HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
OpenVMS Version 7.3 Release Notes
Chapter 7
|
SYSMAN> IO SET/EXCLUDE=(device_name) SYSMAN> IO AUTOCONFIGURE/EXCLUDE=(device_name) and/or /SELECT=(device_name) |
These commands cannot be used selectively to autoconfigure SCSI device names that include a port allocation class or device names that have an HSZ allocation class. The commands also cannot be used for Fibre Channel devices. This restriction applies to class-driver devices only (DK, MK, DG). Selective autoconfiguration can be used for all SCSI and Fibre Channel port-driver devices (PK, PG, and FG).
This restriction also applies to OpenVMS Version 7.1 systems that use
port allocation classes.
7.4 Changes to the IO$_DIAGNOSE Function
The following sections contain IO$_DIAGNOSE changes.
7.4.1 Change to S2DGB$L_32PHSTMO and S2DGB$L_64PHSTMO
V7.3
The legal values for S2DGB$L_32PHSTMO and S2DGB$L_64PHSTMO are now 0 to
65,535 [about 18 hours]. Previously the values were 0 to 300 [5
minutes].
7.4.2 IO$_DIAGNOSE Behavior Changes
V7.3
Appendix B of the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for Version 7.2 formerly stated that the following values are ignored when S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ is 1:
S2DGV$L_32PHSTMO
S2DGV$L_64PHSTMO
S2DGV$L_32DSCTMO
S2DGV$L_64DSCTMO
S2DGB$L_DISCPRIV
Although not documented at the time, the PAD counts, S2DGV$L_32PADCNT and S2DGV$L_64PADCNT were included in this group.
The implementation inadvertently conditionalized on the port's ability to handle command queuing instead of S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ.
The code has now been changed to conditionalize on S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ. The PAD counts are still included in this group.
The documentation also stated that ports that do not support tagged command queuing always behave as if S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ is 0. This applies to the tagged queuing behavior of the ports. S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ still controls whether the parameters previously mentioned are ignored, even on ports that do not support tagged command queuing.
The reason these values are ignored when tagged command queuing is in use is that they can affect other commands to the logical unit until the IO$_DIAGNOSE command completes. (The timeout values are used as defaults for all commands to the logical unit for the duration of the command.)
The OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for Version 7.3 has been updated to reflect these
changes and corrections.
7.5 Changed Behavior of IO$_SKIPFILE Function
V7.2
The performance of the IO$_SKIPFILE function was significantly improved in OpenVMS Version 7.1 for certain SCSI tape drives. The new IO$_SKIPFILE implementation functions correctly with all built-in OpenVMS tape functions such as INIT, MOUNT, BACKUP, and COPY when tapes are formatted according to the ANSI Standard X3.27-1987. This is the default tape standard for OpenVMS.
Higher performance for the IO$_SKIPFILE function is requested with the modifier (IO$M_ALLOWFAST). When the IO$M_ALLOWFAST modifier is used, IO$_SKIPFILE stops at the end of data rather than at double filemarks. For more information about the IO$M_ALLOWFAST modifier, refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
In OpenVMS Version 7.2, SKIPFILE support is implemented through a
standard DCL interface, making the old SYS$ETC:MKSET.TXT and
SYS$ETC:MKSET.EXE files obsolete. Refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for
details about using the DCL interface.
7.6 CRCTX Routines Enhanced (Alpha Only)
V7.1-2
The system routines that you can use to manage the Counted Resource Context Block (CRCTX) data structure have been improved. The following routines now set and check the status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID) of the CRCTX data structure:
These routines have changed as follows:
If you call IOC$DEALLOC_CRCTX with a valid CRCTX status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 1), the service returns a bad status. If the SYSBOOT parameter SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. This prevents users from deallocating a CRCTX when they have valid resources that have not been deallocated.
You must call IOC$ALLOC_CNT_RES with an invalid CRCTX status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 0). If you call this routine with a valid status, OpenVMS assumes that you will lose the resources mapped by this CRCTX. OpenVMS does not allocate new resources and returns a bad status. If SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. IOC$ALLOC_CNT_RES sets the valid bit before it returns.
IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES must be called with a valid CRCTX (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 1). If you call IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES with an invalid CRCTX, OpenVMS assumes that the other parameters are not valid, and returns a bad status. If SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES clears the valid bit before it returns.
IOC$LOAD_MAP must be called with a valid CRCTX. If it is called with an invalid CRCTX (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 0), it assumes that the other parameters are also invalid, and returns a bad status. If the SYSBOOT parameter SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash.
These improvements indicate to device support and privileged-code
application developers whether they need to deallocate scatter gather
registers, which are treated by OpenVMS as generic resources. If the
CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID bit is set, IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES still needs to be
called.
7.7 Device Driver MON Version Handling (Alpha Only)
V7.3
As of OpenVMS V7.3, when SYSTEM_CHECK is enabled, device driver images
with names of the form SYS$nnDRIVER_MON.EXE will be automatically
loaded by the system loader. If a corresponding _MON version does not
exist, the system will use the default image name: SYS$nnDRIVER.EXE.
7.8 New Values for Length Parameter in System Routines (Alpha Only)
V7.1-2
The following system routines called by OpenVMS Alpha device drivers have new values for the length parameter:
IOC$READ_PCI_CONFIG
IOC$WRITE_PCI_CONFIG
IOC$READ_IO
IOC$WRITE_IO
The two new length values (IOC$K_BYTE and IOC$K_WORD) allow byte and word data to be passed in right-aligned fashion. Table 7-1 shows the accepted values for the length parameter.
| Value (hex) | Keyword |
|---|---|
| 1 | IOC$K_BYTE_LANED |
| 2 | IOC$K_WORD_LANED |
| 4 | IOC$K_LONGWORD |
| 8 | IOC$K_QUADWORD |
| 100 | IOC$K_BYTE |
| 200 | IOC$K_WORD |
IOC$K_BYTE_LANED and IOC$K_WORD_LANED lane bytes in the following way:
IOC$K_BYTE_LANED (1) Byte-Laned Byte
Depending on bits <1:0> of the address, the byte resides in a longword in one of the following lanes:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | | X | bits <1:0> = 0 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | | X | | bits <1:0> = 1 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | X | | | bits <1:0> = 2 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | X | | | | bits <1:0> = 3 +---+---+---+---+ |
The driver must use the low 2 bits of the address to select the correct byte.
IOC$K_WORD_LANED (2) Byte-Laned Word
Depending on bits <1:0> of the address, the word resides in a longword in one of the following locations.
+---+---+---+---+ | | | XXXXX | bits <1:0> = 0 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | XXXXX | | bits <1:0> = 1 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | XXXXX | | | bits <1:0> = 2 +---+---+---+---+ |
The driver must use the low 2 bits of the address to select the correct word.
However, if IOC$K_BYTE and IOC$K_WORD are used, the data is always right-aligned:
IOC$K_BYTE (hex 100) Right-Aligned Byte
The byte is always in the right-most lane:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | | X | bits <1:0> = 0,1,2,3 +---+---+---+---+ |
Note that the high-order byte contains unpredictable data and must be masked to operate correctly.
IOC$K_WORD (hex 200) Right-Aligned Word
The word is always in the right-most lane:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | XXXXX | bits <1:0> = 0,1,2 +---+---+---+---+ |
Note that the high-order word contains unpredictable data and must be masked to operate correctly.
By using the new values for the length parameter, programmers who write
device drivers no longer have to put data into the correct lanes before
writes and after reads.
7.9 ISA_CONFIG.DAT Unsupported in Future Release (Alpha Only)
V7.1
Support for using the SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT file to configure ISA
devices will be discontinued in a future release of OpenVMS Alpha. If
you use this file, you should convert both to using the ISACFG utility
from the console and to using the new file-based autoconfiguration
method for loading device drivers (as described in OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 1: Essentials).
7.10 Required Change in ISA_CONFIG.DAT on AlphaStation 200/400
V7.1
Customers configuring ISA devices on AlphaStation 200/400 Family systems must change their SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT file, so that the node information for each device appears at the end of each device description block.
For upgrades from OpenVMS Version 6.2 or 7.0 systems, this change must be made before starting the upgrade procedure. |
The following table shows the changes to the device description block.
| Before Version 7.1 | After Version 7.1 |
|---|---|
| [AUA0] | [AUA0] |
| NAME=AU | NAME=AU |
| NODE=3 | DRIVE=SYS$MSBDRIVER |
| DRIVER=SYS$MSBDRIVER | IRQ=9 |
| IRQ=9 | DMA=(0,1) |
| DMA=(0,1) | PORT=(388:4,530:8) |
| PORT=(388:4.530:8) | NODE=3 |
Customers using SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT files should read
Section 7.9.
7.11 Memory Holes on AlphaServer 4100 Systems
V7.1
Physical memory holes may exist on AlphaServer 4100 systems. As illustrated in Figure 7-1, there are three different sizes of memory daughter card pairs: 512 MB, 256 MB, and 128 MB. In accordance with AlphaServer 4100 systems configuration rules, memory card pairs must be arranged in descending order of size.
The AlphaServer 4100 hardware reads the first set of memory daughter cards and assumes that any memory card pairs that follow are the same size. Memory holes occur because memory card pairs following the first set of cards read by the hardware may not be the same size. As shown in Figure 7-1, the hole at 3000.0000 must be dealt with by OpenVMS. The hole at 4800.0000 is at the top of the address space and can be ignored by OpenVMS.
Previous versions of OpenVMS Alpha did not efficiently support systems with physical memory holes and ultimately led to an inefficient use of system memory. The memory management data structures in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and later have been slightly modified to recognize the memory holes. As a result, inefficiencies in previous versions of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system have been eliminated. |
Figure 7-1 Example Memory Diagram
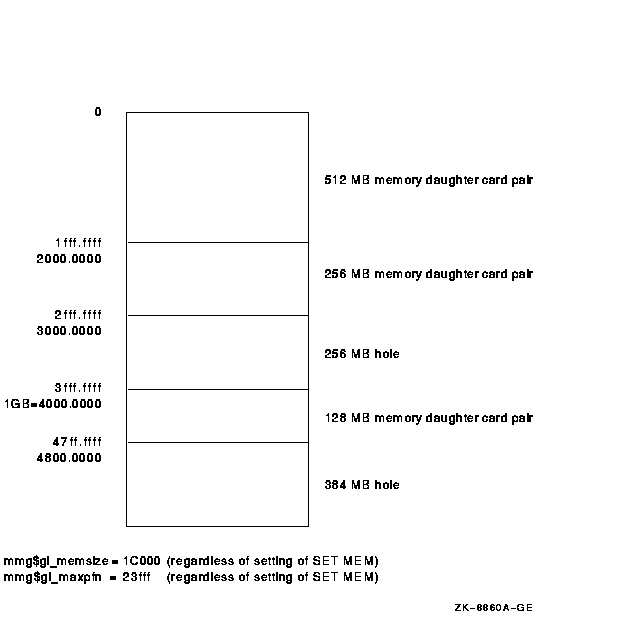
Note that this configuration impacts the algorithm used to determine whether a driver needs to use map registers. In releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, device drivers do the following:
The mmg$gl_memsize global cell does not contain the memory hole. As a result, the system has only 7/8 GB of memory, but according to the algorithm in releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, it appears that the device can use the direct DMA window. Yet there is 128 MB of memory beyond the 1 GB border, which requires that the drivers use map registers. To eliminate this problem, drivers using the algorithm in releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 must substitute it with the following algorithm:
int dma_size;
int pages;
status = IOC$NODE_DATA (crb, IOC$K_DIRECT_DMA_SIZE, &dma_size);
/* dma_size contains the number of megabytes.
* convert number of megabytes to bytes.
*/
dma_size = dma_size * (1024 * 1024);
/* Convert number of bytes to number of pages by
* dividing by number of bytes per page.
*/
pages = dma_size / MMG$GL_PAGE_SIZE;
|
The driver for the Microsoft Windows Sound System ISA sound card (MSB), SYS$MSBDRIVER, has been removed from the OpenVMS Alpha distribution as of Version 7.0. The following files have been removed:
An enhanced version of this driver, called MMOV$MSBDRIVER, is included in Multimedia Services Version 2.0 for OpenVMS Alpha. This layered product also includes support for video capture and playback, an enhanced version of DECsound, and other audio and video applications.
MMOV$MSBDRIVER provides the same $QIO programming interface as
SYS$MSBDRIVER. Compaq recommends that the WAVE Applications Programming
Interface provided by Multimedia Services for OpenVMS be used instead
because it is more flexible and is portable to other platforms.
(Multimedia Services Version 2.0 for OpenVMS is described in SPD
64.24.00.)
7.13 Device IPL Setup for OpenVMS Alpha Drivers
V6.2
Alpha hardware platforms that support PCI, EISA, and ISA buses deliver I/O device interrupts at different IPLs, either 20 or 21. The IPL at which device interrupts are delivered can change if you move the device from one platform to another. This is a problem if the driver declares its device IPL to be 20, and then that driver is executed on a machine that delivers I/O device interrupts at IPL 21.
The simplest solution to this problem is for PCI, EISA, and ISA device drivers to use IPL 21. This works correctly on platforms that deliver I/O device interrupts at IPL 20 and on platforms that deliver I/O device interrupts at IPL 21.
A future release of OpenVMS Alpha may provide a platform-independent
mechanism for drivers to determine the device IPL dynamically.
7.14 AlphaStation 255: PCI Configuration Restriction
V7.1
The OpenVMS Alpha operating system does not support PCI option cards configured in PCI slot 0 on any AlphaStation 255 series systems.
PCI slot 0 is the lowest physical PCI option slot on AlphaStation 255
series systems. The interrupt signal for this slot is shared with the
built-in Ethernet port. Because the OpenVMS Alpha operating system does
not currently permit PCI devices to share an interrupt line, a PCI
device installed in slot 0 will not function correctly or may cause
errors to occur with the built-in Ethernet port. As a result of this
restriction, AlphaStation 255 series systems support a maximum of two
PCI option cards, configured in slot 1 and slot 2.
7.15 Recommendation for RZ25M and RZ26N Disk Drives (Alpha)
V7.1
During the testing of Compaq supported SCSI disk drives on configurations with DWZZAs and long differential SCSI buses, two drives (RZ25M and RZ26N) were found to have bus phase problems. For this reason, do not use these drives in configurations where the differential bus length connecting DWZZAs equals or exceeds 20 meters.
This recommendation applies only to the RZ25M and RZ26N drives. All
other disk drives, listed as supported in the OpenVMS SPD, may be used
in configurations to the full bus lengths of the SCSI-2 specification.
7.16 SCSI Controller Restriction on AlphaServer 2100 Systems
The Adaptec 1740/1742 SCSI controller (PB2HA--SA) is not supported on AlphaServer 2100 systems having more than 1 gigabyte (GB) of memory. If the controller is connected to such a system, the following message appears on the operator's console:
%PKJDRVR-E- PKX0, Port is going OFFLINE. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |