user_action_procedure is a Windows command or valid file
name. The file must contain one or more Windows command statements to
form a valid command procedure. (See the example in this section.)
Enter the name of the procedure you want Windows to execute using
the following format:
device:\(directory\filename.BAT
where:
- device is the disk on which the procedure is located.
- directory is the folder in which the procedure is located.
- filename.BAT is the name of the command file to be
executed.
Notes
The file name must follow Windows file-naming conventions. However, due
to the processing of spaces in the Java JRE, HP recommends that you do
not use spaces in a path or file name.
HP recommends that you use a
batch file to process and call procedures and applications.
|
- The arguments are listed in the table in Section 7.6.2.1.
The Availability Manager does not interpret the string contents. You
can supply any content in the string that the Windows command-line
interpreter accepts for the user account running the Data Analyzer.
However, if you include arguments in the User Action procedure, they
might displace or overwrite arguments supplied by the Availability
Manager.
You cannot specify positional command-line switches or arguments to the
AT command, although you can include switches in the User Action
procedure substring as qualifiers to the user-supplied command. This is
a limitation of both the Windows command-line interpreter and the way
the entire string is passed from the Availability Manager to Windows.
The Schedule service must be running on the Data Analyzer computer in
order to use the AT command. However, the Schedule service does not run
by default. To start the Schedule service, see the Windows
documentation for instructions in the use of the CONTROL
PANEL->SERVICES->SCHEDULE->[startup button].
Windows Example
To set up a user action, follow these steps:
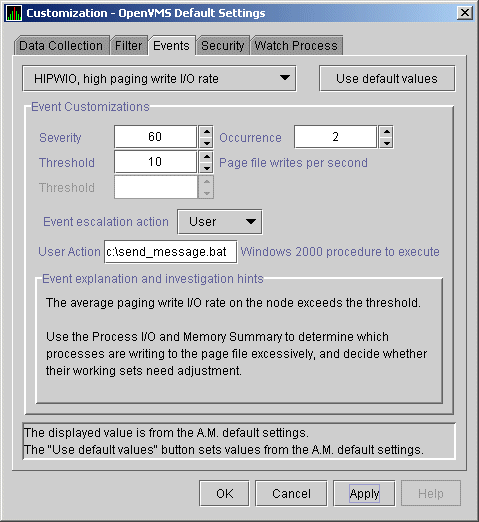
- Select an event on the Events Customization page, for example,
HIBIOR (see Figure 7-17).
- Change the Event escalation action to User.
- Enter the name of the program to run, for example:
Figure 7-17 User Action Example
The command line parameters are automatically added when Availability
Manager passes the command to the command processor.
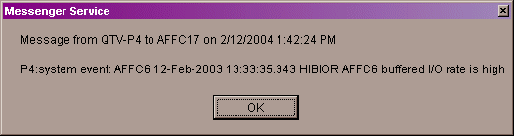
The contents of "send_message.bat" are the following:
net send affc17 "P4:system event: %1 %2 %3 %4"
|
On the target node, AFFC17, a message similar to the following is
displayed:
You can now apply the User Action to one node, all nodes, or a group of
nodes, as explained in Section 7.6.2.
7.7 Customizing Security Features
The following sections explain how to change these security features:
- Data Analyzer passwords for OpenVMS and Windows Data Collector nodes
- OpenVMS Data Collector security triplets
- A Windows Data Collector password
Note
OpenVMS Data Collector nodes can have more than one password: each
password is part of a security triplet. (Windows nodes allow you to
have only one password per node.)
|
7.7.1 Changing Data Analyzer Passwords
You can change the passwords that the Windows Data Analyzer uses for
OpenVMS Data Collector nodes and for Windows Data Collector nodes. The
following sections explain how to perform both actions.
7.7.1.1 Changing a Data Analyzer Password for an OpenVMS Data Collector Node
When you click Customize OpenVMS... on the
Customize menu of the Application window, the
Availability Manager displays a default customization page. On it is a tab
marked Security, which, if you select it, displays the
OpenVMS Security Customization page shown in Figure 7-18.
Figure 7-18 OpenVMS Security Customization Page
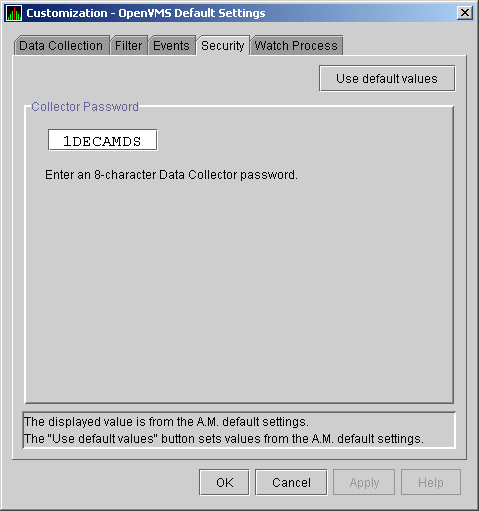
To change the default password for the Data Analyzer to use to access
OpenVMS Data Collector nodes, enter a password of exactly 8 uppercase
alphanumeric characters. The Availability Manager will use this password to
access OpenVMS Data Collector nodes. This password must match the
password that is part of the OpenVMS Data Collector security triplet
(see Section 7.7.2).
When you are satisfied with your password, click OK.
Exit the Availability Manager, and restart the application for the password to
take effect.
7.7.1.2 Changing a Data Analyzer Password for a Windows Data Collector Node
When you click Customize Windows NT... on the
Customize menu of the Application window, the
Availability Manager displays a Windows Security Customization page
(Figure 7-19).
Figure 7-19 Windows Security Customization Page
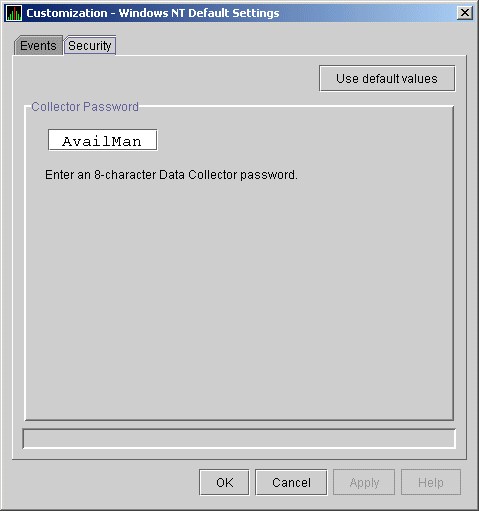
To change the default password for the Data Analyzer to use to access
Windows Data Collector nodes, enter a password of exactly 8
alphanumeric characters. Note that this password is case sensitive; any
time you type it, you must use the original capitalization.
This password must also match the password for the Windows Data
Collector node that you want to access. (See Section 7.7.3 for
instructions for changing that password.)
When you are satisfied with your password, click OK.
Exit and restart the Availability Manager for the password to take effect. affc
7.7.2 Changing Security Triplets on OpenVMS Data Collector Nodes
To change security triplets on an OpenVMS Data Collector node, you must
edit the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file, which is installed on all Data
Collector nodes. The following sections explain what a security triplet
is, how the Availability Manager uses it, and how to change it.
7.7.2.1 Understanding OpenVMS Security Triplets
A security triplet determines which nodes can access system data from
an OpenVMS Data Collector node. The AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file on
OpenVMS Data Collector nodes lists security triplets.
On OpenVMS Data Collector nodes, the AMDS$AM_CONFIG logical translates
to the location of the
default security file, AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT.
This file is installed on all OpenVMS Data Collector nodes.
A security triplet is a three-part record whose fields are separated by
backslashes (\). A triplet consists of the following fields:
- A network address (hardware address or wildcard character)
- An 8-character alphanumeric password
The password is not case
sensitive (so the passwords "testtest" and
"TESTTEST" are considered to be the same).
- A read, write, or control (R, W, or C) access verification code
The exclamation point (!) is a comment delimiter; any characters to the
right of the comment delimiter are ignored.
Example
All Data Collector nodes in group FINANCE have the following
AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file:
*\FINGROUP\R ! Let anyone with FINGROUP password read
!
2.1\DEVGROUP\W ! Let only DECnet node 2.1 with
! DEVGROUP password perform fixes (writes)
|
7.7.2.2 How to Change a Security Triplet
Note
The configuration files for DECamds and the Availability Manager are
separate; only one set is used, depending on which startup command
procedure you use to start the driver.
See Installing the Availability Manager on OpenVMS Alpha Systems
and Running DECamds and the Availability Manager Concurrently for
a further explanation of the configuration file setup for both DECamds
and the Availability Manager.
|
On each Data Collector node on which you want to change security, you
must edit the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file. The data in the
AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file is set up as follows:
Network address\password\access
|
Use a backslash character (\) to separate the three fields.
To edit the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file, follow these steps:
- Edit the network address.
The network address can be either of
the following:
- Hardware address
The hardware address field is the physical
hardware address in the LAN device chip. It is used if you have
multiple LAN devices or are running the HP DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS
networking software on the system (not the HP DECnet Phase IV for
OpenVMS networking software).
For devices provided by HP, the
hardware address is in the form 08-00-2B-xx-xx-xx, where the
08-00-2B portion is HP's valid range of LAN addresses as defined by the
IEEE 802 standards, and the xx-xx-xx portion is chip specific.
To determine the value of the hardware address on a node, use the
OpenVMS System Dump Analyzer (SDA) as follows:
$ ANALYZE/SYSTEM
SDA> SHOW LAN
|
These commands display a list of available devices. Choose the
template device of the LAN device you will be using, and then enter the
following command:
SDA> SHOW LAN/DEVICE=xxA0
|
- Wildcard address
The wildcard character (*) allows any incoming
triplet with a matching password field to access the Data Collector
node. Use the wildcard character to allow read access and to run the
console application from any node in your network.
Because the Data
Analyzer does not use this field, use the wildcard character in this
field in the AMDS$CONSOLE_ACCESS.DAT file.
Caution: Use of the wildcard character for
write-access security triplets enables any person using that node to
perform system-altering fixes.
- Edit the password field.
The password field must
be an 8-byte alphanumeric field. The Availability Manager forces
upper-case on the password, so "aaaaaaaa" and "AAAAAAAA" are
essentially the same password to the Data Collector.
The password
field gives you a second level of protection when you want to use the
wildcard address denotation to allow multiple modes of access to your
monitored system.
- Enter R, W, or C as an access code:
- R means READONLY access to the Data Analyzer.
- W means READ/WRITE access to the Data Analyzer. (WRITE implies
READ.)
- C means CONTROL access to the Data Analyzer. CONTROL allows you to
manipulate objects from which data are derived. (CONTROL implies both
WRITE and READ.)
The following security triplets are all valid; an explanation follows
the exclamation point (!).
*\1decamds\r ! Anyone with password "1decamds" can monitor
*\1decamds\w ! Anyone with password "1decamds" can monitor or write
2.1\1decamds\r ! Only node 2.1 with password "1decamds" can monitor
2.1\1decamds\w ! Only node 2.1 with password "1decamds" can monitor and write
08-00-2b-03-23-cd\1decamds\w ! Allows a particular hardware address to write
08-00-2b-03-23-cd\1decamds\r ! Allows a particular hardware address to read node
|
OpenVMS Data Collector nodes accept more than one password. Therefore,
you might have several security triplets in an AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT
file for one Data Collector node. For example:
*\1DECAMDS\R
*\KOINECLS\R
*\KOINEFIX\W
*\AVAILMAN\C
|
In this example, Data Analyzer nodes with the passwords 1DECAMDS and
KOINECLS would be able to see the Data Collector data, but only the
Data Analyzer node with the KOINEFIX password would be able to write or
change information, including performing fixes, on the Data Collector
node. The Data Analyzer node with the AVAILMAN password would be able
to perform switched LAN fixes.
If you want, you can set up your AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file to allow
anyone in the world to read from your system but allow only certain
nodes to write or change process or device characteristics on your
system.
Note
After editing the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file, you must stop and then
restart the Data Collector. This action loads the new data into the
driver.
|
7.7.2.3 How the Availability Manager Ensures Security
The Availability Manager performs these steps when using security triplets to
ensure security among Data Analyzer and Data Collector nodes:
- A message is broadcast at regular intervals to all nodes within the
LAN indicating the availability of a Data Collector node to communicate
with a Data Analyzer node.
- The node running the Data Analyzer receives the availability message
and returns a security triplet that identifies it to the Data
Collector, and requests system data from the Data Collector.
- The Data Collector examines the security triplet to determine
whether the Data Analyzer is listed in the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file
to permit access to the system.
- If the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT file lists Data Analyzer access
information, then the Data Provider and the Data Analyzer can exchange
information.
- If the Data Analyzer is not listed in the AMDS$DRIVER_ACCESS.DAT
file or does not have appropriate access information, then access is
denied and a message is logged to OPCOM. The Data Analyzer receives a
message stating that access to that node is not permitted.
Table 7-4 describes how the Data Collector node interprets a
security triplet match.
Table 7-4 Security Triplet Verification
| Security Triplet |
Interpretation |
|
08-00-2B-12-34-56\HOMETOWN\W
|
The Data Analyzer has write access to the node only when the Data
Analyzer is run from a node with this hardware address (multiadapter or
DECnet-Plus system) and with the password HOMETOWN.
|
|
2.1\HOMETOWN\R
|
The Data Analyzer has read access to the node when run from a node with
DECnet for OpenVMS Phase IV address 2.1 and the password HOMETOWN.
|
|
*\HOMETOWN\R
|
Any Data Analyzer with the password HOMETOWN has read access to the
node.
|
7.7.3 Changing a Password on a Windows Data Collector
To change the Data Collector password in the Registry, follow these
steps:
- Click the Windows Start button. On the menu
displayed, first click Programs, then
Accessories, and then Command Prompt.
- Type
regedit
after the angle prompt (>).
The system displays a screen for the
Registry Editor, with a list of entries under My Computer.
- On the list displayed, expand the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
entry.
- Double-click SYSTEM.
- Click CurrentControlSet.
- Click Services.
- Click damdrvr.
- Click Parameters.
- Double-click Read Password. Then type a new
8-character alphanumeric password, and click OK to
make the change.
- To store the new password, click Exit under File
on the main menu bar.
- On the Control Panel, click Services and then
Stop for "PerfServ."
- Again on the Control Panel, click Devices and then
Stop for "damdrvr."
- First restart damdrvr under "Devices"
and then restart PerfServ under "Services."
This step completes the change of your Data Collector password.