 |
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
SNMP Programming and Reference
Order Number:
AA--R04BC--TE
January 2001
Revision/Update Information:
This manual supersedes the DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
eSNMP Programming and Reference, Version 5.0.
Software Version:
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Version 5.1
Operating Systems:
OpenVMS Alpha Versions 7.1, 7.2-1 OpenVMS VAX Versions 7.1, 7.2
Compaq Computer Corporation Houston, Texas
© 2001 Compaq Computer Corporation
COMPAQ, VAX, VMS, and the Compaq logo Registered in U.S. Patent and
Trademark Office.
OpenVMS and Tru64 are trademarks of Compaq Information Technologies
Group, L.P. in the United States and other countries.
All other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their
respective companies.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Compaq required for
possession, use, or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212,
Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and
Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government
under vendor's standard commercial license.
Compaq shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein. The information in this document is
provided "as is" without warranty of any kind and is subject to change
without notice. The warranties for Compaq products are set forth in the
express limited warranty statements accompanying such products. Nothing
herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
ZK6530
This document is available on CD-ROM.
Preface
The Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS product is the Compaq implementation of the TCP/IP
networking protocol suite and internet services for OpenVMS Alpha and
OpenVMS VAX systems.
A layered software product, TCP/IP Services provides a comprehensive suite
of functions and applications that support industry-standard protocols
for heterogeneous network communications and resource sharing.
This manual describes the features of the Simple Network Managment
Protocol (SNMP) provided with TCP/IP Services. It also describes the
extensible SNMP (eSNMP) application programming interface (API) and
development environment.
See the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Installation and Configuration manual for information about installing,
configuring, and starting this product.
Intended Audience
This manual is for experienced OpenVMS and UNIX system managers and
assumes a working knowledge of TCP/IP networking, TCP/IP terminology,
and some familiarity with the TCP/IP Services product.
Document Structure
This manual contains the following chapters:
- Chapter 1 describes the implementation of eSNMP provided with
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS.
- Chapter 2 describes the groups and objects implemented with the
Host Resources MIB and MIB II that are provided with the eSNMP software.
- Chapter 3 describes how to use the eSNMP API to create a MIB
subagent to manage entities or applications.
- Chapter 4 describes the trap sender, trap receiver, and MIB
browser utilities provided with TCP/IP Services.
- Chapter 5 provides reference information about the eSNMP API
routines.
- Chapter 6 describes some troubleshooting aids provided with
TCP/IP Services.
Related Documents
Table 1 lists the documents available with this version of
TCP/IP Services.
Table 1 TCP/IP Services Documentation
| Manual |
Contents |
|
DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Concepts and Planning
|
This manual provides conceptual information about networking and the
TCP/IP protocol including a description of the Compaq implementation of
the Berkeley Internet Name Domain (BIND) service and the Network File
System (NFS). It outlines general planning issues to consider before
configuring your system to use the TCP/IP Services software.
This manual also describes the manuals in the documentation set,
provides a glossary of terms and acronyms for the TCP/IP Services software
product, and documents how to contact the InterNIC Registration Service
to register domains and access Request for Comments (RFCs).
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Release Notes
|
This text file describes new features and changes to the software
including installation, upgrade, configuration, and compatibility
information. These notes also describe new and existing software
problems and restrictions, and software and documentation corrections.
Print this text file at the beginning of the installation procedure
and read it before you install TCP/IP Services.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Installation and Configuration
|
This manual explains how to install and configure the TCP/IP Services
layered application product.
|
|
DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS User's Guide
|
This manual describes how to use the applications available with
TCP/IP Services such as remote file operations, email, TELNET, TN3270, and
network printing. This manual explains how to use these services to
communicate with systems on private internets or on the worldwide
Internet.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management
|
This manual describes how to configure and manage the TCP/IP Services
product.
Use this manual with the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management Command Reference manual.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management Command Reference
|
This manual describes the TCP/IP Services management commands.
Use this manual with the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management manual.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management Commands Quick Reference Card
|
This reference card lists the TCP/IP management commands by component
and describes the purpose of each command.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS UNIX Commands Quick Reference Card
|
This reference card contains inforomation about commonly performed
network management tasks and their corresponding TCP/IP management and
Compaq Tru64 UNIX command formats.
|
|
DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS ONC RPC Programming
|
This manual presents an overview of high-level programming using open
network computing remote procedure calls (ONC RPC). This manual also
describes the RPC programming interface and how to use the RPCGEN
protocol compiler to create applications.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Sockets API and System Services Programming
|
This manual describes how to use the Sockets API and OpenVMS system
services to develop network applications.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS SNMP Programming and Reference
|
This manual describes the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and
the SNMP application programming interface (eSNMP). It describes the
subagents provided with TCP/IP Services, utilities provided for
managing subagents, and how to build your own subagents.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Tuning and Troubleshooting
|
This manual provides information about how to isolate the causes of
network problems and how to tune the TCP/IP Services software for the best
performance.
|
|
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Guide to IPv6
|
This manual describes the IPv6 environment, the roles of systems in
this environment, the types and function of the different IPv6
addresses, and how to configure TCP/IP Services to access the 6bone
network.
|
For additional information about Compaq OpenVMS products and
services, access the Compaq website at the following location:
http://www.openvms.compaq.com/
|
For a comprehensive overview of the TCP/IP protocol suite. you might
find the book Internetworking with TCP/IP: Principles, Protocols,
and Architecture, by Douglas Comer, useful.
Reader's Comments
Compaq welcomes your comments on this manual. Please send comments to
either of the following addresses:
|
Internet
|
openvmsdoc@compaq.com
|
|
Mail
|
Compaq Computer Corporation
OSSG Documentation Group, ZKO3-4/U08
110 Spit Brook Rd.
Nashua, NH 03062-2698
|
How to Order Additional Documentation
Visit the following World Wide Web address for information about how to
order additional documentation:
http://www.openvms.compaq.com/
|
If you need help deciding which documentation best meets your needs,
call 800-282-6672.
Conventions
The name TCP/IP Services means both:
- Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Alpha
- Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS VAX
The name UNIX refers to the Compaq Tru64 UNIX operating system.
The following conventions are used in this manual. In addition, please
note that all IP addresses are fictitious.
|
Ctrl/
x
|
A sequence such as Ctrl/
x indicates that you must hold down the key labeled Ctrl while
you press another key or a pointing device button.
|
|
PF1
x
|
A sequence such as PF1
x indicates that you must first press and release the key
labeled PF1 and then press and release another key or a pointing device
button.
|
|
[Return]
|
In examples, a key name enclosed in a box indicates that you press a
key on the keyboard. (In text, a key name is not enclosed in a box.)
In the HTML version of this document, this convention appears as
brackets, rather than a box.
|
|
...
|
A horizontal ellipsis in examples indicates one of the following
possibilities:
- Additional optional arguments in a statement have been omitted.
- The preceding item or items can be repeated one or more times.
- Additional parameters, values, or other information can be entered.
|
.
.
.
|
A vertical ellipsis indicates the omission of items from a code example
or command format; the items are omitted because they are not important
to the topic being discussed.
|
|
( )
|
In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate that you must
enclose choices in parentheses if you specify more than one.
|
|
[ ]
|
In command format descriptions, brackets indicate optional choices. You
can choose one or more items or no items. Do not type the brackets on
the command line. However, you must include the brackets in the syntax
for OpenVMS directory specifications and for a substring specification
in an assignment statement.
|
|
|
|
In command format descriptions, vertical bars separate choices within
brackets or braces. Within brackets, the choices are optional; within
braces, at least one choice is required. Do not type the vertical bars
on the command line.
|
|
{ }
|
In command format descriptions, braces indicate required choices; you
must choose at least one of the items listed. Do not type the braces on
the command line.
|
|
bold text
|
This typeface represents the introduction of a new term. It also
represents the name of an argument, an attribute, or a reason.
|
|
italic text
|
Italic text indicates important information, complete titles of
manuals, or variables. Variables include information that varies in
system output (Internal error
number), in command lines (/PRODUCER=
name), and in command parameters in text (where
dd represents the predefined code for the device type).
|
|
UPPERCASE TEXT
|
Uppercase text indicates a command, the name of a routine, the name of
a file, or the abbreviation for a system privilege.
|
|
Monospace text
|
Monospace type indicates code examples and interactive screen displays.
This typeface indicates UNIX system output or user input, commands,
options, files, directories, utilities, hosts, and users.
In the C programming language, this typeface identifies the
following elements: keywords, the names of independently compiled
external functions and files, syntax summaries, and references to
variables or identifiers introduced in an example.
|
|
-
|
A hyphen at the end of a command format description, command line, or
code line indicates that the command or statement continues on the
following line.
|
|
numbers
|
All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless otherwise noted.
Nondecimal radixes---binary, octal, or hexadecimal---are explicitly
indicated.
|
Chapter 1
Overview
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the de facto industry
standard for managing TCP/IP networks. The protocol defines the role of
a network management station (NMS) and the SNMP agent. SNMP allows
remote users on an NMS to monitor and manage network entities such as
hosts, routers, X terminals, and terminal servers.
TCP/IP Services provides support for SNMP Version 2, using the
Extensible Simple Network Management Protocol (eSNMP) architecture,
under which a single master agent can support any number of subagents.
The TCP/IP Services implementation of eSNMP includes a master agent,
two subagents, an application programming interface (API), tools used
to build additional subagents, startup and shutdown procedures, and
text-based configuration files.
This chapter provides an overview of the Compaq implementation of
eSNMP. Topics include:
- eSNMP master agent and subagent architecture ( Section 1.1)
- The procedure for handling SNMP requests ( Section 1.2)
- The components of the TCP/IP Services software kit that implement
SNMP ( Section 1.3)
- The files useful in developing your own subagent ( Section 1.4)
- The eSNMP API ( Section 1.5)
- The management information base (MIB) compiler ( Section 1.6)
- The impact of running SNMP Version 1 subagents against the SNMP
Version 2 implementation provided with TCP/IP Services ( Section 1.7)
- Sources of additional information about implementing subagents
( Section 1.8)
1.1 SNMP Architecture
Figure 1-1 illustrates the SNMP architecture.
Figure 1-1 SNMP Architecture
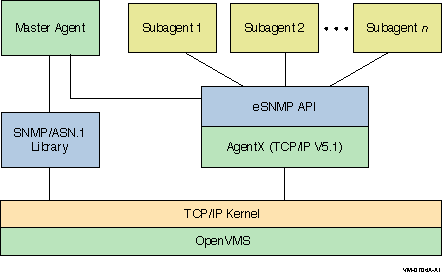
The SNMP environment consists of the following elements:
- The master agent, a process that runs on the host and handles SNMP
requests from clients over the standard SNMP well-known port 161.
- One or more subagents, each of which provides access to the MIB
data specified in client requests. In the TCP/IP Services implementation,
the master agent contains two resident subagents, one that handles a
subset of MIB II variables, and another that handles the Host Resources
MIB. These MIBs are described in Chapter 2.
- The SNMP ASN.1 library, used by the master agent to interpret ASN.1
messages.
- The eSNMP API, the application programming interface that provides
routines for programming your own subagents. This API runs on the
AgentX routines, which are internal to the SNMP architecture.
- The TCP/IP kernel running on the OpenVMS operating system.
The
master agent and subagents communicate by means of the AgentX protocol,
which is based on RFC 2741.
For information about configuring and managing the SNMP service, refer
to the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Management guide.
1.2 Request Handling
The eSNMP software manages network communication by having the master
agent listen for requests and then passes the requests to the
appropriate subagent.
Figure 1-2 illustrates communication between the master agent and
subagents.
Figure 1-2 eSNMP Data Flow
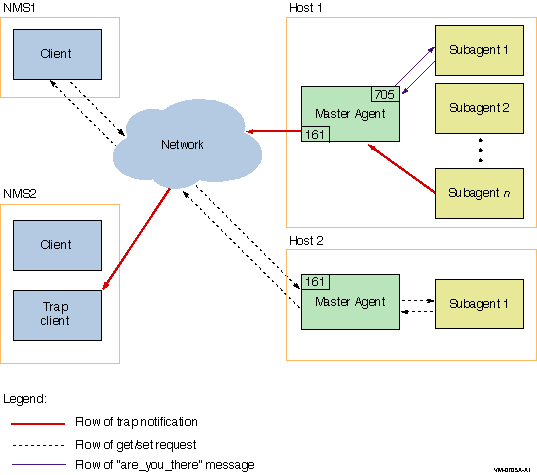
The process of communication for a request is illustrated with dashed
lines and includes the following steps:
- The network management station (NMS) (sometimes called the client),
originates SNMP requests to obtain and set information.
Note
The client component is not provided with TCP/IP Services.
To provide access to MIBs and to test SNMP communication, TCP/IP Services
provides the following utilities:
- MIB browser
- Trap sender
- Trap receiver
These utilities are described in Chapter 4.
|
The network management station sends an SNMP request to the master
agent running on the host, using port 161. An SNMP request is made
using one of the following commands:
Note
TCP/IP Services does not support the standard SNMP
Inform
command.
|
The request specifies the object identifer (OID) of the data to be
accessed. For information about formatting
get
and
set
requests, refer to Section 5.2. Request formats are specified in RFC
1905.
- The master agent sends the request to the subagent that registered
the subtree containing the OID.
The subagent receives
communications from the master agent over the socket that was assigned
when the subagent registered the subtree.
- The appropriate subagent processes the request.
- The subagent sends the response message to the master agent using
the port that was assigned when the subagent registered the MIB.
When they are idle, subagents periodically send a message to port 705
to ensure that the master agent is still running. In Figure 1-2,
subagent 1 is sending the
esnmp_are_you_there
message.
A
trap
is generated by the subagent and sent to the client. In Figure 1-2,
subagent n is generating a trap for the trap client on NMS 2.
The
trap
and
esnmp_are_you_there
routines are described in Section 5.1.
1.3 TCP/IP Services Components for SNMP
Table 1-1 lists the components of SNMP and the command procedures
for managing SNMP that are supplied with TCP/IP Services.
Table 1-1 SNMP Component Files
| File |
Location |
Function |
|
TCPIP$ESNMP_SERVER.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
Master agent image.
|
|
TCPIP$OS_MIBS.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
MIB II subagent image.
|
|
TCPIP$HR_MIB.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
Host Resources MIB subagent image.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_REQUEST.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
Simple MIB browser.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_TRAPSND.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
Utility for sending trap messages.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_TRAPRCV.EXE
|
SYS$SYSTEM
|
Utility for receiving trap messages.
|
|
TCPIP$ESNMP_SHR.EXE
|
SYS$SHARE
|
Image file containing eSNMP application programming interface (API)
routines.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_STARTUP.COM
|
SYS$STARTUP
|
Command procedure that installs master and subagent images and runs
TCPIP$SNMP_RUN.COM.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_SYSTARTUP.COM
|
SYS$STARTUP
|
Command procedure initiated by TCPIP$SNMP_STARTUP.COM. Provided for
site-specific customizations, such as parameter settings.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_RUN.COM
|
TCPIP$SYSTEM
|
Command procedure that starts the master agent and subagents.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_SHUTDOWN.COM
|
SYS$STARTUP
|
Command procedure that stops the master agent and subagents.
|
|
TCPIP$SNMP_SYSHUTDOWN.COM
|
SYS$STARTUP
|
Command procedure initiated by TCPIP$SNMP_SHUTDOWN.COM. Provided for
site-specific customization, such as parameter settings.
|
|
TCPIP$EXTENSION_MIB_STARTUP.COM
|
SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]
|
|
|
|
|
Command procedure invoked by TCPIP$SNMP_SYSTARTUP.COM to start custom
subagents.
|
|
TCPIP$EXTENSION_MIB_SHUTDOWN.COM
|
SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]
|
|
|
|
|
Command procedure invoked by TCPIP$SNMP_SYSHUTDOWN.COM to stop custom
subagents.
|
|
TCPIP$EXTENSION_MIB_RUN.COM
|
SYS$SYSDEVICE:[TCPIP$SNMP]
|
|
|
|
|
Command procedure invoked by TCPIP$SNMP_SYSTARTUP.COM when the service
is enabled and starts detached processes to run subagents.
|
|