 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
DTI$_SEARCH_RESOLVED_STATE uses the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item
in the itmlst argument to write the following
information:
| Item |
Description |
|
DTI$B_STATE
|
A byte containing the state of the transaction identified by DTI$T_TID.
Table SYS-41 lists the possible values returned in the state field.
|
|
DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN
|
A byte containing the length of the participant name field
DTI$T_PART_NAME.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_NAME
|
A character field containing DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN characters that
specifies a resource manager name. When the resource manager name
string is supplied, a wildcard search can be specified. The left-most
characters supplied in this string will be matched against all resource
managers with the same leftmost characters. If the string entered has a
length of 0, all resource managers will be selected.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_LOG_ID
|
Reserved by HP.
|
|
DTI$T_TID
|
A 16-byte field containing the transaction identifier.
|
Table SYS-41 $GETDTI Transaction States
| Item |
Description |
|
DTI$K_STARTING
|
The transaction is in the starting state.
|
|
DTI$K_ACTIVE
|
The transaction is in the active state.
|
|
DTI$K_ONE_P_COMMITTING
|
The transaction is committing to phase one.
|
|
DTI$K_PREPARING
|
The transaction is in the preparing state.
|
|
DTI$K_PREPARED
|
The transaction has prepared.
|
|
DTI$K_COMMITTING
|
The transaction is in the committing state.
|
|
DTI$K_COMMITTED
1
|
The transaction has committed.
|
|
DTI$K_ONE_P_COMMITTED
|
The transaction has committed to phase one.
|
|
DTI$K_ABORTING
|
The transaction is in the aborting state.
|
|
DTI$K_ABORTED
1
|
The transaction has been aborted or forgotten. Note that, if the
transaction was aborted before the call to $GETDTI, then the alternate
status SS$_NOSUCHTID is returned; if the transaction was aborted during
the call to $GETDTI, then the DTI$K_ABORTED state is returned in the
transaction record.
|
1The DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED transaction states
are the only values that can be returned when the DDTM$M_FULL_STATE
flag is specified.
Itmlst Item Codes
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION
When you specify DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, $GETDTI returns the
following fields dependent on the search criteria established by the
search argument.
Each record may be composed of some of the following items:
| Item |
Description |
|
DTI$B_STATE
|
A byte containing the state of the transaction identified by DTI$T_TID.
Table SYS-41 lists the possible values returned in the state field.
|
|
DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN
|
A byte containing the length of the participant name field
DTI$T_PART_NAME.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_NAME
|
A character field containing DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN characters that
specifies a resource manager name.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_LOG_ID
|
Reserved by HP.
|
|
DTI$T_TID
|
A 16-byte field containing the transaction identifier.
|
The DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item buffer size should be at least
equal to the symbolic value DTI$S_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION defined by
$DTIDEF.
Description
During recovery from a failure, a resource manager calls $GETDTI to
request the state of certain transactions with which it had been
involved. As part of the recovery, the resource manager identifies any
unresolved transactions, so that they can be processed to completion.
The $GETDTI service returns the resolved state of in-doubt transactions
to recovering resource managers. The DDTM$M_FULL_STATE flag instructs
$GETDTI to return only the transactions in the DTI$K_COMMITTED or
DTI$K_ABORTED states (or an error status of SS$_NOSUCHTID). The action
taken depends on whether a transaction identifier is specified:
- If a transaction identifier is specified in DTI$T_TID, $GETDTI does
not return until the resolved state of the transaction is available.
- If DTI$T_TID is 0, $GETDTI ignores transactions that are not in the
DTI$K_COMMITTED or DTI$K_ABORTED states.
This can mean that the $GETDTI call may have to wait for other DECdtm
nodes or a coordinating CRM to become available. This is the
recommended method of obtaining an in-doubt transaction outcome for
recovering resource managers.
Alternatively, $GETDTI can be used to return the current known state of
transactions. Intermediate states may be returned. In particular,
DTI$K_PREPARED indicates that a DECdtm node is unavailable and
DTI$K_PREPARING indicates that a coordinating CRM is unavailable.
If $GETDTI is called during normal system operation to resolve the
state of transactions that have not failed, then the returned
transaction state can be any of the states listed in Table SYS-41.
A $GETDTI call may also be used in an OpenVMS Cluster environment to
perform recovery on behalf of a resource manager on a failed node. To
perform this action, the DTI$_SEARCH_AS_NODE search item descriptor is
used to inform $GETDTI of the node for which recovery is being
performed. This action is equivalent to performing the $GETDTI request
on the failed node. The use of DTI$_SEARCH_AS_NODE will perform
correctly when the target node is either available or unavailable. If
the target node is available when the $GETDTI call is executed, the
request is re-routed to the target node for execution.
To obtain information about transactions, $GETDTI must be given a set
of search criteria. The criteria are specified as parameters and as
part of an itemlist for the search argument using the
DTI$_SEARCH_RESOLVED_STATE item descriptor. The transaction information
required by $GETDTI to resolve a transaction includes:
- Transaction Identifier (TID).
- Resource Manager name.
- Transaction Manager log identifier.
- Resource Manager log identifier.
- Optionally, a remote node name.
If you specify a TID as 0, $GETDTI assumes a wildcard operation and
returns the requested information for each TID in the log that it has
privilege to access, one TID per call. To perform a wildcard operation,
you must call $GETDTI in a loop, testing for the condition value
SS$_NOSUCHTID after each call and exiting the loop when SS$_NOSUCHTID
is returned.
A resource manager is identified by its name in DTI$T_PART_NAME. A
wildcard search can be specified for the resource manager with this
item. The leftmost characters supplied in this string are matched
against all resource managers with the same leftmost characters in
their names.
If a resource manager name entered as the item has a length of 0, all
resource managers are selected.
Transaction managers and resource managers maintain log files to keep a
record of transactions and their related states. During recovery, it is
important that the transaction manager and resource manager use
matching log files. The transaction manger log identifier is returned
by the $DECLARE_RM service call. It should be recorded in the resource
manager's log records and supplied to $GETDTI as the value of the
log-id argument. If the wrong resource manager log, or
the wrong transaction manager log, is used, the discrepancy will result
in an error from $GETDTI or $SETDTI.
The contxt argument is used by $GETDTI to establish a
search context when it is returning the resolved state of a
transaction. The search context indicates the node and transaction
manager log identifier for use in a subsequent $SETDTI operation to
delete the resource manager from the transaction. The search context is
created when the contxt argument is invalid, or
re-used if the contxt argument is valid. The search
context is deleted when a call is made to $GETDTI that returns
SS$_NOSUCHTID. The search context is maintained exclusively by $GETDTI
and $SETDTI and should not be modified by the caller, with an exception
of initially zeroing the context. SYSPRV privilege is required to
retrieve or modify information about transactions with which the
process is not currently associated.
Required Privileges
SYSPRV is required to retrieve information about transactions with
which the process is not currently associated.
Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM
Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,
$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW,
$END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTIW,
$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,
$START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in
the I/O status block, the service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_SYNCH
|
The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if
the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set).
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
An argument was not accessible to the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADLOGVER
|
There is an invalid or unsupported log version.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The option flags, SEARCH or ITMLST are invalid.
|
|
SS$_BUGCHECK
|
A failure has occurred during the processing of the request.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded.
|
|
SS$_ILLEFC
|
The event flag number was invalid.
|
|
SS$_INSFARGS
|
A required argument was missing.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation.
|
|
SS$_INVLOG
|
The log format is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHFILE
|
The transaction manager log cannot be found.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHNODE
|
The subordinate DECnet node is unknown.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHPART
|
The participant is not part of the transaction.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHTID
|
The designated TID is unknown.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSPRV
|
The caller is not authorized to examine the specified transaction.
|
|
SS$_PROTOCOL
|
There is a message protocol error.
|
|
SS$_REMOTE_PROC
|
There was an attempt to use a node when it is not part of the OpenVMS
Cluster.
|
|
SS$_REMRSRC
|
There are insufficient resources at the remote node.
|
|
SS$_UNREACHABLE
|
A superior node is unreachable.
|
$GETDTIW
Returns information about the resolved state of transactions and the
process default transaction identifier.
$GETDTIW always waits for the request to complete before returning to
the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $GETDTI.
Format
SYS$GETDTIW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[contxt]
,[log_id] ,search ,itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$getdtiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
log_id [4], unsigned int *contxt, void *search, void *itmlst);
$GETDVI
Returns information related to the primary and secondary device
characteristics of an I/O device.
Note
All pathname-related information pertains only to
Alpha and Integrity server systems.
|
For synchronous completion, use the Get Device/Volume Information and
Wait ($GETDVIW) service. The $GETDVIW service is identical to the
$GETDVI service in every way except that $GETDVIW returns to the caller
with the requested information.
For additional information about system service completion, see the
Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
Note About Item
Codes
For item codes that return a string data type, failure to pass in a
buffer that is large enough to hold the returned data results in silent
data truncation. When $GETDVI completes, HP recommends that you check
the returned length field of an item list descriptor for each item code
that can return a string. If the returned length is equal to the size
of the buffer allocated to hold the returned data, the data might have
been truncated. In that case, call $GETDVI iteratively with a larger
buffer until the length of the returned data is less than the size of
the buffer allocated.
Unless the description of an item code specifies otherwise, HP
recommends that you use a buffer of 32 bytes to hold the returned
string. $GETDVI pads the unused portion of the buffer with null
characters.
|
Format
SYS$GETDVI [efn] ,[chan] ,[devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
[,nullarg] [,pathname]
C Prototype
int sys$getdvi (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void
*devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, struct _generic_64
*nullarg,...);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag to be set when $GETDVI returns the requested
information. The efn argument is a longword containing
this number; however, $GETDVI uses only the low-order byte.
Upon request initiation, $GETDVI clears the specified event flag (or
event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when
$GETDVI returns the requested information, it sets the specified event
flag (or event flag 0).
HP strongly recommends the use of the EFN$C_ENF "no event
flag" value as the event flag if you are not using an event flag
to externally synchronize with the completion of this system service
call. The $EFNDEF macro defines EFN$C_ENF. For more information, see
the HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
chan
| OpenVMS usage: |
channel |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which
information is desired. The chan argument is a word
containing this number.
To identify a device to $GETDVI, you can specify either the
chan or devnam argument, but do not
specify both. If you specify both arguments, the chan
argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $GETDVI uses a default value of 0 for
chan.
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the device about which $GETDVI is to return information.
The devnam argument is the address of a character
string descriptor pointing to this name string.
The device name string can be either a physical device name or a
logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore
(_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the
string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is
performed until either a physical device name is found or the system
default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the
characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $GETDVI, you can specify either the
chan or devnam argument, but do not
specify both. If both arguments are specified, the
chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor
devnam, $GETDVI uses a default value of 0 for
chan.
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be
returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information.
The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0. The
following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
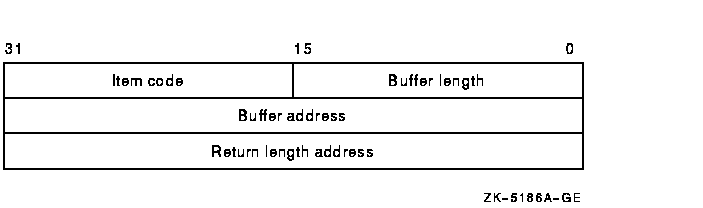
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETDVI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length
is too long, $GETDVI truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETDVI is to return. The $DVIDEF macro defines these
codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which
$GETDVI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which
$GETDVI is to write the information.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the address of the quadword I/O
status block.
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETDVI sets the
quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a
condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword
is reserved to HP.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $GETDVI service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$GETDVI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETDVI completes. The
astadr argument is the address of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of the $GETDVI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is the longword parameter.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: |
null_arg |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
pathname
| OpenVMS usage: |
path_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, the name of the path about which
$GETDVI is to return information. The pathname
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
this name string. The pathname can be used with either
the chan or the devnam argument.
Check the definitions of the item codes to see if the
pathname argument is used. In general, item codes that
return information that can vary by path make use of the
pathname argument. Use the SHOW DEVICE /FULL command,
the SYS$DEVICE_PATH_SCAN system service, or the F$MULTIPATH DCL lexical
function to see the paths for a multipath device.
If the pathname argument is used, it is validated
against the existing paths for the device specified. If the path does
not exist, the error SS$_NOSUCHPATH is returned, even if the item code
or codes used do not make use of the pathname argument.
Item Codes
DVI$_ACCESSTIMES_RECORDED
On Alpha and Integrity server systems, returns an unsigned longword,
which is interpreted as Boolean. A value of 1 indicates the volume
supports the recording of access times.
DVI$_ACPPID
Returns the ACP process ID as an unsigned integer longword.
DVI$_ACPTYPE
Returns the ACP type code as an unsigned integer longword. The
following symbols define each of the ACP type codes that $GETDVI can
return:
| Symbol |
Description |
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V1
|
Files-11 Level 1
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V2
|
Files-11 Level 2
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V3
|
Files-11 presentation of ISO 9660
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V4
|
Files-11 presentation of High Sierra
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V5
|
Files-11 Level 5
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F11V6
|
Files-11 Level 6
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_F64
|
Files 64 support for Spiralog
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_HBS
|
Not used
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_HBVS
|
Host Based Volume Shadowing
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_MTA
|
Magnetic tape
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_NET
|
Networks
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_REM
|
Remote I/O
|
|
DVI$C_ACP_UCX
|
ACP for TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
|
DVI$_ALL
Returns an unsigned longword, interpreted as Boolean. A value of 1
indicates that the device is allocated.
DVI$_ALLDEVNAM
Returns the allocatable device name as a string.
|
