 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$MOD_HOLDER
Modifies the specified holder record of the target identifier in the
rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_HOLDER id ,holder ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib]
C Prototype
int sys$mod_holder (unsigned int id, struct _generic_64 *holder,
unsigned int set_attrib, unsigned int clr_attrib);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary value of target identifier whose holder record is modified when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The id argument is a
longword containing the identifier value.
holder
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_holder |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Identifier of holder being modified when $MOD_HOLDER completes
execution. The holder argument is the address of a
quadword containing the UIC identifier of the holder in the first
longword and the value of 0 in the second longword.
set_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The set_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified
and the attributes of the identifier. If you specify the same attribute
in set_attrib and clr_attrib, the
attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the
identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
clr_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when
$MOD_HOLDER completes execution. The clr_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the
identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
Description
The Modify Holder Record in Rights Database service modifies the
specified holder record in the rights database. Identifier attributes
can be added or removed.
When you specify both the set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first.
Thus, if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the
result is that the bit is set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD,
$FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC,
$MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
holder argument cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier or holder identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database, or the
specified holder identifier does not exist in the rights database.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOD_IDENT
Modifies the specified identifier record in the rights database.
Format
SYS$MOD_IDENT id ,[set_attrib] ,[clr_attrib] ,[new_name] ,[new_value]
C Prototype
int sys$mod_ident (unsigned int id, unsigned int set_attrib, unsigned
int clr_attrib, void *new_name, unsigned int new_value);
Arguments
id
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Binary value of identifier whose identifier record is modified when
$MOD_IDENT completes execution. The id argument is a
longword containing the identifier value.
set_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be enabled for the identifier when $MOD_IDENT
completes execution. The set_attrib argument is a
longword containing the attribute mask.
The attributes actually enabled are the intersection of those specified
and the attributes of the identifier. If you specify the same attribute
in set_attrib and clr_attrib, the
attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN
|
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier,
unless they own the identifier themselves.
|
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN
|
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated---either from
binary to ASCII or vice versa---but prevents unauthorized users from
translating the identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
clr_attrib
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Bit mask of attributes to be disabled for the identifier when
$MOD_IDENT completes execution. The clr_attrib
argument is a longword containing the attribute mask.
If you specify the same attribute in set_attrib and
clr_attrib, the attribute is enabled.
Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also
obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the
prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit
position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF):
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
KGB$V_DYNAMIC
|
Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the
process rights list by using the DCL command SET_RIGHTS_LIST.
|
|
KGB$V_HOLDER_HIDDEN
|
Prevents someone from getting a list of users who hold an identifier,
unless they own the identifier themselves.
|
|
KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN
|
Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated---either from
binary to ASCII or vice versa---but prevents unauthorized users from
translating the identifier.
|
|
KGB$V_NOACCESS
|
Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute
is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem
attribute.
|
|
KGB$V_RESOURCE
|
Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier.
It is used only for file objects.
|
|
KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM
|
Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected
subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in
the subsystem.
|
new_name
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
New name to be given to the specified identifier. The
new_name argument is the address of the descriptor
pointing to the identifier name string.
An identifier name consists of 1 to 31 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_), and must contain at
least one nonnumeric character. Any lowercase characters specified are
automatically converted to uppercase.
new_value
| OpenVMS usage: |
rights_id |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
New value to be assigned to the specified identifier. The
new_value argument is a longword containing the binary
value of the specified identifier. When the identifier value is
changed, $MOD_IDENT also changes the value of the identifier in all of
the holder records in which the specified identifier appears.
Description
The Modify Identifier in Rights Database service modifies the specified
identifier record in the rights database. Identifier attributes can be
added or removed. The identifier name or value can be changed. When you
specify both the set_attrib and
clr_attrib arguments, the attribute is cleared first.
Thus, if you specify the same attribute bit with each argument, the
result is that the bit is set.
Required Access or Privileges
Write access to the rights database is required.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HELD,
$FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER,
$REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The specified attributes contain invalid attribute flags.
|
|
SS$_DUPIDENT
|
The specified identifier value already exists.
|
|
SS$_DUPLNAM
|
The specified identifier name already exists in the rights database.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The specified identifier is of invalid format.
|
|
RMS$_PRV
|
The user does not have write access to the rights database.
|
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS
RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with
operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes,
refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
$MOUNT
Mounts a tape, disk volume, or volume set and specifies options for the
mount operation.
Format
SYS$MOUNT itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$mount (void *itmlst);
Argument
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying options for the mount operation. The
itmlst argument is the address of a list of item
descriptors, each of which specifies an option and provides the
information needed to perform the operation.
The item list must include at least one device item descriptor and is
terminated by a longword value of 0.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
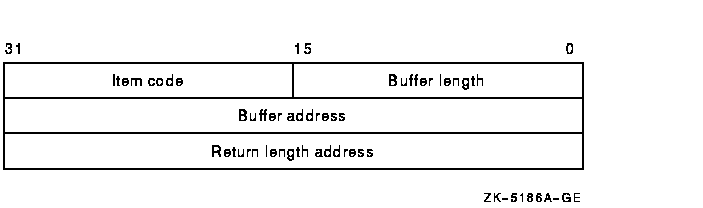
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer that supplies the
information $MOUNT needs to process the specified item code. The
required length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer
length is too small, $MOUNT truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code that specifies an
option for the MOUNT operation. The $MNTDEF macro defines these codes.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the address of the buffer that supplies
information to $MOUNT.
|
|
Return length address
|
This field is not used.
|
Item Codes
MNT$_ACCESSED
Specifies the number of directories that will be in use, concurrently,
on the volume. The buffer must contain a longword integer value in the
range 0 to 255. This value overrides the number of directories
specified when the volume was initialized. To specify MNT$_ACCESSED,
the caller must have OPER privilege. The MNT$_ACCESSED item code
applies only to disks.
MNT$_BLOCKSIZE
Specifies the default block size for tape volumes. The buffer must
contain a longword integer value in the range 20 to 65,532 bytes for
OpenVMS RMS operations or 10 to 65,534 bytes for operations that do not
use RMS. The MNT$_BLOCKSIZE item code applies only to tapes.
If you do not specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE, the default block size is 2048
bytes for Files-11 tape volumes and 512 bytes for foreign and unlabeled
tapes.
You must specify MNT$_BLOCKSIZE when mounting (1) tapes that do not
have ANSI HDR2 labels, (2) tapes to which data will be written from
compatibility mode, and (3) tapes that are to contain records whose
size is larger than the default value.
MNT$_COMMENT
Specifies text to be associated with an operator request. The buffer
must contain a character string of no more than 78 characters. This
text will be printed on the operator's console if an operator request
is issued for the device being mounted.
MNT$_DENSITY
Specifies the density at which data is to be written to a foreign or
unlabeled tape. The DENSITY item code suppled is dependent on the type
of tape device. If a tape device is capable of using the MT3 density
codes, the buffer for the MNT$DENSITY item code must contain a longword
with one of the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET
(MT3$K_TK50, MT3$K_3480, MT3$K_SDLT, MT3$K_AIT2, and so on). Refer to
the MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
If the device does not support MT3 densities, the buffer must contain a
longword value that specifies one of the following legal densities: 800
bpi, 1600 bpi, or 6250 bpi.
The specified density will be used only if (1) the tape is foreign or
unlabeled and (2) the first operation is a write.
MNT$_DEVNAM
Specifies the name of the device to be mounted. The buffer must contain
a character string of from 1 to 64 characters, which is the device
name. The device name can be a physical device name or a logical name;
if it is a logical name, it must translate to a physical device name.
The MNT$_DEVNAM item code must appear at least once in an item list,
and it can appear more than once. It appears more than once when a
volume set is being mounted, because, in this case, one device is being
mounted for each volume in the volume set.
MNT$_EXTENSION
Specifies the number of blocks by which files will be extended. The
buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 65,535. The
MNT$_EXTENSION item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_EXTENT
Specifies the size of the extent cache in units of extent pointers. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To
specify MNT$_EXTENT, you need OPER privilege. The value 0 (the default)
disables caching. The MNT$_EXTENT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FILEID
Specifies the size of the file-ID cache in units of file numbers. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies this size. To
specify MNT$_FILEID, you need OPER privilege. The value 1 disables
caching. The MNT$_FILEID item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_FLAGS
Specifies a 2-longword bit vector wherein each bit specifies an option
for the mount operation. The buffer must contain a quadword, which is
the bit vector.
The $MNTDEF macro defines symbolic names for each option (bit) in the
bit vector. You construct the bit vector by specifying the symbolic
names for the desired options in a logical OR operation. In the first
longword you logically OR the MNT$M_ mask bits, and in the second
longword you logically OR the MNT2$M_ mask bits. The following table
describes the symbolic names for each option. The MNT2$M_ options are
at the end of the table.
| Option |
Description |
|
MNT$M_CLUSTER
|
The volume is to be mounted for clusterwide access; that is, every
OpenVMS Cluster node can access the volume. $MOUNT mounts the volume
first on the caller's node and then on every other node in the existing
cluster.
Only system or group volumes can be mounted clusterwide. If you do
not specify MNT$M_GROUP or MNT$M_SYSTEM, $MOUNT mounts the volume as a
system volume, provided the caller has SYSNAM privilege. To mount a
group volume clusterwide, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. To
mount a system volume clusterwide, the caller must have SYSNAM
privilege.
MNT$M_CLUSTER has no effect if the system is not a member of a
cluster. MNT$M_CLUSTER applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_FOREIGN
|
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is
not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_FOREIGN, the following
item codes can each appear in the item list only once: the caller must
either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_GROUP
|
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the group
logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to other users
with the same UIC group number as that of the calling process. To
specify MNT$M_GROUP, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. MNT$M_GROUP
applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_INCLUDE
|
Automatically reconstructs a shadow set to the state it was in before
the shadow set was dissolved (due to dismounting or system failure).
Use this option to mount a shadow set or a volume set of shadow sets.
You must specify the exact name of the original virtual unit and the
device name of at least one of the shadow set members. The shadowing
software reads the shadow set membership information from the named
device to determine the membership of the original shadow set. You can
include the MNT$M_INCLUDE option in executable images to have a shadow
set reconstructed. Using MNT$M_INCLUDE prevents your having to manually
reinstate shadow sets after they have been dismounted.
If you do not select this option, $MOUNT does not automatically
reconstruct the former shadow set.
|
|
MNT$M_INIT_CONT
|
Additional volumes in the volume set are to be initialized without
operator intervention. $MOUNT initializes new volumes with the
protections specified for the first magnetic tape of the volume set and
creates unique volume label names for up to 99 volumes in a volume set.
|
|
|
If MNT$M_INIT_CONT is specified, you must allocate multiple magnetic
tape drives to the volume set. If $MOUNT switches to a drive that has
no magnetic tape loaded or has the wrong magnetic tape loaded or if
$MOUNT tries to read a magnetic tape that is not loaded, it notifies
the operator to load the correct magnetic tape. $MOUNT will dismount
and unload volumes as soon as they have been read or written. The
operator can load the next volume in the volume set before the current
reel of the volume set reaches the end of the magnetic tape.
|
|
|
If writing to the volume set, $MOUNT automatically (1) switches to the
next magnetic tape drive, (2) initializes that magnetic tape with the
same volume name and protection as specified in the volume labels of
the first volume in the set, and (3) notifies the operator that the
switch has occurred. If reading the volume set, $MOUNT generates the
label for the next volume in the volume set and reads that volume.
|
|
|
The label name that $MOUNT generates for each additional volume in the
volume set consists of six characters: the first four characters are
the same as the first four characters of the label name of the previous
volume; the fifth and sixth characters represent the number of the
volume in the volume set.
MNT$M_INIT_CONT applies only to magnetic tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_MESSAGE
|
Messages will be sent to the caller's SYS$OUTPUT device.
|
|
MNT$M_MINICOPY_OPTIONAL
|
$MOUNT fails if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk.
|
|
MNT$M_MINICOPY_REQUIRED
|
$MOUNT continues even if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk.
|
|
MNT$M_MULTI_VOL
|
Specifies, for foreign or unlabeled magnetic tapes, that subsequent
volumes can be processed by overriding MOUNT's access checks. You can
use this option when a utility that supports multivolume magnetic tape
sets needs to process subsequent volumes, and these volumes do not
contain labels that MOUNT can interpret. You need VOLPRO privilege to
specify the MNT$M_MULTI_VOL option. MNT$M_MULTI_VOL can only be used
with the MNT$M_FOREIGN option.
HP recommends the use of this qualifier only when it is not
possible to alter the utility to explicitly perform MOUNT and DISMOUNT
operations on each reel in the set.
|
|
MNT$M_NOASSIST
|
$MOUNT does not request operator assistance if errors are encountered
during the mount operation. If not specified, $MOUNT requests operator
assistance to recover from some error conditions.
|
|
MNT$M_NOAUTO
|
Automatic volume labeling (AVL) and automatic volume recognition (AVR)
are to be disabled. If MNT$M_NOAUTO is specified, the operator must
enter commands from the console to process each additional volume in a
volume set. When a volume is finished processing, the operator
specifies the drive on which the next volume is loaded and the label
name of the next volume. You might want to use MNT$M_NOAUTO to disable
AVL and AVR when not reading a volume set sequentially.
You can enable AVL and AVR by specifying MNT$M_INIT_CONT.
MNT$M_NOAUTO applies only to magnetic tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_NOCACHE
|
All caching associated with the volume is turned off. Specifying
MNT$M_NOCACHE is equivalent to (1) specifying MNT$M_WRITETHRU, (2)
specifying a value of 1 for the item descriptor MNT$_FILEID, and (3)
specifying a value of 0 for the item descriptors MNT$M_EXTENT and
MNT$M_QUOTA.
|
|
MNT$M_NOCOPY
|
Disables full copy operations on all physical devices being mounted or
added to a shadow set. This option provides you with the opportunity to
confirm the states of all of the devices or members of a shadow set
before proceeding with any full copy operation. This prevents any
accidental loss of data that could occur if an unintended device is
added to the shadow set.
If you do not select this option, $MOUNT automatically overwrites
the data on shadow set members that are not current. When you select
this option, a $MOUNT operation fails if any of the specified potential
shadow set members require full copy operations.
|
|
MNT$M_NODISKQ
|
Disk quotas are not to be enforced for the volume to be mounted. If not
specified, disk quotas are enforced. To specify MNT$M_NODISKQ, the
caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
MNT$M_NODISKQ applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_NOHDR3
|
ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are not to be written to magnetic tapes as
they are mounted. If not specified, ANSI HDR3 and HDR4 labels are
written to all tapes.
Use MNT$M_NOHDR3 when writing to volumes that will be read by a
system, such as the RT-11 system, which does not process HDR3 and HDR4
labels correctly. MNT$M_NOHDR3 applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_NOLABEL
|
The volume is to be mounted as a foreign volume; a foreign volume is
not Files-11 structured. If you specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the following
item codes can each appear in the item list only once: MNT$_DEVNAM,
MNT$_VOLNAM, and MNT$_LOGNAM. To specify MNT$M_NOLABEL, the caller must
either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_NOMNTVER
|
The volume is not marked as a candidate for automatic mount
verification. If not specified, the volume is marked as a candidate for
mount verification.
|
|
MNT$M_NOREBUILD
|
The volume to be mounted should be returned to active use immediately,
without performing a rebuild operation. This flag defers the disk
rebuild operation, so that the volume to be mounted is returned to
active use immediately. A rebuild operation can consume a considerable
amount of time, depending on the number of files on the volume and on
the number of different file owners (if quotas are in use). The volume
can be rebuilt later with the DCL command SET VOLUME/REBUILD to recover
the free space; for more information, refer to the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
If a disk volume is improperly dismounted, for example, during a
system failure, it must be rebuilt to recover any caching limits that
were enabled on the volume at the time of the dismount. By default,
$MOUNT attempts to rebuild.
When mounting a volume set, you must mount all members of the set
to reclaim all available free space.
MNT$M_NOREBUILD applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_NOUNLOAD
|
The volume to be mounted is not to be unloaded when it is dismounted.
Specifying MNT$M_NOUNLOAD causes the volume to remain loaded when it is
dismounted unless the dismount explicitly requests that the volume be
unloaded.
|
|
MNT$M_NOWRITE
|
The volume to be mounted is software write locked. If not specified,
the volume is assumed to have read and write access.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS
|
If the installation allows, this option overrides any character in the
accessibility field of the volume. The necessity of this option is
defined by the installation. That is, each installation has the option
of specifying a routine that the magnetic tape file system will use to
process this field. By default, the operating system provides a routine
that checks this field in the following manner:
- If the magnetic tape was created on a version of the operating
system that conforms to Version 3 of ANSI, then you must use this
option to override any character other than an ASCII space.
- If a protection is specified and that magnetic tape conforms to an
ANSI standard that is higher than Version 3, then you must use this
option to override any character other than an ASCII 1.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume
or have VOLPRO privilege. MNT$M_OVR_ACCESS applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_EXP
|
A tape that has not yet reached its expiration date can be overwritten.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_EXP, the caller must own the volume or have VOLPRO
privilege.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_IDENT
|
You can mount the volume without specifying the volume name (by using
the MNT$_VOLNAM item code). If specified, the following options must
not be specified: MNT$M_CLUSTER, MNT$M_GROUP, MNT$M_SHARE, and
MNT$M_SYSTEM.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_LOCK
|
The software write lock that occurs when a volume has a corrupted
storage bit mask can be overridden.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_SETID
|
Checks on the volume set identification are not to be performed when
subsequent reels in the volume set are mounted. MNT$M_OVR_SETID applies
only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_SHAMEM
|
Allows you to mount former shadow set members outside of the shadow
set. If you do not specify this option, $MOUNT automatically mounts the
volume write-locked to prevent accidental deletion of data. To specify
this option, you must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
When you use this option, the shadow set generation number is
erased from the volume. If you then remount the volume in the former
shadow set, $MOUNT considers it an unrelated volume and marks it for a
full copy operation.
|
|
MNT$M_OVR_VOLO
|
The volume label's owner identifier field is not to be processed.
$MOUNT reads volume owner and protection information from the volume
owner field of the volume labels.
The operating system requires that you specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO to
process magnetic tapes when all of the following conditions exist: (1)
the volume was created on an operating system other than OpenVMS; (2)
the volume was initialized with a protection specified; and (3) the
volume conforms to the Version 3 ANSI label standard.
To specify MNT$M_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either have VOLPRO
privilege or own the volume. MNT$M_OVR_VOLO applies only to tapes.
|
|
MNT$M_READCHECK
|
Read checks are to be performed following all read operations.
|
|
MNT$M_REQUIRE_MEMBERS
|
Controls whether every physical device specified with the /SHADOW
qualifier must be accessible when the MOUNT command is issued in order
for the $MOUNT system service to take effect.
|
|
MNT$M_SHARE
|
Volume is to be mounted shared and is therefore accessible to other
users. MNT$M_SHARE applies only to disks.
If the volume was previously mounted shared by another user and
MNT$M_SHARE is specified in the current call, all other options
specified in the current call are ignored.
If the caller allocated the device and specified MNT$M_SHARE in the
call to $MOUNT, $MOUNT will deallocate the device so that other users
can access the volume.
|
|
MNT$M_SYSTEM
|
The logical name for the volume to be mounted is entered in the system
logical name table, and the volume is made accessible to all other
users, provided that UIC-based protection allows access to the volume.
To specify MNT$M_SYSTEM, the caller must have SYSNAM privilege.
MNT$M_SYSTEM applies only to disks.
|
|
MNT$M_TAPE_DATA_WRITE
|
Enables the tape controller's write cache for this device. Enabling the
write cache improves data throughput for write operations. By default,
the tape controller's write cache is disabled for the device.
This option applies only to tape systems that support a write cache.
|
|
MNT$M_VERIFY_LABEL
|
Requires that any member to be added to the shadow set have a volume
label of SCRATCH_DISK. This helps ensure that the wrong disk is not
added to a shadow set. If you plan to use VERIFY_LABEL, you must first
assign the disk to a label. You can do this either by initializing the
disk to be added to the set with the label SCRATCH_DISK, or by
specifying the label for the disk with the SET VOLUME/LABEL command.
|
|
MNT$M_WRITECHECK
|
Write checks are to be performed after all write operations.
|
|
MNT$M_WRITETHRU
|
Disables the deferred write feature for file headers. By default this
feature is enabled, which improves the performance of the applications,
such as PATHWORKS, that use it. The deferred write feature is not
available on Files-11 ODS-1 volumes.
|
|
MNT2$M_CDROM
|
Mounts a volume assuming the media to be ISO 9660 (or High Sierra)
formatted.
|
|
MNT2$M_COMPACTION
|
Enables data compaction for those magnetic tapes that support data
compaction (TA90, TA91, and others).
|
|
MNT2$M_DISKQ
|
Controls whether quotas are to be enforced on the specified disk volume.
|
|
MNT2$_DSI
|
Enables XAR permissions Owner and Group for XARs containing DIGITAL
System Identifiers (DSI). For more information, refer to the
OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
|
|
MNT2$_INCLUDE
|
Automatically reconstructs a former shadow set to the way it was before
the shadow set was dissolved. Applicable only if you have the volume
shadowing option. For more information, refer to HP Volume Shadowing for OpenVMS.
|
|
MNT2$M_NOCOMPACTION
|
Forces the density to no compaction for those magnetic tapes that
support data compaction (TA90, TA91, and others).
|
|
MNT2$_OVR_LIMITED_SEARCH
|
For disk type devices that do not provide for bad-block revectoring, it
is possible that the Files-11 homeblock has been placed numerous I/Os
from the start of the volume. To decrease the failover time when
accessing media which does not contain a valid Files-11 homeblock, a
limited-search algorithm was implemented. This switch overrides the
limited-search algorithm so that the entire volume will be searched for
a valid Files-11 homeblock.
|
|
MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE
|
This bit mask is set to override those SCSI devices that do not support
forced error functionality. By overriding those SCSI devices not
supporting forced error capabilities, MNT2$M_OVR_NOFE enables those
devices to be mounted; otherwise, the shadowing code would report to
$MOUNT that the device does not support forced error, and the device
would not be mounted.
|
|
MNT2$_OVR_SECURITY
|
Enables you to continue mounting a volume if an error is returned
because the volume has an invalid SECURITY.SYS file. You must have the
VOLPRO privilege or own the volume to use this keyword.
|
|
MNT2$M_SUBSYSTEM
|
Enables the processing of protected subsystem identifiers on the
volume. By default, subsystem identifiers are ignored on all but the
system disk. Requires SECURITY privilege.
|
|
MNT2$M_XAR
|
Enables enforcement of the extended record attribute (XAR) access
controls. For more information about XAR, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
|
MNT$_LIMIT
Specifies the maximum amount of free space in the extent cache. The
buffer must contain a longword value, which specifies the amount of
free space in units of tenths of a percent of the disk's total free
space. The MNT$_LIMIT item code applies only to disks.
MNT$_LOGNAM
Specifies a logical name for the volume; this logical name is equated
to the device name specified by the first MNT$_DEVNAM item code. The
buffer must contain a character string from 1 to 64 characters, which
is the logical name.
|
