 |
Guidelines for OpenVMS Cluster Configurations
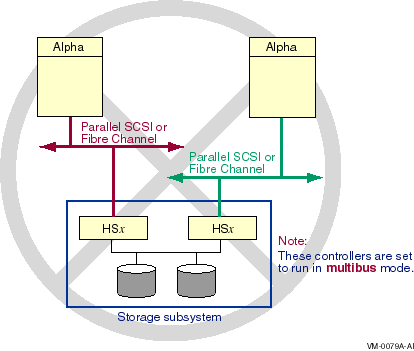
6.7.2 Invalid Multipath Configuration
Figure 6-20 shows an invalid multipath configuration. The
configuration is invalid because, if multiple hosts in a cluster are
connected to an HSZ or HSG, they must all have connections to the same
controller modules (see Table 6-1). In this configuration, each
host is connected to a different controller module.
Figure 6-20 Invalid Multipath Configuration
6.7.3 Multipath System Parameters
Multipath support is enabled and qualified by the use of the system
parameters described in Table 6-3. (Certain multipath system
parameters are reserved for the operating system.)
Table 6-3 Multipath System Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
|
MPDEV_ENABLE
|
Enables the formation of multipath sets when set to ON (1). If set to
OFF (0), the formation of additional multipath sets and the addition of
new paths to existing multipath sets is disabled. However, existing
multipath sets remain in effect. The default is ON.
MPDEV_REMOTE and MPDEV_AFB_INTRVL have no effect when MPDEV_ENABLE
is set to OFF.
|
|
MPDEV_LCRETRIES
|
Controls the number of times the system retries direct paths to the
controller that the logical unit is online to, before moving on to
direct paths to the other controller, or to an MSCP served path to the
device. The valid range for retries is 1 through 256. The default is 1.
|
|
MPDEV_POLLER
|
Enables polling of the paths to multipath set members when set to ON
(1). Polling allows early detection of errors on inactive paths. If a
path becomes unavailable or returns to service, the system manager is
notified with an OPCOM message. If set to OFF (0), multipath polling is
disabled. The default is ON. Note that this parameter must be set to ON
to use the automatic failback feature.
|
|
MPDEV_REMOTE
|
Enables MSCP served paths to become members of a multipath set when set
to ON (1). If set to OFF (0), only local paths to a SCSI or Fibre
Channel device will be used in the formation of additional multipath
sets. However, setting this parameter to OFF will not have any effect
on existing multipath sets that have remote paths. If MPDEV_ENABLE is
OFF (0), the setting of MPDEV_REMOTE has no effect because the addition
of all new paths to multipath sets is disabled. The default is OFF.
|
|
MPDEV_AFB_INTRVL
|
Specifies the automatic failback interval in seconds. The automatic
failback interval is the minimum number of seconds that must elapse
before the system will attempt another failback from an MSCP path to a
direct path on the same device.
MPDEV_POLLER must be ON to enable automatic failback. You can
disable automatic failback without disabling the poller by setting
MPDEV_AFB_INTRVL to 0. The default is 300 seconds.
|
|
MPDEV_D1
|
Reserved for use by the operating system.
|
|
MPDEV_D2
|
Reserved for use by the operating system.
|
|
MPDEV_D3
|
Reserved for use by the operating system.
|
|
MPDEV_D4
|
Reserved for use by the operating system.
|
6.7.4 Path Identifiers
The system management commands described in the following sections
allow you to monitor and control the operation of multipath failover.
These commands provide a path identifier to uniquely specify each path
in a multipath set.
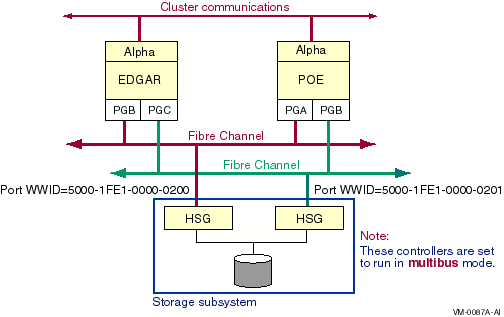
Direct Fibre Channel paths are identified by the local host adapter
name and the remote Fibre Channel port WWID --- that is, the initiator
and the target. For example, in Figure 6-21, the path identifier for
the path from the host adapter on the left to the HSG storage
controller on the left is PGB0.5000-1FE1-0000-0200. (The second port on
each HSG is omitted for convenience.) You can obtain the WWID for a
storage controller from its console.
Figure 6-21 Fibre Channel Path Naming
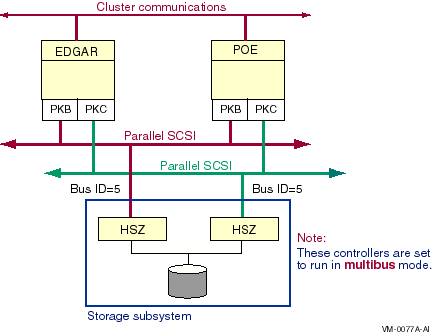
Direct parallel SCSI paths are identified by the local host adapter
name and the remote SCSI bus ID --- that is, the initiator and the
target. For example, in Figure 6-22, the path identifiers for node
Edgar's two direct paths to the disk would be named PKB0.5 and PKC0.5.
The path identifier for MSCP served paths is
MSCP
.
Figure 6-22 Configuration With Multiple Direct Paths
6.7.5 Displaying Paths
When multipath support is enabled, you can display the multiple paths
to a device using either of the following variants of the SHOW DEVICE
DCL command:
SHOW DEVICE/FULL device-name
SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH_SET device-name
|
The SHOW DEVICE/FULL device-name command displays the
traditional information about the device first and then lists all the
paths to a device by their path identifiers (described in
Section 6.7.4).
The SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH_SET device-name command lists only
some brief multipath information about devices that have multiple paths.
Multipath information is displayed only on nodes that are directly
connected to the multipath device.
6.7.5.1 Displaying Paths With SHOW DEVICE/FULL
The following example shows the output of a SHOW DEVICE/FULL
device-name command. Note that the use of multiple paths is
shown at the beginning of the display (
device has multiple I/O paths
), and the multiple path descriptions are shown toward the end of the
display, beneath
I/O paths to device
. Note, too, that the values for
Error count
and
Operations completed
shown at the beginning of the display are the sums of the counts for
each path.
$ SHOW DEVICE/FULL $1$DGA23:
Disk $1$DGA23: (WILD8), device type HSG80, is online, mounted, file-oriented
device, shareable, device has multiple I/O paths, served to cluster via MSCP
Server, error logging is enabled.
Error count 3 Operations completed 32814199
Owner process "" Owner UIC [SYSTEM]
Owner process ID 00000000 Dev Prot S:RWPL,O:RWPL,G:R,W
Reference count 9 Default buffer size 512
WWID 01000010:6000-1FE1-0000-0D10-0009-8090-0677-0034
Total blocks 17769177 Sectors per track 169
Total cylinders 5258 Tracks per cylinder 20
Host name "WILD8" Host type, avail Compaq AlphaServer GS160 6/731, yes
Alternate host name "W8GLX1" Alt. type, avail Compaq AlphaServer GS160 6/731, yes
Allocation class 1
Volume label "S5SH_V72_SSS" Relative volume number 0
Cluster size 18 Transaction count 8
Free blocks 12812004 Maximum files allowed 467609
Extend quantity 5 Mount count 8
Mount status System Cache name "_$1$DGA8:XQPCACHE"
Extent cache size 64 Maximum blocks in extent cache 1281200
File ID cache size 64 Blocks currently in extent cache 0
Quota cache size 0 Maximum buffers in FCP cache 1594
Volume owner UIC [1,1] Vol Prot S:RWCD,O:RWCD,G:RWCD,W:RWCD
Volume Status: ODS-2, subject to mount verification, file high-water marking,
write-back caching enabled.
Volume is also mounted on H2OFRD, FIBRE3, NORLMN, SISKO, BOOLA, FLAM10,
W8GLX1.
I/O paths to device 5
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D12 (WILD8), primary path.
Error count 2 Operations completed 130666
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D13 (WILD8), current path.
Error count 1 Operations completed 30879310
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D11 (WILD8).
Error count 0 Operations completed 130521
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D14 (WILD8).
Error count 0 Operations completed 130539
Path MSCP (W8GLX1).
Error count 0 Operations completed 1543163
|
For each path of the multipath device, the path identifier, the host
name associated with that path, the path status, the error count, and
the operations count are displayed.
The terms that may appear in the multiple paths portion of the display
are described in Table 6-4.
Table 6-4 SHOW DEVICE/FULL Multipath Terms
| Term |
Description |
|
WWID
|
The World Wide ID of the SCSI logical unit.
|
|
Host name
|
The name of the system that is being used by the current path. The host
name is displayed if there is an MSCP path to a multipath device.
|
|
Alternate host name
|
The name of another system that can also provide access to the device.
If the current path is a direct path, this will be the host currently
associated with the MSCP path. If the current path is an MSCP path,
this will be the name of the local system. The altername host name is
displayed if there is an MSCP path to a multipath device.
|
|
Primary path
|
This was the first path to the device found by the operating system.
|
|
Current path
|
This path is currently used for I/O.
|
|
User disabled
|
The DCL command SET DEVICE/NOENABLE has been executed for this path.
|
|
Polling disabled
|
The DCL command SET DEVICE/NOPOLL has been executed for this path.
|
|
Unavailable
|
The path is unavailable because the software driver has disconnected
from the path.
|
6.7.5.2 Displaying Paths With SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH_SET
You can obtain a brief listing of multiple paths for a specific device,
for all the devices in an allocation class, or for all devices with the
DCL command:
SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH_SET [device-name]
|
The device name is optional; when omitted, all devices that have formed
multipath sets are shown. For each multipath device found, the device
name, host name, device status, error count, number of accessible
paths, total number of paths, and the current path's path identifier
are displayed.
The host name displayed is the host name of the current path. For
direct paths, this will be the local system's host name. For MSCP
served paths, this will be the host name of the remote system which is
serving access to the device.
The following example shows the output of a SHOW DEVICE /MULTIPATH
command.
$ SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH
Device Device Error Paths Current
Name Status Count Avl/Tot path
$1$DGA8: (H2OFRD) Mounted 3 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D12
$1$DGA10: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 1 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D14
$1$DGA11: (WILD8) ShadowSetMember 3 3/ 3 MSCP
$1$DGA23: (H2OFRD) Mounted 6 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D13
$1$DGA30: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 8 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D13
$1$DGA31: (WILD8) ShadowMergeMbr 5 3/ 3 MSCP
$1$DGA33: (H2OFRD) Online 0 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D12
$1$DGA40: (H2OFRD) Mounted 2 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D13
$1$DGA41: (H2OFRD) ShadowMergeMbr 8 5/ 5 PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D12
$70$DKA100: (H2OFRD) Mounted 0 3/ 3 PKD0.1
$70$DKA104: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.1
$70$DKA200: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.2
$70$DKA300: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKC0.3
$80$DKA1104: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.11
$80$DKA1200: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.12
$80$DKA1204: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKC0.12
$80$DKA1207: (H2OFRD) Mounted 0 3/ 3 PKD0.12
$80$DKA1300: (H2OFRD) Mounted 0 3/ 3 PKD0.13
$80$DKA1307: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.13
$80$DKA1500: (H2OFRD) Mounted 0 3/ 3 PKD0.15
$80$DKA1502: (H2OFRD) ShadowSetMember 0 3/ 3 PKD0.15
|
If you choose to specify a partial device name, such as $70$DKA, the
display shows all devices with multiple paths whose names begin with
$70$DKA.
6.7.6 Path Polling
When SCSI multipath support is in effect, the system periodically polls
all the I/O paths from each host adapter to each HSZ or HSG controller
to determine the status of each I/O path. If the system detects any
changes to a path, it outputs a message, similar to the following
messages, to the console and to the operator's log:
All multipath devices on path PKB0.5 are either disabled or not reachable.
|
or
At least one multipath device on path PKB0.5 is enabled and reachable.
|
If all the devices on a path are removed, a path failure is reported.
The path from the host to the HSx controller may still
function, but this cannot be determined when there are no devices to
poll.
You can turn polling on or off with the following command:
SET DEVICE device/[NO]POLL/PATH=path-identifier
|
Turning off polling for a path that will be out of service for a
prolonged period is useful because it can reduce system overhead.
6.7.7 Switching Current Paths Manually
You can switch a device's current path manually using the SET DEVICE
command with the /SWITCH qualifier. The most common reason for doing
this is to balance the aggregate I/O load across multiple HSx
controller modules and buses.
The command syntax for switching the current path is:
SET DEVICE device-name/SWITCH/PATH=path-identifier
|
The following command switches the path of device $2$DKA502 to an MSCP
served path.
$ SET DEVICE $2$DKA502/SWITCH/PATH=MSCP
|
Note that this command initiates the process of switching the path and
then returns to the DCL prompt immediately. A delay may occur between
when the DCL prompt reappears and when the path switch is complete.
A manual path switch of a mounted device takes place within mount
verification, which is triggered by the path switch command. It is
accompanied by the usual mount verification messages and a path switch
message. This is shown in Example 6-1:
| Example 6-1 Messages Resulting from Manual
Path Switch |
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:23.05 %%%%%%%%%%%
Device $1$DGA23: (H2OFRD PGA) is offline.
Mount verification is in progress.
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:25.76 %%%%%%%%%%%
09:04:25.76 Multipath access to device $1$DGA23: has been manually switched
from path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D11 to path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D14
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:25.79 %%%%%%%%%%%
Mount verification has completed for device $1$DGA23: (H2OFRD PGA)
|
You can check for completion of a path switch by issuing the SHOW
DEVICE/FULL command, or the SHOW DEVICE/MULTIPATH command.
Note that if the path that is designated in a manual path switch fails
during the switch operation, then automatic path switching takes over.
This can result in a switch to a path different from the one designated
in the command.
If a manual path switch causes a logical unit to switch from one HSG80
controller to another controller, then the command can affect other
nodes in the cluster. These nodes will experience a mount verification
on their current path. This will cause an automatic switch to a path on
the other HSG80 controller. The messages indicating this event are
shown in Example 6-2:
| Example 6-2 Messages Displayed When Other
Nodes Detect a Path Switch |
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:26.48 %%%%%%%%%%%
Device $1$DGA23: (WILD8 PGA) is offline.
Mount verification is in progress.
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:26.91 %%%%%%%%%%%
09:04:29.91 Multipath access to device $1$DGA23: has been auto switched from
path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D12 to path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D13
%%%%%%%%%%% OPCOM 15-JUN-2001 09:04:27.12 %%%%%%%%%%%
Mount verification has completed for device $1$DGA23: (WILD8 PGA)
|
6.7.8 Path Selection by OpenVMS
In a multipath configuration, the first path to a device that OpenVMS
configures is the initial current path to the device by default.
However, the current path can change as a result of a MOUNT command to
a multipath device. The I/O performed by the MOUNT command triggers a
search for a direct path that does not require the device to failover
from one HSx controller module to another. This has the following
benefits:
- Minimizes the disruption on other hosts
- Tends to preserve any static load balancing that has been manually
set up
- Enables the use of HSx console commands to set up an initial
default distribution of devices between the two HSx controllers
- Prefers direct paths over MSCP served paths
The MOUNT-time path selection proceeds as follows:
- If the current path is a direct path and access to the device on
this path does not require a controller failover, the current path is
used.
- If the current path is an MSCP path and it was selected by a manual
path switch command, the current path is used.
- All direct paths are checked. If a path is found where access to
the device does not require a controller failover, that path is
selected. If the selected path is not the current path, an automatic
path switch is performed and an OPCOM message is issued.
- All direct paths are tried. If necessary, an attempt is made to
failover the device to the HSx controller on the selected path.
- The MSCP served path is tried.
The MOUNT utility might trigger this path selection algorithm a number
of times until a working path is found. The exact number of retries
depends on the elapsed time for the prior attempts and the qualifiers
specified with the MOUNT command.
Note that this selection process allows devices to be distributed
between the two HSx controllers. You can accomplish this by using HSx
console commands such as the following:
HSG> SET UNIT PREFERRED_PATH=THIS_CONTROLLER
HSG> SET UNIT PREFERRED_PATH=OTHER_CONTROLLER
|
In addition, you can use the manual path switching DCL commands,
described in Section 6.7.7, to select a different host bus adapter, a
different port on the same HSx controller, or to force the device to
failover to a different HSx controller.
6.7.9 How OpenVMS Performs Multipath Failover
When an I/O operation fails on a mounted device and the failure status
suggests that retries are warranted, mount verification is invoked. If
the device is a multipath device, alternate paths to the device are
tried during mount verification. This allows the system to
transparently recover from cases where the device has failed over from
one HSx controller to another and to transparently recover from
failures in the path to the device. The path selection during mount
verification proceeds as follows:
- If the current path is a direct path and access to the device on
this path does not require a controller failover, the current path is
tried.
- If the current path is an MSCP path and it was selected by a manual
path switch command, the current path is tried.
- All direct paths that do not require a controller failover are
tried.
- Step 3 is repeated the number of times specified by the
MPDEV_LCRETRIES system parameter. This provides additional bias towards
selection of a path that does not require an HSx controller failover.
The default value for MPDEV_LCRETRIES is 1.
- All direct paths are tried.
- If present, the MSCP served path is tried.
Steps 1 through 6 are repeated until either a working path is found or
mount verification times out. If a working path is found and the path
is different, the current path is automatically switched to the new
path and an OPCOM message is issued. Mount verification then completes,
the failed I/O is restarted, and new I/O is allowed to proceed. This
path selection procedure attempts to avoid unnecessary failover of
devices from one HSx controller to another because:
- Failover from one HSx controller module to another causes a delay
of approximately 1 to 15 seconds, depending on the amount of cached
data that needs to be synchronized.
- Other nodes that share access to the device must reestablish
communication using an alternate path.
This path selection procedure prefers direct paths over MSCP served
paths because the use of an MSCP served path imposes additional CPU and
I/O overhead on the server system. In contrast, the use of a direct
path imposes no additional CPU or I/O overhead on the MSCP-server
system. This procedure selects an MSCP served path only if none of the
available direct paths are working.
|


