OpenVMS RTL Library (LIB$) Manual
LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC
The Translate EBCDIC to ASCII routine translates an EBCDIC string to an
ASCII string.
Format
LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC byte-integer-source-string ,destination-string
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
byte-integer-source-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
String (EBCDIC) to be translated by LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC. The
byte-integer-source-string argument contains the
address of a descriptor pointing to this source string.
destination-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Destination string (ASCII). The destination-string
argument contains the address of the descriptor of this destination
string.
The LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC routine uses the EBCDIC to ASCII translation table,
LIB$AB_EBC_ASC.
Description
LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC translates an EBCDIC string to an ASCII string. If the
destination string is a fixed-length string, its length must match the
length of the input string. The length of both the source and
destination strings is limited to 65,535 characters. No filling is done.
A similar operation can be accomplished by specifying the EBCDIC to
ASCII translation table, LIB$AB_EBC_ASC, in a routine using LIB$MOVTC,
but no testing for untranslatable characters is done under these
circumstances.
The LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC routine uses the EBCDIC to ASCII translation shown
in Figure lib-26.
Figure lib-26 LIB$AB_EBC_ASC
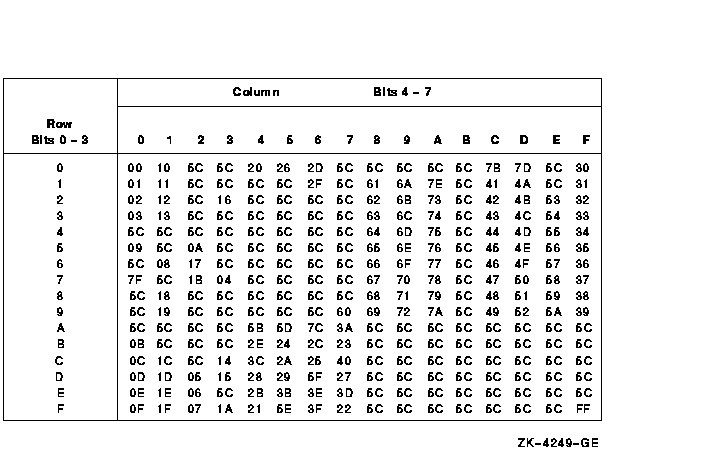
EBCDIC to ASCII Translation Table
- The numbers on the left represent the low-order bits of the EBCDIC
characters in hexadecimal notation.
- The numbers across the top represent the high-order bits of the
EBCDIC characters in hexadecimal notation.
- The numbers in the body of the table represent the equivalent ASCII
characters in hexadecimal notation.
All EBCDIC graphics are translated to their equivalent ASCII graphic
except for the graphics noted in Figure lib-27.
Figure lib-27 EBCDIC Graphics Not Translated to ASCII
Equivalent by LIB$TRA_EBC_ASC

Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_INVARG
|
If the destination string is a fixed-length string and its length is
not the same as the source string length, or if the length of the input
string is greater than 65,535 characters, no translation is attempted.
|
|
LIB$_INVCHA
|
One or more occurrences of an untranslatable character have been
detected during the translation.
|
LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC
The Fit Long File Specification into Fixed Field routine takes a file
specification, such as an OpenVMS RMS resultant name string, and
shortens it (if necessary) so that it fits into a field of fixed width.
Format
LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC old-filespec ,new-filespec [,word-integer-width]
[,resultant-length]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
old-filespec
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
File specification to be trimmed. The old-filespec
argument contains the address of a descriptor pointing to this file
specification string.
The file specification should be an RMS resultant name string.
new-filespec
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Trimmed file specification. The new-filespec argument
contains the address of a descriptor pointing to this trimmed file
specification string. LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC writes the trimmed file
specification into new-filespec.
word-integer-width
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Maximum field width desired. The word-integer-width
argument is the address of an unsigned word that contains this maximum
field width.
If omitted, the current length of new-filespec is
used. If new-filespec is not a fixed-length string,
you should specify word-integer-width to ensure that
the desired width is used.
resultant-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of the trimmed file specification, not including any blank
padding or truncated characters. The resultant-length
argument is the address of an unsigned word that contains this length.
This is an optional argument.
Description
This routine trims file specifications in a consistent, predictable
manner to fit in a fixed-length field using the same algorithm that
Compaq software uses.
LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC allows compilers and other utilities which need to
display file specifications in fixed-length fields, such as listing
headers, to display file specifications in a consistent fashion.
If necessary to make the file specification fit into the specified
field width, LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC removes portions of the file
specification in this order:
- Node (including access control)
- Device
- Directory
- Version
- Type
If, after removing all these fields, the file name is still longer than
the field width, the file name is truncated and the alternate success
status LIB$_STRTRU is returned.
LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC supports any string class for the
old-filespec and new-filespec string
arguments.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_STRTRU
|
Success, but the output string was truncated. Significant characters of
the trimmed file specification were truncated.
|
|
LIB$_INVSTRDES
|
Invalid string descriptor.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Wrong number of arguments.
|
Any condition values returned by LIB$SCOPY_R_DX, or the $FILESCAN
system service.
Example
|
PROGRAM TRIM_FILESPEC(INPUT,OUTPUT);
{+}
{ This PASCAL example program demonstrates the
{ use of LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC.
{-}
TYPE
WORD = [WORD] 0..65535;
VAR
INPUT_FILESPEC : VARYING [255] OF CHAR;
OUTPUT_FILESPEC : VARYING [32] OF CHAR;
RETURNED_STATUS : INTEGER;
[EXTERNAL] FUNCTION LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC(
IN_FILE : VARYING [LEN1] OF CHAR;
VAR OUT_FILE : VARYING [LEN2] OF CHAR;
WIDTH : WORD := %IMMED 0;
OUT_LEN : [REFERENCE] WORD := %IMMED 0
) : INTEGER; EXTERNAL;
[EXTERNAL] FUNCTION LIB$STOP(
CONDITION_STATUS : [IMMEDIATE,UNSAFE] UNSIGNED;
FAO_ARGS : [IMMEDIATE,UNSAFE,LIST] UNSIGNED
) : INTEGER; EXTERNAL;
BEGIN
{+}
{ Start with a large INPUT_FILESPEC.
{-}
INPUT_FILESPEC := 'DISK$NAME:[DIRECTORY1.DIRECTORY2]FILENAME.EXTENSION;1';
{+}
{ Use LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC to shorten it to fit a smaller variable.
{-}
RETURNED_STATUS := LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC(
INPUT_FILESPEC,
OUTPUT_FILESPEC,
SIZE(OUTPUT_FILESPEC.BODY));
IF NOT ODD(RETURNED_STATUS)
THEN
LIB$STOP(RETURNED_STATUS);
{+}
{ Print out the original file name along with the
{ shortened file name.
{-}
WRITELN('Original file specification ',INPUT_FILESPEC);
WRITELN('Shortened file specification ',OUTPUT_FILESPEC);
END.
|
This Pascal example program demonstrates the use of LIB$TRIM_FILESPEC.
The output generated by this program is as follows:
Original file specification DISK$NAME:[DIRECTORY1.DIRECTORY2]FILENAME.EXTENSION;1
Shortened file specification FILENAME.EXTENSION;1
|
LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME
The Trim a Full Name to Fit into a Desired Output Field routine trims a
full name to fit into a desired output field. The trimming preserves
the most significant part of the full name.
Note
No support for arguments passed by 64-bit address reference or for use
of 64-bit descriptors, if applicable, is planned for this routine.
|
Format
LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME fullname, trimmed-nodename [,output-width]
[,resultant-length]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
fullname
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Full name to be trimmed. The fullname argument
contains the address of a descriptor pointing to this full name string.
The error LIB$_INVARG is returned if fullname contains
an invalid full name, points to a null string, or contains more than
1024 characters. The error LIB$_INVSTRDES is returned if
fullname is an invalid descriptor.
trimmed-nodename
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Trimmed node name. The trimmed-nodename argument
contains the address of a descriptor pointing to the trimmed node-name
string. LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME writes the trimmed node name into the buffer
pointed to by trimmed-nodename.
The error LIB$_INVSTRDES is returned if
trimmed-nodename is an invalid descriptor.
The length field of the trimmed-nodename descriptor is
not updated unless trimmed-nodename is a dynamic
descriptor with a length less than the resultant trimmed node name.
Refer to the OpenVMS RTL String Manipulation (STR$) Manual for dynamic string descriptor usage.
The trimmed-nodename argument contains an unusable
result when LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME returns in error.
output-width
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Field width desired for the trimmed node name. The
output-width argument is the address of an unsigned
word that contains this field width in bytes.
If output-width is omitted, the current length of
trimmed-nodename is used. If
trimmed-nodename is not a fixed-length string, specify
output-width to ensure that the desired width is used.
If the lengths of both trimmed-nodename and
output-width are specified, the length in
output-width is used. In this case, if the current
length of trimmed-nodename is smaller than the length
of output-width, the output trimmed node name is
truncated at the end, and the alternate successful status LIB$_STRTRU
is returned.
resultant-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of the trimmed node name. The resultant-length
argument is the address of an unsigned word that contains this length
in bytes.
The resultant-length argument contains an unusable
result when LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME returns in error.
Description
This routine trims a full name to the length that fits the desired
output field. It allows applications to trim long full names for
displaying in a fixed-length field, such as listing headers, in a
consistent manner.
Full names are validated. Valid full names are defined as full names
expanded from using LIB$EXPAND_NODENAME. A node name must be expanded
to a full name using LIB$EXPAND_NODENAME before calling
LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME. The error LIB$_INVARG is returned if the input full
name is invalid.
If the length of fullname is less than or equal to the
desired output width, no trimming is performed, and
fullname is returned in
trimmed-nodename. Trailing blanks are padded if
necessary.
Trimming is performed when the length of fullname is
larger than the desired output width. The alternate successful status
LIB$_STRTRU is returned.
The trimmed node name contains the significant part of the full name.
This allows the most important information of a full name to be
retained for display purposes. The significant part of a full name is
determined by the underlying network services.
In a DECnet environment, trimming a DECnet-Plus full name results in
the error condition LIB$_INVARG.
If a usable short form of a node name is desired for display purposes,
call LIB$COMPRESS_NODENAME first. If LIB$COMPRESS_NODENAME returns
LIB$_STRTRU, LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME can then be used to return the trimmed
node name.
LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME adds padding spaces to the end of the output buffer
if the trimmed node name is shorter than the size of the output buffer.
The argument resultant-length, if supplied, is set to
the length of the trimmed node name, excluding any padding spaces.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_STRTRU
|
Routine successfully completed. Characters are truncated in the output
buffer pointed to by
trimmed-nodename.
|
|
LIB$_INVARG
|
Invalid argument:
-
fullname is invalid.
-
fullname points to a null string.
- The length of the input full name is more than 1024 characters.
- The trimmed DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS node name is invalid in a DECnet for OpenVMS
environment.
|
|
LIB$_INVSTRDES
|
Invalid string descriptor.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Wrong number of arguments.
|
Any condition value returned by LIB$SCOPY_R_DX, or the $IPC
DECnet service.
Examples
The following table gives some examples of the results of using
LIB$TRIM_FULLNAME:
| Full Name |
Size of Output Field |
Trimmed Node Name |
|
NODE
|
3
|
NOD
|
|
NODE
|
8
|
NODE
|
|
DEC:.FOO.NODE
|
5
|
.NODE
|
|
DEC:.FOO.NODE
|
8
|
FOO.NODE
|
|
DEC:.FOO.NODE
|
20
|
DEC:.FOO.NODE
|
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE
The Verify a Zone routine performs verification of a 32-bit zone.
Note
No support for arguments passed by 64-bit address reference or for use
of 64-bit descriptors, if applicable, is planned for this routine.
|
Format
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE zone-id
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Argument
zone-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Zone identifier of the zone to be verified. The
zone-id argument is the address of an unsigned
longword that contains this zone identifier. A value of 0 indicates the
32-bit default zone.
Description
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE verifies a zone. LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE performs
verification of the zone header and scans all of the queues and lists
maintained in the zone header; this includes the lookaside lists and
the free lists. If the zone was created with LIB$M_VM_FREE_FILL0 or
LIB$M_VM_FREE_FILL1, LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE also checks the contents of the
free blocks.
As soon as an error is encountered, processing stops. If LIB$_BADZONE
is returned, use the routine LIB$SHOW_VM_ZONE to dump the zone
information.
You must have exclusive access to the zone while the verification is
proceeding. Results are unpredictable if another thread of control
modifies the zone while this routine is analyzing control data or
scanning control blocks.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_BADZONE
|
Invalid zone.
|
|
LIB$_INSVIRMEM
|
Insufficient virtual memory.
|
|
LIB$_INVARG
|
Invalid or null argument.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Wrong number of arguments.
|
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE_64 (Alpha Only)
The Verify a Zone routine performs verification of a 64-bit zone.
Format
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE_64 zone-id
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Argument
zone-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Zone identifier of the zone to be verified. The
zone-id argument is the address of an unsigned
quadword that contains this zone identifier. A value of 0 indicates the
64-bit default zone.
Description
LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE_64 verifies a zone. LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE_64 performs
verification of the zone header and scans all of the queues and lists
maintained in the zone header; this includes the lookaside lists and
the free lists. If the zone was created with the LIB$M_VM_FREE_FILL0 or
LIB$M_VM_FREE_FILL1 algorithm, LIB$VERIFY_VM_ZONE_64 also checks the
contents of the free blocks.
As soon as an error is encountered, processing stops. If LIB$_BADZONE
is returned, use the routine LIB$SHOW_VM_ZONE_64 to dump the zone
information.
You must have exclusive access to the zone while the verification is
proceeding. Results are unpredictable if another thread of control
modifies the zone while this routine is analyzing control data or
scanning control blocks.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_BADZONE
|
Invalid zone.
|
|
LIB$_INVARG
|
Invalid or null argument.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Wrong number of arguments.
|
|

