9.7 LAN Function Codes
The LAN drivers can perform logical, virtual, and physical I/O operations. The basic functions are read, write, set mode, set characteristics, sense mode, and sense characteristics. Table 9-28 lists these functions and their codes. The following sections describe these functions in greater detail.
Table 9-28 LAN I/O Functions
| Function Code | Arguments | Type[1] | Function Modifiers | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IO$_READLBLK[2] | P1,P2,[P5] | L | IO$M_NOW | Read logical block. |
IO$_READVBLK[3] | P1,P2,[P5] | V | IO$M_NOW | Read virtual block. |
IO$_READPBLK[2] | P1,P2,[P5] | P | IO$M_NOW | Read physical block. |
IO$_WRITELBLK[4] | P1,P2,[P4],P5 | L | IO$M_RESPONSE | Write logical block. |
IO$_WRITEVBLK[4] | P1,P2,[P4],P5 | V | IO$M_RESPONSE | Write virtual block. |
IO$_WRITEPBLK[4] | P1,P2,[P4],P5 | P | IO$M_RESPONSE | Write physical block. |
IO$_SETMODE | P1,[P2],P3[2] | L | IO$M_CTRL IO$M_STARTUP IO$M_SHUTDOWN IO$M_ATTNAST IO$M_SET_MAC IO$M_UPDATE_MAP IO$M_ROUTE | Set controller characteristics and controller state for subsequent operations. |
IO$_SETCHAR | P1,[P2],P3[2] | P | IO$M_CTRL IO$M_STARTUP IO$M_SHUTDOWN IO$M_ATTNAST IO$M_SET_MAC IO$M_UPDATE_MAP IO$M_ROUTE | Set controller characteristics and controller state for subsequent operations. |
IO$_SENSEMODE | [P1],[P2] | L | IO$M_CTRL IO$M_SENSE_MAC IO$M_SHOW_MAP IO$M_SHOW_ROUTE | Sense controller characteristics and return them in specified buffers. |
IO$_SENSECHAR | [P1],[P2] | P | IO$M_CTRL IO$M_SENSE_MAC IO$M_SHOW_MAP IO$M_SHOW_ROUTE | Sense controller characteristics and return them in specified buffer. |
[1] V= virtual, L=logical, P=physical ( There is no functional difference in these operations.) [2] On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity servers , P1 and P5 support 64-bit addresses. [3] On OpenVMS Alpha, P1, P4, and P5 support 64-bit address. [4] The P1 and P3 arguments are only for attention AST QIOs. | ||||
Note that the LAN device drivers do not differentiate among logical, virtual, and physical I/O functions; all are treated identically.
Read functions directly transfer data from a packet received from another port on the Ethernet into the virtual memory address space of the user process. The operating system provides the following function codes:
Received messages are buffered in system memory and then copied to the user's buffer when a read operation is performed.
The read functions take the following device- or function-dependent arguments:
P1—The starting virtual address of the buffer that is to receive data. On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems, P1 can be a 64-bit address.
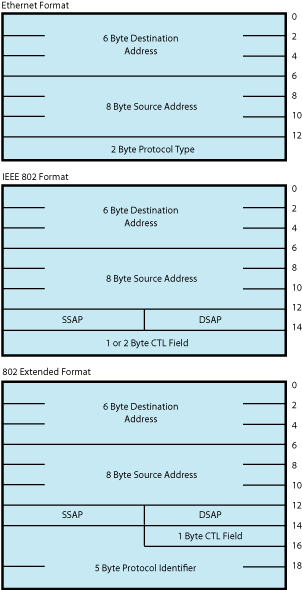
P5—The address of a buffer where the LAN driver returns packet header information. This is an optional argument. The information returned depends on the packet format enabled with the set mode QIO. The size of the buffer must be 14 bytes for an Ethernet format packet, 16 bytes for an IEEE 802 format packet, and 20 bytes for an 802 extended format packet. Note that the information returned is not the entire packet header but the header information less any length or size fields. The IOSB, if specified, is where the packet length information is returned. For FDDI, if received access control (RAC) is on, then 1 byte must be added to these sizes.
For Token Ring, this buffer must be at least 54 bytes in length due to a possible variable length source routing header.
If NMA$C_PCLI_PRM (see Table 9-33) is enabled, the P5 buffer must be at least 20 bytes for Ethernet and 21 bytes for FDDI. Figure 9-12 shows the format of the three buffers. On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems, P5 can be a 64-bit address.
The P1 and P2 arguments must always be specified; the P5 argument is optional. However, if P5 is not specified, you will not be able to determine the source of the received message .
If the size of the user data in a receive message is larger than the value of the NMA$C_PCLI_BUS parameter, the message is not given to the user, even if there is sufficient space in the user's receive buffer.
If the size of the user data in a receive message is larger than the size specified in P2 (and less than or equal to the value of the NMA$C_PCLI_BUS parameter), the P1 buffer is filled and SS$_DATAOVERUN is returned in the I/O status block.
Table 9-29 lists the maximum user data sizes that can be received for Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring protocols.
Table 9-29 Maximum User Data Sizes for Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring
| Packet Format | Ethernet | FDDI | Token Ring |
|---|---|---|---|
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4470 | 4418 |
Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4468 | 4416 |
802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4475 | 4423 |
802 format with 2-byte CTL field | 1496 | 4474 | 4422 |
802E format | 1492 | 4470 | 4418 |
Table 9-30 lists the maximum user data sizes that can be received for LAN emulation over ATM protocol.
Table 9-30 Maximum User Data Sizes for LAN Emulation over ATM
| Packet Format | ATM ELAN size: | 1516 | 4544 | 9234 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4528 | 9218 | |
Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4526 | 9216 | |
802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4525 | 9215 | |
802 format with 2-byte CTL field | 1496 | 4524 | 9214 | |
802E format | 1492 | 4520 | 9210 |
For 802 format packets, the P5 buffer always contains the DSAP and SSAP in the bytes at offset 12 and 13. The next one or two bytes (offsets 14 and 15) following the SSAP contain the control field value. For Class I service, the control field value is always 1 byte in length and is always placed in the byte at offset 14 of this buffer. For user-supplied service, you have to determine the length of the control field value according to the IEEE 802.2 Standard.
For Token Ring, if received access control (RAC) is on, the first byte of the P5 buffer contains the frame control (FC) field.
For FDDI, if RAC is on, the first byte of the P5 buffer contains the FC field.
The read functions can take the following function modifier:
IO$M_NOW—Complete the read operation immediately with a received message (if no message is currently available, return a status of SS$_ENDOFFILE in the I/O status block).
Write functions provide for the direct transfer of data from the virtual memory address space of the user process to the communications medium. The operating system provides the following function codes:
IO$_WRITELBLK—Write logical block
IO$_WRITEVBLK—Write virtual block
IO$_WRITEPBLK—Write physical block
Transmitted messages are copied from the buffer of the requesting process to a system buffer for transmission.
The write function takes the following device- or function-dependent arguments:
P1—The starting virtual address of the buffer containing the data to be transmitted. On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems, P1 can be a 64-bit address.
P2—The size of the buffer in bytes.
P4—The address of a quadword that points to a buffer that contains the DSAP and CTL field values (optional). (See “Service Access Point (SAP) Use and Restrictions”.) The first longword is the buffer length; the second longword is the address of the buffer. This argument is used only for ports with the 802 packet format. The format of the buffer is:

On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems, P4 can be a 64-bit address.
P5—The address of a 6-byte buffer that contains the destination address. For FDDI, if XFC is specified as zero on startup, the first byte of the P5 buffer contains the low-order 3 bits of the FC field to be transmitted. On OpenVMS Alpha and Integrity server systems, P5 can be a 64-bit address.
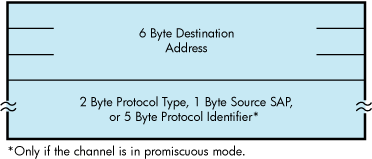
If the device is in promiscuous mode (NMA$C_PCLI_PRM; see Table 9-33), you must pass a larger buffer with additional information positioned after the destination address. For Ethernet packet format, the buffer must be 8 bytes with the 2-byte protocol type following the destination address. For 802 packet format, the buffer must be 7 bytes with the 1-byte source SAP following the destination address. For 802 extended packet format, the buffer must be 11 bytes with the 5-byte protocol identifier following the destination address. The Source SAP cannot be a group SAP or the SNAP SAP. Figure 9-13 shows the format of the P5 buffer. For FDDI with XFC specified as zero on startup, 1 byte must be added to these sizes for the FC field.
Table 9-31 lists the maximum user data sizes that can be specified by P2 and received for Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring protocols.
Table 9-31 Maximum Message Sizes for Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring
| Packet Format | Ethernet | FDDI | Token Ring |
|---|---|---|---|
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4470 | 4418 |
Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4468 | 4416 |
802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4475 | 4423 |
802 format with 2-byte CTL field | 1496 | 4474 | 4422 |
802E format | 1492 | 4470 | 4418 |
Table 9-32 lists the maximum user data sizes that can be specified by P2 and received for LAN emulation over ATM protocol.
Table 9-32 Maximum Message Sizes for LAN Emulation over ATM
| Packet Format | ATM ELAN size: | 1516 | 4544 | 9234 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4528 | 9218 | |
Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4526 | 9216 | |
802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4525 | 9215 | |
802 format with 2-byte CTL field | 1496 | 4524 | 9214 | |
802E format | 1492 | 4520 | 9210 |
If P2 specifies a message size larger than that allowed, the driver returns the status SS$_IVBUFLEN in the I/O status block.
If the P4 buffer is specified, it must be at least 3 bytes long. The first byte is always the DSAP; the next two bytes are used to determine the CTL field value. The DSAP value cannot be the SNAP SAP.
The CTL field value is either a 1-byte or 2-byte value. If the two least significant bits of the low-order byte of the CTL field contain the bit values 11, just the low-order byte of the CTL field is used as the CTL field value. Otherwise, both bytes of the CTL field are used as the CTL field value.
If the driver uses only the low-order byte of the CTL field, you still must pass at least a 3-byte buffer. In this case, the driver uses the low-order byte of the CTL field and ignores the high-order byte.
If Class I service is enabled, only 1-byte CTL field values can be passed. If user-supplied service is enabled, then both 1- and 2-byte CTL field values are valid. If Class I service is enabled, the CTL field value must be one of the three command values: UI, XID, or TEST.
Regarding 802 ports, you can receive packets for the SAP enabled with the IO$_SETMODE or IO$_SETCHAR QIOs and can transmit packets destined for a different SAP. This is similar to an Ethernet port receiving packets for one protocol type and transmitting packets with a different protocol type (which is not possible with the current Ethernet $QIO interface). It is expected that most 802 format applications wants to process only receive packets from a source SAP that matches the SAP enabled on their port. To do this, the read function (see “Read”) has been enhanced to return the source SAP to you. To verify that the source SAP of an incoming packet matches the SAP enabled on the port, you need only match the source SAP returned by the read function with the SAP enabled on the port.
The write function can take the following function modifier:
IO$M_RESPONSE—Transmit a response packet (sets the low-order bit in the SSAP field). This allows users with user-supplied service enabled to respond to certain 802 format command packets. IO$M_RESPONSE can be specified only when you have the 802 packet format enabled. The 802 packet format ports, with Class I service enabled, result in an error if you attempt to transmit a response message with a CTL field value of unnumbered information (UI).
The operating system provides the following two function codes:
Other than the privilege check, these two function codes are treated the same by the LAN drivers. This section refers to the IO$_SETMODE function code only, even though applications can use either function code.
The set mode function code is used to perform many different functions. These different functions are distinguished by the modifiers set with the function code. The LAN drivers support the following set mode requests:
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_CTRL — Set or modify port attributes
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_CTRL!IO$M_STARTUP — Set port attributes and start port
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_SET_MAC — Set medium attributes
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_CTRL!IO$M_SHUTDOWN — Shut down port
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_ATTNAST — Enable attention AST
IO$M_SETMODE!IO$M_UPDATE_MAP — Update functional address mapping table (Token Ring only)
IO$M_SETMODE!IO$M_ROUTE — Update source routing cache table (Token Ring only)
The following sections describe these functions in detail.
Once a port is created using the $ASSIGN system service, you can set the port attributes and start the port using the requests listed in the previous section. Note that in most cases only IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_CTRL!IO$M_STARTUP is issued because it sets the port attributes and starts the port with one request. IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_CTRL is most often used to modify port attributes after the port has been started.
If the function modifier IO$M_STARTUP is specified, the LAN port is started. If IO$M_STARTUP is not specified, the specified characteristics are modified.
This function takes the following device- or function-dependent argument:
P2—The address of a quadword descriptor for an extended characteristics buffer. The first longword of the descriptor is the buffer length; the second longword is the address of the buffer. The P2 argument is optional.
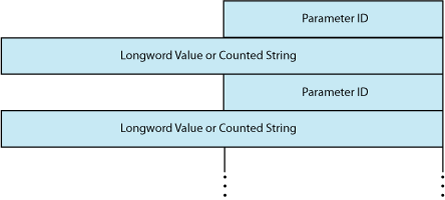
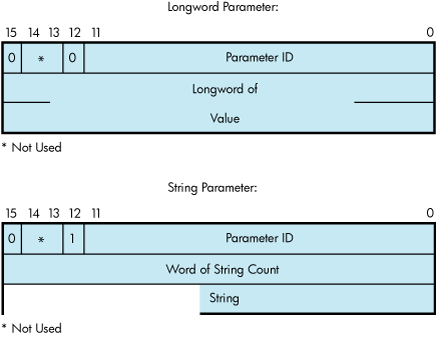
The P2 buffer consists of a series of 6-byte or counted string entries. The first word of each entry contains the parameter identifier (ID) of an attribute, followed by either a longword that contains one of the (binary) values that can be associated with the parameter ID or a counted string. Counted strings consist of a word that contains the size of the character string followed by the character string. Figure 9-14 shows the format for this buffer.
Table 9-33 is an alphabetic listing of the parameter IDs and values that can be specified in the P2 buffer. These parameter IDs are applicable to all LAN controllers, except where otherwise noted. The $NMADEF macro defines these values. The $NMADEF macro is included in the macro library SYS$LIBRARY:LIB.MLB. (Table 9-33 lists the parameters that can be used with each of the packet formats, and indicates which are required, which are optional, and which generate the SS$_BADPARAM error.)
If the status SS$_BADPARAM is returned in the first word of the I/O status block, the second longword contains the parameter ID of the parameter in error.
Table 9-33 P2 Attributes
| Parameter ID | Meaning | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
NMA$C_PCLI_ACC | Protocol access mode. This optional parameter determines the access mode for the protocol type. NMA$C_PCLI_ACC is valid only for ports using Ethernet packet format. NMA$C_PCLI_ACC is valid for ports using 802E packet format. One of the following values can be specified:
“Protocol Type and PID Sharing ” provides a description of protocol type sharing. “Protocol Type and PID Sharing ” provides a description of protocol type PID sharing. NMA$C_PCLI_ACC is passed as a longword value. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_BFN | Number of receive buffers to preallocate (default = 1). NMA$C_PCLI_BFN can have a maximum value of 255. This optional parameter is specified on a per-port basis. NMA$C_PCLI_BFN is passed as a longword value. NMA$C_PCLI_BFN represents the number of receive messages the LAN driver holds for a port when the port has no read QIOs posted to the driver. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_BUS | Any message received for this port that is larger than this parameter value is discarded. Maximum allowable port receive data size, that is, message length (default = 512 bytes). NMA$C_PCLI_BUS can have a maximum value of 9234.This optional parameter is specified on a per-port basis. It is passed as a longword value. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_CCA | Can change address. This optional parameter enables applications to start before DECnet starts. DECnet may attempt to set the physical address of the controller when it starts. Ethernet devices support only one physical address, and so all applications that are using the same device must also use the same physical address. If applications that do not use the DECnet address start before DECnet, DECnet is not able to start on that controller unless the other applications that have already started have all specified NMA$C_PCLI_CCA to be ON. This parameter is not applicable to FDDI because FDDI devices can run with more than one physical address; however, no error is returned if this parameter is supplied for FDDI devices. The application receives no indication whatsoever that the physical address has changed. This parameter is passed as a longword. One of the following values can be specified:
| ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_CON[1] | Controller mode. This optional parameter determines whether transmit packets are to be looped back at the controller. One of the following values can be specified:
The only messages looped back are those acceptable to the controller as receive messages, that is, those messages that possess at least one of the following characteristics:
NMA$C_PCLI_CON affects all ports on a single controller. It is passed as a longword value. For the DELUA, DEBNA, DEBNI, DEQTA, PMAD, DEMNA, and DESVA, the following list shows the maximum amount of user data that can be looped:
When the DEUNA is in loopback mode, the driver always enables echo mode (NMA$C_PCLI_EKO is in the ON state). Not all devices support loopback mode. If normal mode is not specified, the request is completed with SS$_BADPARAM status. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_CRC[1] | Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) generation state for transmitted messages (optional). One of the following values can be specified: NMA$C_STATE_ON — Controller generates a CRC (default).NMA$C_STATE_OFF — Controller does not generate a CRC.NMA$C_PCLI_CRC affects all ports on a single controller. There is no effect onchecking a receive message’s CRC (it is always checked). NMA$C_PCLI_CRC is passed as a longword value. If NMA$C_PCLI_CRC is turned off, all users of the controller must supply the 4-byte CRC value for all messages transmitted. The CRC is passed at the end of the P1 transmit buffer; the additional 4 bytes are included in the size of the P1 buffer. The CRC value is not checked for correctness. For the DEQNA, DELQA, and Token Ring devices, the NMA$C_PCLI_CRC parameter cannot be turned off. For the DEQNA, DELQA, and Token Ring devices, the NMA$C_PCLI_CRC parameter cannot be turned off. Not all devices support user-supplied CRC. If a controller-generated CRC is specified, the request is completed with SS$_BADPARAM status. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_DES | Shared protocol destination address. Passed as a counted string that consists of a modifier word (NMA$C_LINMC_SET or NMA$C_LINMC_CLR) followed by a 6-byte (48-bit) physical destination address. The size of the counted string must always be 8. NMA$C_PCLI_DES only has meaning when protocol access (NMA$C_PCLI_ACC) is defined as shared-with-destination mode (NMA$C_ ACC_LIM). The destination address specified must be a physical address—not a multicast address—and it must be unique among all ports sharing the same protocol. NMA$C_PCLI_DES is required when the access mode is defined as ‘‘shared-with-destination.’’ NMA$C_PCLI_DES should not be specified on a port where the 802 or 802E packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLIFMT is set to NMA$C_LIFM_802 or NMA$C_LIFM_802E). For 802 packet format, the concept of shared protocol type is handled by using group SAPs. NMA$C_PCLI_DES should not be specified on a port where the 802 packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLIFMT is set to NMA$C_LIFM_802). For 802 packet format, the concept of shared protocol type is handled by using group SAPs. “Protocol Type and PID Sharing ” provides a description of protocol type sharing. “Protocol Type and PID Sharing ” provides a description of protocol type PID sharing. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_EKO[1] | Echo mode. Applicable only to the DEUNA device driver. If echo mode is on, transmitted messages are returned to the sender. This optional parameter controls the condition of the half-duplex bit in the DEUNA mode register. One of the following values can be specified:
If NMA$C_STATE_ON is specified, the only transmitted messages echoed are those acceptable to the DEUNA as receive messages, that is, those messages that have at least one of the following characteristics:
If the DEUNA is placed in loopback mode (NMA$C_LINCN_LOO is specified in the NMA$C_PCLI_CON parameter), the driver enables echo mode. NMA$C_PCLI_EKO affects all ports on a single controller. It is passed as a longword value. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_FMT | Packet format. This optional parameter specifies the packet format as either Ethernet, IEEE 802, or 802 extended. This characteristic is passed as a longword value and affects single ports on a single controller. One of the following values can be specified:
NMA$C_PCLI_PTY, NMA$C_PCLI_ACC, and NMA$C_PCLI_DES should only be specified on those ports where the Ethernet packet format (NMA$C_LINFM_ ETH) is selected. NMA$C_PCLI_SRV, NMA$C_PCLI_SAP, and NMA$C_PCLI_GSP should only be specified on those ports where the 802 packet format (NMA$C_LINFM_802) is selected. NMA$C_PCLI_PID should only be specified on those ports where the 802 extended packet format (NMA$C_LINFM_802E) is selected. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_GSP | Group SAP. This is an optional parameter if the 802 packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLIFMT is set to NMA$C_LINFM_802). If the Ethernet or 802 extended packet format is selected, NMA$C_PCLI_GSP cannot be specified. Group SAPs can be shared among multiple ports on the same controller. If the 802 packet format is selected, NMA$C_PCLI_GSP defines up to four 802 group SAPs that are to be enabled for matching incoming packets to complete read operations on this port. By default, no group SAPs are enabled. NMA$C_PCLI_GSP is passed as a longword value and is read as four 8-bit unsigned integers. Each integer must be either a group SAP or zero. To enable a single group SAP on a port, you need only specify the group SAP value to be enabled in one of the four integers and place a value of zero in the three remaining integers. To disable group SAPs on the port, you need only place a value of zero in all four integers and issue the QIO. If this characteristic is correctly specified, any group SAPs that were previously enabled on the port are now replaced by the SAPs specified by the current request. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_ILP[1] | Internal loopback mode. This optional parameter places the device in internal loopback mode (not for the DEUNA, DEQNA, or DELQA devices). One of the following values can be specified:
If NMA$C_STATE_ON is specified, the NMA$C_PCLI_CON parameter must be in loopback (NMA$C_LINCN_LOO) mode. When the controller is in loopback mode (generally for testing), it can loop packets in external loopback or internal loopback. This parameter places the controller in one of these loopback modes. NMA$C_PCLI_ILP is passed as a longword value and affects all ports on the controller. Not all devices support loopback mode. If NMA$C_STATE_OFF is not specified, the request is completed with SS$_BADPARAM status. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_MCA | Multicast address (optional). Passed as a counted string that consists of a modifier word followed by a list of 6-byte (48-bit) multicast addresses. The value specified in the modifier word determines whether the addresses are set or cleared. If NMA$C_LINMC_CAL is specified, all multicast addresses in the list are ignored. The following mode values can be specified in the low byte of the modifier word:
The driver filters all multicast addresses on a per-port basis; therefore, only messages received with the port's physical address or the multicast addresses enabled on the port are used to complete the user's read operations. Note that each LAN controller supports a limited number of multicast addresses. If this limit is exceeded, the LAN driver enables the “accept all multicast” feature on the controller and all multicast packets on the LAN must be filtered by the LAN driver. This may cause a minor performance loss. NMA$C_PCLI_MCA is specified on a per-port basis. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_MLT | Multicast address state. This optional parameter instructs the controller hardware whether to accept all multicast addresses for this port. One of the following values can be specified:
NMA$C_PCLI_MLT allows you to receive all multicast address packets that also match the port's protocol type, SAP, or protocol identifier. Generally, you enable only your individual set of multicast addresses using the NMA$C_PCLI_MCA parameter, and leave the NMA$C_PCLI_MLT parameter in the off state. There could be a minor performance loss when the NMA$C_PCLI_MLT parameter is in the ON state because the LAN driver may have to process all multicast addresses on the medium; the number of multicast addresses on the line determines the amount of processing required. The NMA$C_PCLI_MLT parameter is passed as a longword value. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_PAD | Use message size field on transmit and receive messages (optional). One of the following values can be specified:
NMA$C_PCLI_PAD affects only the protocol type that issued the set mode request. It is passed as a longword value. On Ethernet, if padding is enabled on Ethernet format packets, the driver adds a 2-byte count field to the transmitted data. This field allows short packets (packets fewer than 46 bytes long) to be received with the proper length returned by the driver. The minimum Ethernet packet contains 46 bytes of user data. When fewer than 46 bytes are sent, the packet is padded and the receiver always receives 46 bytes of data. When padding is enabled, the maximum message size for transmit or receive operations is 1498 bytes (8998 bytes for jumbo packets) and the minimum is zero bytes. See “Ethernet Protocol Types” for additional information. NMA$C_PCLI_PAD should be specified only on a port where the Ethernet packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLI_FMT is set to NMA$C_LINFM_ETH). For FDDI, the same 2-byte count field is added; however, because FDDI packets can be as short as 22 bytes, FDDI transmit requests are never padded. | ||||||||
| NMA$C_PCLI_PHA[1] | Physical address (optional). It is passed as a counted string that consists of a modifier word followed by the 48-bit physical address. If the request is to clear the physical address or to set the physical address to the default address, the physical address (if present) is not read. One of the following mode values can be specified in the low byte of the modifier word:
If not specified for Ethernet, the default is the current address set by a previous set mode function on this controller, or the hardware address if no address was defined by a previous set mode function. If not specified for FDDI, the default is the hardware address. The physical address must be passed as a 6-byte (48-bit) quantity. The first byte is the least significant byte. A return value of -1 on a sense mode request implies that a physical address is not defined. The NMA$C_PCLI_PHA parameter affects all ports on a single controller. If the address specified is already being used on the extended LAN, SS$_IVADDR is returned. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_PID | Protocol identifier. This parameter is required for, and valid only on, ports that use 802 extended format packets. NMA$C_PCLI_PID is passed as a counted 5-byte string, which is the unique protocol identifier required for each 802 extended format user. All protocol identifiers specified on a controller must be unique except when the PID is being shared. NMA$C_PCLI_PID may only be specified on a port when the 802 extended packet format is selected; that is, NMA$C_PCLIFMT is set to NMA$C_LIFM_802E. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_PRM | Promiscuous (optional). One of the following values can be specified:
The NMA$C_PCLI_PRM parameter is passed as a longword value. Only one port on each controller can be active with promiscuous mode enabled. Enabling promiscuous mode requires PHY_IO privilege. THe NMA$C_PCLI_PRM parameter is passed as a longword value. HP does not recommend promiscuous mode for normal usage. Some Token Ring devices do not support real promiscuous access to the ring. See “Promiscuous Mode” for additional information. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_PTY | Protocol type. This value is read as a 16-bit unsigned integer and must be unique on the controller except when the protocol type is being shared. For Ethernet format ports, this is a required parameter. Valid protocol types are in the range 05-DD through FF. NMA$C_PCLI_PTY may only be specified on a port where the Ethernet packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLI_FMT is set to NMA$C_LINFM_ETH). NMA$C_PCLI_PTY is passed as a longword value; however, only the low-order word is used. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_RAC | Receive access control (Token Ring only). This optional parameter specifies whether the application receives a copy of the access control (AC) field for each Token Ring frame received. It is passed as a longword value. It must be passed with one of the following values:
The AC is returned in the P5 buffer. The P5 buffer size for Token Ring should always be a minimum of 54 bytes. This is due to the variable size of the Token Ring header. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_RES | Restart. This optional parameter allows the user to enable the automatic port restart feature of the LAN drivers. One of the following values can be specified:
The LAN drivers shut down all users of a controller if there is a fatal error on the controller or if the LAN driver determines that the controller has stopped functioning. All outstanding I/O operations on the LAN driver are completed with either an SS$_ABORT or SS$_TIMEOUT status. All ports that have the NMA$C_PCLI_RES parameter enabled (set to NMA$C_LINRES_ENA) have the port automatically restarted by the LAN driver approximately one second after it has been shut down due to a fatal error. If the user issues read or write QIOs to the port during the time the port is shut down, the driver completes the QIOs with an SS$_OPINCOMPL status. All ports that have the automatic restart feature disabled must be restarted by the application program when the port is shut down by the LAN driver. The application program should wait approximately 2 seconds to allow the LAN driver to stabilize. Once the LAN driver shuts down a port, it attempts a maximum of 30 consecutive automatic restarts. If there are 30 consecutive failures to restart the port, the port remains shut down. Note that it is unusual to have fatal errors on a LAN controller or to have a LAN driver detect that a LAN controller has stopped functioning. Having the ability to automatically restart a user's port makes the program easier to design because the program does not have to take into account the possibility of the LAN driver shutting down the port. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLL_RFC | Receive frame control (FDDI only). This optional parameter specifies whether the application receives a copy of the Frame Control (FC) field for each FDDI frame received. It is passed as a longword value. However, only the low-order byte is used. It must be passed with one of the following values:
For $QIO Read operations, the FC is passed to the application in the P5 buffer. The following are the sizes required for the P5 buffer for various packet formats and settings of NMA$C_PCLI_RFC:
| ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_SAP | 802 format SAP. This parameter is required if the 802 packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLI_FMT is set to NMA$C_LINFM_802)> NMA$C_PCLI_SAP defines an 802 SAP and is read as an 8-bit unsigned integer. The least significant bit of the SAP must be 0 and the SAP cannot be the null SAP (all 8 bits equal 0) or the SNAP SAP. NMA$C_PCLI_SAP is passed as a longword value. However, only the low-order byte is used. The SAP specified by NMA$C_PCLI_SAP is the SAP used to match incoming packets to complete read requests. It is used as the source SAP (SSAP) in all transmissions (write QIOs). Because it is illegal to transmit using a group SAP as the source SAP, the SAP specified by this NMA$C_PCLI_SAP cannot be a group SAP. NMA$C_PCLI_GSP describes how to set up group SAPs on a port. All individual SAPs specified on a controller must be unique on that controller; therefore, the SAP specified using the NMA$C_PCLI_SAP parameter is checked for uniqueness on the controller. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_SRMODE | Sets the source routing (SR) mode for the $QIO user (Token Ring only). This optional parameter allows the application to perform the source routing discovery. It must be passed with one of the following values:
The $QIOs exist to further manipulate the source routing cache. HP recommends that applications use the NMA$C_SR_TRANSPARENT mode. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_SRV | Port service. This optional parameter specifies the service supplied by the driver for the port. It can only be specified if the 802 packet format is selected (NMA$C_PCLI_FMT is set to NMA$C_LINFM_802). This characteristic is passed as a longword value. One of the following values can be specified:
| ||||||||
NMAC$C_PCLI_XAC | Transmit access control (Token Ring only). This is an optional parameter that enables applications to control the setting of the priority bits in the access control (AC) for frames being transmitted in a $QIO write operations. When set to a wanted value, all subsequent transmits use this AC value. | ||||||||
NMA$C_PCLI_XFC | Transmit frame control (FDDI) only). NMA$C_PCLI_XFC is an optional parameter that enables applications to control the setting of the priority bits in the FC for frames being transmitted in a $QIO write operation. NMA$C_PCLI_XFC is passed as a longword parameter that has many valid settings. If specified with a value of 0, the application supplies an FC value on each $QIO write operation. The FC value to be used in this case is supplied in the P5 buffer for the $QIO write operation. If the parameter is specified with a value other than 0, that value is inserted into the FC field of every transmit by the FDDI drivers. NO FC is present in the P5 buffer for the $QIO write in this case. If this parameter is not specified, the default setting (0) of the priority bits is used. Regardless of how the FC is supplied, the value specified must be valid. The allowable values for FC are between 50 hexadecimal and 57 hexadecimal. If NMA$C_PCLI_XFC is specified with a nonzero value outside the valid range, the application receives a SS$_BADPARAM error. The priority bits are the three low-order bits. | ||||||||
[1] If the LAN controller is active and you do not specify this parameter, the parameter defaults to current setting. If the LAN controller is not controller is not active, this parameter defaults to the default value indicated. | |||||||||
Table 9-34 summarizes the use of the set mode parameters for the Ethernet, 802, and 802 extended (802E) packet formats.
Table 9-34 Set Mode Parameters for Packet Formats
| Parameter ID | Ethernet | IEEE 802 | 802E |
|---|---|---|---|
FMT | Default | Required | Required |
PTY | Required | Error | Error |
SAP | Error | Required | Error |
PID | Error | Error | Required |
ACC | Optional | Error | Error |
DES | Optional | Error | Error |
PAD | Optional | Error | Error |
SRV | Error | Optional | Error |
GSP | Error | Optional | Error |
BFN, BUS, CCA, CON, CRC, EKO, ILP, MCA, MLT, PHA, PRM, RAC, RES, RFC, SRMODE, XAC, XFC | Optional | OPT | OPT |
When starting a LAN port, the LAN driver checks that the mode of the new port is compatible with the mode of the LAN ports already started. There are two sets of compatibility checks: one for ports running in shared mode and one for all ports.
The following parameters must match for all ports on the same controller:
NMA$C_PCLI_CON
NMA$C_PCLI_CRC
NMA$C_PCLI_EKO
NMA$C_PCLI_ILP
NMA$C_PCLI_PHA (need only match for Ethernet controllers)
Once a port is started, only the following parameters can be changed:
The shutdown controller function shuts down the LAN port. On completion of a shutdown request all outstanding I/O requests are completed. This port cannot be used again until another startup request has been issued (see “Set Controller Mode” ).
The following function code is used to shut down a port:
The shutdown controller function takes no device- or function-dependent arguments.
This function requests that an attention AST be delivered to the requesting process when a status change occurs on the assigned port. An AST is queued when a message is available and there is no waiting read request. The enable attention AST function is legal at any time, regardless of the condition of the unit status bits.
The following function code and modifier is used to enable an attention AST:
This function takes the following device- or function-dependent arguments:
The enable attention AST function enables an attention AST to be delivered to the requesting process once only. After the AST occurs, it must be explicitly reenabled by the function before the AST can occur again. The function is subject to AST quotas.
The AST service routine is called with an argument list. The first argument is the current value of the second longword of the I/O status block (see “I/O Status Block”).
The IO$M_SET_MAC qualifier, when used with IO$_SETMODE, is used to set medium specific parameters. The Token Ring parameters require PHY_IO privilege to be set. Table 9-35 shows the parameters that may be set for Ethernet. Table 9-36 shows the parameters that may be set for FDDI. Table 9-37 shows the parameters that may be set for Token Ring, and Table 9-38 shows the parameters that may be set for ATM.
Table 9-35 Parameters of IO$M_SET_MAC for Ethernet
| Parameter ID | Meaning |
|---|---|
MA$C_PCLI_FDE | Enables or disables full duplex operation. The values for this parameter are NMA$C_STATE_ON or NMA$C_STATE_OFF. |
NMA$C_PCLI_LINEMEDIA | Sets the connection media type for the Ethernet adapter. Valid values for this parameter are:
|
NMA$C_PCLI_LINESPEED | Sets the speed of the Ethernet adapter. Valid values for this parameter are:
|
Table 9-36 Parameters of IO$M_SET_MAC for FDDI
| Parameter ID | Meaning |
|---|---|
NMA$C_PCLI_TREQ | Requested value for token rotation timer, ANSI MAC T_req parameter. Units are in 80 nanoseconds, the default is 8000, minimum is 4000, and maximum is 167772. |
NMA$C_PCLI_TVX | Maximum time between arrivals of a valid frame or unrestricted token, ANSI MAC TVX parameter. Units are in 80 nanoseconds, the default is 2621, minimum is 2500, and maximum is 5222. |
NMA$C_PCLI_REST_TTO | Restricted token timeout which limits how long a single restricted mode dialog may last before being terminated. Units are in milliseconds, the default is 1000, minimum is 0, and maximum is 10000. |
NMA$C_PCLI_RPE | Ring purge enable. If 1 (TRUE), this link participates in the Ring Purger election and, if elected, perform the Ring Purger function. |
NMA$C_PCLI_NIF_TARG | Neighbor information frame target. |
NMA$C_PCLI_SIF_CONF_TARG | Station information frame configuration target. A 6-byte string specifying the LAN address of the target. Used only by DECnet/OSI. |
NMA$C_PCLI_SIF_OP_TARG | Station information frame operation target. A 6-byte string specifying the LAN address of the target. Used only by DECnet/OSI. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ECHO_TARG | Echo test target. A 6-byte string specifying the LAN address of the target. Used only by DECnet/OSI. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ECHO_DAT | Data pattern to use for the echo test. Used only by DECnet/OSI. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ECHO_LEN | Length of the echo packet. Used only by DECnet/OSI. |
Table 9-37 Parameters of IO$M_SET_MAC for Token Ring
| Parameter ID | Meaning |
|---|---|
NMA$C_PCLI_RNG_SPD | Sets the speed of the ring. This longword may be either:
The default is NMA$C_LINRNG_SIXTN. |
NMA$C_PCLI_LINEMEDIA | Sets the connection media type for the Token Ring adapter. Valid values for this longword parameter are:
The default is NMA$C_MEDIA_STP. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ETR | Controls the Early Token release feature of the Token Ring hardware. This feature can greatly improve throughput, and is only valid on 16 Mb/s rings. The values for this longword parameter are NMA$C_STATE_ON or NMA$C_STATE_OFF. The default is NMA$C_STATE_ON. |
NMA$C_PCLI_MONCONTEND | Specifies whether the controller participates in the monitor contention process when another adapter detects the need for contention and initiates the process. The values for this longword parameter are NMA$C_STATE_ON or NMA$C_STATE_OFF. The default is NMA$C_STATE_OFF. |
NMA$C_PCLI_CACHE_ENT | The number of source routing (SR) entries to make available for caching. The default is 200, minimum is 20, and maximum is 2000. Each cache entry consumes 64 bytes. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ROUTEDIS | The source routing discovery timer. This is the amount of seconds to wait after the transmission of ring explorer packets before declaring the route of a path to be unknown. The default is 2 seconds, minimum is 1, and maximum is 255. |
NMA$C_PCLI_A_TIM | The source routing aging timer. After traffic is neither received from nor sent to a given node for this number of seconds, the entry is marked stale. After the entry is marked stale, rediscovery is required to communicate with the node. The default is 60 seconds, minimum is 1, and maximum is 65535. |
NMA$C_PCLI_SRC_ROU | Enables and disables source routing. The values for this longword parameter are NMA$C_LINSRC_ENA or NMA$C_LINSRC_DIS. The default is NMA$C_LINSRC_ENA. |
NMA$C_PCLI_AUTH_PR | Specifies the highest priority that a user may transmit a frame. The priority is set within the NMA$C_PCLI_XAC parameter. The default for this parameter is 3, minimum is 0, and maximum is 6. |
Table 9-38 Parameters of IO$M_SET_MAC for ATM
| Parameter ID | Meaning |
|---|---|
NMA$C_PCLI_MED | Medium. This longword parameter defaults to and may only be set to NMA$C_LINMD_CSMACD. |
NMA$C_PCLI_BUS | Buffer size. This longword parameter specifies the requested maximum packet size of the emulated LAN. The value may be either 1516, 4544, or 9234. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ELAN_PAR | Parent device name. This is a 3- or 4-character string parameter that specifies the name of the ATM device to associate with this emulated LAN. |
NMA$C_PCLI_NET | ELAN name. This is a string of up to 64 characters that specifies the name of the emulated LAN to join. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ELAN_DESC | ELAN description. This is a string of up to 64 characters long that provides additional description of the emulated LAN for status displays. |
NMA$C_PCLI_LES_HWA | LES ATM address. This is specified as a 40-character string as the hexadecimal representation of a 20-byte ATM address. |
NMA$C_PCLI_ELAN_STATE_REQ | ELAN change state request value. This longword parameter directs the driver to either start or shutdown the emulated LAN. Start is specified by a value of 2. Shutdown is specified by a value of 4. |
NMA$C_PCLI_EVENT_REQ | Event mask request. If set to 1, this longword parameter directs the driver to set the event reporting mask to the value given by the event parameter. |
NMA$C_PCLI_EVENT | Event mask value. This is a longword bit mask that controls the event reporting done by the driver. A bit set in the mask enables the reporting of corresponding event(s). |
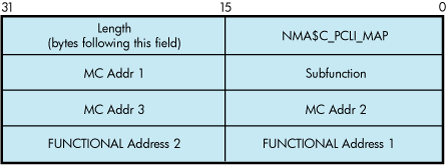
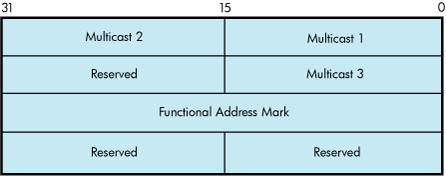
Using Token Ring only, the IO$M_UPDATE_MAP qualifier, when used with IO$_SETMODE, manipulates the adapter's functional address mapping table. Figure 9-15 shows the format of the P2 buffer for this operation. This QIO requires PHY_IO privilege.
The subfunction is one of the following:
NMA$C_MAP_CHANGE — This function adds or changes a mapping in the functional address table. If the specified multicast entry does not exist, an entry is created with the specified functional address mask. If the specified multicast entry does exist, the corresponding functional address mask is changed to the specified mask. All users who currently have the multicast enabled when the functional mask is changed will automatically update the functional address table as part of this operation.
Possible errors returned include the following:
NMA$C_MAP_DELETE — This function deletes the specified MC address in the table. For this function, the functional address mask is not required to pass the P2 buffer. If the functional address mask is passed, its contents are ignored.
Possible errors returned include the following:
The following example maps multicast address AB-01-01-01-02-03 to the functional address 03-00-00-01-00-00 for device ICA0:.
LANCP>SET DEVICE/MAP= -_LANCP>(MULTICAST=AB-01-01-01-02-03, -_LANCP>FUNCTIONAL=00-01-00-00) ICA0: |
The following example deletes the mapping of the multicast address of AB-01-01-01-02-03 for the device ICA0:.
LANCP>SET DEVICE/NOMAP=(MULTICAST=AB-01-01-01-02-03) ICA0: |
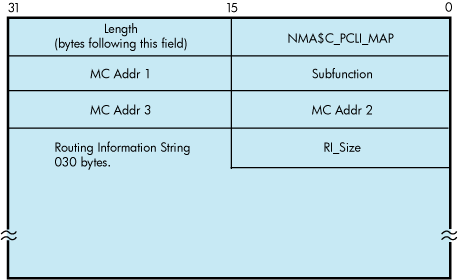
For Token Ring only, the IO$M_ROUTE qualifier, when used with IO$_SETMODE, manipulates the source routing cache table. This command is successful only when source routing is enabled. Source routing is enabled with the set mac qualified set mode QIO. Figure 9-16 shows the format of the P2 buffer. This QIO requires the PHY_IO privilege.
The subfunction is one of the following:
NMA$C_SR_ADD — This function adds or changes a source routing cache entry. It enters the LAN address into the table with the enclosed routing information. The routing information string format is documented in “Token Ring Frames ” . If RI_size is passed as 0, the entry is created (or modified) to be in the EXPLORING state (this is useful for users who are doing their own source routing). If the RC 'Lth' field is 0, the LAN address is entered in the table as being in the local state.
Possible errors returned include:
NMA$C_SR_DELETE — This function deletes a source routing cache entry. The RI_size and the routing information string are not required for this QIO. If one or both of the fields are passed for this operation, they are ignored. The result of this command is to put the entry into the deleted state. When the entry goes into the deleted state, it is deleted within 10 minutes.
Possible errors returned include the following:
The sense mode function returns the port attributes in the specified buffer. These attributes include the device characteristics described in “LAN Device Information” and, with the exceptions noted below, the attributes listed in Table 9-33.
The following combinations of function code and modifier are provided:
IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_CTRL—Read characteristics
IO$_SENSECHAR!IO$M_CTRL—Read characteristics
IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_SENSE_MAC—Medium specific characteristics
IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_SHOW_MAP—Returns current functional address to multicast address mapping (Token Ring only)
IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_SHOW_ROUTE—Returns current source routing cache table (Token Ring only)
These functions take the following device- or function-dependent arguments:
P1—The address of a two-longword buffer where the device characteristics are stored. (Figure 9-17 shows the format for, and “LAN Device Information” describes the contents of, the P1 buffer.) The P1 argument is optional.
P2—The address of a quadword descriptor where the attributes buffer is stored. The first longword of the descriptor is the buffer length; the second longword is the address of the buffer. The P2 argument is optional.
The P2 buffer is not read by the LAN driver. The driver stores the port's attributes in the buffer, which contains multiple entries. The format of each entry depends on whether a longword or a counted string is returned, as shown in Figure 9-18. Each parameter ID contains a string indicator bit (bit 12) that describes whether the data item is a string or a longword.
Except for the following differences, P2 returns the same attributes as those listed in Table 9-31:
All parameters that are valid for the enabled packet format are returned (see Table 9-32).
The sense-mode P2 buffer does not return the modifier word for the NMA$C_PCLI_PHA, NMA$C_PCLI_MCA, and NMA$C_PCLI_DES parameter IDs.
The NMA$C_PCLI_DES parameter is only returned on Ethernet ports whose access mode is set to “shared with destination.”
In addition to the parameter IDs listed in Table 9-31, the sense-mode P2 buffer contains the following parameter IDs:[2]
| Packet Format | Ethernet | FDDI | Token Ring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4470 | 4418 | |
Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4468 | 4416 | |
802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4475 | 4423 | |
802E format | 1492 | 4470 | 4418 | |
The values for LAN emulation over ATM are: | ||||
Packet Format | ATM ELAN size: | 1516 | 4544 | 9234 |
Ethernet format without padding | 1500 | 4528 | 9218 | |
| Ethernet format with padding | 1498 | 4526 | 9216 | |
| 802 format with 1-byte CTL field | 1497 | 4525 | 9215 | |
| 802E format | 1492 | 4520 | 9210 | |
It is suggested that a size of 250 bytes be used for the P2 buffer. This allows space for additional parameters that may be returned in future releases of OpenVMS.
All attributes that fit into the buffer specified by P2 are returned; however, if all the attributes cannot be stored in the buffer, the I/O status block returns the status SS$_BUFFEROVF. The second word of the I/O status block contains the number of bytes used in the P2 buffer (see “I/O Status Block”).
The IO$M_SENSE_MAC qualifier, when used with IO$_SENSEMODE, returns the parameters specified in “IO$M_SET_MAC Functional Modifier to IO$M_SETMODE”. In addition to the set mac parameters, Table 9-39 shows the returns of the following parameters:
Table 9-39 Parameters of IO$M_SENSE_MAC
| Parameter ID | Meaning |
|---|---|
NMA$C_PCLI_T_NEG | The negotiated value of the token rotation timer (ANSI MAC parameter T_neg) (FDDI only). |
NMA$C_PCLI_DAT | The duplicate address test flag (FDDI only). If set, this indicates that there is another station on the ring with the same hardware LAN address. |
NMA$C_PCLI_UNA | Upstream neighbor's address (FDDI and Token Ring). This is a string parameter specifying the 6-byte LAN address of the upstream neighbor. Not all devices may support this feature. |
NMA$C_PCLI_OLD_UNA | The old (previous) upstream neighbor address (FDDI only). Neighbor addresses change as nodes insert and deinsert into the ring. |
NMA$C_PCLI_UN_DAT | The upstream neighbor's duplicate address test flag (FDDI only). |
NMA$C_PCLI_DNA | The downstream neighbor's LAN address (FDDI only). |
NMA$C_PCLI_OLD_DNA | The old (previous) downstream neighbor's LAN address (FDDI only). |
NMA$C_PCLI_RPS | The current ring purger state (FDDI only). This longword parameter is one of the following values:
|
NMA$C_PCLI_RER | The latest ring error reason (FDDI only). This longword parameter is one of the following values:
|
NMA$C_PCLI_NBR_PHY | Neighbor's PHY type (FDDI only). This longword parameter is one of the following values:
|
NMA$C_PCLI_RJR | Ring reject reason (FDDI only). This longword parameter is one of the following values:
|
NMA$C_PCLI_LEE | Link error estimate (FDDI only). The longword value is a negative exponent of 10 representing the Link error rate. For example, the value of X represents the error rate of 10^X. |
NMA$C_PCLI_RNG_NUM | The longword value contains the ring number that the controller is running on (Token Ring only). It is only valid for a controller that is started, and also only valid for rings that have a ring parameter server that is configured for providing this information. |
For Token Ring only, the IO$M_SHOW_MAP qualifier, when used with IO$_SENSEMODE, returns the current setting of the mapping table. The P2 buffer is filled with the current multicast to functional address mapping information. The entries are 16 bytes long and are in the format shown in Figure 9-19. This QIO requires PHY_IO privilege.
The multicast address and functional address mask are returned in canonical format (that is, not bit-reversed). The following errors may occur:
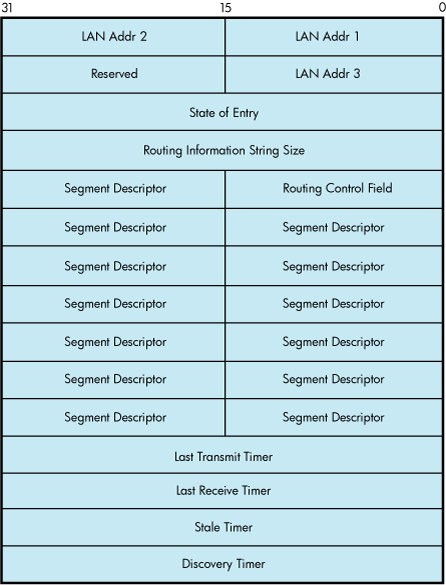
For Token Ring only, the IO$M_SHOW_ROUTE qualifier, when used with IO$_SENSEMODE, returns the current value of the source routing cache table. Each entry is 64 bytes long. Figure 9-20 shows the format of the returned P2 buffer.
Table 9-40 shows possible states of the entry.
Table 9-40 State of the Entry
| Value | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
0 | LOCAL | Address is reachable on the attached ring. |
1 | STALE | Entry is stale (inactive). |
2 | UNKNOWN | Route to the address is unknown. |
3 | DELETED | Entry is marked for deletion. |
4 | KNOWN | Route is known and the route is stored in the routing information string. |
5 | EXPLORING | Route to the address is currently being explored. |
The LAN address is returned in canonical format (that is, not bit-reversed). The timers are recorded as seconds before expiration. The transmit and receive timers are initialized from the NMA$C_PCLI_A_TIM parameter, the discovery timer is initialized from the NMA$C_PCLI_ROUTEDIS parameter, and the stale timer is initialized to 10 minutes (600 seconds). The following errors may occur:
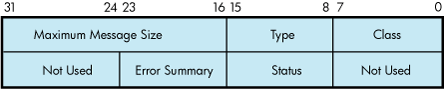
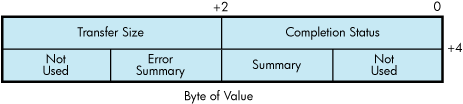
The I/O status block (IOSB) for all LAN driver functions is shown in Figure 9-21. Appendix A lists the completion status returned for these functions. (The OpenVMS system messages documentation provides explanations and suggested user actions for these status codes.)
The first longword of the IOSB returns, in addition to the completion status, either the size (in bytes) of the data transfer or the size (in bytes) of the attribute buffer (P2) returned by a sense mode function. The second longword returns the unit and line status bits listed in Table 9-26 and the error summary bits listed in Table 9-27.