HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
OpenVMS License Management Utility Manual
2.4.4.1 Using Data Files with VMSLICENSE.COMYou can use VMSLICENSE.COM in batch mode as well as interactively. Instead of entering the PAK data interactively from your terminal or workstation, you can create a VMSLICENSE data file with an editor and enter data obtained from your product PAKs (Example 2-2 shows sample PAK data). You can then invoke VMSLICENSE.COM, specifying the name of the new VMSLICENSE data file as a parameter on the same command line. The procedure displays the license data and performs the requested operation or operations using data only from the VMSLICENSE data file.
You can create a file that registers multiple licenses. VMSLICENSE.COM
exits only when it reaches the end of the VMSLICENSE data file.
To pass a VMSLICENSE data file to VMSLICENSE.COM, use the following format:
When you invoke VMSLICENSE with a data file, you must specify REGISTER as the license-option. You cannot use data files with any of the other options that are available when using VMSLICENSE interactively. You can specify a License Database on the command line or in the data file. Any License Database you specify in the data file overrides a License Database you specify on the command line. For example, you can pass the data in the sample VMSLICENSE data file, shown in Example 2-2, with the following command line:
2.4.4.3 Creating VMSLICENSE Data FilesWhen you create a VMSLICENSE data file to be processed by VMSLICENSE.COM, you must follow these rules (refer to Example 2-2):
2.4.4.4 Using VMSLICENSE.COM Default Value RulesIf you do not specify a value for a parameter in a VMSLICENSE data file, VMSLICENSE substitutes default values. The current default values are ISSUER=DEC and PRODUCER=DEC. All other license parameters have null values until you specify a value. After you specify a license parameter in the VMSLICENSE data file, the parameter becomes the new default value until the next occurrence of the parameter sets a new default value. To set or reset the value of a parameter to null, use a line of the following form:
For example, if the most recent PAK data set the INCLUDE_NODE parameter to a specific node, reset the parameter to null for the current and subsequent PAKs by entering the following:
Example 2-2 shows how using default data can eliminate typing for the
second PAK listed in the VMSLICENSE data file.
You can directly register (and load) a license with LICENSE commands. For example:
After you successfully register a license in the License Database (the default file specification is SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE]LMF$LICENSE.LDB), you can enter the LICENSE LIST/FULL command to display the data in the database (see Example 2-3).
When a license is successfully loaded with VMSLICENSE.COM or the
LICENSE LOAD command, LMF displays an informational message.
To display information from the License Database about specific licenses, enter the LICENSE LIST command.
To display information in memory about loaded licenses, enter the SHOW
LICENSE command. This command displays licenses loaded on the current
node, and displays any reservation list associated with each license.
To allow users to access a product, you must load each registered license. Loading a license transfers data from the on-disk License Database into system memory. The following table shows the methods of license loading for LMF:
Figure 2-4 illustrates the license loading process for a standalone system. Whether the license manager enters the LICENSE LOAD command or the system automatically loads all registered licenses during startup, the license information is transferred to the system memory of node ART. Figure 2-4 Loading a License 
2.5.1 Loading Licenses in an OpenVMS Cluster EnvironmentIn an OpenVMS Cluster environment, multiple nodes load licenses from a single common database. LMF provides this capability to let you share licenses as well as control access to a product on a node-by-node basis (provided this is allowed by the terms and conditions of the license). Typically, any node can load a license registered in the common License Database. For predictability, security, performance, or economic reasons, you can limit which nodes can access a product license intended to be shared among nodes. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, you control access by modifying the license's include list. Use the LICENSE MODIFY command and either the /INCLUDE or /EXCLUDE qualifier to specify which cluster nodes can load the license. By changing the include list, you can create the effect of moving a product from node to node. Section 2.6.2 describes the process in detail. Note that you cannot share licenses that have the NO_SHARE option. They must be assigned to a single node. You can also control which users in an OpenVMS Cluster environment can access a product license. Control access by modifying the license's reservation list. Use the LICENSE MODIFY command with the /RESERVE qualifier to specify which users can access the license. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, license loading involves transferring, or loading, license information from the on-disk License Database into system memory of the current node. The number and combination of licenses for an OpenVMS Cluster environment can be complex, which in turn makes the loading process complex and sometimes confusing. The general rule is that nodes specified on include lists or not specified on exclude lists of the LICENSE MODIFY command can load a registered license. As each system starts up, it loads any licenses to which it has access. If you need to load a license for all assigned nodes of a running cluster, you can use the OpenVMS System Management utility (SYSMAN), which is described in the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. Figure 2-5 illustrates the loading process in an OpenVMS Cluster environment. Figure 2-5 Loading a License in an OpenVMS Cluster Environment 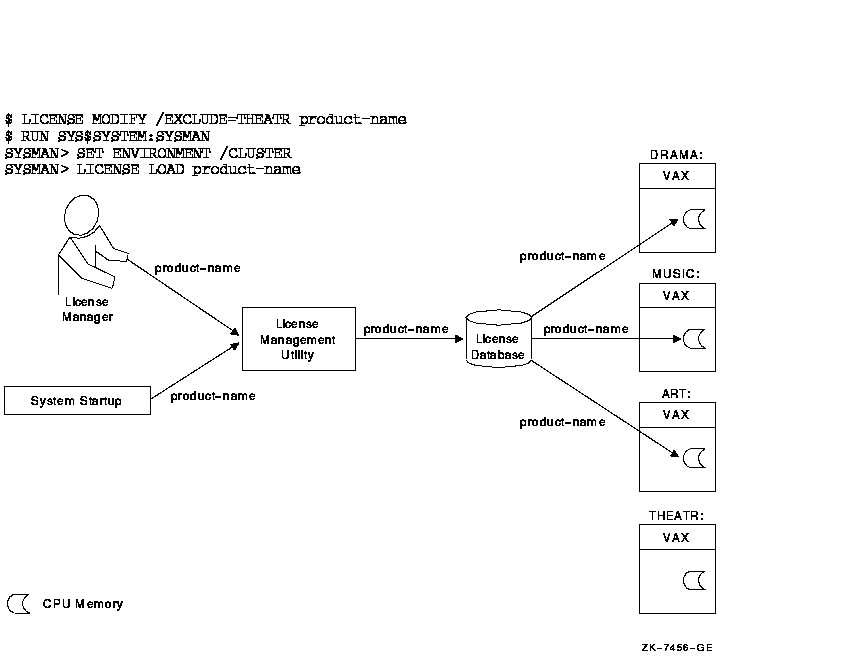
See Section 2.6.2 for further details of license loading.
After you register licenses, you can manage them. While system managers can perform these tasks, managers of cluster environments and large multiple-user systems may also have an interest in managing products and product licenses. For example, a cluster manager can use LMF to control which nodes can access a database product using important data (see Section 2.6.2). All system managers, however, may want to monitor license data using LICENSE commands. VMSLICENSE.COM, LICENSE commands, and the DCL command SHOW LICENSE can perform most license management tasks, including:
The quickest method to restrict access to products registered in the License Database is to unload the license with a LICENSE UNLOAD command. The product becomes unavailable to new users and unavailable to all users when the last process using the product finishes. The product remains inaccessible until either you or the system reloads the license.
Although LICENSE UNLOAD is fast, it is not permanent. Typically, at
system startup, LMF loads all the licenses registered in the License
Database. In addition, a license that is loaded remains loaded until
either the system is shut down or you intervene.
The following commands control license loading, which restricts product access. However, they do not unload loaded licenses or alter in-memory license data. For loaded licenses, use LICENSE UNLOAD.
2.6.1.3 Permanent MethodsFor more permanent access restrictions, issue one of the following commands:
2.6.2 Controlling Node Access to Licenses in ClustersIn an OpenVMS Cluster environment, you can control which nodes have access to a product. Some product licenses require you to control access by creating include or exclude lists with the LICENSE MODIFY command. In an OpenVMS Cluster environment, license units are available to all nodes by default. If you need to control which nodes in a cluster have access to a product license, you must use the LICENSE MODIFY command with the /INCLUDE or /EXCLUDE qualifiers. These qualifiers take an argument list of System Communications Services (SCS) node names. SCS node names are system parameters set with the System Generation utility (SYSGEN). For example, if your cluster includes nodes MUSIC, ART, DANCE, and THEATR, you can specify that nodes MUSIC and ART have access to the software products registered in the License Database, while nodes DANCE and THEATR do not have access. The following command allows two nodes access to Pascal:
You can perform the same task by using the /EXCLUDE qualifier. The following command specifies the same product access as the previous command:
If a license does not provide enough license units for full availability across the cluster, use LICENSE MODIFY and one of these qualifiers. Otherwise, product availability is unpredictable. Products are authorized for use on nodes in the order in which they load the licenses. Unless you use an include list to control which nodes can load a product, the authorization to use a product can move from processor to processor during a series of system shutdowns and startups. When you shut down a system, LMF automatically unloads all loaded licenses on that system. If another cluster member boots before the first system reboots, the second system, referring to the common License Database, can automatically load the same license. Although this can be helpful, it may not be your intention. You can use the /INCLUDE and /EXCLUDE qualifiers with the LICENSE MODIFY command to determine who has access to the pool of units created by LMF when it loads combinable licenses. However, note the following:
For example, if you assign an include list to four out of five combinable licenses, the default---all nodes are authorized---is in effect for the fifth license, and it overrides the lists on the other licenses. All nodes then have access to the product despite the include lists. Units for the product are allocated on a first-come, first-served basis as the nodes in the cluster are booted, until the pool of units is depleted. To ensure access exactly as you intend it, assign the same include or exclude list to each license. Purchasing more license units to fulfill requirements to run across the cluster is another option.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||