 |
VMS DECwindows Guide to Xlib (Release 4)
Programming: MIT C Binding
Xlib removes the next event from the event queue and copies it into an
event data structure. The program executes one of two routines,
depending on the flag returned in the event data structure type field.
Xlib indicates an exposure event by setting the Expose flag in the type
field; it indicates a button press event by setting the ButtonPress
flag.
When creating window1 and window2, the client
indicated an interest in exposures and button presses by setting the
event mask field of the set window attributes data structure, as
follows:
XSetWindowAttributes xswa;
.
.
.
xswa.event_mask = ExposureMask | ButtonPressMask;
|
For more information about selecting event types, see Section 9.2.
The event data structure includes other data structures Xlib uses to
report information about various kinds of events. The client-defined
doButtonPress routine checks the window field of one of these
data structures (the expose event data structure) to determine whether
or not the server has mapped window2.
If the server has mapped window2, the client calls a series of
shutdown routines when the user presses the mouse button.
9.3.2 Handling Pointer Motion
To only receive pointer motion events when a specified button is
pressed, pass the window identifier and one of the following masks when
using the selection method described in Section 9.2:
|
ButtonMotionMask
|
Button1MotionMask
|
|
Button2MotionMask
|
Button3MotionMask
|
|
Button4MotionMask
|
Button5MotionMask
|
Xlib reports pointer motion events to interested clients whenever the
pointer moves and the movement begins and ends in the window. Spatial
and temporal resolution of the events is not guaranteed, but clients
are assured they will receive at least one event when the pointer moves
and then rests. The following illustrates the data structure Xlib uses
to report these events:
typedef struct {
int type;
unsigned long serial;
Bool send_event;
Display *display;
Window window;
Window root;
Window subwindow;
Time time;
int x, y;
int x_root, y_root;
unsigned int state;
char is_hint;
Bool same_screen;
} XMotionEvent;
typedef XMotionEvent XPointerMovedEvent;
|
Table 9-6 describes members of the motion event data structure.
Note that Xlib defines the pointer moved event data structure as type
motion event.
Table 9-6 Motion Event Data Structure Members
| Member Name |
Contents |
|
type
|
Type of event reported. The member can have only the value specified by
the constant MotionNotify.
|
|
serial
|
Number of the last request processed by the server.
|
|
send_event
|
Value defined by the constant true if the event came from a SEND EVENT
request.
|
|
display
|
Address of the display on which the event occurred.
|
|
window
|
Event window.
|
|
root
|
Root window in which the event occurred.
|
|
subwindow
|
Source window in which the event occurred.
|
|
time
|
Time in milliseconds at which the event occurred.
|
|
x
|
The x value of the pointer coordinates in the source window.
|
|
y
|
The y value of the pointer coordinates in the source window.
|
|
x_root
|
The x value of the pointer coordinates relative to the root window.
|
|
y_root
|
The y value of the pointer coordinates relative to the root window.
|
|
state
|
State of the button just prior to the event. Xlib can set this member
to the bitwise OR of the following masks:
|
Button1Mask
|
Button2Mask
|
|
Button3Mask
|
Button4Mask
|
|
Button5Mask
|
Mod1Mask
|
|
Mod2Mask
|
Mod3Mask
|
|
Mod4Mask
|
Mod5Mask
|
|
|
is_hint
|
Indicates that motion hints are active. No other events reported until
pointer moves out of window.
|
|
same_screen
|
Indicates whether or not the event window is on the same screen as the
root window.
|
Example 9-3 illustrates pointer motion event handling.
| Example 9-3 Handling Pointer Motion |
/***** Handle events *****/
static void doHandleEvents( )
{
XEvent event;
for ( ; ; ) {
XNextEvent(dpy, &event);
switch (event.type) {
case Expose: doExpose(&event); break;
case MotionNotify: doMotionNotify(&event); break;
case ButtonPress: sys$exit(1);
}
}
}
.
.
.
static void doMotionNotify(eventP)
XEvent *eventP;
{
int x = eventP->xmotion.x;
int y = eventP->xmotion.y;
int width = 5;
int length = 5;
XFillRectangle(dpy, win, gc, x, y, width, length);
}
|
Each time the pointer moves, the program draws a small filled rectangle
at the resulting x and y coordinates.
To receive pointer motion events, the client specifies the
MotionNotify flag when removing events from the queue.
The client indicated an interest in pointer motion events when creating
window win, as follows:
xswa.event_mask = ExposureMask | ButtonPressMask |
PointerMotionMask;
win = XCreateWindow(dpy, RootWindowOfScreen(screen),
winX, winY, winW, winH, 0,
DefaultDepthOfScreen(screen), InputOutput,
DefaultVisualOfScreen(screen), CWEventMask, &xswa);
|
The server reports pointer movement. Xlib records the resulting
position of the pointer in a motion data structure, one of the event
data structures that constitute the event data structure. The
client-defined doMotionNotify routine determines the origin of
the filled rectangle it draws by referring to the motion event data
structure x and y members.
9.4 Window Entries and Exits
Xlib reports window entries and exits to interested clients when one of
the following occurs:
- The pointer moves into or out of a window due to either pointer
movement or to a change in window hierarchy. This is normal window
entry and exit.
- A client calls WARP POINTER, which moves the pointer to any
specified point on the screen.
- A client calls CHANGE ACTIVE POINTER GRAB, GRAB KEYBOARD, GRAB
POINTER, or UNGRAB POINTER. This is pseudomotion,
which simulates window entry or exit without actual pointer movement.
To receive event notification of window entries and exits, pass the
window identifier and either the EnterWindowMask mask
or the LeaveWindowMask mask when using the selection
method described in Section 9.2.
Xlib uses the crossing event data structure to report window entries
and exits. The following illustrates the data structure:
typedef struct {
int type;
unsigned long serial;
Bool send_event;
Display *display;
Window window;
Window root;
Window subwindow;
Time time;
int x, y;
int x_root, y_root;
int mode;
int detail;
Bool same_screen;
Bool focus;
unsigned int state;
} XCrossingEvent;
typedef XCrossingEvent XEnterWindowEvent;
typedef XCrossingEvent XLeaveWindowEvent;
|
Table 9-7 describes members of the crossing event data structure.
Note that Xlib defines the enter window event and leave window event
data structures as type crossing event.
Table 9-7 Crossing Event Data Structure Members
| Member Name |
Contents |
|
type
|
Value defined by either the EnterNotify or the LeaveNotify constant.
|
|
serial
|
Number of the last request processed by the server.
|
|
send_event
|
The value defined by the constant true if the event came from a SEND
EVENT request.
|
|
display
|
Address of the display on which the event occurred.
|
|
window
|
Event window.
|
|
root
|
Root window on which the event occurred.
|
|
subwindow
|
Source window in which the event occurred.
|
|
time
|
Time in milliseconds at which the key event occurred.
|
|
x
|
The x value of the pointer coordinates in the source window.
|
|
y
|
The y value of the pointer coordinates in the source window.
|
|
x_root
|
The x value of the pointer coordinates relative to the root window.
|
|
y_root
|
The y value of the pointer coordinates relative to the root window.
|
|
mode
|
Indicates whether the event is normal or pseudomotion. Xlib can set
this member to the value specified by the constants NotifyNormal,
NotifyGrab, and NotifyUngrab. See Section 9.4.1 and Section 9.4.2 for
descriptions of normal and pseudomotion events.
|
|
detail
|
Indicates which windows Xlib notifies of the window entry or exit
event. Xlib can specify one of the following constants:
|
NotifyAncestor
|
NotifyVirtual
|
|
NotifyInferior
|
NotifyNonlinear
|
|
NotifyNonlinearVirtual
|
|
|
|
same_screen
|
Indicates whether or not the event window is on the same screen as the
root window.
|
|
focus
|
Specifies whether the event window or an inferior is the focus window.
If true, the event window is the focus window. If false, an inferior is
the focus window.
|
|
state
|
State of buttons and keys just prior to the event. Xlib can return
values specified by the following constants:
|
Button1Mask
|
Button2Mask
|
|
Button3Mask
|
Button4Mask
|
|
Button5Mask
|
Mod1Mask
|
|
Mod2Mask
|
Mod3Mask
|
|
Mod4Mask
|
Mod5Mask
|
|
ShiftMask
|
ControlMask
|
|
LockMask
|
|
|
9.4.1 Normal Window Entries and Exits
A normal window entry or exit event occurs when the pointer moves from
one window to another due to either a change in window hierarchy or the
movement of the pointer. In either case, Xlib sets the mode member of
the crossing event data structure to the constant
NotifyNormal.
If the pointer leaves or enters a window as a result of one of the
following changes in window hierarchy, Xlib reports the event after
reporting the hierarchy event:
|
Mapping
|
Unmapping
|
|
Configuring
|
Circulating
|
|
Changing gravity
|
|
Xlib can report a window entry or exit event caused by changes in
focus, visibility, and exposure either before or after reporting these
events.
See the X Window System for a description of the events that Xlib reports
when the pointer moves from window A to window B as a result of normal
window entry or exit.
Example 9-4 illustrates window entry and exit event handling. The
program changes the color of a window when the pointer enters or leaves
the window.
Figure 9-1 shows the resulting output.
| Example 9-4 Handling Window Entries and
Exits |
/* Create windows win, subwin1, *
* subwin2, subwin3, and *
* subwin4 on *
* display dpy, defined as follows: *
* #define windowWidth 600 *
* #define windowHeight 600 *
* #define subwindowWidth 120 *
* #define subwindowHeight 120 *
* win position: x = 100,y = 100 *
* subwin1 position: x = 120,y = 120 *
* subwin2 position: x = 360,y = 120 *
* subwin3 position: x = 120,y = 360 *
* subwin1 position: x = 360,y = 360 */
.
.
.
/**** Handle events *****/
static void doHandleEvents( )
{
XEvent event;
for ( ; ; ) {
XNextEvent(dpy, &event);
switch (event.type) {
case Expose: doExpose(&event); break;
case ButtonPress: sys$exit(1);
case EnterNotify: doEnterNotify(&event); break;
case LeaveNotify: doLeaveNotify(&event); break;
}
}
}
.
.
.
/***** Change window color when pointer enters window *****/
static void doEnterNotify(eventP)
XEvent *eventP;
{
(1) Window window = eventP->xcrossing.window;
XSetWindowBackground(dpy, window, doDefineColor(4));
(2) XClearArea(dpy, window, 0, 0, subwindowWidth, subwindowHeight, 0);
return;
}
/***** Change window color when pointer leaves window *****/
static void doLeaveNotify(eventP)
XEvent *eventP;
{
Window window = eventP->xcrossing.window;
XSetWindowBackground(dpy, window, doDefineColor(2));
XClearArea(dpy, window, 0, 0, subwindowWidth, subwindowHeight, 0);
return;
}
|
- Xlib gives the window identifier in the
crossing event data structure window field. This occurs when the
pointer cursor enters the new window. The program uses the identifier
to define the window background and clear the window.
- The CLEAR AREA routine clears the window and
repaints it with the newly defined window background.
Figure 9-1 Window Entries and Exits
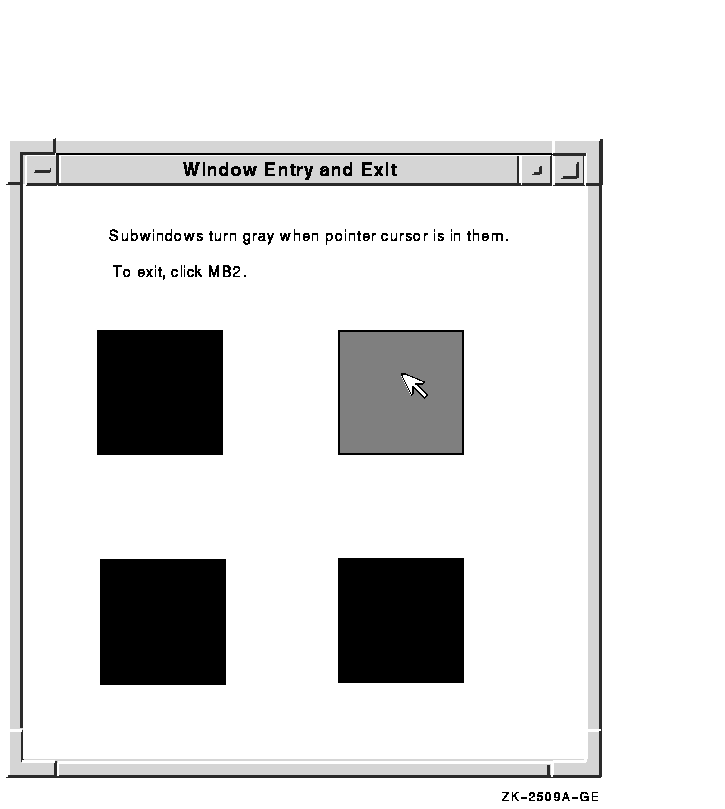
9.4.2 Pseudomotion Window Entries and Exits
Pseudomotion window entry and exit events occur when the pointer cursor
moves from one window to another due to activating or deactivating a
pointer grab.
Xlib reports a pseudomotion window entry if a client grabs the pointer,
causing the pointer cursor to change from one window to another even
though the pointer cursor has not moved. For example, if the pointer
cursor is in window A and a client maps window B over window A, the
pointer cursor changes from being in window A to being in window B. If
possible, the pointer cursor remains in the same position on the
screen. When the placement of the two windows prevents the pointer
cursor from maintaining the same position, the pointer cursor moves to
the location closest to its original position.
Clients can grab pointers actively by calling the GRAB POINTER routine
or passively by calling the GRAB BUTTON routine. Whether the grab is
active or passive, Xlib sets the following members of the crossing
event data structure to the indicated constants after the pointer
cursor moves from one window to another:
- Type member---EnterNotify
- Mode member---NotifyGrab
When a client passively grabs the pointer by calling the GRAB BUTTON
routine, Xlib reports a button press event after reporting the pointer
grab.
Xlib reports a pseudomotion window exit when a client deactivates a
pointer grab, causing the pointer cursor to change from one window to
another even though the pointer cursor has not moved.
Clients can deactivate pointer grabs either actively by calling the
UNGRAB POINTER routine or passively by calling the UNGRAB BUTTON
routine. Whether deactivating the grab is active or passive, Xlib sets
the following members of the crossing event data structure to the
indicated constants after the pointer cursor moves from one window to
another:
- Type member---LeaveNotify
- Mode member---NotifyUngrab
When a client passively deactivates a pointer grab by calling the
UNGRAB BUTTON routine, Xlib reports a button release event before
reporting that the pointer has been released.
9.5 Input Focus Events
Input focus defines the window to which Xlib sends keyboard input.
The keyboard is always attached to some window. Typically, keyboard
input goes to either the root window or to a window at the top of the
stack called the focus window. The focus window and
the position of the pointer determine the window that receives keyboard
input.
When the keyboard input focus changes from one window to another, Xlib
reports a focus out event and a focus in event. The window that loses
the input focus receives the focus out event. The window that gains the
focus receives a focus in event. Additionally, Xlib notifies other
windows in the hierarchy of focus in and focus out events.
To receive notification of input focus events, pass the window
identifier and the FocusChangeMask mask when using the
selection method described in Section 9.2.
Xlib uses the focus change event data structure to report keyboard
input focus events.
9.6 Exposure Events
Xlib reports an exposure event when one of the following conditions
occurs:
- A formerly obscured window or window region becomes visible.
- A destination region cannot be computed.
- A graphics request exposes one or more regions.
This section describes how to handle window exposures and graphics
exposures.
9.6.1 Handling Window Exposures
A window exposure occurs when a formerly obscured window becomes
visible again.
Because Xlib does not guarantee to preserve the contents of regions
when windows are obscured or reconfigured, clients are responsible for
restoring the contents of the exposed window.
To receive notification of window exposure events, pass the window
identifier and the ExposureMask mask when using the
selection method described in Section 9.2. Xlib notifies clients of
window exposures using the expose event data structure.
The following illustrates the data structure:
typedef struct {
int type;
unsigned long serial;
Bool send_event;
Display *display;
Window window;
int x, y;
int width, height;
int count;
} XExposeEvent;
|
Table 9-8 describes members of the expose event data structure.
Table 9-8 Expose Event Data Structure Members
| Member Name |
Contents |
|
type
|
Value defined by the Expose constant.
|
|
serial
|
Number of the last request processed by the server.
|
|
send_event
|
Value defined by the constant true if the event came from a SEND EVENT
request.
|
|
display
|
Address of the display on which the event occurred.
|
|
window
|
Event window.
|
|
x
|
The x value of the coordinates that define the upper left corner of the
region that is exposed. The coordinates are relative to the origin of
the drawable.
|
|
y
|
The y value of the coordinates that define the upper left corner of the
region that is exposed. The coordinates are relative to the origin of
the drawable.
|
|
width
|
Width of the exposed region.
|
|
height
|
Height of the exposed region.
|
|
count
|
Number of exposure events that are to follow. If Xlib sets the count to
zero, no more exposure events follow for this window.
Clients that do not want to optimize redisplay by distinguishing
between subareas of its windows can ignore all exposure events with
nonzero counts and perform full redisplays on events with zero counts.
|
The following fragment from the sample program in Chapter 1
illustrates window exposure event handling:
/***** Handle events *****/
static void doHandleEvents( )
{
XEvent event;
for ( ; ; ) {
XNextEvent(dpy, &event);
switch (event.type) {
case Expose: doExpose(&event); break;
.
.
.
static void doExpose(eventP)
XEvent *eventP;
{
char message[] = {"Click here to exit"};
if (eventP->xexpose.window != window2) return;
XDrawImageString(dpy, window2, gc, 75, 75, message,
strlen(message));
}
|
The program checks exposure events to verify that the server has mapped
the second window. After the window is mapped, the program writes text
into it.
The client-defined doExpose routine checks the window and
count members of the expose event data structure to determine whether
or not the server has completed mapping window2. If the window
is mapped, the program writes the message "Click here to
exit" in it.
|
