 |
OpenVMS DCL Dictionary
SET SYMBOL
Controls access to local and global symbols in command procedures.
Format
SET SYMBOL
Description
The SET SYMBOL command controls access to local and global symbols in
command procedures by treating symbols as undefined. Because all global
and local symbols defined in an outer procedure level are accessible to
inner procedure levels, it is often necessary to mask these symbols
without deleting them.
The SET SYMBOL command also controls whether DCL will attempt to
translate the verb string (the first token on the command line) as a
symbol before processing the line. The default behavior is that the
translation is attempted. The advantage to changing this behavior is
that a command procedure will not be affected by outer procedure level
environments when invoking a command.
The symbol scoping context is different for local and global symbols.
Local symbols are procedure level dependent. Local symbols defined in
an outer subroutine level can be read at any inner subroutine level,
but they cannot be written to. If you assign a value to a symbol that
is local to an outer subroutine level, a new symbol is created at the
current subroutine level; however, the symbol in the outer procedure
level is not modified.
This means that the SET SYMBOL/SCOPE=NOLOCAL command causes all local
symbols defined at an outer procedure level to be inaccessible to the
current procedure level and any inner levels. For example, if SET
SYMBOL/SCOPE=NOLOCAL was specified at procedure levels 2 and 4,
procedure level 2 can read (but not write to) only level 2 local
symbols. Level 3 can read (but not write to) level 2 local symbols and
can read and write to level 3 local symbols. Level 4 can read and write
to only level 4 local symbols.
Global symbols are procedure-level independent. The current global
symbol scoping context is applied subsequently to all procedure levels.
Specifying the /SCOPE=NOGLOBAL qualifier causes all global symbols to
become inaccessible for all subsequent commands until either the
/SCOPE=GLOBAL qualifier is specified or the procedure exits to a
previous level at which global symbols were accessible. In addition,
specifying the /SCOPE=NOGLOBAL qualifier prevents you from creating any
new global symbols until the /SCOPE=GLOBAL qualifier is specified.
When you exit a procedure level to return to a previous procedure, the
symbol scoping context from the previous level is restored for both
local and global symbols.
To display the current symbol scoping state, use the lexical function
F$ENVIRONMENT("SYMBOL_SCOPE").
Qualifiers
/ALL (default)
Specifies that the values of the /SCOPE qualifier pertain both to the
translation of the first token on a command line and to general symbol
substitution.
The /ALL qualifier is incompatible with the /GENERAL or the /VERB
qualifier.
/GENERAL
Specifies that the values of the /SCOPE qualifier pertain to the
translation of all symbols except the first token on a command line.
The /GENERAL qualifier is incompatible with the /ALL or the /VERB
qualifier.
/SCOPE=(keyword,...)
Controls access to local and global symbols. Lets you treat symbols as
being undefined. Possible keywords are as follows:
|
NOLOCAL
|
Causes all local symbols defined in outer procedure levels to be
treated as being undefined by the current procedure and by all inner
procedure levels.
|
|
LOCAL
|
Removes any symbol translation limit set by the current procedure level.
|
|
NOGLOBAL
|
Causes all global symbols to be inaccessible to the current procedure
level and to all inner procedure levels unless otherwise changed.
|
|
GLOBAL
|
Restores access to all global symbols.
|
/VERB
Specifies that the values of the /SCOPE qualifier pertain to the
translation of the first token on a command line as a symbol before
processing only. It does not affect general symbol substitution.
Note
Caution must be used if the SET SYMBOL/VERB/SCOPE command is used more
than once in a command procedure. Because DCL uses the translation
behavior when looking for a label or subroutine, execution may be
different running in one mode than in another. Compaq recommends that
the SET SYMBOL/VERB/SCOPE command be used once as part of the command
procedure setup and left in that mode for the duration of the
procedure.
|
The /VERB qualifier is incompatible with the /ALL or the /GENERAL
qualifier.
Examples
| #1 |
$ SET SYMBOL/SCOPE=NOLOCAL
|
In this example, all local symbols defined in outer procedure levels
are now undefined for the current procedure level and all inner
procedure levels.
| #2 |
$ SET SYMBOL/SCOPE=NOGLOBAL
|
In this example, all global symbols are now inaccessible to the current
procedure level and all inner procedure levels unless otherwise changed.
| #3 |
$ NOW :== SHOW TIME
$ !
$ NOW
3-NOV-2001 11:48:58
$ !
$ SET SYMBOL /VERB /SCOPE=NOGLOBAL
$ NOW
%DCL-W-IVVERB, unrecognized command verb-check validity and spelling
\NOW\
$ !
$ SHOW SYMBOL NOW
NOW == "SHOW TIME"
|
This example demonstrates the use of the /VERB qualifier.
The symbol NOW is assigned to the SHOW TIME command. The next line
shows the default behavior, where DCL attempts to translate the first
string on the command line (NOW). Because NOW translates to the SHOW
TIME command, this is used instead of NOW.
The SET SYMBOL command on the next line changes the behavior so that
DCL does not attempt a translation. When NOW is subsequently entered,
DCL uses the string NOW as the command verb and cannot find it in the
command table. This results in the error message.
Notice that the scoping of the verb translation has no effect on
general symbol translations, as demonstrated by the SHOW SYMBOL command
in the example.
SET TERMINAL
Sets the characteristics of a terminal. Entering a qualifier changes a
characteristic; omitting a qualifier leaves the characteristic
unchanged.
Format
SET TERMINAL [device-name[:]]
Parameter
device-name[:]
Specifies the device name of the terminal. The default is SYS$COMMAND
if that device is a terminal. If the device is not a terminal, an error
message is displayed.
Description
The SET TERMINAL command modifies specific terminal characteristics for
a particular application or overrides system default characteristics.
(These defaults are defined at each installation, based on the most
common type of terminal in use.) The default characteristics for
terminals are listed in Figure DCLII-2.
The terminal characteristics, local or remote, are determined
automatically by the terminal driver for terminals that have the modem
characteristic enabled. These characteristics are not affected by the
SET TERMINAL command. For example, when you successfully dial in to an
OpenVMS system processor, you establish your terminal as remote. When
you hang up, the terminal characteristic is set back to local.
The set of terminals supported by the OpenVMS system includes a set of
VT100 family terminals that support special DIGITAL ANSI
characteristics and escape sequences. For a description of these
special characteristics and escape sequences, refer to the
OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
Figure DCLII-2 Default Characteristics for Terminals
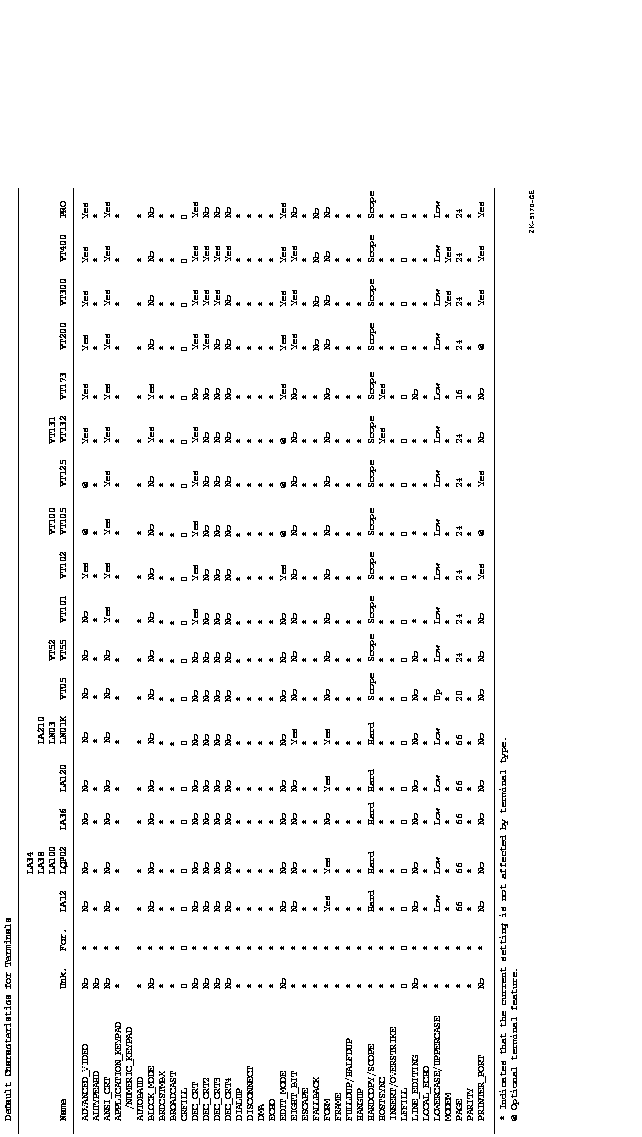
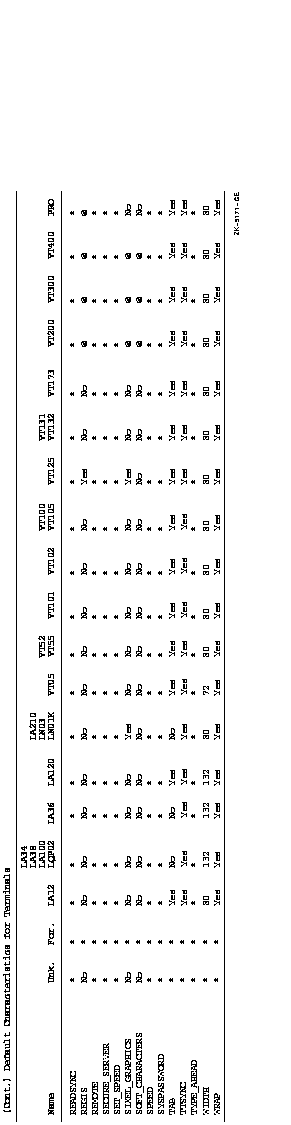
Qualifiers
/ADVANCED_VIDEO
/NOADVANCED_VIDEO
Controls whether the terminal has advanced video attributes and is
capable of 132-column video. If the terminal width is set to 132
columns and you specify the /ADVANCED_VIDEO qualifier, the terminal
page limit is set to 24 lines. If you specify the /NOADVANCED_VIDEO
qualifier, the terminal page limit is set to 14 lines.
/ALTYPEAHD
Causes the terminal driver to create a permanent, alternate type-ahead
buffer. The system parameter TTY_ALTYPEAHD determines the size of the
type-ahead buffer. This specification is effective at your next login
and stays in effect until you reboot your VAX computer.
To enable /ALTYPEAHD, you must also set the qualifier /TYPE_AHEAD.
You should specify SETTERMINAL/PERMANENT/ALTYPEAHD in
SYS$STARTUP:SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM for those communication lines that
require this capability.
To use this feature interactively, specify SET
TERMINAL/PERMANENT/ALTYPEAHD. This specification is effective at your
next login.
/ANSI_CRT (default)
/NOANSI_CRT
Controls whether the terminal conforms to ANSI CRT programming
standards. Because ANSI standards are a proper subset of the DEC_CRT
characteristics, the default for all VT100 family terminals is
/ANSI_CRT.
/APPLICATION_KEYPAD
Specifies that the keypad is to be set to application keypad mode,
which allows you to enter DCL commands defined with the DEFINE/KEY
command. By default, the terminal is set to numeric keypad mode.
/AUTOBAUD
/NOAUTOBAUD
Controls whether the terminal baud rate is set when you log in and sets
the default terminal speed to 9600. You must press Return two or more
times at intervals of at least 1 second for the baud rate to be
determined correctly. If you press a key other than Return, the
/AUTOBAUD qualifier may detect the wrong baud rate. If this happens,
wait for the login procedure to time out before continuing. The
/AUTOBAUD qualifier must be used with the /PERMANENT qualifier.
The valid baud rates are as follows:
50 150 1800 4800 38400
75 300 2000 7200 57600
110 600 2400 9600 76800
134 1200 3600 19200 115200
|
/BLOCK_MODE
/NOBLOCK_MODE
Controls whether block mode transmission, local editing, and field
protection are performed.
/BRDCSTMBX
/NOBRDCSTMBX
Controls whether broadcast messages are sent to an associated mailbox
if one exists.
/BROADCAST (default)
/NOBROADCAST
Controls whether reception of broadcast messages (such as those issued
by MAIL and REPLY) is enabled. Specify the /NOBROADCAST qualifier when
you are using a terminal as a noninteractive device or when you do not
want special output to be interrupted by messages. Use the SET
BROADCAST command to exclude certain types of messages from being
broadcast, rather than eliminating all messages.
/COLOR
Sets the ANSI_COLOR terminal characteristic and identifies the terminal
as capable of supporting the ANSI color escape sequences.
/COMMSYNC
/NOCOMMSYNC (default)
Allows connection of asynchronous printers and other devices to
terminal ports, using standard modem control signals as flow control.
Transmission to the device stops if either data set ready (DSR) or
clear to send (CTS) EIA modem control signals are dropped. Transmission
resumes when both signals are present.
The /COMMSYNC qualifier and the /MODEM qualifier are mutually exclusive.
The COMMSYNC feature has the following limitations:
- Cannot be used on LAT ports
- Can only be used on ports with full modem control
- Should not be used in conjunction with Xon/Xoff flow control (the
port may hang)
Caution
The /COMMSYNC qualifier should never be set on a line with a modem that
is intended for interactive use. The qualifier disables the modem
terminal characteristic that disconnects a user process from the
terminal line in case of a modem phone line failure. With the /COMMSYNC
qualifier enabled, the next call on the terminal line could be attached
to the previous user's process. Security administrators should be aware
that the characteristic should not be used on interactive terminal
ports. In addition, the /COMMSYNC qualifier is not supported on a port
connected to a LAT line.
|
/CRFILL[=fill-count]
Generates the specified number of null characters after each carriage
return before transmitting the next meaningful character (to ensure
that the terminal is ready for reception). The value must be an integer
in the range 0 to 9. The default is the /CRFILL=0 qualifier.
/DEC_CRT[=(value1,value2,value3)]
/NODEC_CRT[=(value1,value2,value3)]
Controls whether the terminal conforms to DIGITAL VT100-, VT200-,
VT300-, VT400-, or VT500-family standards and supports the minimum
standards, including the additional DIGITAL escape sequences.
You can specify one of the following values:
|
1 (default)
|
Requests that the DEC_CRT terminal characteristic be set.
|
|
2
|
Requests that the DEC_CRT2 terminal characteristic be set.
|
|
3
|
Requests that the DEC_CRT3 terminal characteristic be set. A level 3
terminal supports the following additional features:
- A status line (line 25, at the bottom of the screen)
- The ISO Latin1 character set
- Terminal state interrogation (describes what state your terminal is
in)
|
|
4
|
Requests that the DEC_CRT4 terminal characteristic be set. A level 4
terminal supports the following additional features:
- Extended keyboard
- Key position mode
- Secure reset
- Novice mode
- Selective erase
- On-line transaction processing (OLTP) features:
- Page memory
- Rectangular editing
- Text macros
- Data integrity reports
|
Note that DEC_CRT2, DEC_CRT3, and DEC_CRT4 are supersets of DEC_CRT.
Clearing DEC_CRT causes DEC_CRT2, DEC_CRT3, and DEC_CRT4 to be cleared.
Similarly, setting DEC_CRT4 causes all subsets of DEC_CRT4 (including
ANSI_CRT) to be set.
/DEVICE_TYPE=terminal-type
Informs the system of the terminal type and sets characteristics
according to the device type specified. You can specify any of the
following terminal types:
UNKNOWN
FT1--FT8
LA12
LA34
LA36
LA38
|
LA100
LA120
LA210
LN01K
LN03
LQP02
|
PRO_SERIES
VT05
VT52
VT55
VT100
VT101
|
VT102
VT105
VT125
VT131
VT132
VT173
|
VT200
VT300
VT400
VT500
|
The default characteristics for the VT100-, VT102-, and VT125-series
terminals are as follows:
|
/ADVANCEDVIDEO
|
/NOALTYPEAHD
1
|
/ANSI_CRT
|
|
/NOAUTOBAUD
|
/NOBLOCK_MODE
|
/NOBRDCSTMBX
|
|
/BROADCAST
|
/CRFILL=0
|
/ECHO
|
|
/NOEIGHT_BIT
|
/NOESCAPE
|
/NOFORM
|
|
/FULLDUP
|
/NOHOSTSYNC
|
/LFFILL=0
|
|
/LOWERCASE
|
/NODMA
|
/PAGE=24
|
|
/NOPARITY
|
/NOPASTHRU
|
/NOREADSYN
|
|
/SPEED=9600
|
/TAB
|
/TTSYNC
|
|
/TYPE_AHEAD
|
/WIDTH=80
|
/WRAP
|
1This is the default characteristic set by the system and is
not a valid qualifier for your use.
The terminal types and characteristics that can be set are listed in
Figure DCLII-2.
/DIALUP
/NODIALUP (default)
Controls whether the terminal is a dialup terminal.
/DISCONNECT
/NODISCONNECT (default)
Controls whether the process connected to this terminal is disconnected
if the line detects a hangup. The /DISCONNECT qualifier is valid only
when the /PERMANENT qualifier is specified.
/DISMISS
/NODISMISS (default)
Controls whether the terminal driver ignores data that causes a parity
error (instead of terminating the currently outstanding I/O with an
error status).
/DMA
/NODMA
Controls whether direct memory access (DMA) mode is used on a
controller that supports this feature.
/ECHO (default)
/NOECHO
Controls whether the terminal displays the input it receives. With the
/NOECHO qualifier, the terminal displays only system or user
application output, or both.
/EDIT_MODE
/NOEDIT_MODE
Controls whether the terminal can perform ANSI-defined advanced editing
functions.
/EIGHT_BIT
/NOEIGHT_BIT
Controls whether the terminal uses the 8-bit ASCII protocol rather than
the 7-bit ASCII protocol. You can use the Terminal Fallback Facility
(TFF) to set the 8-bit characteristic on terminals. If the terminal you
specify has the TFF enabled, the /EIGHT_BIT qualifier has no effect.
For more information on terminal fallback, refer to the OpenVMS Terminal Fallback Utility Manual
(available on the Documentation CD-ROM).
/ESCAPE
/NOESCAPE (default)
Controls whether escape sequences are validated.
/FALLBACK
/NOFALLBACK
Controls whether the 8-bit DEC Multinational character set characters
are displayed on the terminal in their 7-bit representation. The
default depends on the /EIGHTBIT setting of the terminal. If the
OpenVMS Terminal Fallback Facility (TFF) is enabled, it activates the
default character conversion tables for the named terminal. For more
information, refer to the OpenVMS Terminal Fallback Utility Manual (available on the Documentation
CD-ROM). If TFF is not enabled on your system, the /FALLBACK qualifier
has no effect and no error message is displayed.
/FORM
/NOFORM
Controls whether a form feed is transmitted rather than translated into
multiple line feeds.
/FRAME=n
Specifies the number of data bits that the terminal driver expects for
every character that is input or output. The value of n can be
from 5 to 8. The default value depends on the settings for the terminal
established by the /PARITY and /EIGHTBIT qualifiers.
/FULLDUP (default)
/NOFULLDUP
Controls whether the terminal operates in full-duplex mode. The
/FULLDUP qualifier is equivalent to the /NOHALFDUP qualifier.
/HALFDUP
/NOHALFDUP (default)
Controls whether the terminal operates in half-duplex mode. The
/HALFDUP qualifier is equivalent to the /NOFULLDUP qualifier.
/HANGUP
/NOHANGUP (default)
May require LOG_IO (logical I/O) or PHY_IO (physical I/O)
privilege depending on system generation parameter settings.
Controls whether the terminal modem is hung up when you log out.
/HARDCOPY
/NOHARDCOPY
Controls whether the device is established as a hardcopy terminal and
outputs a backslash (\) when the Delete key is pressed. The /HARDCOPY
qualifier is equivalent to the /NOSCOPE qualifier.
/HOSTSYNC
/NOHOSTSYNC (default)
Controls whether system transmission from the terminal is stopped (by
generating a Ctrl/S) when the input buffer is full and resumed (by
generating a Ctrl/Q) when the input buffer is empty.
/INQUIRE
Sets the device type when the /INQUIRE qualifier is specified and the
DEC_CRT characteristic is set. The SET TERMINAL command reads the
current screen size from the terminal and sets the corresponding page
length and page width values appropriately. The default device type is
UNKNOWN. Works only on DIGITAL terminals, and not on LA36 or VT05
terminals. Some VT100 family terminals, including the VT101 and VT105,
return a VT100 type response. LA38 terminals respond as LA43 terminals.
Note
The SET TERMINAL/INQUIRE command works correctly on DIGITAL supplied
VT100 and later terminals. Some personal computer terminal emulators
may not work correctly, because they do not correctly emulate all VT100
escape sequences. Compaq recommends that users who experience problems
with these terminal emulators contact the terminal emulator supplier.
|
You can include the SET TERMINAL/INQUIRE command in your LOGIN.COM file
to detect the terminal type automatically.
If you specify /INQUIRE=OLD, OpenVMS sets the terminal window to 24
lines by 80 columns and ignores the real terminal size. (This is the
behavior of the SET TERMINAL/INQUIRE command prior to OpenVMS Version
6.2.)
Caution
This qualifier clears the type-ahead buffer. If the response sequence
is unrecognized, no action message or error message is displayed. The
/INQUIRE qualifier should be used only on DIGITAL terminals; however,
the LA36 and VT05 terminals do not support this feature.
|
/INSERT
Sets the terminal to insert mode. This feature allows you to insert
characters when editing command lines. The default mode is overstrike,
which allows you to type over the current character when editing a
command line. Press Ctrl/A to switch from one mode to the other.
/LFFILL[=fill-count]
Transmits to the terminal the specified number of null characters after
each line feed before transmitting the next meaningful character (to
ensure that the terminal is ready for reception). The value must be an
integer in the range 0 to 9. The default is installation dependent. See
Figure DCLII-2 for a list of default terminal characteristics.
/LINE_EDITING
/NOLINE_EDITING
Controls whether advanced line-editing features are enabled for editing
command lines: pressing Return and pressing Ctrl/Z are recognized as
line terminators, as are escape sequences.
/LOCAL_ECHO
/NOLOCAL_ECHO (default)
Controls whether the terminal echoes characters locally (rather than
the host echoing them) for command level terminal functions. (Do not
use the /LOCAL_ECHO qualifier with utilities that require control over
echoing, such as line editing or EDT's screen mode.)
Caution
When logging in to terminals with the LOCAL_ECHO characteristic, the
OpenVMS system has no control over the echoing of passwords.
|
/LOWERCASE
/NOLOWERCASE
Controls whether lowercase characters are passed to the terminal. The
/NOLOWERCASE qualifier translates all input to uppercase. The
/LOWERCASE qualifier is equivalent to the /NOUPPERCASE qualifier.
/MANUAL
Indicates manual switching of terminal lines to dynamic asynchronous
DDCMP lines when your local terminal emulator does not support
automatic switching. The /MANUAL qualifier should be specified with the
/PROTOCOL=DDCMP and /SWITCH=DECNET qualifiers.
/MODEM
/NOMODEM
Specifies whether the terminal is connected to a modem or a cable that
supplies standard EIA modem control signals. If your terminal has the
MODEM characteristic, entering SET TERMINAL/NOMODEM automatically logs
you out. The /MODEM qualifier and the /COMMSYNC qualifier are mutually
exclusive.
/NUMERIC_KEYPAD (default)
Specifies whether the keys of the numeric keypad are used to type
numbers and punctuation marks (/NUMERIC_KEYPAD) or to enter DCL
commands defined with the DEFINE/KEY command (/APPLICATION_KEYPAD).
/OVERSTRIKE (default)
Sets the terminal to overstrike mode. This feature allows you to type
over the current character when you are editing a command line. Set
your terminal to insert mode if you want to insert characters when
editing command lines. Press Ctrl/A to switch from one mode to the
other.
/PAGE[=lines-per-page]
Specifies the number of print lines between perforations for hardcopy
terminals. (When the terminal reads a form feed, it advances the paper
to the next perforation.) The value of the lines-per-page
parameter can be from 0 to 255 and defaults to 0 (which treats a form
feed as a line feed).
/PARITY[=option]
/NOPARITY (default)
Controls whether the terminal passes data with only odd or even parity,
where option equals ODD or EVEN. If you specify the /PARITY
qualifier without an option, the value defaults to EVEN.
/PASTHRU
/NOPASTHRU (default)
Controls whether the terminal passes all data (including tabs, carriage
returns, line feeds, and control characters) to an application program
as binary data. The setting of /TTSYNC is allowed.
Make sure that you spell both these qualifiers exactly as they appear
in the text.
/PERMANENT
Requires LOG_IO (logical I/O) or PHY_IO (physical I/O)
privilege.
Sets characteristics on a permanent basis, that is, over terminal
sessions; however, the characteristics revert to their initial values
if the system is halted and restarted. Use in a system startup file to
establish characteristics for all terminals on the system.
/PRINTER_PORT
/NOPRINTER_PORT
Specifies whether the terminal has a printer port (an attribute not set
by the SET TERMINAL/INQUIRE command). The default is installation
dependent. See Figure DCLII-2 for a list of default terminal
characteristics.
/PROTOCOL=DDCMP
/PROTOCOL=NONE (default)
On VAX, controls whether the terminal port specified is changed into an
asynchronous DDCMP line. The /PROTOCOL=NONE qualifier changes an
asynchronous DDCMP line back into a terminal line. Note that
/PROTOCOL=DDCMP is a permanent characteristic; therefore, the
/PERMANENT qualifier is not required.
/READSYNC
/NOREADSYNC (default)
Controls whether the terminal uses the Ctrl/S and Ctrl/Q functions to
synchronize data transmitted from the terminal.
Caution
SET TERMINAL/READSYNC should not be used on LAT terminal lines. Setting
this characteristic may cause unexpected results.
|
The default is the /NOREADSYNC qualifier; the system does not use the
Ctrl/S and Ctrl/Q functions to control reads to the terminal. The
/READSYNC qualifier is useful for certain classes of terminals that
demand synchronization or for special-purpose terminal lines where data
synchronization is appropriate.
/REGIS
/NOREGIS
Specifies whether the terminal understands ReGIS graphic commands.
/SCOPE
/NOSCOPE
Controls whether the device is established as a video terminal. The
/SCOPE qualifier is equivalent to the /NOHARDCOPY qualifier.
/SECURE_SERVER
/NOSECURE_SERVER (default)
Requires either LOG_IO (logical I/O) or PHY_IO (physical I/O)
privilege.
|

