| Previous | Contents | Index |
Displays the settings and explanations of the RAD_SUPPORT system parameter fields, and the assignment of CPUs and memory to the Resource Affinity Domains (RADs). This command is only useful on platforms that support RADs. By default, the SHOW RAD command displays the settings of the RAD_SUPPORT system parameter fields.
SHOW RAD [number | /ALL | /PXML]
number
Displays information on CPUs and memory for the specified RAD.
/ALL
Displays settings of the RAD_SUPPORT parameter fields and the CPU and memory assignments for all RADs./PXML (Integrity servers only)
SDA displays the proximity database derived from the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) tables. The proximity database is used to set up the RAD data structures.
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RAD
Resource Affinity Domains
-------------------------
RAD information header address: FFFFFFFF.81032340
Maximum RAD count: 00000008
RAD containing SYS$BASE_IMAGE: 00000000
RAD support flags: 0000004F
3 2 2 1 1
1 4 3 6 5 8 7 0
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
|..|..| skip|ss|gg|ww|pp|..|..|..|..|.p|fs|cr|ae|
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
|..|..| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|..|..|..|..|.1|00|11|11|
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
Bit 0 = 1: RAD support is enabled
Bit 1 = 1: Soft RAD affinity support is enabled
(Default scheduler skip count of 16 attempts)
Bit 2 = 1: System-space replication support is enabled
Bit 3 = 1: Copy on soft fault is enabled
Bit 4 = 0: Default RAD-based page allocation in use
Allocation Type RAD choice
--------------- ----------
Process-private pagefault Home
Process creation or inswap Random
Global pagefault Random
System-space page allocation Current
Bit 5 = 0: RAD debug feature is disabled
Bit 6 = 1: Per-RAD non-paged pool is enabled
|
This example shows the settings of the RAD_SUPPORT system parameter fields.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RAD 2
Resource Affinity Domain 0002
-----------------------------
CPU sets:
Active 08 10 11
Active 08 10 11
Configure 08 09 10 11
Potential 08 10 11
PFN ranges:
Start PFN End PFN PFN count Flags
--------- -------- --------- -----
01000000 0107FFE7 0007FFE8 000A OpenVMS Base
0107FFE8 0107FFFF 00000018 0009 Console Base
SYSPTBR: 01002A01
RAD data: B817C000
|
This example shows information on the CPUs and memory for RAD 2.
Displays information about all resources in the system or about a resource associated with a specific lock.
SHOW RESOURCES [ /ADDRESS=n
| /ALL (d)
| /BRIEF
| /CACHED
| /CONTENTION [=ALL][/FULL]
| /LOCKID=lock-id
| /LIST
| /NAME=name
| /OWNED
| /STATUS=(keyword[,...]) ]
None.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays information from the resource block at the specified address./ALL
Displays information from all resource blocks (RSBs) in the system. This is the default behavior of the SHOW RESOURCES command./BRIEF
Displays a single line of information for each resource./CACHED
Displays resource blocks that are no longer valid. The memory for these resources is saved so that later requests for resources can use them./CONTENTION [=ALL]
Displays only resources that have at least one lock on either the waiting or conversion queue. Unless you specify the ALL keyword, resources with locks on the waiting or conversion queues that are not participating in deadlock searches are ignored. (Locks not participating in deadlock searches are requested with either the LCK$M_NODLCKWT or LCK$M_NODLCKBLK flags.) By default, a single line summary is displayed for each resource, followed by a single line summary for each lock on the resource. Use /FULL to obtain a detailed display for each resource that is in contention./FULL
When used with /CONTENTION [=ALL], causes SDA to display details of each resource that is in contention instead of a single line summary./LIST
Displays summary information for each resource, followed by a list of all locks associated with the resource./LOCKID=lock-id
Displays information on the resource associated with the lock with the specified lock-id./NAME=name
Displays information about the specific resource. Name may be the actual name of the resource, if it only contains uppercase letters, numerals, the underscore (_), dollar sign, colon (:), and some other printable characters, as for example, /NAME=MY_LOCK. If it contains other printable characters (including lowercase letters), you may need to enclose the name in quotation marks (""), as for example, /NAME="My_Lock/47". If it contains nonprintable characters, the name may be specified as a comma-separated list comprised of strings and hexadecimal numbers, as for example, /NAME=("My_Lock",0C00,"/47") would specify the name "My_Lock<NUL><FF>/47". The hexadecimal number can be no more than 8 digits (4 bytes) in length. Nonprintable sequences or more than 4 bytes must be split into multiple hexadecimal numbers. The maximum length of a resource name is 32 characters./OWNED
Displays only owned resources./STATUS=(keyword[,...])
Displays only resources that have the specified status bits set in the RSB$L_STATUS field. If you specify only one keyword, you can omit the parentheses. Status keywords are as follows:
Keyword Meaning 2PC_IP Indicates a two-phase convert operation in progress BRL Indicates byte range resource CHK_BTR Checks for better master CVTFULRNG Indicates full-range requests in convert queue CVTSUBRNG Indicates sub-range requests in convert queue DIRENTRY Indicates directory entry during failover DIR_IP Creates directory entry DIR_RQD Indicates directory entry required INVPEND Checks for value block invalidation RBLD_ACT Indicates lock rebuild active for this tree RBLD_IP Indicates rebuild operation in progress RBLD_RQD Indicates rebuild required for this resource tree RM_ACCEPT Accepts new master RM_DEFLECT Deflects remote interest RM_FORCE Forces tree move RM_FREEZE Freeze resource tree on this node RM_INTEREST Remaster due to master having no interest RM_IP Indicates resource remaster in progress RM_PEND Indicates a pending resource remaster operation RM_RBLD Indicates to always rebuild resource tree RM_WAIT Blocks local activity VALCUR Indicates value block is current VALINVLD Indicates value block invalid WTFULRNG Indicates full-range requests in wait queue WTSUBRNG Indicates a sub-range requests in wait queue XVAL_VALID Indicates last value block was long block
The SHOW RESOURCES command displays the information listed in Table 4-26 either for each resource in the system or for the specific resource associated with the specified lock-id, address, or name.
Table 4-26 Resource Information in the SHOW RESOURCES Display Field (in order of display) Contents RSB Address of the resource block (RSB) that describes this resource. GGMODE Indication of the most restrictive mode in which a lock on this resource has been granted. Table 4-27 shows the values and their meanings. For information on conflicting and incompatible lock modes, see the HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual.
Status The contents of the resource block status field. Parent RSB Address of the RSB that is the parent of this RSB. This field is 00000000 if the RSB itself is a parent block. CGMODE Indication of the most restrictive lock mode to which a lock on this resource is waiting to be converted. This does not include the mode for which the lock at the head of the conversion queue is waiting. See Table 4-27. Sub-RSB count Number of RSBs of which this RSB is the parent. This field is 0 if the RSB has no sub-RSBs. FGMODE Indication of the full-range grant mode. See Table 4-27. Lock Count The total count of all locks on the resource. RQSEQNM Sequence number of the request. BLKAST count Number of locks on this resource that have requested a blocking AST. CSID Cluster system identification number (CSID) and name of the node that owns the resource. Resource Dump of the name of this resource, as stored at the end of the RSB. The first two columns are the hexadecimal representation of the name, with the least significant byte represented by the rightmost two digits in the rightmost column. The third column contains the ASCII representation of the name, the least significant byte being represented by the leftmost character in the column. Periods in this column represent values that correspond to nonprinting ASCII characters. Valblk Hexadecimal and ASCII dump of the first 16 bytes of the value block associated with this resource. See Extended Value Block later in this table for the display of the rest of the value block. Length Length in bytes of the resource name. x mode Processor mode of the namespace in which this RSB resides (Group, Kernel, User). owner Owner of the resource. Certain resources, owned by the operating system, list "System" as the owner. Locks owned by a group have the number (in octal) of the owning group in this field. Seqnum Sequence number associated with the resource's value block. If the number indicates that the value block is not valid, the words "Not valid" appear to the right of the number. Extended Valblk If any of the last 48 bytes of the value block (see Valblk earlier in this table) are non-zero, then the entire 64-byte value block is displayed as hexadecimal and ASCII dumps. Otherwise this display is omitted. The display appears only when value block contents are non-zero, without regard to the state of the RSB$M_XVAL_VALID flag. Granted queue List of locks on this resource that have been granted. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock and the lock mode in which the lock was granted. Conversion queue List of locks waiting to be converted from one mode to another. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock, the mode in which the lock was granted, and the mode to which the lock is to be converted. Waiting queue List of locks waiting to be granted. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock and the mode requested for that lock.
| Value1 | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NL | Null mode |
| CR | Concurrent-read mode |
| CW | Concurrent-write mode |
| PR | Protected-read mode |
| PW | Protected-write mode |
| EX | Exclusive mode |
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RESOURCES
Resource Database
-----------------
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7FEECE40 GGMODE: PW Status: VALID XVALID
Parent RSB: 00000000.00000000 CGMODE: PW
Sub-RSB count: 0 FGMODE: PW
Lock Count: 1 RQSEQNM: 0000
BLKAST count: 0 CSID: 00000000 (SAND41)
Resource: 00000000 0043524A JRC..... Valblk: 5F73695F 73696854
Length 3 00000000 00000000 ........ 6F5F7473 65745F61
User mode 00000000 00000000 ........ This_is_a_test_o
Group 001 00000000 00000000 ........ Seqnum: 00000001
Extended Valblk: 6F5F7473 65745F61 5F73695F 73696854 This_is_a_test_o
565F6465 646E6574 78455F65 68745F66 f_the_Extended_V
00000000 00006B63 6F6C425F 65756C61 alue_Block......
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
Granted queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range):
1500082F PW 00000000-FFFFFFFF
Conversion queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range -> Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Waiting queue (Lock ID / Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
SDA> SHOW RESOURCES
Resource Database
-----------------
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7FEECE40 GGMODE: PW Status: VALID
Parent RSB: 00000000.00000000 CGMODE: PW
Sub-RSB count: 0 FGMODE: PW
Lock Count: 1 RQSEQNM: 0002
BLKAST count: 0 CSID: 00000000 (SAND41)
Resource: 00000000 0043524A JRC..... Valblk: 5F74726F 68735F41
Length 3 00000000 00000000 ........ 00000000 00656E6F
User mode 00000000 00000000 ........ A_short_one.....
Group 001 00000000 00000000 ........ Seqnum: 00000003
Extended Valblk: 00000000 00656E6F 5F74726F 68735F41 A_short_one.....
565F6465 646E6574 78455F65 68745F66 f_the_Extended_V
00000000 00006B63 6F6C425F 65756C61 alue_Block......
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
Granted queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range):
3900080C PW 00000000-FFFFFFFF
Conversion queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range -> Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Waiting queue (Lock ID / Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
|
These examples for Alpha and Integrity server systems show two cases:
- output from a program writing a longer block
- output where the last writer wrote a short value block (XVALID not set), but because a previous writer wrote non-zero data to the high portion of the block and these data are still present, the data in the Extended Value Block are shown.
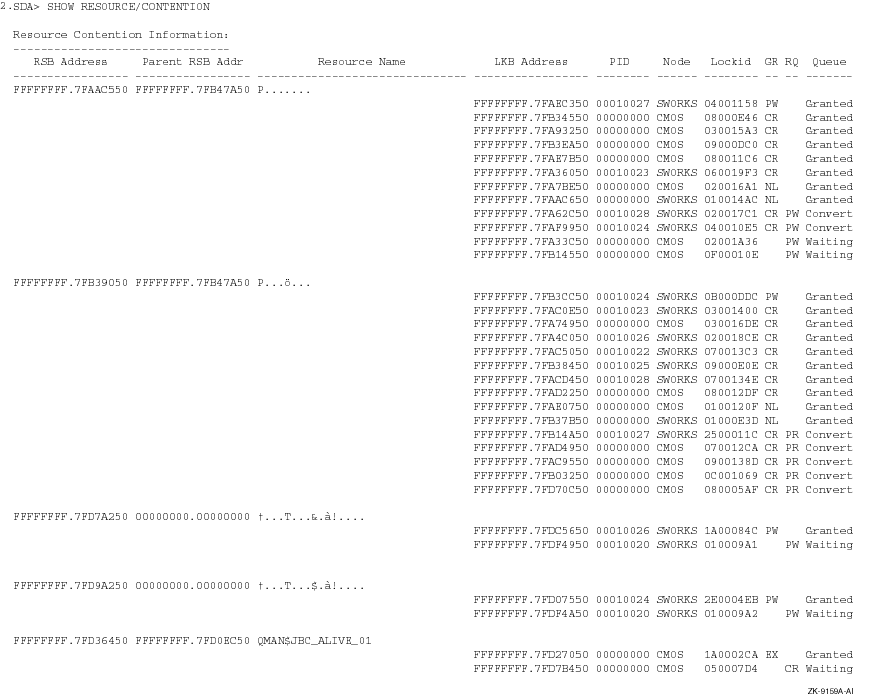
This example of the SHOW RESOURCES/CONTENTION command shows all the resources for which there is contention, and which are to be included in deadlock searches.
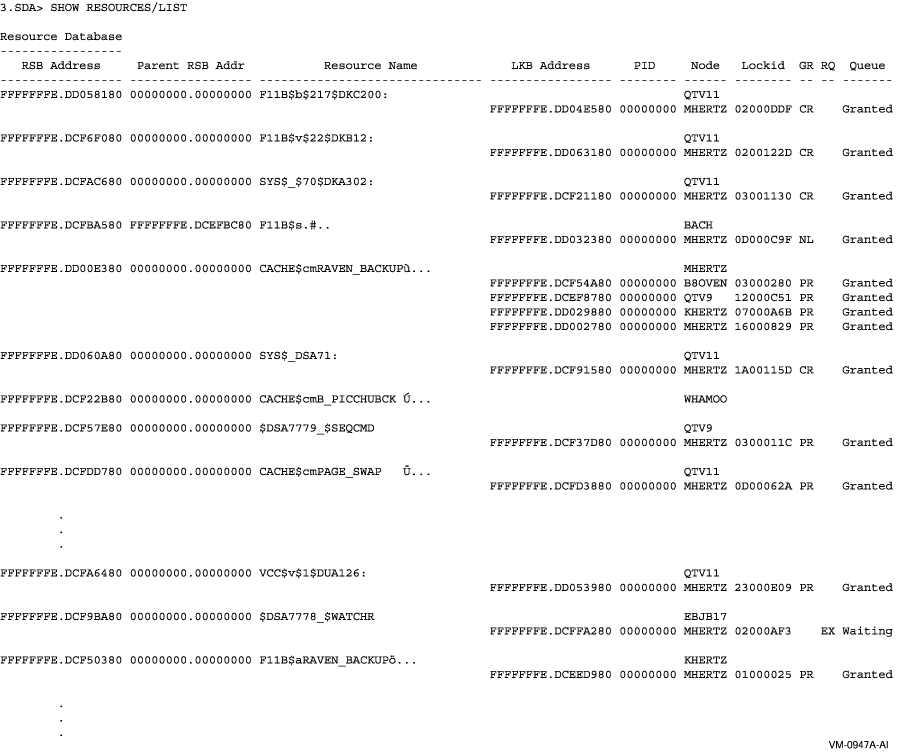
This example shows the output from the SHOW RESOURCES/LIST command.
Displays information contained in the reserved memory descriptors. Reserved memory is used within the system by memory-resident global sections.
SHOW RMD [/qualifiers]
None.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays a specific reserved memory descriptor entry, given its address./ALL
Displays information in all the reserved memory descriptors. This qualifier is the default.
The SHOW RMD command displays information that resides in the reserved memory descriptors. Table 4-28 shows the fields and their meanings.
Table 4-28 RMD Fields Field Meaning Address Gives the address of the reserved memory descriptor. Name Gives the name of the reserved memory descriptor. Group Gives the UIC group that owns the reserved memory. This is given as -S- for system global reserved memory. RAD Gives the required RAD for the reserved memory. Displays "Any" if no RAD specified. PFN Gives starting page number of the reserved memory. Count Gives the number of pages reserved. In_Use
(Error)Gives the number of pages in use. If an error occurred when the reserved memory was being allocated, the error condition code is displayed in parentheses. A second line, giving the text of the error, is also displayed in this case. Zero_PFN Gives the next page number to be zeroed. Flags Gives the settings of flags for specified reserved memory descriptor as a hexadecimal number, then displays key flag bits by name. The names may use multiple lines in the display.
SDA> SHOW RMD Reserved Memory Descriptor List ------------------------------- In_Use Address Name Group RAD PFN Count (Error) Zero_PFN Flags -------- ------------------- ----- ---- -------- -------- -------- -------- ------------------------------ 814199C0 LARGE 00022 Any 00000000 000004E2 00000000 00000000 000000E0 Group Page_Tables GBLSec 81419940 LARGE 00022 Any 00000000 00138800 (0000244C) 00000000 000001A0 Error Group GBLSec Error = %SYSTEM-F-INSFLPGS, insufficient Fluid Pages available 81419AC0 SMALL 00011 0001 00000180 00000001 00000000 00000180 000000E1 Alloc Group Page_Tables GBLSec 81419A40 SMALL 00011 0001 00000E00 00000080 00000000 00000E00 000000A1 Alloc Group GBLSec
This example shows the default output of a SHOW RMD command.
Displays the RMS data structures selected by the SET RMS command to be included in the default display of the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command.
SHOW RMS
None.
None.
The SHOW RMS command lists the names of the data structures selected for the default display of the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command.For a description of the significance of the options listed in the SHOW RMS display, see the description of the SET RMS command and Table 4-3.
For an illustration of the information displayed by the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command, see the examples included in the description of the SHOW PROCESS command.
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RMS
RMS Display Options: IFB,IRB,IDX,BDB,BDBSUM,ASB,CCB,WCB,FCB,FAB,RAB,NAM,
XAB,RLB,BLB,BLBSUM,GBD,GBH,FWA,GBDSUM,JFB,NWA,RU,DRC,SFSB,GBSB
Display RMS structures for all IFI values.
|
The SHOW RMS command displays the full set of options available for display by the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command. SDA, by default, selects the full set of RMS options at the beginning of an analysis.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SET RMS=(IFAB=1,CCB,WCB)
SDA> SHOW RMS
RMS Display Options: IFB,CCB,WCB
Display RMS structures only for IFI = 0001
|
The SET RMS command establishes the IFB, CCB, and WCB as the structures to be displayed, and only for the file whose internal File Identifer has the value 1, when the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command is issued. The SHOW RMS command verifies this selection of RMS options.
Displays information about response IDs (RSPIDs) of all System Communications Services (SCS) connections or, optionally, about a specific SCS connection.
SHOW RSPID [/CONNECTION=cdt-address ]
None.
/CONNECTION=cdt-address
Displays RSPID information for the specific SCS connection whose connection descriptor table (CDT) address is provided in cdt-address. You can find the cdt-address for any active connection on the system in the CDT summary page display of the SHOW CONNECTIONS command. CDT addresses are also stored in many individual data structures related to SCS connections. These data structures include class driver request packets (CDRPs) and unit control blocks (UCBs) for class drivers that use SCS and cluster system blocks (CSBs) for the connection manager.
Whenever a local system application (SYSAP) requires a response from a remote SYSAP, a unique number, called an RSPID, is assigned to the response by the local system. The RSPID is transmitted in the original request (as a means of identification), and the remote SYSAP returns the same RSPID in its response to the original request.The SHOW RSPID command displays information taken from the response descriptor table (RDT), which lists the currently open local requests that require responses from SYSAPs at a remote node. For each RSPID, SDA displays the following information:
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RSPID
--- Summary of Response Descriptor Table (RDT) 805E6F18 ---
RSPID CDRP Address CDT Address Local Process Name Remote Node
----- ------------ ----------- ------------------ -----------
39D00000 8062CC80 805E8710 VMS$VMScluster VANDQ1
EE210001 80637260 805E8C90 VMS$DISK_CL_DRVR ROMRDR
EE240002 806382E0 805E8DF0 VMS$DISK_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
EE440003 806393E0 805E8F50 VMS$TAPE_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
5DB90004 80636BC0 805E8870 VMS$VMScluster ROMRDR
5C260005 80664040 805E8870 VMS$VMScluster ROMRDR
38F80006 80664A80 805E8710 VMS$VMScluster VANDQ1
|
This example shows the default output for the SHOW RSPID command.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RSPID/CONNECTION=805E8F50
--- Summary of Response Descriptor Table (RDT) 805E6F18 ---
RSPID CDRP Address CDT Address Local Process Name Remote Node
----- ------------ ----------- ------------------ -----------
EE440003 806393E0 805E8F50 VMS$TAPE_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
|
This example shows the output for a SHOW RSPID/CONNECTION command.
Displays information about the shared memory common property partitions (CPPs). The default display shows a single-page summary that includes a single line for each CPP.
SHOW SHM_CPP [/qualifiers]
None.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays a detailed page of information about an individual shared memory CPP given the address of the SHM_CPP structure./ALL
Displays a detailed page of information about each shared memory CPP./IDENT=n
Displays a detailed page of information about an individual shared memory CPP./PFN [=(option[,option,...])]
Displays PFN data in addition to the basic SHM_CPP. The default is to display all lists (free, bad, untested), plus the PFN database pages and the complete range of PFNs in the CPP.You can limit which lists are displayed by specifying one or more keywords from the following table. If you specify multiple keywords, enclose them in parentheses and separate keywords with a comma.
ALL_FRAGMENTS Displays the complete range of PFNs in the CPP. BAD Displays only the bad page list. FREE Displays only the free page list. PFNDB Displays the PFNs containing the PFN database. UNTESTED Displays only the untested page list. If you specify /PFN without /ALL, /IDENT, or /ADDRESS, the system displays the PFN lists from the last shared memory CPP accessed.
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW SHM_CPP
Summary of Shared Memory Common Property Partitions
---------------------------------------------------
Base address of SHM_CPP array: FFFFFFFF.7F2BA140
Maximum number of SHM_CPP entries: 00000007
Size of each SHM_CPP: 00000240
Maximum fragment count per SHM_CPP: 00000010
Valid CPP count: 00000001
ID SHM_CPP address MinPFN MaxPFN Page count Free pages Flags
---- ----------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
-- SHM_CPP IDs 0000 to 0002: VALID flag clear --
0003 FFFFFFFF.7F2BA800 00060000 0007FFFF 00020000 0001FCF7 00000001 VALID
-- SHM_CPP IDs 0004 to 0006: VALID flag clear --
|
This example shows the default output for the SHOW SHM_CPP command.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW SHM_CPP/IDENT=3
Shared Memory CPP 0003
----------------------
SHM_CPP address: FFFFFFFF.7F2BA800
Version: 00000001 Flags: 00000001 VALID
Size: 00000000.000000C0 Page count: 00020000
Actual fragment count: 00000001 Minimum PFN: 00060000
Maximum fragment count: 00000010 Maximum PFN: 0007FFFF
Length of free page list: 0001FCF7
Length of bad page list: 00000000
Length of untested page list: 00000000
PMAP array for PFN database pages
PMAP Start PFN PFN count
----- -------- --------
0. 00060053 00000280
PMAP array for all fragments
PMAP Start PFN PFN count
----- -------- --------
0. 00060000 00020000
GLock address: FFFFFFFF.7F2BA8C0 Handle: 80000000.00010D19
GLock name: SHM_CPP00000003 Flags: 00
Owner count: 00 Owner node: 00
Node sequence: 0000 Owner: 000000
IPL: 08 Previous IPL: 00
Wait bitmask: 00000000.00000000 Timeout: 00249F00
Thread ID: 00000000.00000000
Connected GNode bitmask: FFFFFFFF.7F2BA900
Valid bits: 00000004 State: 00000000.00000000
Unit count: 0001 Unit size: QUADWORD
Unit bitmask:
........ ........ ........ .......7 00000000
Ranges of free pages
Range Start PFN PFN count
----- -------- --------
1. 000602F6 00000002
2. 0006030B 0001FCF5
|
This example shows the details for a single SHM_CPP.
Displays information about shared memory regions. The default display shows a single page summary that includes a single line for each region.
SHOW SHM_REG [/qualifiers] [name]
name
Detailed page of information about the named region.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays a detailed page of information about an individual region given the address of the SHM_REG structure./ALL
Displays a detailed page of information about each region./IDENT=n
Displays a detailed page of information about the specified region.
1. SDA> SHOW SHM_REG Summary of Shared Memory Regions -------------------------------- Base address of SHM_REG array: FFFFFFFF.7F2BB140 Maximum number of SHM_REG entries: 00000040 Size of each SHM_REG: 00000208 Base address of SHM_DESC array: FFFFFFFF.7F2DC000 Valid region count: 00000009 ID SHM_REG address Region Tag SysVA / GSTX Flags ---- ----------------- ------------------------------ ----------------- -------- 0000 FFFFFFFF.7F2BB140 SYS$GALAXY_MANAGEMENT_DATABASE FFFFFFFF.7F234000 00000001 VALID 0001 FFFFFFFF.7F2BB348 SYS$SHARED_MEMORY_PFN_DATABASE FFFFFFFE.00000000 00000001 VALID 0002 FFFFFFFF.7F2BB550 SMCI$SECTION_PBA_04001 -<None>- 00000001 VALID 0003 FFFFFFFF.7F2BB758 GLX$CPU$BALANCER$SYSGBL 0000013F 00000005 VALID SHARED_CONTEXT_VALID 0004 FFFFFFFF.7F2BB960 SMCI$CHANNEL_PBA_0_1 FFFFFFFF.8F3AE000 00000001 VALID 0005 FFFFFFFF.7F2BBB68 SMCI$CHANNEL_PBA_0_2 FFFFFFFF.8FAEE000 00000001 VALID 0006 FFFFFFFF.7F2BBD70 SMCI$CHANNEL_PBA_1_2 -<Not Attached>- 00000001 VALID 0007 FFFFFFFF.7F2BBF78 LAN$SHM_REG FFFFFFFF.7F20C000 00000009 VALID ATTACH_DETACH 0008 FFFFFFFF.7F2BC180 GLX$CPU_BAL_GLOCK $000006 00000140 00000005 VALID SHARED_CONTEXT_VALID -- SHM_REG IDs 0009 to 003F: never used --This example shows the summary of all shared memory regions in the system.
2. SDA> SHOW SHM_REG SMCI$CHANNEL_PBA_0_1 -------------------------------------- SHM_REG address: FFFFFFFF.7F2BB960 Version: 00000001 Flags: 00000001 VALID Index/Sequence: 0004/00000003 Size: 00000000.00000120 Region tag: SMCI$CHANNEL_PBA_0_1 Creation time: 31-MAR-1999 14:11:11.37 SHM_DESC address: FFFFFFFF.7F2DC200 Version: 00000001 Flags: 00000005 ATTACHED SYS_VA_VALID System VA: FFFFFFFF.8F3AE000 Virtual size: 00000000.00274000 I/O ref count: 00000000.00000000 Index/Sequence: 0004/00000003 Context: FFFFFFFF.80F42480 Callback: FFFFFFFF.8F38E5C0 SYS$PBDRIVER+185C0 MMAP address: FFFFFFFF.7F2BB9E0 Level count: 0001 Flags: 0001 VALID Top page count: 00000001 Virtual size: 00000000.00274000 PFN list page count: 00000001 First PFN: 000602D4 Data page count: 00000009 GLock address: FFFFFFFF.7F2BBA80 Handle: 80000000.00010F51 GLock name: SHM_REG00000004 Flags: 00 Owner count: 00 Owner node: 00 Node sequence: 0000 Owner: 000000 IPL: 08 Previous IPL: 00 Wait bitmask: 00000000.00000000 Timeout: 002DC6C0 Thread ID: 00000000.00000000 Attached GNode bitmask: FFFFFFFF.7F2BBAC0 Valid bits: 00000004 State: 00000000.00000012 AUTO_LOCK SET_COUNT Unit count: 0001 Unit size: QUADWORD Lock IPL: 08 Saved IPL: 00000008 Count of bits set: 00000002 Unit bitmask: ........ ........ ........ .......3 00000000 I/O in progress bitmask: FFFFFFFF.7F2BBAF8 Valid bits: 00000004 State: 00000000.00000012 AUTO_LOCK SET_COUNT Unit count: 0001 Unit size: QUADWORD Lock IPL: 08 Saved IPL: 00000000 Count of bits set: 00000000 Unit bitmask: ........ ........ ........ .......0 00000000 SHM_CPP bitmask: FFFFFFFF.7F2BBB30 Valid bits: 00000007 State: 00000000.00000000 Unit count: 0001 Unit size: QUADWORD Unit bitmask: ........ ........ ........ ......08 00000000 )This example shows the details for a single shared memory region.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |