 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for
future use by HP. The condition value SS$_IVREGFLG is returned if any
undefined bits are set.
return_region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
region identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the created region. The
return_region_id_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit
virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service
returns the region ID.
return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
return address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the region. The
return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the lowest virtual address of the region.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the returned virtual address is
aligned to a CPU-specific page table page boundary. If the global
section mapped by this shared page table region is large enough that
multiple page table pages are required to map the global section, the
page tables themselves can be mapped with granularity hints; therefore,
the alignment of the returned virtual address can be even greater than
that of a single CPU-specific page table page boundary.
return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
byte count |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the region actually created. The
return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual
address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns
the length of the region in bytes.
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the returned length is the input
length rounded up to an even multiple of bytes mapped by a single
CPU-specific page table page.
start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: |
address |
| type: |
quadword address |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The starting address for the created virtual region. The specified
virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.
If the start_va_64 argument is not specified or is
specified as 0, the region can be created anywhere within the following
address spaces:
- P2 space (if the flags VA$M_P0_SPACE and VA$M_P1_SPACE are clear)
- P0 space (if the flag VA$M_P0_SPACE is set and VA$M_P1_SPACE is
clear)
- P1 space (if the flag VA$M_P1_SPACE is set and VA$M_P0_SPACE is
clear)
If the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set and this argument is specified, the
specified starting address must be aligned to the larger of a natural
page table boundary or the largest possible page size used to map the
section. If the alignment is less than a page table boundary, the
$CREATE_REGION_64 service returns an error. If the alignment is less
than the largest page size used in the section, an error might be
returned when you attempt to map the section.
If you do not specify a starting address, OpenVMS automatically ensures
correct alignment.
Description
The Create Virtual Region service allows a process to create a virtual
region within its P0, P1, or P2 address space. Once a virtual region
has been created, virtual address space can be created within it using
the system services that accept a region identifier argument. Note that
the virtual region is simply a reservation of virtual address space. No
physical memory is occupied for a virtual region until virtual address
space is created within the region.
If the VA$M_SHARED_PTS flag is set in the flags
argument, only memory-resident global sections can be mapped into the
virtual region. The $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 and $MGBLSC_64 system services are
available for mapping to memory-resident global sections. If a
memory-resident global section was not created with shared page tables,
private page tables are used to map to the global section.
If a memory-resident global section with shared page tables is mapped
into a virtual region that does not have the shared page table
attribute, the global section is mapped with process private page
tables. Other address-space creation services (see Table SYS-18) are
not allowed to create address space into a shared page table region
because they have an implicit dependency on process-private page
tables.
Table SYS-18 Services That Do Not Accept Shared Page Table Regions
| Service |
Description |
|
$CRETVA[_64]
|
Adds a range of demand-zero allocation pages to a process's virtual
address space for the execution of the current image. The new pages are
added at the virtual address specified by the caller.
|
|
$CRMPSC
|
Allows a process to create a private or global section and to map a
section of its address space to the private or global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_FILE_64
|
Allows a process to map a section of its address space to a specified
portion of a file. This service maps a private disk file section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64
|
Allows a process to create a global disk file section and to map a
section of its address space to the global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64
|
Allows a process to create a global page file section and to map a
section of its address space to the global section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64
|
Allows a process to create a permanent global page frame section and to
map a section of its address space to the global page frame section.
|
|
$CRMPSC_PFN_64
|
Allows a process to map a section of its address space to a specified
physical address range represented by page frame numbers. This service
creates and maps a private page frame section.
|
|
$DELTVA
|
Deletes a specified number of pages from a process's virtual address
space.
|
|
$EXPREG_[64]
1
|
Adds a specified number of demand-zero allocation pages to a process's
virtual address space for the execution of the current image. Expansion
occurs at the next free available address within the specified region.
|
|
$MGBLSC
|
Establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space
of the process and the pages occupied by a global section.
|
|
$MGBLSC_GPFN_64
|
Establishes a correspondence between pages in the virtual address space
of the process and the pages occupied by a global page frame section.
|
1$EXPREG can specify only the P0 or P1 region and thus
cannot specify a shared page table region.
$CREATE_REGION_64 creates the virtual region on a CPU-specific page
aligned boundary; however, if the VA$M_SHARED_PTS flag is set in the
flags argument, the virtual region is created on a
CPU-specific page table page aligned boundary.
HP recommends that you not specify the start_va_64
argument when creating a shared page table region due to the particular
alignment that must prevail for virtual addresses created within the
virtual region to exploit page table sharing. If the
start_va_64 argument does not contain the proper
alignment, $CREATE_REGION_64 returns SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN.
If a starting virtual address must be specified for a shared page table
region, use the following steps to compute a properly aligned
start_va_64:
- Determine the CPU-specific page size by using the $GETSYI system
service and specifying the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code.
- Determine the number of CPU-specific pages mapped by a single page
table page by using the $GETSYI system service and specifying the
SYI$_PTES_PER_PAGE item code.
- Multiply the CPU-specific page size by the number of pages mapped
by a page table page. The product represents the minimum virtual
alignment required for a shared page table region. It also represents
the number of bytes mapped by a single CPU-specific page table page.
Assuming a system with an 8 kilobyte page size, the alignment of the
start_va_64 argument must be an even multiple of
8,388,608 (8 megabytes). The virtual address, therefore, must have 23
low-order zero bits.
- If the shared page tables are to be mapped with granularity hints
(GH), the address computed in the previous step should to be adjusted
to account for the granularity hint factor:
- On Alpha systems, granularity hints mean multiples of pages,
regardless of page size. The multiples 8, 64, and 512 pages are
architected.
- On Integrity server systems, OpenVMS initially supports page sizes
of 64KB, 256KB, and 4MB instead of granularity hints. Additional pages
sizes will be supported in the future.
The virtual address alignment factors required for shared page table
regions (and mappings using shared page tables) are more stringent than
the simple CPU-specific page alignment. Global pages provide a level of
data sharing in which the unit is a single CPU-specific page or, on
today's systems, 8 kilobytes (KB). Shared page tables increase the
level of sharing by an order of magnitude, such that the unit of
sharing is a CPU-specific page table page or, on today's systems, 8
megabytes (MB); therefore, virtual regions that are to be used for
shared page tables and mappings that use shared page tables require an
alignment of at least 8 MB.
Table SYS-19 highlights the values $CREATE_REGION_64 returns for
various region lengths. When the length_64 argument is not an even
multiple of 8 MB, the returned length is rounded up to an even multiple
of 8 MB. This must occur so that a shared page table region ends on an
even CPU-specific page table page boundary.
Note
The requirement for CPU-specific page table page multiples for shared
page table regions does not imply that memory-resident global sections
must also be sized at even CPU-specific page table page multiples.
Memory-resident global sections must be specified in single
CPU-specific page multiples as is the case for global page file
sections.
|
The virtual alignment of the returned address is further biased by the
ability to map the shared page tables with granularity hints. All
values listed are based upon an 8 KB page size. All of the virtual
addresses in the return_va_64 column accommodate the
maximum GH factor for 8 KB page table pages.
Table SYS-19 Sample Returned Values from$CREATE_REGION_64
| length_64 |
return_va_64 |
return_length_64 |
Comments |
|
1,048,576 (1 MB)
|
FFFFFFFB00800000 at least 23 zero bits
|
8,388,608 (8 MB)
|
GH not possible for shared page table pages. Region occupies 1 page
table page.
|
|
67,108,864 (64 MB)
|
FFFFFFFBFC000000 at least 26 zero bits
|
67,108,864 (64 MB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 8 for shared page table pages.
|
|
73,400,320 (70 MB)
|
FFFFFFFBF8000000 at least 26 zero bits
|
75,497,472 (72 MB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 8 for shared page table pages.
Region occupies 9 page table pages. Only the first 8 can be mapped with
GH.
|
|
1,073,741,824 (1 GB)
|
FFFFFFFBC0000000 at least 30 zero bits
|
1,073,741,824 (1 GB)
|
Returned VA accommodates GH factor of 64 for shared page table pages.
Region occupies 128 page table pages. In this case, there would be two
GH regions, each containing 64 page table pages.
|
If the returned value of the service is not a successful condition
value, a value is not returned in the memory locations pointed to by
the return_region_id_64,
return_va_64, or return_size_64
arguments.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_GDZRO, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,
$DELTVA_64, $EXPREG_64, $GET_REGION_INFO, $MGBLSC_64, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The
return_region_id_64 argument, the
return_va_64 argument, or the
return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the
caller.
|
|
SS$_IVREGFLG
|
One or more of the reserved bits in the
flags argument is set, or an illegal combination of
flags bits are set.
|
|
SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT
|
The
length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific
pages.
|
|
SS$_VASFULL
|
The process private address space is full, or no space is available in
the process private address space for a region of the specified size.
|
|
SS$_VA_IN_USE
|
A page in the specified virtual address range is within another virtual
region or is otherwise inaccessible.
|
|
SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN
|
The
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned;
or, if the flag VA$M_SHARED_PTS is set, the
start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table
page aligned.
|
$CREATE_UID
Generates a universally unique identifier (UID).
Format
SYS$CREATE_UID uid
C Prototype
int sys$create_uid (unsigned int uid [4]);
Arguments
uid
| OpenVMS usage: |
uid |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of an octaword in which the unique identifier is returned to
the calling process.
Description
Generates an identifier that is unique across all computer systems.
Required Privileges
None
Required Quotas
None
Related Services
None
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The request was successful.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE
Returns an encoded security profile for the specified user.
Format
SYS$CREATE_USER_PROFILE usrnam ,[itmlst] ,[flags] ,usrpro ,usrprolen
,[contxt]
C Prototype
int sys$create_user_profile (void *usrnam, void *itmlst, unsigned int
flags, void *usrpro, unsigned int *usrprolen, unsigned int *contxt);
Arguments
usrnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Name of the user whose security profile is to be returned. The
usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to a text string containing the user name. The user name
string can contain a maximum of 12 alphanumeric characters.
For more information about user names, see the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying the portions of the user's security profile to be
replaced or augmented.
The item list is a standard format item list. The following figure
depicts the general format of an item descriptor. See the Item Codes
section for a list of valid item codes for $CREATE_USER_PROFILE.
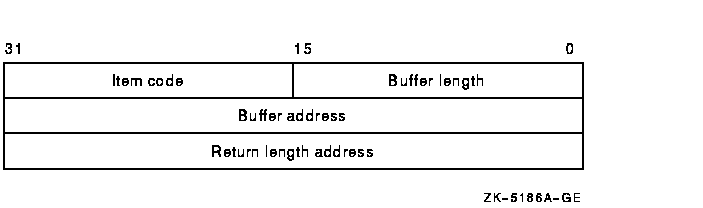
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer from which the service is to read the information.
The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in
the item code field of the item descriptor.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword that normally contains the user-supplied address of a word
in which the service writes the length (in bytes) of the information it
returned. This is not used by $CREATE_USER_PROFILE and should contain a
0.
|
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The flags argument is used to control the behavior of
the $CREATE_USER_PROFILE service. This argument does not accept ISS$
mask values; therefore, continue to use the CHP$ mask values for this
argument.
The following table describes each flag:
| Symbol |
Description |
|
CHP$M_DEFCLASS
|
By default, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE initializes the security profile with
the user's maximum authorized classification. When this flag is set,
the service initializes the security profile from the user's default
classification instead. This flag is reserved to HP.
|
|
CHP$M_DEFPRIV
|
By default, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE initializes the security profile with
the user's authorized privilege mask. When this flag is set, the
service initializes the security profile from the user's default
privilege mask instead.
|
|
CHP$M_NOACCESS
|
Instructs the service not to access the user authorization file
(SYSUAF.DAT) or rights database (RIGHTSLIST.DAT) to build the security
profile. This flag can be used as an optimization when all the
information necessary to build the security profile is known to the
caller.
|
usrpro
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
opaque byte stream |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Buffer to receive the security profile. The usrpro
argument is the address of a buffer to receive the encoded security
profile. If an address of 0 is specified, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns
the size of the buffer needed in the usrprolen
argument.
usrprolen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read/write |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Word to receive the full size of the security profile. On input, the
usrprolen argument specifies the length of the buffer
pointed to by the usrpro argument. The
usrprolen argument is the address of a word to which
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE writes the actual length of the security profile.
If the caller specifies a usrpro address of 0,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns the anticipated size, in bytes, of the
buffer needed to hold the user's security profile in the
usrprolen argument.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Longword used to maintain authorization file context. The
contxt argument is the address of a longword to
receive a $GETUAI context value. On the initial call, this longword
should contain the value --1. On subsequent calls, the value of the
contxt argument from the previous call should be
passed back in.
Using the contxt argument keeps the UAF open across
all calls, thereby improving the performance of the system on
subsequent calls. To close the UAF, you must run down the image.
The resulting context value from a $CREATE_USER_PROFILE call can also
be used as the input contxt argument to the $GETUAI
system service, and vice versa.
Item Codes
CHP$_ADDRIGHTS
A rights list segment containing additional identifiers to be appended
to the set of identifiers held by the user. A rights list segment is a
list of quadword identifier/attributes pairs, each containing a
longword identifier value, followed by a longword mask identifying the
attributes of the holder. The buflen argument should
be set to the total size, in bytes, of the rights list segment. The
bufadr argument points to a descriptor that points to
the first byte in the rights list segment (that is, the first byte of
the first identifier value).
This item code can be repeated to add up to 256 additional rights list
segments. If more than 256 identifiers are granted to the user,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns SS$_INSFMEM.
CHP$_CLASS
The classification to be associated with the created security profile.
This item code is reserved to HP.
CHP$_PRIV
A quadword privilege mask specifying the user's privileges. The $PRVDEF
macro defines the list of available privileges.
CHP$_UIC
A longword describing the user identification code (UIC).
ISS$_ACCOUNT
Variable-length buffer containing the account name. The maximum size of
this buffer is 32 bytes.
ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS
A rights list segment containing additional identifiers to be appended
to the set of identifiers held by the user. A rights list segment is a
list of quadword identifier/attributes pairs, each containing a
longword identifier value, followed by a longword mask identifying the
attributes of the holder. The buflen argument should
be set to the total size, in bytes, of the rights list segment. The
bufadr argument points to a descriptor that points to
the first byte in the rights list segment (that is, the first byte of
the first identifier value).
This item code can be repeated to add up to 256 additional rights list
segments. If more than 256 identifiers are granted to the user,
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns SS$_INSFMEM.
ISS$_AUTHPRIV
Quadword containing the authorized privileges. See $PRVDEF macro for
definitions.
ISS$_FLAGS
Longword containing user flags. The following flag is supported:
ISS$M_FLAG_SECAUDIT - Mandatory audit flag.
ISS$_MAXCLASS
Buffer containing the maximum classification. The maximum size of this
buffer is CLS$K_LENGTH. This item code is reserved to HP. See the
$CLSDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_MINCLASS
Buffer containing the minimum classification. The maximum size of this
buffer is CLS$K_LENGTH. This item code is reserved to HP. See the
$CLSDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_MODE
Longword containing the access mode. See $PSLDEF macro for definitions.
ISS$_PERMPRIV
Quadword containing the permanent privileges. See $PRVDEF macro for
definitions.
ISS$_RIGHTS
Descriptor pointing to a vector of quadwords containing
identifier/attribute pairs used to initialize the rights identifier
list. See the $KGBDEF macro for definitions. Any identifiers specified
by the ISS$_ADD_RIGHTS item code will be added to this list.
The format of this vector is as follows:
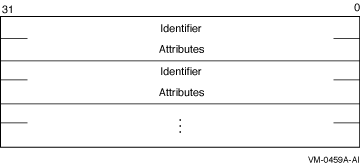
ISS$_UIC
A longword describing the user identification code (UIC).
ISS$_WORKCLASS
The classification to be associated with the created security profile.
This item code is reserved to HP.
ISS$_WORKPRIV
A quadword privilege mask specifying the user's privileges. The $PRVDEF
macro defines the list of available privileges.
Description
The Create User Profile service returns a security profile for a user.
This profile can be generated in two ways:
- If the caller does not specify the CHP$_NOACCESS flag in the
flags argument, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE accesses the
system authorization database (SYSUAF.DAT) or the rights database
(RIGHTSLIST.DAT) for the specified user name and builds a
representation of the privileges and rights granted to that user. The
security profile is returned as an opaque byte stream.
$CREATE_USER_PROFILE returns a representation of the security
profile that the user would have when logged in at the highest
authorized classification with all authorized privileges enabled.
- When the caller specifies the CHP$M_NOACCESS flag in the
flags argument, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE creates a
security profile without accessing the user authorization file
(SYSUAF.DAT) or the rights database (RIGHTSLIST.DAT). When
CHP$M_NOACCESS is specified, all of the information is obtained from
the item list. The caller must supply the CHP$_PRIV and CHP$_UIC items.
In addition, an address of 0 can be specified for the
usrnam argument.
|

