HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
|
| Previous | Contents |
An anycast address is an identifier for a set of interfaces typically belonging to different nodes. Packets sent to an anycast address are delivered to one of the interfaces identified as the "nearest" address, according to the routing protocol's measure of distance.
The format for anycast addresses is identical to the unicast format.
1.2.2.3 Multicast Address
A multicast address is an identifier for a group of nodes. It is similar to an IPv4 multicast address. Figure 1-7 shows the format for multicast addresses.
Figure 1-7 IPv6 Multicast Address
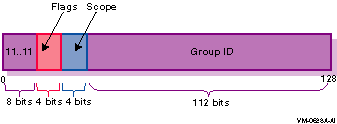
In the multicast address format, the fields have the following definitions:
| 11..11 | Identifies the address as multicast. | ||||||||||||
| Flags |
Can be either of the following values:
|
||||||||||||
| Scope |
Indicates the scope of the multicast group. The following table lists
the scope values:
|
||||||||||||
| Group ID | Identifies the multicast group within the specified scope. |
Table 1-1 lists some well-known multicast addresses.
| Multicast Address | Meaning |
|---|---|
| FF02::1 | All nodes (link-local) |
| FF02::2 | All routers (link-local) |
| FF02::9 | All RIPng routers (link-local) |
Each IPv6 address has a unique pattern of leading bits that indicates its address type. These leading bits are called the format prefix. Table 1-2 lists some IPv6 address types and their prefixes.
| Address Type | Prefix |
|---|---|
| Aggregatable global unicast | 2000::/3 |
| Link-local | FE80::/10 |
| Site-local | FEC0::/10 |
| Multicast | FF00::/8 |
The IPv6 address changes have led to the following definitions for configuring addresses:
In the stateless model, nodes learn address prefixes by listening for Router Advertisement packets. Addresses are formed by combining the prefix with a data link-specific interface token, which is typically derived from the data link address of the interface. This model is favored by administrators who do not need tight control over address configuration. See RFC 2462 for more information.
In DHCPv6, hosts may request addresses, configuration information and services from dedicated configuration servers. This model is favored by administrators who want to delegate addresses based on a client/server model. The DHCPv6 Internet Drafts are currently undergoing revision. See the DHCP charter web page for more information:
www.ietf.org/html.charters/dhc-charter.html |
Version 5.1 of Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS does not support DHCPv6. |
In both cases, the resulting addresses have associated lifetimes, and
systems must be able to acquire new addresses and release expired
addresses. Combined with the ability to register updated address
information with Domain Name System (DNS) servers, these mechanisms
provide a path towards network renumbering and provide network
administrators with control over the use of network addresses without
manual intervention on each host on the network.
1.2.5 Address Resolution
The Domain Name System (DNS) provides support for mapping names to IP addresses and mapping IP addresses back to their corresponding names. Because of the increased size of the IPv6 address, the DNS has the following new features:
b.a.9.8.7.6.5.0.4.0.0.0.3.0.0.0.2.0.0.0.1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.1.2.3.4.IP6.INT |
IPv6 addresses are now being deployed by the regional registries. See the IANA web page at the following location for more information:
http://www.ipv6.org/iana-ann.html |
In addition, you can contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to obtain an IPv6 address.
Because of the need to test various implementations of the IPv6 RFCs, the IETF has defined a temporary IPv6 address allocation scheme. You can assign the addresses in this scheme to hosts and routers for testing IPv6 on the 6bone (a prototype IPv6 implementation that can be used for testing). See the 6bone home page at the following location for more information about 6bone address allocation and assignment:
http://www.6bone.net |
At the present time, the 6bone test addresses are aggregatable global unicast addresses. Contact your 6bone service provider (for example, gw-6bone@pa.dec.com ) for a 6bone address delegation.
The following sections describe the formats for the aggregatable IPv6
addresses.
1.3.1 Aggregatable Global Unicast Addresses
The aggregatable global unicast address format for IPv6 is designed to support current provider-based aggregation and new exchange-based aggregation. Whether a site connects to a provider or to an exchange, the address format enables efficient route aggregation for either type. Figure 1-8 shows the format for an aggregatable global unicast address. (See RFC 2374 for additional information.)
Figure 1-8 Aggregatable Global Unicast Address Format
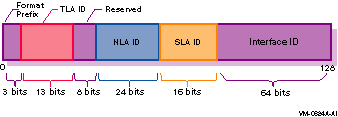
In this address format, the fields have the following definitions:
| Format Prefix | The format prefix. For aggregatable global unicast addresses, the value for this field is 001. |
| TLA ID | The top-level aggregation identifier. |
| Reserved | Reserved for future use. At present, set to all zeros (0). |
| NLA ID | The next-level aggregation identifier. These are assigned by the TLA ID administrator to create an addressing hierarchy and to identify end-user sites. Each organization assigned a TLA ID is also assigned 24 bits of NLA ID space whose layout and use is the responsibility of the organization. |
| SLA ID | The site-level aggregation identifier. These are used by an individual organization to create its own local addressing hierarchy and to identify subnets. |
| Interface ID | The 64-bit interface identifier of the interface that is connected to the link. |
Figure 1-9 shows the format for aggregatable global unicast addresses for IPv6 testing. (See RFC 2471 for more information about the proposed testing address allocation plan.)
Figure 1-9 Aggregatable Testing Address Format
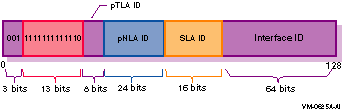
In this address format, the fields have the following definitions:
| 001 | The format prefix for aggregatable global unicast addresses. |
| 1111111111110 | The 6bone top-level aggregation (TLA) identifier, 0x1FFE, which is reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Naming Authority (IANA) and is used temporarily for IPv6 testing. |
| pTLA ID | The pseudo top-level aggregation identifier. This is assigned by the pTLA ID administrator to define the top level of aggegation (backbone sites) for the 6bone network. |
| pNLA ID | The pseudo next-level aggregation identifier. This is the ID assigned by the pTLA ID administrator to create an addressing hierarchy and to identify end-user sites on the 6bone network. |
| SLA ID | The site-level aggregation identifier. This is the ID assigned by an organization to create its own local addressing hierarchy and to identify subnets. |
| Interface ID | The 64-bit interface identifier of the interface that is connected to the link. |
For the most current information about pTLA and pNLA assignments, see the 6bone home page at the following location:
http://www.6bone.net |
This section shows some example IPv6 configurations. Select a configuration that most closely matches the environment in which you want to configure IPv6 on your system.
Figure 1-10 shows a simple LAN configuration in which host A and host B communicate using IPv6 with no router.
Figure 1-10 Host-to-Host Configuration with No Router
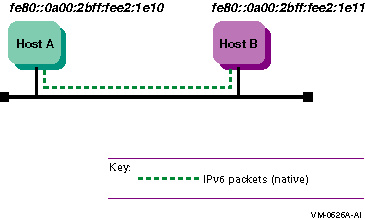
Figure 1-11 shows a simple LAN configuration in which host A, host B, and router A communicate using IPv6. Host A and host B obtain global addresses from router A.
Figure 1-11 Host-to-Host Configuration with Router
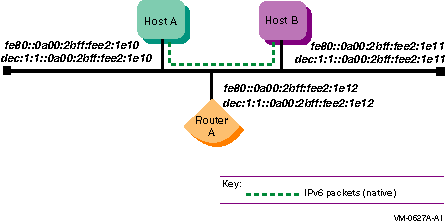
Figure 1-12 shows a configuration in which two IPv6 networks are connected through an IPv6 router (router A).
Figure 1-12 IPv6 Network to IPv6 Network with Router Configuration
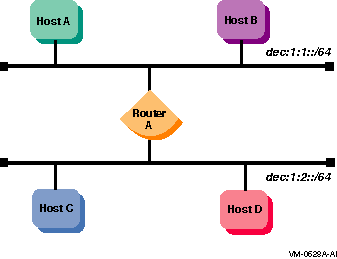
Figure 1-13 shows a configuration in which four IPv6 networks are connected using three routers. The three routers exchange routing information with each other using the RIPng protocol.
Figure 1-13 Multiple IPv6 Networks and Multiple Routers Configuration
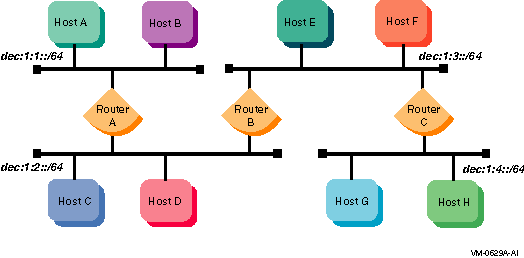
Figure 1-14 shows a configuration in which host A and host B, connected to an IPv4 network, communicate using IPv6 through an IPv4 tunnel.
Figure 1-14 Host-to-Host Configuration over Tunnel
Figure 1-15 shows a configuration in which host X is connected to an IPv4 network. Router A, an IPv6 router, is connected to the same IPv4 network and is also connected to two IPv6 networks. Host X communicates with host B using IPv6 through an IPv4 tunnel between host X and router A.
Figure 1-15 Host-to-Router Configuration over Tunnel
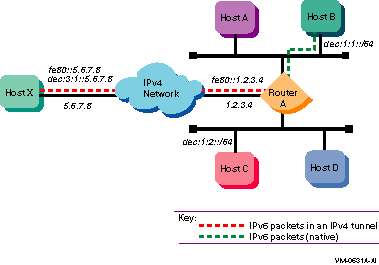
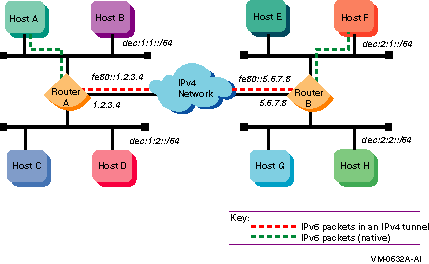
Figure 1-16 shows a configuration in which four IPv6 networks are connected through two routers and an IPv4 network. Host A communicates with host F through an IPv4 tunnel between router A and router B.
Figure 1-16 IPv6 Network-to-IPv6 Network Configuration over Tunnel
After installimg Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Version 5.1, you can configure your system to communicate in an IPv6 network environment by performing the tasks described in the following sections. You can configure your node as either of the following:
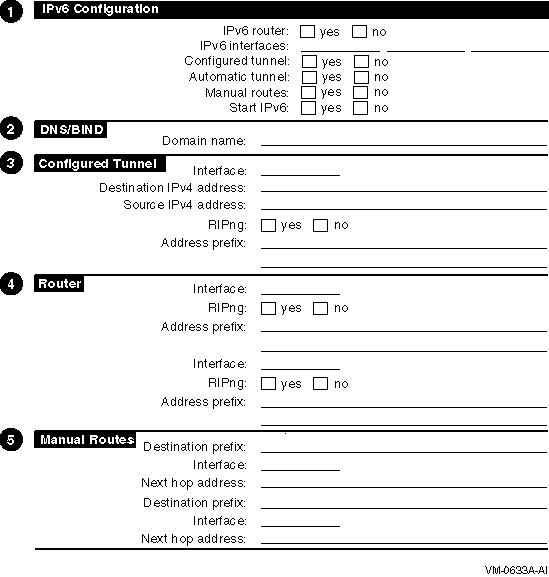
Before you configure the network software, you must gather information about your system and network environment. The Configuration Worksheet shown in Figure 2-1 can help you assemble this information in an orderly fashion. The following sections describe the information that you need to record on the worksheet.
Figure 2-1 Configuration Worksheet
When you run the TCPIP$IP6_SETUP configuration utility, it gathers
information from the system and prompts you for additional
configuration information.
2.2 IPv6 System Configuration Examples
This section shows how to use the configuration worksheet to assemble information for selected configurations. Each example shows how individual systems are configured. In some cases, additional options for you to consider are provided.
OpenVMS interface names must be in uppercase. |
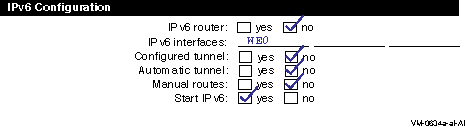
In a simple host-to-host configuration (shown in Figure 1-10), host A and host B use IPv6 link-local addresses. By default, the TCPIP$IP6_SETUP command configures the hosts automatically with a link-local address for your system. Figure 2-2 shows the completed worksheet for host A.
Figure 2-2 Simple Host-to-Host Configuration
After you configure IPv6 on host A, add a link-local address for host B to the TCPIP$ETC:IPNODES.DAT file. (For more information about these files, see Section 3.4.) The configuration process for host B in this configuration is similar to that for host A.
In this configuration, no global address prefix is advertised on the LAN. If you want to advertise a global address prefix, you can either configure one of the hosts as a router by using TCPIP$IP6_SETUP or add an IPv6 router to the LAN configuration. An IPv6 router advertises a global prefix on the link.
You can use the netstat -in command to view a local node's link-local and global addresses.
The following TELNET command connects host A to host B using host B's link-local address:
$ TELNET fe80::0a00:2bff:fee2:1e11 |
Alternately, you can place the address and node name in the
TCPIP$ETC:IPNODES.DAT file. Then use the node name as the argument to
the
TELNET
command. (For more information about this file, see Section 3.4.)
2.2.2 Host-to-Host with Router Configuration
In a host-to-host with router configuration (shown in Figure 1-11), host A and host B are on a LAN with router A. In this case, router A advertises the global address prefix dec:1:1::/64 on the LAN. Host A and host B use this address prefix to create global IPv6 addresses. (See Chapter 1 for information about obtaining experimental testing addresses.) Figure 2-3 shows the completed worksheet for router A.
Figure 2-3 Host-to-Host with Router Configuration
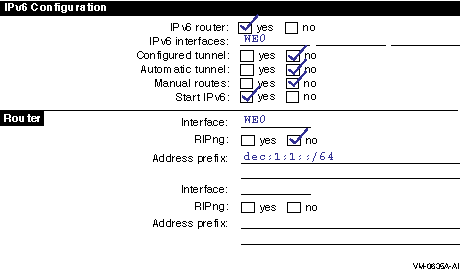
After you configure IPv6 on router A, add the global addresses for the other hosts to the TCPIP$ETC:IPNODES.DAT file. (For more information about this file, see Section 3.4.) Repeat this step on host A and host B. Alternatively, you could establish DNS/BIND in your network using the global addresses.
| Previous | Next | Contents |