 | OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual
5.4.3.3 Set Modem Function ModifierThe set modem function modifier is used in maintenanceoperations to allow a process to activate and deactivate modem controlsignals. Both set mode and set characteristics functions can take theset modem function modifier. The following combinations of functioncode and modifier are provided: - IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_SET_MODEM!IO$M_MAINT
- IO$_SETCHAR!IO$M_SET_MODEM!IO$M_MAINT
Note
For LAT devices, the set modem field for maintenance operations of theIO$M_SET_MODEM!IO$M_MAINT function modifier is unsupported and mayreturn unpredictable results. |
These function code modifier pairs take the following device- orfunction-dependent argument: P1---The address of a quadword block that specifies which modem control signals to activate or deactivate Figure 5-9 shows the format of this block. Figure 5-9 Set Mode P1 Block
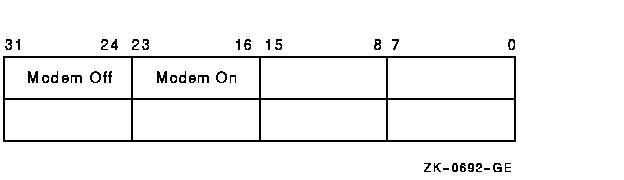 The modem on and modem off fields, in combination or separately, canspecify one or more of the following values: - TT$M_DS_RTS---Request to send (RTS)
- TT$M_DS_DTR---Data terminal ready (DTR)
- TT$M_DS_SECTX---Transmitted backward channel data (Sec Txd)
The $TTDEF macro defines the values for these values. These values canonly be specified if the terminal characteristic TT$M_MODEM is not set.Otherwise, an error (SS$_ABORT) will result. Notes
The set modem function is not supported for remote terminals. Thestatus SS$_DEVREQERR is returned in the I/O status block.Because the DMF32 does not provide the secondary transmitted datasignal (Sec Txd), the driver sets the secondary request to send thesignal. Users should connect a jumper cable between pins 14 and 19 onthe DMF32. |
5.4.3.4 Loopback Function ModifierThe loopback function modifier is used in maintenance operationsto place the terminal line in a hardware loopback mode. Datatransmitted to a line in this mode is returned as receive data. If thecontroller does not support loopback mode or the terminal line has theTT$M_MODEM characteristic set, an error status (SS$_ABORT) is returned.Both set mode functions can take the loopback function modifier. Note
The loopback function is not supported for remote terminals. The statusSS$_DEVREQERR is returned in the I/O status block. |
The following combinations of function code and modifier are provided: - IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_LOOP!IO$M_MAINT
- IO$_SETCHAR!IO$M_LOOP!IO$M_MAINT
Data transmitted in the loopback mode should only be written in recordsless than or equal to the size of the type-ahead buffer (seeSection 5.2.1.5). Programs that use the loopback function modifier shouldincorporate a 1-second delay to allow the controller to enable theloopback mode after the request is posted. Write requests should alsoinclude the IO$M_NOFORMAT function modifier to prevent terminal driverfrom formatting input or output data. Note
The serial line interfaces for the VAX 8200 processor implement aninternal loopback bus that is common to all four serial lines. Thehardware allows all serial lines operating in loopback mode to transmitdata to the bus at the same time. If more than one serial line writesdata to the bus, all of the transmitted data is combined and madeavailable to the receiving end of those same serial lines. Therefore,the received data may be different from the transmitted data if morethan one serial line is operating in loopback mode at the same time. Toprevent receiving such spurious data, you must not operate multipleserial lines in loopback mode. |
The operating system provides another function modifier to reset aterminal line previously placed in loopback mode. The followingcombinations of function code and modifier are provided: - IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_UNLOOP!IO$M_MAINT
- IO$_SETCHAR!IO$M_UNLOOP!IO$M_MAINT
Programs that use the unloop function modifier should incorporate a1-second delay to allow the controller to reset the loopback mode afterthe request is posted. Note
IO$M_LOOP and IO$M_UNLOOP are not supported for LAT devices. |
5.4.3.5 Enable Out-of-Band AST Function ModifierThe enable out-of-band AST function modifier requests that the terminaldriverqueue an AST for the requesting process when you enter any one of 32control characters.The following combinations of function code and modifier are provided: - IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_OUTBAND---Enable out-of-band AST
- IO$_SETCHAR!IO$M_OUTBAND---Enable out-of-band AST
These function code modifier pairs take the following device- orfunction-dependent arguments: - P1---Address of the AST service or 0 if the AST entered on this channel is to be canceled. (The AST parameter will be the out-of-band character.)
- P2---Address of a character mask with the same format as the short form terminator mask (see Section 5.4.1.2).
- P3---Access mode to deliver AST (maximized with the caller's access mode).
The IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_OUTBAND function can optionally take the followingfunction modifiers: - IO$M_INCLUDE---Include the character typed in the data stream.
- IO$M_TT_ABORT---Allow current read and write operations to be aborted. (The IOSB for aborted operations returns the status SS$_CONTROLC.)
If an out-of-band AST is in effect, pressing any control characterspecified in the P2 mask gains the attention of the enabling process.Figure 5-8 shows the relationship of the out-of-band function withsome of the control characters. You can have only one out-of-band AST enabled per channel. Out-of-band ASTs are repeating ASTs; they continue to be delivereduntil specifically disabled. Out-of-band AST enables are flushed by theCancel I/O on Channel ($CANCEL) system service.5.4.3.6 Broadcast Function Modifier The broadcast function modifier allows you to turn on or turn offselected broadcast requester identifiers (IDs). The followingcombination of function code and modifier is provided: IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_BRDCST This function code modifier pair takes the following device- orfunction-dependent arguments: - P1---A buffer that contains the bits that specify the requester IDs to be broadcast
- P2---The length of the P1 buffer (default is 8 bytes)
The first longword of P1 is reserved for use by Compaq facilities, asshown in Table 5-12. The symbols are defined in the system macrolibrary ($BRKDEF). The second longword is for customer use to specifyselected bits. If any bit is set in the P1 buffer, that particularrequester ID is turned off for broadcast. Table 5-12 Broadcast Requester IDs | Bit | Meaning | | BRK$C_DCL | Disables broadcasts by Ctrl/T | | BRK$C_GENERAL | Disables broadcasts by the DCL command REPLY and the SYS$BRDCST system service | | BRK$C_MAIL | Disables broadcasts by the Mail utility | | BRK$C_PHONE | Disables broadcasts by the Phone utility | | BRC$C_QUEUE | Disables broadcasts about batch and print queues | | BRK$C_SHUTDOWN | Disables broadcasts about system shutdown | | BRK$C_URGENT | Disables broadcasts labeled URGENT by the REPLY command | | BRK$C_USER n | Disables broadcasts by images associated with the specified value; n can be any decimal integer between 1 and 16 | 5.4.4 LAT Port Driver QIO InterfaceThe LAT port driver (LTDRIVER) accommodates I/O requests fromapplication programs for connections to remote devices on one or moreterminal servers; for connections to remote services; and forconfiguring LTDRIVER and retrieving configuration information aboutLTDRIVER. A remote device, such as a printer, can be shared in a LATconfiguration. Before an application program can access a remotedevice, the system manager must create logical devices and map them tophysical devices connected to terminal servers. Creating and mappingthese logical devices can be done either with the LAT Control Program(LATCP) utility or with a $QIO request from a program that has OPERprivilege. Once mapped, application programs can establish andterminate connections to these remote devices. This section describes the capabilities of the QIO interface to the LATport driver (LTDRIVER). The QIO interface allows application programsto access and modify information contained in the LTDRIVER datastructures and to initiate events and obtain status information. Youmust use these QIO functions to establish a connection to a remotedevice or service from an application program. Compaq does not supportany other methods of connection. The LTDRIVER responds to TEST SERVICE commands issued at terminalservers that support the TEST SERVICE command, such as the DECserver200 and DECserver 500 servers. LAT devices can use all read and write function modifiers listed forthe terminal driver function codes except those modifiers that apply tomodems (see Sections 5.4.1 and 5.4.2). The operating system does not support the following set mode or setcharacteristics function code modifiers for LAT devices: - IO$M_LOOP
- IO$M_UNLOOP
- TT$M_ALTRPAR
- TT$M_ALTFRAME
- TT$M_MODEM
- TT$M_READSYNC
- TT2$M_SETSPEED
With LAT devices, the terminal server, rather than the host, handlesflow control to the physical device. A separate flow control mechanismexists between the server and the host.5.4.4.1 LAT Port Types QIO functions can be used to create the following LAT port types: - Application Port. This type of port can be used to connect to a remote device (typically a printer) on a terminal server or to a dedicated port on another LAT service node. This is the default port type. See Section 5.4.4.5 for a description of programming an application port.
- Dedicated Port. This type of port specifies that the logical port on your node is dedicated to an application service. When users on a terminal server (or on another node that supports outgoing connections) request a connection to this service name, they are connected to a dedicated port. See Section 5.4.4.6 for a description of programming a dedicated port and application service.
- Forward Port. This type of port is used for outgoing LAT connections (to remote services) and is created by assigning a channel to the LAT template device _LTA0: with the $ASSIGN system service.
QIO functions can also be used to configure and read information about these ports; for more information: - See Section 5.4.4.3 for a description of configuring a LAT port
- See Section 5.4.4.4 for a description of reading configuration information about a LAT port
- See Section 5.4.4.7 for a description of programming a forward port in order to make a connection to a LAT service
5.4.4.2 LAT Port Driver FunctionsThe operating system provides the following combinations of functioncode and modifier: - IO$_TTY_PORT!IO$M_LT_CONNECT. Requests that the LAT port driver make a connection to a remote device on a server (or dedicated port on another LAT service node) or to a remote service, depending on whether the port is an application port or a forward port respectively. For dedicated ports, this QIO completes when an incoming connection to the port is established. See Section 5.4.4.5 for a description of programming an application port, Section 5.4.4.6 for a description of programming a dedicated port, and Section 5.4.4.7 for a description of programming a forward port.
- IO$_TTY_PORT!IO$M_LT_DISCON. Depending on the port type, requests that the LAT port driver terminate the LAT connection to the remote device, service, or local application service. IO$M_FLUSH_DATA can be specified in the P2 argument to IO$M_LT_DISCON. The flush flag indicates that any data not delivered to the remote device is to be flushed when the disconnect is issued.
- IO$_TTY_PORT!IO$M_LT_SETMODE. Requests that the LAT port driver create or configure a LAT entity. See Section 5.4.4.3 for more information.
- IO$_TTY_PORT!IO$M_LT_SENSEMODE. Requests that the LAT port driver return configuration information about a LAT entity. See Section 5.4.4.4 for more information.
5.4.4.3 Creating and Configuring LAT EntitiesThe LAT SETMODE $QIO function (IO$_TTY_PORT!IO$M_LT_SETMODE) is used tocreate, delete, and modify LAT nodes, services, ports, and links. Creation, deletion, or modification of any entity requires the OPERprivilege. The LAT SETMODE $QIO function accepts four arguments: P1, P2, P3, andP4. P1 is the address of an item list; P2 is the length of this itemlist. P3 specifies the type of entity to which the SETMODE operation applies.The entity type can be one of five types: - Node (LAT$C_ENT_NODE). Only the local node name may be specified, with the exception of a SETMODE itemlist containing no item codes other than LAT$_ITM_COUNTERS.
- Service (LAT$C_ENT_SERVICE). Only local service names may be specified, with the exception of a SETMODE itemlist containing no item codes other than LAT$_ITM_COUNTERS.
- Link (LAT$C_ENT_LINK). The data link associated with the LAN.
- Port (LAT$C_ENT_PORT).
- Queue Entry (LAT$C_ENT_QUEUE_ENTRY). Indicates queue entry entities. When this entity is used, the only valid SETMODE operation is delete.
The value for the entity type occupies the low-order 16 bits (bits0--15) of the P3 parameter. For all four entity types, bits 16--19 areused as a status field to indicate the expected current status of theentity. These bits are used to decide whether the entity needs to becreated before its characteristics are set. The possible values forthis field are: - LAT$C_ENTS_OLD---The entity must already exist. An SS$_NOSUCHDEV error is returned if the entity does not exist.
- LAT$C_ENTS_NEW---The entity must be created. An SS$_DUPLNAM error is returned if the entity already exists.
- LAT$C_ENTS_UNK---If the entity does not exist, it is created. If it does exist, its characteristics are modified.
- LAT$C_ENTS_DEL---If the entity exists, delete it. Otherwise, an SS$_NOSUCHDEV error is returned and the item list is not used.
P4 may contain the address of an entity name string descriptor. If thisparameter is omitted (contains a 0 or the address of a descriptor thatpoints to an empty buffer), a default may be used in some cases. Thedefaults for each entity type are as follows: - LAT$C_ENT_NODE---The local node.
- LAT$C_ENT_SERVICE---No default; you must specify the service name.
- LAT$C_ENT_LINK---The string LAT$LINK.
- LAT$C_ENT_PORT---The device name associated with the currently assigned channel (the CHAN parameter of the $QIO function).
SETMODE can return the following status codes: - SS$_NOPRIV---No privilege to complete the desired operation.
- SS$_ACCVIO---Part of the argument list or itemlist is not addressable.
- SS$_BADPARAM---One of the parameters in the itemlist is in error. If this value is returned, the second longword of the IOSB contains the item code of the parameter in error.
SETMODE Item Codes
Each item in the itemlist consists of a one-word (16-bit) item code,followed by a value associated with the item. Item codes in which the bit named LAT$V_STRING is zero take a longwordvalue. The associated value is contained in the longword immediatelyfollowing the item code in the itemlist. Item codes in which this bitis 1 take a counted string for their value. The byte immediatelyfollowing the item code contains a byte count, which describes thelength of the string that immediately follows it. If you set bit LAT$V_CLEAR in the item code to 1, the current valueassociated with the item code is cleared or set to its default value.In this case, the actual value specified in the itemlist is ignored,although the byte count field skips to the next item in the itemlist. Figure 5-10 shows an example of a SETMODE itemlist. Figure 5-10 Example SETMODE Itemlist
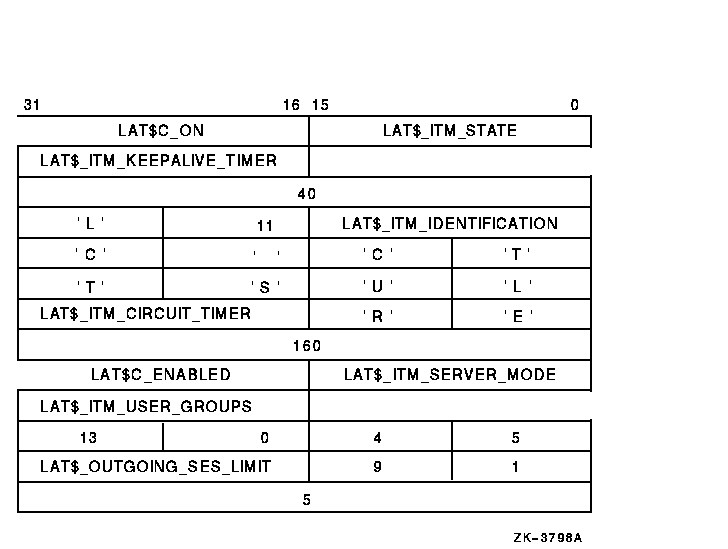 This SETMODE itemlist is the P1 parameter for a $QIO SETMODE functionon the local node. P4 is omitted, and P3 is#LAT$C_ENT_NODE!<LAT$C_ENTS_OLD@16>. P2 is the length of theitemlist (52). A $QIO SETMODE function for this itemlist would performthe following operations: - Set the state of the node to on.
- Set the LAT keepalive timer to 40 seconds.
- Set the node identification to LTC CLUSTER.
- Set the LAT circuit timer to 160 milliseconds.
- Enable LAT outbound connections.
- Turn on user groups 2, 8, 10, 11, 12, 16, and 19. LAT$_ITM_USER_GROUPS is represented by a bit field.
- Set the outgoing session limit to five sessions.
For each entity type, only a subset of item codes may be set.Table 5-13 lists the item codes that may be set for theLAT$C_ENT_NODE entity type. Table 5-13 LAT$C_ENT_NODE Item Codes | Item Code | Meaning | | LAT$_ITM_STATE | Operating state of the LAT protocol. The following values are allowed: | LAT$C_OFF | Turns off LAT protocol processing. No new connections allowed in either direction. Existing connections are terminated immediately. This is the default. | | LAT$C_SHUT | Disallows new LAT connections in either direction. Existing connections are allowed to remain active. | | LAT$C_ON | Turns on LAT protocol processing. | | | LAT$_ITM_CIRCUIT_TIMER | Circuit timer value in milliseconds. Valid values are 10 to 1000 milliseconds. The default is 80 milliseconds. | | LAT$_ITM_CPU_RATING | CPU rating. Valid values are 0 to 100. If this value is 0, then the CPU rating value is not used in the rating calculation. Refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for a complete description of this feature. | | LAT$_ITM_DEVICE_SEED | Overrides the default lower boundary for new LTA devices. Valid values are 0 to 9999; the default is 0. Refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for more information on this feature. | | LAT$_ITM_KEEPALIVE_TIMER | Keepalive timer value in seconds. Valid values are 10 to 255 seconds. The default is 20 seconds. | | LAT$_ITM_MULTICAST_TIMER | Multicast timer value in seconds. Valid values are 10 to 180 seconds. The default is 60 seconds. | | LAT$_ITM_NODE_LIMIT | Maximum number of nodes in LAT database. The default is 0, where the maximum is determined by system resources. | | LAT$_ITM_RETRANSMIT_LIMIT | LAT retransmit limit. Valid values are 4 to 120 retransmissions. The default is 8 retransmissions. | | LAT$_ITM_SERVER_MODE | Controls whether the node allows the use of the MASTER side of the LAT protocol for outbound connections. Valid values are: | LAT$C_DISABLED | Server mode disabled (this is the default). | | LAT$C_ENABLED | Server mode enabled. | | | LAT$_ITM_SERVICE_RESPONDER | Indicates whether the node is to respond to service inquiries originating from a remote system. These inquiries are not necessarily directed at services being offered by the node. Refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for a complete description of this feature. Valid values are: | LAT$C_DISABLED | Service responder disabled (this is the default). | | LAT$C_ENABLED | Service responder enabled. | | | LAT$_ITM_OUTGOING_SES_LIMIT | Maximum number of outgoing LAT sessions. A value of 0, which is the default, indicates that the limit is determined by system resources. | | LAT$_ITM_INCOMING_SES_LIMIT | Maximum number of interactive LAT sessions. A value of 0, which is the default, indicates that the limit is determined by system resources. | | LAT$_ITM_CONNECTIONS | Controls whether inbound connections can be accepted. Valid values are: | LAT$C_DISABLED | Inbound connections disabled. | | LAT$C_ENABLED | Inbound connections enabled (this is the default). | | | LAT$_ITM_NODE_NAME | Causes the LAT node name to be set to the given name. This item code may be specified only if the entity status field of the P3 parameter is LAT$C_ENTS_NEW; otherwise, a LAT$_ENTNOTFOU error results. | | LAT$_ITM_IDENTIFICATION | Node identification string. The default is the translation of SYS$ANNOUNCE. | | LAT$_ITM_SERVICE_GROUPS | Specifies a default service group code bit mask. This mask is then used when creating new local services. The default is group code 0 enabled and all others disabled when the LAT software is initialized. Note that the use of the LAT$V_CLEAR bit is an exception for this parameter code. If you clear bit LAT$V_CLEAR, group codes corresponding to the group code mask, as specified in the itemlist, are set. Alternatively, if you set LAT$V_CLEAR, group codes corresponding to the group code mask, as specified in the itemlist, are cleared. | | LAT$_ITM_USER_GROUPS | LAT group codes to be used when attempting outbound connections using the MASTER side of the LAT protocol. The default is all group codes disabled when the LAT software is initialized. Note that the use of the LAT$V_CLEAR bit is an exception for this parameter code. If you clear bit LAT$V_CLEAR, group codes corresponding to the group code mask, as specified in the itemlist, are set. Alternatively, if you set LAT$V_CLEAR, group codes corresponding to the group code mask, as specified in the itemlist, are cleared. | | LAT$_ITM_COUNTERS | Node counters block. Allows for zeroing of all node counters. This item code may be specified only if the entity status field of the P3 parameter is LAT$C_ENTS_OLD and the LAT$V_CLEAR bit is set. Violating either of these two rules results in a returned status of SS$_BADPARAM. | | LAT$_ITM_MAXIMUM_UNITS | Maximum unit number. Sets the highest value for a LTA unit number. Must be between 1 and 9999; defaults to 9999. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_CIRCUITS | Indicates the highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized for LAT connections to node. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_CIRCUITS | Indicates current count of active connections to node. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_CIRCUITS | Indicates maximum allowed virtual circuits to node. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_SESSIONS | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized for LAT sessions. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_SESSIONS | Indicates current number of active sessions. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_SESSIONS | Indicates maximum possible sessions. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_OUT_QUEUE | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of outgoing queued connect requests. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_OUT_QUEUE | Indicates current count of outgoing queued connect requests. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_OUT_QUEUE | Indicates maximum number of simultaneous outgoing queued connect requests. | | ++ LAT$_TIM_HI_IN_QUEUE | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of incoming queued requests. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_IN_QUEUE | Indicates current number of entries in the incoming connect queue. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_IN_QUEUE | Indicates maximum number of entries allowed on the incoming connect queue. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_SAMS_QUEUED | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of outstanding, unprocessed service announcement messages by LATACP. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_SAMS_QUEUED | Indicates current number of outstanding, unprocessed service announcement messages on LATACP's queue. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_SAMS_QUEUED | Indicates maximum number of outstanding, unprocessed service announcement messages allowed on LATACP's queue. If this limit is ever reached, subsequent service announcement messages are not delivered or processed by LATACP. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_SOL_QUEUED | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of outstanding, unprocessed solicit information messages by LATACP. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_SOL_QUEUED | Indicates current number of outstanding, unprocessed solicit information messages on LATACP's queue. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_SOL_QUEUED | Indicates maximum number of outstanding, unprocessed solicit information messages allowed on LATACP's queue. If this limit is ever reached, subsequent solicit information messages are not delivered or processed by LATACP. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_AVAIL_SVCS | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of number of available services in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_AVAIL_SVCS | Indicates count of currently available LAT services in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_AVAIL_SVCS | Indicates maximum number of available services possible in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_REACH_NODES | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of reachable nodes in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_REACH_NODES | Indicates current number of reachable nodes in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_REACH_NODES | Indicates maximum number of nodes allowed in LATACP database. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_HI_LCL_SVCS | Indicates highest number the resource attained since the host was initialized of locally offered services. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_CUR_LCL_SVCS | Indicates current count of locally offered service. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_MAX_LCL_SVCS | Indicates maximum number of locally offered services. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_DISCARDED_NODES | Indicates number of discarded service announcement messages. | | ++ LAT$_ITM_SERVICE_CLASSES | Indicates returned service class bit mask for supported service classes on node. It is returned for both local and remote nodes. If service class 1 is enabled, then bit <1> is set in this mask. When bit setting equals 1, this indicates the corresponding service class for that bit is enabled. That is, when bit <3> equal 1, then service class 3 is enabled. | | LAT$_ITM_LARGE_BUFFERS | Indicates in Boolean logic whether or not the LAT software is using large packet support by default. | | LAT$_ITM_ANNOUNCEMENTS | Indicates in Boolean logic whether or not the LAT software is transmitting LAT service advertisement messages. |
++Alpha specific.
|

