ADDRESS references
found.
Note that you can reduce linker and image activator processing time by
removing .ADDRESS directives from input files.
5.2.3 Image Section Synopsis Section
The Image Section Synopsis section of the linker map file lists the
image sections created by the linker. The image sections appear in the
order in which the linker created them, which is the same order as the
clusters in the linker's cluster list. (For more information about
clusters, see Chapter 2.) The section includes other information
about these image sections, formatted in columns, as in the following
example:
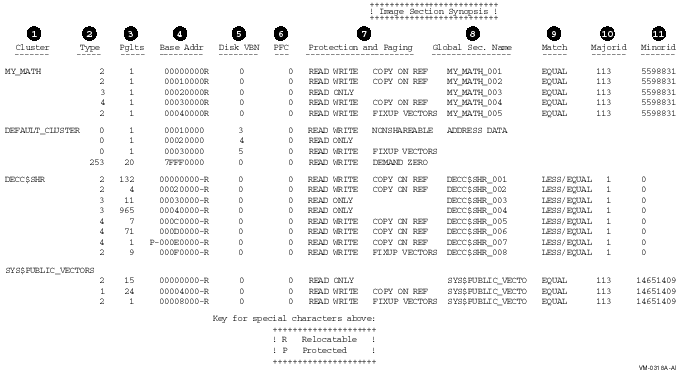
The items in the following list correspond to the numbered items in the
preceding figure:
- Cluster. The name of each cluster the linker
created, listed in the order in which the linker created them.
- Type. The type of image section, expressed as
one of the following codes:
| Code |
Image Section Type |
|
1
|
Shareable fixed image section
|
|
2
|
Private fixed image section
|
|
3
|
Shareable position-independent image section
|
|
4
|
Private position-independent image section
|
|
253
|
Stack image section
|
For more information about the types of image sections the linker
creates, see Section 3.3.5.
- Pages or pagelets. The length of each image
section, expressed in pages or pagelets.
- Base Address. The base address assigned to
the image section. Note that if the cluster is relocatable, the image
activator relocates the base address. In this case, the base address
entry for each image section in the cluster MY_MATH has the letter
"R" appended to it, indicating that the base address entry is
an offset to be added to the cluster base address assigned by the image
activator.
For Alpha linking, when images are installed as resident images, the
Install utility moves image sections containing code into system space.
This invalidates the base addresses listed for these image sections in
this section of the map file. Note, however, that the relative
positions of the program sections within the image section, listed in
the Program Section Synopsis section of the map file, remain valid when
the image section is moved into system space.
- Disk VBN (virtual block number). The virtual
block number of the image file on disk where the image section begins.
The number 0 indicates that the image section is not in the image file.
- Page fault cluster (PFC). The number of
pagelets read into memory by the operating system when the initial page
fault occurs for that image section. The number 0 indicates that the
system parameter PFCDEFAULT determines this value, rather than the
linker.
- Protection and Paging. A keyword phrase that
characterizes the settings of certain attributes of the image section,
such as the attributes that affect protection and paging. The following
table lists the keywords used by the linker to indicate these
characteristics of an image section:
| Keyword |
Meaning |
|
COPY ON REF
|
Indicates that the image section is a copy-on-reference image section.
Because a copy-on-reference image section is readable and writable, but
not shareable, each process receives a copy of it.
|
|
DEMAND ZERO
|
Indicates that the image section is a demand-zero image section. (For
more information, see Section 3.4.3.)
|
|
EXECUTABLE
|
Indicates that the image section contains code.
|
|
FIXUP VECTORS
|
Indicates that the image section contains the fix-up section. There is
always a change-protection fix-up for the fix-up section, so that when
the image activator is done, the image activator changes the protection
of the image section to READ ONLY.
|
|
NON-SHAREABLE ADDRESS DATA
|
Indicates that the linker set a READ ONLY page in the image section to
WRITE so that the image activator can fix up address references
(.ADDRESS) in the image section. The linker creates a change-protection
fix-up for these image sections that causes the image activator to set
the attributes of the image section back to READ ONLY when it finishes
processing the address references.
|
|
READ ONLY
|
Indicates that the image section is protected against write access.
|
|
READ WRITE
|
Indicates that the image section allows both read and write access.
|
The linker may use more than one keyword to describe an image
section. For example, to describe an image section that contains code,
the linker uses the READ ONLY and EXECUTABLE keywords.
Note that a
program section that you may have protected from write access (by
setting the NOWRT program section attribute) may appear in the map file
as writable (with the READ WRITE keyword). If this program section also
has the NON-SHAREABLE ADDRESS DATA keyword (as the first image section
in DEFAULT_CLUSTER illustrates), the linker has enabled write access to
the program section to allow the image activator to fix up address
references in the image section at run time. The image activator resets
the program section attributes to READ ONLY after it is finished.
- Global Section Name. The name assigned by the
linker to each image section comprising a shareable image. The linker
creates the names by appending the characters "_00x" after
the file name, where "x" is an integer, starting with 1, and
incremented for each image section in a shareable image.
- Match. The algorithm the image activator uses
when comparing identification numbers in a shareable image, expressed
by the keyword LESS/EQUAL, EQUAL, or ALWAYS. For more information about
this topic, see the description of the GSMATCH= option in Part 2.
- Majorid. An identification number assigned to
the image. The linker assigns the number to the image if it is not
specified as part of the link operation in the GSMATCH= option.
- Minorid. An identification number assigned to
the image. The linker assigns the number to the image if it is not
specified as part of the link operation in the GSMATCH= option.
5.2.4 Program Section Synopsis Section
The Program Section Synopsis section lists the program sections that
comprise the image, with information about the size of the program
section, its starting- and ending-addresses, and its attributes. The
Module Name column in this section lists the modules that contribute to
each program section. The following example illustrates this format:

The items in the following list correspond to the numbered items in the
preceding figure:
- Psect Name. The name of each program section
in the image in ascending order of its base virtual address.
- Module Name. The names of the modules that
contribute to the program section whose name appears on the line
directly above in the Psect Name column. If a shareable image appears
in this column, the linker processed the program section as a shareable
image reference.
- Base. The starting virtual address of the
program section or of a module that contributes to a program section.
- End. The ending virtual address of the
program section or of a module that contributes to a program section.
- Length. The total length of the program
section or of a module that contributes to a program section.
- Align. The type of alignment used for the
entire program section or for an individual program section
contribution. The alignment is expressed in two ways. In the first
column, the alignment is expressed using a predefined keyword, such as
OCTA. In the second column, the alignment is expressed as an integer
that is the power of 2 that creates the alignment. For example,
octaword alignment would be expressed as the keyword OCTA and as the
integer 4 (because 24 = 16).
If the linker does not
support a keyword to express an alignment, it puts the text "2
**" in the column in which the keyword usually appears. When read
with the integer in the second column, it expresses these alignments,
such as 2 ** 5.
- Attributes. The attributes associated with
the program section. For a list of all the possible attributes, see
Chapter 3.
For Alpha linking, the linker includes the MOD
attribute in the list of program section attributes (as illustrated in
the example). To make room in the display for this attribute, the
linker leaves out the Readability (RD/NORD) and User Library (USR/LIB)
attributes, which are reserved for future use.
For VAX linking, the
list of attributes includes the Readability (RD/NORD) and User Library
(USR/LIB) attributes. The Modified (MOD/NOMOD) attribute, which is not
supported for VAX images, is not included.
Note that, if a routine is extracted from the default system library to
resolve a symbolic reference, the Program Section Synopsis section in a
full map contains information about the program sections comprising
that routine. The Program Section Synopsis section in a default map
does not.
5.2.5 Symbols By Name Section
The Symbols By Name section lists the global symbols contained in all
the modules included in the link operation. The section includes the
value of the symbol, in the following format:
+-----------------+
! Symbols By Name !
+-----------------+
Symbol (1) Value (2) Symbol Value Symbol Value Symbol Value
------ ----- ------ ----- ------ ----- ------ -----
DECC$EXIT 00001FD0-RX
DECC$GPRINTF 00001710-RX
DECC$MAIN 000007D0-RX
MAIN 00010000-R
MYSUB 00000010-RX
MY_SYMBOL 00000050-RX
SYS$IMGSTA 00000340-RX
__MAIN 00010078-R
|
- Symbol. The names of the image's global
symbols in alphabetical order.
- Value. The value of the symbol, expressed in
hexadecimal. The linker appends characters to the end of the symbol
value to describe other characteristics of the symbol. For an
explanation of these symbols, see Section 5.2.7.
Note that this section is replaced by the Symbol Cross-Reference
section when you specify the /CROSS_REFERENCE qualifier in the LINK
command. The Symbols by Value section, described in Section 5.2.7,
lists the same symbols by value.
5.2.6 Symbol Cross-Reference Section
The Symbol Cross-Reference Section, which is produced in place of the
Symbols By Name section when you specify the /CROSS_REFERENCE
qualifier, lists all of the symbols referenced in the image, along with
the module in which they are defined and with all the modules that
reference them. The section formats this information as in the
following example:
+------------------------+
! Symbol Cross Reference !
+------------------------+
Symbol (1) Value (2) Defined By (3) Referenced By ... (4)
------ ----- ---------- -----------------
DECC$EXIT 00001FD0-RX DECC$SHR MY_MAIN
DECC$GPRINTF 00001710-RX DECC$SHR MY_MAIN
DECC$MAIN 000007D0-RX DECC$SHR MY_MAIN
MAIN 00010000-R MY_MAIN
MYSUB 00000010-RX MY_MATH MY_MAIN
MY_SYMBOL 00000050-RX MY_MATH MY_MAIN
SYS$IMGSTA 00000340-RX SYS$PUBLIC_VECTORS
__MAIN 00010078-R MY_MAIN
|
- Symbol. The name of the global symbol.
- Value. The value of the global symbol,
expressed in hexadecimal. The linker appends characters to the end of
the symbol value to describe other characteristics of the symbol. For
an explanation of these symbols, see Section 5.2.7.
- Defined By. The name of the module in which
the symbol is defined. For example, the symbol
mysub
is defined in the module named MY_MATH.
- Referenced By.... The name or names of all
the modules that contain at least one reference to the symbol.
5.2.7 Symbols By Value Section
The Symbols By Value section lists all the global symbols in the image
in order by value, in ascending numeric order. The linker formats the
information into columns, as in the following example:
+------------------+
! Symbols By Value !
+------------------+
Value (1) Symbols...(2)
----- ----------
00000010 RX-MYSUB
00000050 RX-MY_SYMBOL
00000340 RX-SYS$IMGSTA
000007D0 RX-DECC$MAIN
00001710 RX-DECC$GPRINTF
00001FD0 RX-DECC$EXIT
00010000 R-MAIN
00010078 R-__MAIN
|
- Value. The value of each global symbol,
expressed in hexadecimal, in ascending numerical order.
- Symbols... The names of the global symbols.
If more than one symbol has the same value, the linker lists them on
more than one line. The characters prefixed to the symbol names
indicate other characteristics of the symbol, such as its scope.
Table 5-3 lists these codes.
Table 5-3 Symbol Characterization Codes
| Code |
Meaning |
|
asterisk(*)
|
Symbol is undefined.
|
|
++A
|
Symbol is the alias name for a universal symbol.
|
|
++I
|
Symbol is the internal name of a symbol that has a universal alias name.
|
|
U
|
Symbol is a universal symbol.
|
|
R
|
Symbol is a relocatable symbol.
|
|
X
|
Symbol is an external symbol.
|
|
WK
|
Symbol is a weak symbol. (For more information, see Chapter 2.)
|
++Alpha specific
5.2.8 Image Synopsis Section
The Image Synopsis section contains miscellaneous information about the
image, such as its name and identification numbers, and a summary of
various attributes of the image, such as the number of files used to
build the image. The following example illustrates the format of this
section of a map file. The list following the example provides more
information about items in this section that are not self-explanatory.
+----------------+
! Image Synopsis !
+----------------+
Virtual memory allocated:(1) 00010000 0003FFFF 00030000 (196608. bytes, 384. pages)
Stack size: 20. pages
Image header virtual block limits: 1. 2. ( 2. blocks)
Image binary virtual block limits: 3. 5. ( 3. blocks)
Image name and identification: MY_MAIN V1.0
Number of files: 7.
Number of modules: 4.
Number of program sections: 11.
Number of global symbols: 944.
Number of cross references: 13.
Number of image sections: 20.
User transfer address: 00010078
Debugger transfer address: 00000340
Number of code references to shareable images: 6.
Image type: EXECUTABLE.
Map format: FULL WITH CROSS REFERENCE in file WORK:[PROGS]MY_MAIN.MAP;15
Estimated map length: 148. blocks
|
The following list explains the information returned in each line of
the Image Synopsis section:
- Virtual memory allocated. This line contains
the following information:
- The starting-address of the image (base-address)
- The ending-address of the image
- The total size of the image, expressed in bytes, in hexadecimal
radix
The numbers in parentheses at the end of the line indicate the
total size of the image, expressed in bytes and in pagelets. Both these
values are expressed in decimal.
5.2.9 Link Run Statistics Section
The Link Run Statistics section contains miscellaneous statistical
information about the link operation, such as performance indicators,
formatted as in the following example:
+---------------------+
! Link Run Statistics !
+---------------------+
Performance Indicators Page Faults CPU Time Elapsed Time
---------------------- ----------- -------- ------------
Command processing: 93 00:00:00.18 00:00:00.81
Pass 1: 345 00:00:00.55 00:00:12.04
Allocation/Relocation: 9 00:00:00.04 00:00:00.30
Pass 2: 29 00:00:00.14 00:00:00.62
Map data after object module synopsis: 3 00:00:00.05 00:00:00.31
Symbol table output: 0 00:00:00.00 00:00:00.10
Total run values: 479 00:00:00.96 00:00:14.18
Using a working set limited to 2048 pages and 946 pages of data storage (excluding image)
Total number object records read (both passes): 167
of which 0 were in libraries and 0 were DEBUG data records containing 0 bytes
Number of modules extracted explicitly = 0
with 0 extracted to resolve undefined symbols
5 library searches were for symbols not in the library searched
A total of 0 global symbol table records was written
LINK/MAP/FULL/CROSS MY_MAIN,SYS$INPUT/OPT
my_math/share
|
|

