 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
Additional References
6.8.30 REWRITE
Function
The REWRITE statement logically replaces a mass storage file record.
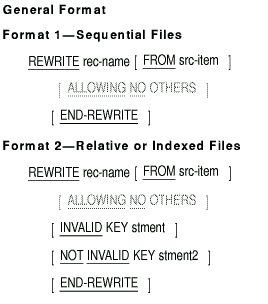
rec-name
is the name of a logical record in the Data Division File Section. It
can be qualified.
src-item
is the identifier of the data item that contains the data.
stment
is an imperative statement executed for an invalid key condition.
stment2
is an imperative statement executed for a not invalid key condition.
Syntax Rules
- To use the ALLOWING option, the program must include these entries:
- APPLY LOCK-HOLDING clause of the I-O-CONTROL paragraph
- ALLOWING clause of the OPEN statement
- The INVALID KEY and the NOT INVALID KEY phrases cannot be specified
in a REWRITE statement that refers to a sequential file or to a
relative file with sequential access mode.
- For a relative file with random or dynamic access mode, or for an
indexed file, the REWRITE statement must have an INVALID KEY phrase
when there is no applicable USE AFTER EXCEPTION procedure for the file.
- If src-item is a function-identifier, it must reference an
alphanumeric function. When src-item is not a
function-identifier, rec-name and src-item must not
reference the same storage area.
- The ALLOWING clause is Hewlett-Packard standard file-sharing
syntax, and cannot be used for a file connector that has had X/Open
standard file-sharing syntax (WITH [NO] LOCK or LOCK MODE) specified.
General Rules
All Files
- The file associated with rec-name must be a mass storage
file. It must be open in the I-O mode when the REWRITE statement
executes.
Because line sequential files (Alpha, I64) cannot be opened in I-O
mode, REWRITE cannot be used with line sequential files. <>
- For sequential access mode files, the last input-output statement
executed for the file before the REWRITE statement must be a
successfully executed READ statement. The REWRITE statement logically
replaces the record accessed by the READ.
- The READ must lock the record for the REWRITE statement to be
successful.
- The record in rec-name is no longer available after the
REWRITE statement successfully executes unless the associated file-name
is in a SAME RECORD AREA clause. In this case, the record is also
available to record areas of other file-names in the SAME RECORD AREA
clause.
- The REWRITE statement does not affect the File Position Indicator.
- The REWRITE statement updates the value of the FILE STATUS data
item for the file.
- The ALLOWING option can be used only in a Hewlett-Packard standard,
manual record-locking environment. To create a manual record-locking
environment, the program must OPEN file-name with an ALLOWING option
and specify the APPLY LOCK-HOLDING phrase of the I-O-CONTROL paragraph.
- The ALLOWING option locks the current record rewritten by the
current access stream. No other concurrent access stream can access
this record until it is unlocked.
However, on Tru64 UNIX
systems, for indexed files the REWRITE statement with the ALLOWING
clause does not acquire a record lock. <>
- See the FROM Phrase section for a list of rules for the FROM phrase.
Sequential Files
- The record named by rec-name must be the same size as the
record being replaced.
Relative Files
- For a random or dynamic access mode file, the REWRITE statement
logically replaces the record specified in the RELATIVE KEY data item
for rec-name's file. If the record is not in the file, the
invalid key condition exists. The update does not occur, and the data
in the record area is not affected.
Indexed Files
- For a sequential access mode file, the prime record key specifies
the record to be replaced. The values of the prime record keys in the
record to be replaced and the last record read from (or positioned in)
the file must be equal.
- For a random access mode file, the prime record key specifies the
record to replace. If the program specifies duplicates on the prime
record key, then it can replace only the first occurrence of a key
value using random access mode. Replacing subsequent records with the
same prime key value is done by sequentially positioning to the desired
record in sequential or dynamic access mode.
- For indexed files in dynamic access mode, the presence of
DUPLICATES on the prime record key determines the behavior. If
DUPLICATES are allowed, Rule 11 applies. If DUPLICATES are not allowed,
Rule 12 applies.
- For a record with an alternate record key:
- When the REWRITE does not change the value of an alternate record
key, the order of retrieval is unchanged when the key is the Key of
Reference.
- When duplicate key values are allowed, and the value of an
alternate record key changes, the later retrieval order of the record
changes when the key is the Key of Reference. The record's logical
position is last in the group of records with the same value in the
alternate record key that changed.
- Any of the following occurrences cause the invalid key condition:
- The access mode is sequential, and the values in the prime record
keys of the record to replace and the last record read from (or
positioned in) the file are not equal.
- The value in the prime record key does not equal that of any record
in the file.
- The value in an alternate record key whose definition does not have
a DUPLICATES clause equals that of a record already in the file.
The update does not occur, and the data in the record area is not
affected.
- If there is an applicable USE AFTER EXCEPTION procedure, it
executes whenever an input or output condition occurs that would result
in a nonzero value in the first character position of a FILE STATUS
data item. However, the INVALID KEY phrase (if present) supersedes a
USE AFTER EXCEPTION procedure when there is an invalid key condition.
In this case, the USE AFTER EXCEPTION procedure does not execute.
See the rules for the INVALID KEY phrase, Section 6.6.10.
- The number of character positions in the record to be updated must
not be less than the lowest or greater than the highest number of
character positions allowed by the RECORD VARYING clause. In either
case, the REWRITE statement is unsuccessful and the following occurs:
- The updating operation does not take place.
- The contents of the record area remain unaffected.
- The I-O status of the file is set to a value that indicates the
cause of the condition.
Technical Notes
- REWRITE statement execution can result in these FILE STATUS data
item values:
File
Status |
File
Organization |
Access
Method |
Meaning |
|
00
|
All
|
All
|
Rewrite is successful.
|
|
02
|
Ind
|
All
|
Created duplicate primary or alternate key.
|
|
21
|
Ind
|
Seq
|
Primary key changed after read.
|
|
22
|
Ind
|
All
|
Duplicate primary or alternate key (invalid key).
|
|
23
|
Ind, Rel
|
Rand
|
Record not in file (invalid key).
|
|
43
|
All
|
Seq
|
No previous read or record not locked by prior READ or START.
|
|
44
|
All
|
All
|
Invalid record size.
|
|
49
|
All
|
All
|
File not open, or incompatible open mode.
|
|
92
|
Ind, Rel
|
All
|
Record locked by another user; record is not available.
|
|
30
|
All
|
All
|
All other permanent errors.
|
Additional References
|
