 | HP OpenVMS System Services Reference ManualHP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$CREPRCCreates, on behalf of the calling process, a subprocess or detachedprocess on the current node, or a detached process on another OpenVMSCluster node.
FormatSYS$CREPRC [pidadr] ,[image] ,[input] ,[output] ,[error] ,[prvadr],[quota] ,[prcnam] ,[baspri] ,[uic] ,[mbxunt] ,[stsflg] ,[itmlst],[node] ,[home_rad]
C Prototypeint sys$creprc (unsigned int *pidadr, void *image, void *input, void*output, void *error, struct _generic_64 *prvadr, unsigned int *quota,void *prcnam, unsigned int baspri, unsigned int uic, unsigned short intmbxunt, unsigned int stsflg,...);
Argumentspidadr
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the newly created process. Thepidadr argument is the address of a longword intowhich $CREPRC writes the PID.image
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the image to be activated in the newly created process. Theimage argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to the file specification of the image.The image name can have a maximum of 63 characters. If the image namecontains a logical name, the logical name is translated in the createdprocess and must therefore be in a logical name table that it canaccess. To create a process that will run under the control of a commandlanguage interpreter (CLI), specify SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE as theimage name. input
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$INPUT inthe logical name table of the created process. Theinput argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.output
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$OUTPUT inthe logical name table of the created process. Theoutput argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.error
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Equivalence name to be associated with the logical name SYS$ERROR inthe logical name table of the created process. Theerror argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to the equivalence name string.Note that the error argument is ignored if theimage argument specifies SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE; inthis case, SYS$ERROR has the same equivalence name as SYS$OUTPUT. prvadr
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_privileges | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Privileges to be given to the created process. Theprvadr argument is the address of a quadword bit maskwherein each bit corresponds to a privilege; setting a bit gives theprivilege. If the prvadr argument is not specified,the current privileges are used.Each bit has a symbolic name; the $PRVDEF macro defines these names.You form the bit mask by specifying the symbolic name of each desiredprivilege in a logical OR operation. Table SYS-20 gives the symbolic name and description of each privilege. Table SYS-20 User Privileges | Privilege | Symbolic Name | Description | | ACNT | PRV$M_ACNT | Create processes for which no accounting is done | | ALLSPOOL | PRV$M_ALLSPOOL | Allocate a spooled device | | ALTPRI | PRV$M_ALTPRI | Set (alter) any process priority | | AUDIT | PRV$M_AUDIT | Generate audit records | | BUGCHK | PRV$M_BUGCHK | Make bugcheck error log entries | | BYPASS | PRV$M_BYPASS | Bypass UIC-based protection | | CMEXEC | PRV$M_CMEXEC | Change mode to executive | | CMKRNL | PRV$M_CMKRNL | Change mode to kernel | | DIAGNOSE | PRV$M_DIAGNOSE | Can diagnose devices | | DOWNGRADE | PRV$M_DOWNGRADE | Can downgrade classification | | EXQUOTA | PRV$M_EXQUOTA | Can exceed quotas | | GROUP | PRV$M_GROUP | Group process control | | GRPNAM | PRV$M_GRPNAM | Place name in group logical name table | | GRPPRV | PRV$M_GRPPRV | Group access via system protection field | | IMPERSONATE 1 | PRV$M_IMPERSONATE | Can create detached processes under another UIC | | IMPORT | PRV$M_IMPORT | Mount a nonlabeled tape volume | | LOG_IO | PRV$M_LOG_IO | Perform logical I/O operations | | MOUNT | PRV$M_MOUNT | Issue mount volume QIO | | NETMBX | PRV$M_NETMBX | Create a network device | | OPER | PRV$M_OPER | All operator privileges | | PFNMAP | PRV$M_PFNMAP | Map to section by physical page frame number | | PHY_IO | PRV$M_PHY_IO | Perform physical I/O operations | | PRMCEB | PRV$M_PRMCEB | Create permanent common event flag clusters | | PRMGBL | PRV$M_PRMGBL | Create permanent global sections | | PRMMBX | PRV$M_PRMMBX | Create permanent mailboxes | | PSWAPM | PRV$M_PSWAPM | Change process swap mode | | READALL | PRV$M_READALL | Possess read access to everything | | SECURITY | PRV$M_SECURITY | Can perform security functions | | SETPRV | PRV$M_SETPRV | Set any process privileges | | SHARE | PRV$M_SHARE | Can assign a channel to a nonshared device | | SYSGBL | PRV$M_SYSGBL | Create system global sections | | SYSLCK | PRV$M_SYSLCK | Queue systemwide locks | | SYSNAM | PRV$M_SYSNAM | Place name in system logical name table | | SYSPRV | PRV$M_SYSPRV | Access files and other resources as if you have a system UIC | | TMPMBX | PRV$M_TMPMBX | Create temporary mailboxes | | UPGRADE | PRV$M_UPGRADE | Can upgrade classification | | VOLPRO | PRV$M_VOLPRO | Override volume protection | | WORLD | PRV$M_WORLD | World process control |
1This privilege replaces the DETACH privilege; however, theprior mask, PRV$M_DETACH, is still valid for existing programs.
You need the user privilege SETPRV to grant a process any privilegesother than your own. If the caller does not have this privilege, themask is minimized with the current privileges of the creating process;any privileges the creating process does not have are not granted, butno error status code is returned. quota
| OpenVMS usage: | item_quota_list | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Process quotas to be established for the created process. These quotaslimit the created process's use of system resources. Thequota argument is the address of a list of quotadescriptors, where each quota descriptor consists of a 1-byte quotaname followed by a longword that specifies the desired value for thatquota. The list of quota descriptors is terminated by the symbolic namePQL$_LISTEND.If you do not specify the quota argument or specify itas 0, the operating system supplies a default value for each quota. For example, in MACRO you can specify a quota list, as follows:
QLIST: .BYTE PQL$_PRCLM ; Limit number of subprocesses .LONG 2 ; Max = 2 subprocesses .BYTE PQL$_ASTLM ; Limit number of asts .LONG 6 ; Max = 6 outstanding asts .BYTE PQL$_LISTEND ; End of quota list | The $PQLDEF macro defines symbolic names for quotas. In C you can specify a quota list, as follows:
#include <pqldef.h>...#pragma member_alignment save#pragma nomember_alignmenttypedef struct { char Quota; int Value; } QUOTA_ENTRY_T;#pragma member_alignment restore... QUOTA_ENTRY_T QuotaArray[] = {{PQL$_PRCLM, 2}, {PQL$_ASTLM, 6}, {PQL$_LISTEND, 0}}; | Individual Quota Descriptions
A description of each quota follows. The description of each quotalists its minimum value (a system parameter), its default value (asystem parameter), and whether it is deductible, nondeductible, orpooled. These terms have the following meaning: | Minimum value | A process cannot be created with a quota less than this minimum. Any quota value you specify is maximized against this minimum. You obtain the minimum value for a quota by running SYSGEN to display the corresponding system parameter. | | Default value | If the quota list does not specify a value for a particular quota, the system assigns the process this default value. You obtain the default value by running SYSGEN to display the corresponding system parameter. | | Deductible quota | When you create a subprocess, the value for a deductible quota is subtracted from the creating process's current quota and is returned to the creating process when the subprocess is deleted. There is currently only one deductible quota, the CPU time limit. Note that quotas are never deducted from the creating process when a detached process is created. | | Nondeductible quota | Nondeductible quotas are established and maintained separately for each process and subprocess. | | Pooled quota | Pooled quotas are established when a detached process is created, and they are shared by that process and all its descendent subprocesses. Charges against pooled quota values are subtracted from the current available totals as they are used and are added back to the total when they are not being used. | To run SYSGEN to determine the minimum and default values of a quota,enter the following sequence of commands:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGENSYSGEN> SHOW/PQL | Minimum values are named PQL_Mxxxxx, where xxxxx arethe characters of the quota name that follow "PQL$_" in thequota name. Default values are named PQL_Dxxxxx, where xxxxx arethe characters of the quota name that follow "PQL$_" in thequota name. Individual Quotas
PQL$_ASTLMAsynchronous system trap (AST) limit. This quota restricts both thenumber of outstanding AST routines specified in system service callsthat accept an AST address and the number of scheduled wakeup requeststhat can be issued. Minimum: PQL_MASTLM
Default: PQL_DASTLM
Nondeductible PQL$_BIOLMBuffered I/O limit. This quota limits the number of outstandingsystem-buffered I/O operations. A buffered I/O operation is one thatuses an intermediate buffer from the system pool rather than a bufferspecified in a process's $QIO request. Minimum: PQL_MBIOLM
Default: PQL_DBIOLM
Nondeductible PQL$_BYTLMBuffered I/O byte count quota. This quota limits the amount of systemspace that can be used to buffer I/O operations or to create temporarymailboxes. Minimum: PQL_MBYTLM
Default: PQL_DBYTLM
Pooled PQL$_CPULMCPU time limit, specified in units of 10 milliseconds. This quotalimits the total amount of CPU time that a created process can use.When it has exhausted its CPU time limit quota, the created process isdeleted and the status code SS$_EXCPUTIM is returned.If you do not specify this quota and the created process is a detachedprocess, the detached process receives a default value of 0, that is,unlimited CPU time. If you do not specify this quota and the created process is asubprocess, the subprocess receives half the CPU time limit quota ofthe creating process. If you specify this quota as 0, the created process has unlimited CPUtime, provided the creating process also has unlimited CPU time. If,however, the creating process does not have unlimited CPU time, thecreated process receives half the CPU time limit quota of the creatingprocess. The CPU time limit quota is a consumable quota; that is, the amount ofCPU time used by the created process is not returned to the creatingprocess when the created process is deleted. Minimum: PQL_MCPULM
Default: PQL_DCPULM
Deductible PQL$_DIOLMDirect I/O quota. This quota limits the number of outstanding directI/O operations. A direct I/O operation is one for which the systemlocks the pages containing the associated I/O buffer in memory for theduration of the I/O operation. Minimum: PQL_MDIOLM
Default: PQL_DDIOLM
Nondeductible PQL$_ENQLMLock request quota. This quota limits the number of lock requests thata process can queue. Minimum: PQL_MENQLM
Default: PQL_DENQLM
Pooled PQL$_FILLMOpen file quota. This quota limits the number of files that a processcan have open at one time. Minimum: PQL_MFILLM
Default: PQL_DFILLM
Pooled PQL$_JTQUOTAJob table quota. This quota limits the number of bytes of system pagedpool used for the job logical name table. If the process being createdis a subprocess, this item is ignored.A value of 0 represents an unlimited number of bytes. Minimum: PQL_MJTQUOTA
Default: PQL_DJTQUOTA
Nondeductible PQL$_PGFLQUOTAPaging file quota. This quota limits the number of pages (on VAXsystems) or pagelets (adjusted up or down to represent CPU-specificpages on Alpha systems) that can be used to provide secondary storagein the paging file for the execution of a process. Minimum: PQL_MPGFLQUOTA
Default: PQL_DPGFLQUOTA
Pooled PQL$_PRCLMSubprocess quota. This quota limits the number of subprocesses aprocess can create. Minimum: PQL_MPRCLM
Default: PQL_DPRCLM
Pooled PQL$_TQELMTimer queue entry quota. This quota limits both the number of timerqueue requests a process can have outstanding and the creation oftemporary common event flag clusters. Minimum: PQL_MTQELM
Default: PQL_DTQELM
Pooled PQL$_WSDEFAULTDefault working set size. This quota defines the number of pages (onVAX systems) or pagelets (adjusted up or down to represent CPU-specificpages on Alpha systems) in the default working set for any image theprocess executes. The working set size quota determines the maximumsize you can specify for this quota. Minimum: PQL_MWSDEFAULT
Default: PQL_DWSDEFAULT
Nondeductible PQL$_WSEXTENTWorking set expansion quota. This quota limits the maximum size towhich an image can expand its working set size with the Adjust WorkingSet Limit ($ADJWSL) system service. Minimum: PQL_MWSEXTENT
Default: PQL_DWSEXTENT
Nondeductible PQL$_WSQUOTAWorking set size quota. This quota limits the maximum size to which animage can lock pages in its working set with the Lock Pages in Memory($LCKPAG) system service. Minimum: PQL_MWSQUOTA
Default: PQL_DWSQUOTA
Nondeductible
Use of the Quota List
The values specified in the quota list are not necessarily the quotasthat are actually assigned to the created process. The $CREPRC serviceperforms the following steps to determine the quota values that areassigned when you create a process on the same node: - It constructs a default quota list for the process being created, assigning it the default values for all quotas. Default values are system parameters and so might vary from system to system.
- It reads the specified quota list, if any, and updates the corresponding items in the default list. If the quota list contains multiple entries for a quota, only the last specification is used.
- For each item in the updated quota list, it compares the quota value with the minimum value required (also a system parameter) and uses the larger value. Then, the following occurs:
- If a subprocess is being created or if a detached process is being created and the creating process does not have IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege, the resulting value is compared with the current value of the corresponding quota of the creating process and the lesser value is used.
Then, if the quota is a deductible quota, that value is deducted from the creating process's quota, and a check is performed to ensure that the creating process will still have at least the minimum quota required. If not, the condition value SS$_EXQUOTA is returned and the subprocess or detached process is not created.
Pooled quota values are ignored. - If a detached process is being created and the creating process has IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege, the resulting value is not compared with the current value of the corresponding quota of the creating process and the resulting value is not deducted from the creating process's quota. A process with IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege is allowed to create a detached process with quota values larger than it has.
When you create a detached process on another OpenVMS Cluster node, thequotas assigned to the process are determined in the following way: - The $CREPRC service reads the specified quota list, if any. If it contains multiple entries for a quota, only the last specification is used. If the process does not have IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege, the service compares each value in the list with the current value of the corresponding quota of the creating process and uses the lesser value. It sends the resulting quota list to the node on which the new process is to be created.
- On that node, the $CREPRC service constructs a default quota list for the process being created, assigning it default values for all quotas based on that node's system parameters.
- It updates the default list with the corresponding values from the quota list.
- For each item in the updated quota list, it compares the quota value with the minimum value required based on that node's system parameters and uses the larger value.
prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name to be assigned to the created process. Theprcnam argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to a process name string.If a subprocess is being created, the process name is implicitlyqualified by the UIC group number of the creating process. If adetached process is being created, the process name is qualified by thegroup number specified in the uic argument. baspri
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Base priority to be assigned to the created process. Thebaspri argument is a longword value.The OpenVMS VAX range is 0 to 31, where 31 is the highest priority and0 is the lowest. Usual priorities are in the range 0 to 15, andreal-time priorities are in the range 16 to 31. The OpenVMS Alpha range is 0 to 63, with real-time priorities in therange 32 to 63. If you want a created process to have a higher priority than itscreating process, you must have ALTPRI privilege to raise the prioritylevel. If the caller does not have this privilege, the specified basepriority is compared with the caller's priority and the lower of thetwo values is used. A process with ALTPRI privilege running on a VAX node can create aprocess with a priority greater than 31 on an Alpha node. If the baspri argument is not specified, the prioritydefaults to 2 for VAX MACRO and VAX BLISS--32 and to 0 for all otherlanguages. uic
| OpenVMS usage: | uic | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
User identification code (UIC) to be assigned to the created process.The uic argument is a longword value containing theUIC.If you do not specify the uic argument or specify itas 0 (the default), $CREPRC creates a process and assigns it the UIC ofthe creating process. If you specify a nonzero value for the uic argument,$CREPRC creates a detached process. This value is interpreted as a32-bit octal number, with two 16-bit fields: bits 0--15---member number
bits 16--31---group number You need IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege to create a detached processwith a UIC that is different from the UIC of the creating process. If the image argument specifies theSYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE, the UIC of the created process will be the UICof the caller of $CREPRC, and the UIC parameter is ignored. mbxunt
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned | | type: | word (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Unit number of a mailbox to receive a termination message when thecreated process is deleted. The mbxunt argument is aword containing this number.If you do not specify the mbxunt argument or specifyit as 0 (the default), the operating system sends no terminationmessage when it deletes the process. The Get Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) service can be used toobtain the unit number of the mailbox. If you specify the mbxunt argument, the mailbox isused when the created process actually terminates. At that time, the$ASSIGN service is issued for the mailbox in the context of theterminating process and an accounting message is sent to the mailbox.If the mailbox no longer exists, cannot be assigned, or is full, theerror is treated as if no mailbox had been specified. If you specify this argument when you create a process on another node,an accounting message will be written to the mailbox when the processterminates. If the node is removed from the cluster before the createdprocess terminates, an accounting message will be simulated. Thesimulated message will contain the created process's PID and name and afinal status of SS$_NODELEAVE, but will lack execution statistics. Note that two processes on different nodes cannot use the terminationmailbox for general interprocess communication. The accounting message is sent before process rundown is initiated butafter the process name has been set to null. Thus, a significantinterval of time can occur between the sending of the accountingmessage and the final deletion of the process. To receive the accounting message, the caller must issue a read to themailbox. When the I/O completes, the second longword of the I/O statusblock, if one is specified, contains the process identification of thedeleted process. The $ACCDEF macro defines symbolic names for offsets of fields withinthe accounting message. The offsets, their symbolic names, and thecontents of each field are shown in the following table. Unless statedotherwise, the length of the field is 4 bytes. | Offset | Symbolic Name | Contents | | 0 | ACC$W_MSGTYP | MSG$_DELPROC (2 bytes) | | 2 | | Not used (2 bytes) | | 4 | ACC$L_FINALSTS | Exit status code | | 8 | ACC$L_PID | External process identification | | 12 | | Not used (4 bytes) | | 16 | ACC$Q_TERMTIME | Current time in system format at process termination (8 bytes) | | 24 | ACC$T_ACCOUNT | Account name for process, blank filled (8 bytes) | | 32 | ACC$T_USERNAME | User name, blank filled (12 bytes) | | 44 | ACC$L_CPUTIM | CPU time used by the process, in 10-millisecond units | | 48 | ACC$L_PAGEFLTS | Number of page faults incurred by the process | | 52 | ACC$L_PGFLPEAK | Peak paging file usage | | 56 | ACC$L_WSPEAK | Peak working set size | | 60 | ACC$L_BIOCNT | Count of buffered I/O operations performed by the process | | 64 | ACC$L_DIOCNT | Count of direct I/O operations performed by the process | | 68 | ACC$L_VOLUMES | Count of volumes mounted by the process | | 72 | ACC$Q_LOGIN | Time, in system format, that process logged in (8 bytes) | | 80 | ACC$L_OWNER | Process identification of owner | The length of the termination message is equated to the constantACC$K_TERMLEN. stsflg
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Options selected for the created process. The stsflgargument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to anoption. Only bits 0 to 22 are used; the others are reserved and must be0.Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $PRCDEF macro defines.You construct the stsflg argument by performing alogical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.The following table describes the symbolic name of each option: | Symbolic Name | Description | | PRC$M_BATCH | Create a batch process. IMPERSONATE privilege is required. | | PRC$M_IMPERSONATE | Create a detached process under another UIC. | | PRC$M_DISAWS | Disable system-initiated working set adjustment. | | PRC$M_HIBER | Force process to hibernate before it executes the image. | | PRC$M_HOME_RAD | Assign process to specified home resource affinity domain (RAD). Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide. | | PRC$M_IMGDMP | Enable image dump facility. If an image terminates due to an unhandled condition, the image dump facility writes the contents of the address space to a file in your current default directory. The file name is the same as the name of the terminated image. The file type is .DMP. | | PRC$M_INTER | Create an interactive process. This option is meaningful only if the image argument specifies SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. The purpose of this option is to provide you with information about the process. When you specify this option, it identifies the process as one that is in communication with another user (an interactive process). For example, if you use the DCL lexical function F$MODE to make an inquiry about a process that has specified the PRC$M_INTER option, F$MODE returns the value INTERACTIVE. | | PRC$M_NETWRK | Create a process that is a network connect object. IMPERSONATE privilege required. | | PRC$M_NOACNT | Do not perform accounting. ACNT privilege is required. | | PRC$M_NOPASSWORD | Do not display the Username: and Password: prompts if the process is interactive and detached and the image is SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. If you specify this option in your call to $CREPRC, the process created by the call is logged in under the user name associated with the creating process. If you do not specify this option for an interactive process, SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE prompts you for the user name and password to be associated with the process. The prompts are displayed at the SYS$INPUT device. | | PRC$M_NOUAF | Do not check authorization file if the process is detached and the image is SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. You should not specify this option if a subprocess is being created. In previous versions of the operating system, the symbolic name of this option was PRC$M_LOGIN. The symbolic name has been changed to more accurately denote the effect of setting this bit. For compatibility with existing user programs, you can still specify this bit as PRC$M_LOGIN. This flag prevents the loading of the new process's security profile from the contents of the UAF record associated with the specified user name. Restrictions are still enforced on the UAF record, if it exists, for account disuser, account expiration, and primary/secondary days/hours. | | PRC$M_PARSE_EXTENDED | Sets the PARSE_STYLE_PERM and the PARSE_STYLE_IMAGE properties for the new process to EXTENDED. | | PRC$M_PSWAPM | Inhibit process swapping. PSWAPM privilege is required. | | PRC$M_SSFEXCU | Enable system service failure exception mode. | | PRC$M_SSRWAIT | Disable resource wait mode. | | PRC$M_SUBSYSTEM | Inherit any protected subsystem identifiers. The default is that the new process does not inherit subsystem identifiers. | | PRC$M_TCB | Mark a process as part of the trusted computing base (TCB). As such, it is expected to perform its own auditing. IMPERSONATE privilege is required. | Note that options PRC$M_BATCH, PRC$M_INTER, PRC$M_NOUAF, PRC$M_NETWRK,and PRC$M_NOPASSWORD are intended for use by HP software. itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: | reserved | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | |
The itmlst argument is reserved by HP.node
| OpenVMS usage: | SCS_nodename | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the OpenVMS Cluster node on which the process is to be created.The node argument is the address of a character stringdescriptor pointing to a 1- to 6-character SCS node name string. If theargument is present but zero or if the string is zero length, theprocess is created on the current node.home_rad
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Sets the home resource affinity domain (RAD) of a process.The home RAD is determined by the operating system, unless youexplicitly request one. If bit PRC$M_HOME_RAD in thestsflg is set, home_rad is the RAD onwhich the process is to start. Note that you may set this bit to 0 onnon-RAD systems. Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
DescriptionThe Create Process service creates a subprocess or detached process onbehalf of the calling process. A subprocess can be created only on thecurrent OpenVMS Cluster node. A detached process can be created on thecurrent OpenVMS Cluster node or on the node specified with thenode argument.A detached process is a fully independent process. For example, theprocess that the system creates when you log in is a detached process.A subprocess, on the other hand, is related to its creating process ina treelike structure; it receives a portion of the creating process'sresource quotas and must terminate before the creating process. Anysubprocesses that still exist when their creator is being deleted areautomatically deleted. The presence of the uic argument,node argument, or the PRC$M_IMPERSONATE flag specifiesthat the created process is detached. Creating a process is synchronous in that the process has actually beencreated and its PID determined before control returns to the programthat requested the system service. Note, however, that the new processhas not necessarily begun to execute at that point. Some errorconditions are not detected until the created process executes. Theseconditions include an invalid or nonexistent image; invalid SYS$INPUT,SYS$OUTPUT, or SYS$ERROR logical name equivalence; inadequate quotas;or insufficient privilege to execute the requested image. In creating a detached or subprocess, you can specify that the processrun the image SYS$SYSTEM:LOGINOUT.EXE. During interactive logins,LOGINOUT performs the following functions: - It validates user name and password.
- It reads the system authorization file record associated with that user and redefines the process environment based on information from the record.
- It maps a command language interpreter (CLI) into the process and passes control to it.
The CLI reads a command from SYS$INPUT, processes it, and reads anothercommand. The presence of the CLI enables the process to executemultiple images. It also enables an image running in the process to useRun-Time Library procedures, such as LIB$SPAWN, LIB$DO_COMMAND, andLIB$SET_LOGICAL, that require a CLI. Running in the context of a process you create through $CREPRC,LOGINOUT can perform some or all of the preceding steps, depending onwhether the process is a subprocess or a detached process and on thevalues of PRC$M_NOPASSWORD and PRC$M_NOUAF in thestsflg argument. Certain characteristics of a created process can be specifiedexplicitly through $CREPRC system service arguments, while othercharacteristics are propagated implicitly from the $CREPRC caller.Implicit characteristics include the following: - Current default directory
- Creator's equivalence name for SYS$DISK
- User and account names
- Command language interpreter (CLI) name and command table file name
Note, however, that after the process has been created, if it runsLOGINOUT and LOGINOUT redefines the process environment, thosecharacteristics will be overridden by information from the systemauthorization file. Several process characteristics are relevant to the creation of aprocess on another OpenVMS Cluster node, in particular, process quotas,default directory, SYS$DISK equivalence name, CLI name, and CLI commandtable name. Quotas for a process created on another OpenVMS Cluster node arecalculated as previously described in the section on the use of thequota list; namely, they are based on explicit values passed by thecreator and system parameters on the other OpenVMS Cluster node. If theother node has its own authorization file with node-specific quotas,you might want to specify in the $CREPRC request that the process runLOGINOUT so it can redefine the process environment based on thatnode's quotas for the user. Unless overridden by LOGINOUT, the new process will use its creator'sdefault disk and directory. If the disk is not mounted clusterwide, thecreated process might need to redefine SYS$DISK with an equivalencename that specifies a disk accessible from that node. When you set the PRC$M_NOUAF flag in the stsflgargument and create a process running LOGINOUT, LOGINOUT will attemptto map a CLI and command table with the same file names as thoserunning in your process. The CLI and command table images musttherefore have already been installed by the system manager on theother node. Problems can arise when you are using something other thanthe DCL CLI and its standard command tables. For example, if you arerunning on a VAX node with MCR as your current CLI, LOGINOUT will beunable to map that CLI on an Alpha node. The new process will becreated but then aborted by LOGINOUT. A detached process is considered an interactive process only if (1) theprocess is created with the PRC$M_INTER option specified and (2)SYS$INPUT is not defined as a file-oriented device. The $CREPRC service requires system dynamic memory. Required Access or Privileges
The calling process must have the following: - IMPERSONATE or CMKRNL privilege to create any of the following types of process:
- A detached process with a UIC that is different from the UIC of the calling process
- A detached process with a larger value specified for some quota than is authorized for the caller
- A detached process on another node if the system parameter CWCREPRC_ENABLE has a value of 0
- IMPERSONATE privilege to create any of the following types of process:
- A batch process
- A network process
- A trusted computing base process
- ALTPRI privilege to create a subprocess with a higher base priority than the calling process
- SETPRV privilege to create a process with privileges that the calling process does not have
- PSWAPM privilege to create a process with process swap mode disabled
- ACNT privilege to create a process with accounting functions disabled
- OPER privilege to create a detached process on another OpenVMS Cluster node on which interactive logins have not yet been enabled
Required Quota
The number of subprocesses that a process can create is controlled bythe subprocess (PRCLM) quota; this quota is returned when a subprocessis deleted. The number of detached processes on any one OpenVMS Cluster node that aprocess can create with the same user name is controlled by theMAXDETACH entry in the user authorization file (UAF). When a subprocess is created, the value of any deductible quota issubtracted from the total value the creating process has available, andwhen the subprocess is deleted, the unused portion of any deductiblequota is added back to the total available to the creating process. Anypooled quota value is shared by the creating process and all itssubprocesses. Related Services
$CANEXH, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,$WAKE
Condition Values Returned | SS$_ACCVIO | The caller cannot read a specified input string or string descriptor, the privilege list, or the quota list; or the caller cannot write the process identification. | | SS$_BADRAD | The specified RAD contains no memory or contains no active CPUs, or the specified RAD is greater than or equal to the maximum number of RADs on the system. Use the $GETSYI item code RAD_MAX_RADS to determine the maximum number of RADs on the system. | | SS$_DUPLNAM | The specified process name duplicates one already specified within that group. | | SS$_EXPRCLM | The creation of a detached process failed because the creating process already reached its limit for the creation of detached processes. This limit is established by the MAXDETACH quota in the user authorization file (UAF) of the creating process. | | SS$_EXQUOTA | At least one of the following conditions is true: - The process has exceeded its quota for the creation of subprocesses.
- A quota value specified for the creation of a subprocess exceeds the creating process's corresponding quota.
- The quota is deductible and the remaining quota for the creating process would be less than the minimum.
| | SS$_INCOMPAT | The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system, namely, one that does not support remote process creation. | | SS$_INSFMEM | The system dynamic memory is insufficient for the requested operation. | | SS$_INVARG | An invalid argument was specified. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | At least one of the following two conditions is true: - The specified process name has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters.
- The specified image name, input name, output name, or error name has more than 255 characters.
| | SS$_IVQUOTAL | The quota list is not in the proper format. | | SS$_IVSTSFLG | A reserved status flag was specified. | | SS$_NODELEAVE | The specified node was removed from the OpenVMS Cluster during the $CREPRC service's execution. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The caller violated one of the privilege restrictions. | | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_NOSLOT | No process control block is available; in other words, the maximum number of processes that can exist concurrently in the system has been reached. | | SS$_NOSUCHNODE | The specified node is not currently a member of the cluster. | | SS$_REMRSRC | The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.) | | SS$_UNREACHABLE | The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process. |
$CRETVAAdds a range of demand-zero allocation pages (on VAX systems) orpagelets (on Alpha systems) to a process's virtual address space forthe execution of the current image.
FormatSYS$CRETVA inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
C Prototypeint sys$cretva (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,unsigned int acmode);
Argumentsinadr
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a 2-longword array containing the starting and endingvirtual addresses of the pages to be created. If the starting andending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is created. Theaddresses are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific pageboundaries. Only the virtual page number portion of the virtual addressis used; the low order byte-within-page bits are ignored.retadr
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference--array reference or descriptor |
Address of a 2-longword array to receive the starting and endingvirtual addresses of the pages created.On Alpha systems, the retadr argument should bechecked by programs for actual allocation. Because the Alphaarchitecture defines more than one page size, more space might becreated than was specified in the inadr argument. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode and protection for the new pages. Theacmode argument is a longword containing the accessmode.The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four accessmodes: | Symbol | Access Mode | | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The protection of the pages is read/write for the resultant access modeand those more privileged.
DescriptionThe Create Virtual Address Space service adds a range of demand-zeroallocation pages to a process's virtual address space for the executionof the current image.Pages are created starting at the address contained in the firstlongword of the location addressed by the inadrargument and ending with the second longword. The ending address can belower than the starting address. The retadr argumentindicates the byte addresses of the pages created. If an error occurs while pages are being created, theretadr argument, if specified, indicates the pagesthat were successfully created before the error occurred. If no pageswere created, both longwords of the retadr argumentcontain the value --1. If $CRETVA creates pages that already exist, the service deletes thosepages if they are not owned by a more privileged access mode than thatof the caller. Any such deleted pages are reinitialized as demand-zeropages. For this reason, it is important to use theretadr argument to capture the address range actuallycreated. Because the Alpha architecture has a larger page size than theVAX architecture, more space is potentially affected on Alpha systems. Required Access or Privileges
None Required Quota
The paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased size of the virtual address space. Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,$UPDSECW The Expand Program/Control Region ($EXPREG) service also adds pages toa process's virtual address space. Note
Do not use the $CRETVA system service in conjunction with otheruser-written procedures or procedures supplied by HP (includingRun-Time Library procedures). This system service provides no means tocommunicate a change in virtual address space with other routines. HPrecommends that you use either $EXPREG or the Run-Time Libraryprocedure Allocate Virtual Memory (LIB$GET_VM) to get memory. You canfind documentation on LIB$GET_VM in the OpenVMS RTL Library (LIB$) Manual. When using$DELTVA, you should take care to delete only pages that you havespecifically created. |
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The inadr argument cannot be read by the caller, or the retadr argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_EXQUOTA | The process has exceeded its paging file quota. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased size of the virtual address space. | | SS$_NOPRIV | A page in the specified range is in the system address space. | | SS$_NOSHPTS | A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the caller. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VASFULL | The process's virtual address space is full; no space is available in the page tables for the requested pages. |
$CRETVA_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, adds a range of demand-zero allocation pages to aprocess's virtual address space for the execution of the current image.The new pages are added at the virtual address specified by the caller.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRETVA_64 region_id_64 ,start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,flags,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
C Prototypeint sys$cretva_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, void *start_va_64,unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags,void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);
Argumentsregion_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to create the virtual addressrange. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space.The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. Also, given a particular virtual address, the region ID forthe region it is in can be obtained by calling the $GET_REGION_INFOsystem service specifying the VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA function. start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting address for the created virtual address range. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the virtual address space to be created. The length specifiedmust be a multiple of CPU-specific pages.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $CRETVA_64. The access modedetermines the owner mode of the pages as well as the read and writeprotection on the pages. The acmode argument is alongword containing the access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The $CRETVA_64 service uses whichever of the following access modes isleast privileged: - Access mode specified by the acmode argument
- Access mode of the caller
The protection of the pages is read/write for the resultant access modeand those more privileged. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask controlling the characteristics of the demand-zero pagescreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $VADEF macro and theVADEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes the flag that is valid for the $CRETVA_64service: | Flag | Description | | VA$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future use by HPand should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVVAFLG isreturned if any undefined bits are set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the created virtual addressrange. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bitvirtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the servicereturns the virtual address.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range created. Thereturn_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtualaddress of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returnsthe length of the virtual address range in bytes.
DescriptionThe Create Virtual Address Space service is a kernel mode service thatcan be called from any mode. The service adds a range of demand-zeroallocation pages, starting at the virtual address specified by thestart_va_64 argument. The pages are added to aprocess's virtual address space for the execution of the current image.Expansion occurs at the next free available address within thespecified region if the range of addresses is beyond the next freeavailable address.The new pages, which were previously inaccessible to the process, arecreated as demand-zero pages. The returned address is always the lowest virtual address in the rangeof pages created. The returned length is always an unsigned byte countindicating the length of the range of pages created. Successful return status from $CRETVA means that the specified addressspace was created of the size specified in thelength_64 argument. If $CRETVA_64 creates pages that already exist, the service deletesthose pages if they are not owned by a more privileged access mode thanthat of the caller. Any such deleted pages are reinitialized asdemand-zero pages. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If an address within the specified address range is not within thebounds of the specified region, the condition value SS$_PAGNOTINREG isreturned. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullyadded before the error occurred. If no pages were added, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
None Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased length of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space. The process's paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA) must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased size of the virtual address space. Related Services
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64, $CREATE_REGION_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,$EXPREG_64, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64,$ULWSET_64
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA | The process has exceeded its paging file quota. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVREGID | An invalid region ID was specified. | | SS$_IVVAFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT | The length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific pages. | | SS$_NOSHPTS | The region ID of a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the caller. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified range is already mapped, and the VA$M_NO_OVERLAP flag was set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. |
$CRMPSCAllows a process to associate (map) a section of its address space witheither a specified section of a file (a disk file section) or specifiedphysical addresses represented by page frame numbers (a page framesection). This service also allows the process to create either type ofsection and to specify that the section be available only to thecreating process (private section) or to all processes that map to it(global section).
FormatSYS$CRMPSC [inadr] ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[flags] ,[gsdnam] ,[ident],[relpag] ,[chan] ,[pagcnt] ,[vbn] ,[prot] ,[pfc]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr,unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, unsigned intrelpag, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int pagcnt, unsigned int vbn,unsigned int prot,unsigned int pfc);
Argumentsinadr
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Starting and ending virtual addresses into which the section is to bemapped. The inadr argument is the address of a2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending processvirtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtualaddress is used to specify which pages are to be mapped; the low-orderbyte-within-page bits are ignored for this purpose.The interpretation of the inadr argument depends onthe setting of SEC$M_EXPREG in the flags argument andon whether you are using an Alpha or a VAX system. The two system typesare discussed separately in this section. Alpha System Usage
On Alpha systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, theinadr argument specifies the starting and endingvirtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system spaceare not allowed. The addresses must be aligned on CPU-specific pages;no rounding to CPU-specific pages occurs. The lower address of theinadr argument must be on a CPU-specific page boundaryand the higher address of the inadr argument must be 1less than a CPU-specific boundary, thus forming a range, from lowest tohighest, of address bytes. You can use the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code inthe $GETSYI system service to set the inadr argumentto the proper values. You do this to avoid programming errors thatmight arise because of incorrect programming assumptions about pagesizes. If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,indicating that the mapping should take place using the first availablespace in a particular region, the inadr argument isused only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) orthe control region (P1). Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, mustbe executed with extreme care. Because the user stack is mapped in P1,it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertentlyread or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC. |
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadrlongword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) ofthe first inadr longword is used to determine theregion of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,P1 is chosen. On Alpha systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) ofthe first inadr longword must be 0. To ensurecompatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadrlongword, any virtual address in the desired region. In general, the inadr argument should be specified;however, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanentglobal sections, you can omit the inadr argument, orspecify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped.Such a request will be granted regardless of the setting of theSEC$M_EXPREG flag; however, to ensure compatibility between VAX andAlpha systems, HP recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear whenthe inadr argument is omitted. VAX System Usage
On VAX systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, theinadr argument specifies the starting and endingvirtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system spaceare not allowed. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are thesame, a single page is mapped. Note
If the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is not set, HP recommends that theinadr argument always specify the entire virtualaddress range, from starting byte address to ending byte address. Thisensures compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems. |
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag,indicating that the mapping should take place using the first availablespace in a particular region, the inadr argument isused only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) orthe control region (P1). Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, mustbe executed with extreme care. Because the user stack is mapped in P1,it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertentlyread or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC. |
When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadrlongword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) ofthe first inadr longword is used to determine theregion of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set,P1 is chosen. On VAX systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of thefirst inadr longword is ignored. To ensurecompatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region,HP recommends that you specify, for the first inadrlongword, any virtual address in the desired region. In general, the inadr argument should be specified;however, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanentglobal sections, you can omit the inadr argument, orspecify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped.You must also ensure that SEC$M_EXPREG is not set in theflags argument. Omitting the inadrargument with SEC$M_EXPREG set is interpreted by VAX systems as arequest to map with no region preference. This latter combination ofargument settings is strongly discouraged, as the chosen region isindeterminate. To ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems,HP recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear when theinadr argument is omitted. retadr
| OpenVMS usage: | address_range | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference--array reference |
Starting and ending process virtual addresses into which the sectionwas actually mapped by $CRMPSC. The retadr argument isthe address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the startingand ending process virtual addresses.On Alpha systems, the retadr argument returns startingand ending addresses of the usable range of addresses. Thismight differ from the total amount mapped. The retadrargument is required when the relpag argument isspecified. If the section being mapped does not completely fill thelast page used to map the section, the retadr argumentindicates the highest address that actually maps the section. If therelpag argument is used to specify an offset into thesection, the retadr argument reflects the offset. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four accessmodes: | Symbol | Access Mode | | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of section to be created or mapped to, aswell as its characteristics. The flags argument is alongword bit vector wherein each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEFmacro defines a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag and the default value that itsupersedes: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. The default is private section. | | SEC$M_CRF | Pages are copy-on-reference. By default, pages are shared. | | SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when copied. For page file sections, the default is demand zero. | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space. By default, pages are mapped into the range specified by the inadr argument. See the inadr argument description for a complete explanation of how to set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. For page file sections, the default is writeable. | | SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary. | | SEC$M_PFNMAP | Pages form a page frame section. By default, pages form a disk file section. Pages mapped by SEC$M_PFNMAP are not included in or charged against the process's working set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a machine check if they are in I/O space. ++On Alpha systems, when the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag is set, the pagcnt and relpag arguments are interpreted in CPU-specific pages, not as pagelets. | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. | | SEC$M_PAGFIL | Pages form a global page file section. By default, pages form a disk file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO. | | SEC$M_EXECUTE | Pages are mapped if the caller has execute access. This flag takes effect only (1) when specified from executive or kernel mode, (2) when the SEC$M_GBL flag is also specified, and (3) when SEC$M_WRT is not specified. By default $CRMPSC performs a read access check against the section. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. Note that, by default, pages can overmap existing address space. |
++Alpha specific
gsdnam
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gsdnam argument is theaddress of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.For group global sections, the operating system interprets the UICgroup as part of the global section name; thus, the names of globalsections are unique to UIC groups. You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mappingto the same global section must specify the same name. Note that thename is case sensitive. Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Validvalues include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and theunderscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), theunderscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be theactual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted. Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after theapplication of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does nottranslate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of thesection. Additional information on logical name translations and on section nameprocessing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual. ident
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global sectionand, for processes mapping to an existing global section, the criteriafor matching the identification. The ident argument isthe address of a quadword structure containing three fields.The version number is in the second longword. The version numbercontains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bitsand a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assignvalues for these fields by installation convention to differentiateversions of global sections. If no version number is specified when asection is created, processes that specify a version number whenmapping cannot access the global section. The first longword specifies, in its low-order two bits, the matchingcriteria. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can bespecified, and their meanings are as follows: | Value/Name | Match Criteria | | 0 SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. | | 1 SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. | | 2 SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. | When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field isignored. If you do not specify the ident argument or specify itas 0 (the default), the version number and match control fields defaultto 0. relpag
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Relative page number within the global section of the first page in thesection to be mapped. The relpag argument is alongword containing this page number.On Alpha systems, the relpag argument is interpretedas an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for afile-backed section or in CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section. On Alpha and VAX systems, you use this argument only for globalsections. If you do not specify the relpag argument orspecify it as 0 (the default), the global section is mapped beginningwith the first virtual block in the file. chan
| OpenVMS usage: | channel | | type: | word (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. Thechan argument is a word containing this number.The file must have been accessed with the OpenVMS RMS macro $OPEN; thefile options parameter (FOP) in the FAB must indicate a user file open(UFO keyword). The access mode at which the channel was opened must beequal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller. pagcnt
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems) in thesection. The pagcnt argument is a longword containingthis number.On Alpha systems, the smallest allocation is an Alpha page, which is8192 bytes. When requesting pagelets, the size requested is a multipleof 512 bytes, but the actual allocation is rounded to 8192. Forexample, when requesting 17 pagelets, the allocation is for two Alphapages, 16384 bytes. On Alpha systems, if the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag bit is set, thepagcnt argument is interpreted as CPU-specific pages,not as pagelets. On Alpha and VAX systems, the specified page count is compared with thenumber of blocks in the section file; if they are different, the lowervalue is used. If you do not specify the page count or specify it as 0(the default), the size of the section file is used. However, forphysical page frame sections, this argument must not be 0. vbn
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Virtual block number in the file that marks the beginning of thesection. The vbn argument is a longword containingthis number. If you do not specify the vbn argument orspecify it as 0 (the default), the section is created beginning withthe first virtual block in the file.If you specified page frame number mapping (by setting the SEC$M_PFNMAPflag), the vbn argument specifies the CPU-specificpage frame number where the section begins in memory. Table SYS-21 shows which arguments are required and which are optionalfor three different uses of the $CRMPSC service. Table SYS-21 Required and Optional Arguments for the$CRMPSC Service | Argument | Create/Map
Global Section | Map Global1
Section | Create/Map
Private Section | | inadr | Optional 2 | Required | Required | | | | | | | retadr | Optional | Optional | Optional | | | | | | | acmode | Optional | Optional | Optional | | | | | | | flags | | | | | SEC$M_GBL | Required | Ignored | Not used | | SEC$M_CRF 3 | Optional | Not used | Optional | | SEC$M_DZRO 3 | Optional | Not used | Optional | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Optional | Optional | Optional | | SEC$M_PERM | Optional 2 | Not used | Not used | | SEC$M_PFNMAP | Optional | Not used | Optional | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Optional | Optional | Not used | | SEC$M_WRT | Optional | Optional | Optional | | SEC$M_PAGFIL | Optional | Not used | Not used | | | | | | | gsdnam | Required | Required | Not used | | | | | | | ident | Optional | Optional | Not used | | | | | | | relpag 3 | Optional | Optional | Not used | | | | | | | chan 3 | Required | | Required | | | | | | | pagcnt | Required | | Required | | | | | | | vbn 3 | Optional | | Optional | | | | | | | prot | Optional | | Not used | | | | | | | pfc 3 | Optional | | Optional |
1The Map Global Section ($MGBLSC) service maps an existingglobal section.
2See the description of inadr for the rulesgoverning the omission of the argument.
3For physical page frame sections: vbnspecifies the starting page frame number; chan must be0; pfc is not used; and the SEC$M_CRF and SEC$M_DZROflag bit settings are invalid. For page file sections,chan must be 0 and pfc not used.
prot
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file and PFN sections. Forfile-backed sections, the protection is taken from the backing file andthe prot argument is ignored.The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to leftin each field. The following diagram depicts the mask:
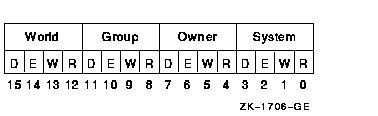 Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, inthat order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read, write, and execute access are meaningful for sectionprotection. Delete access bits are ignored. Read access also grantsexecute access for those situations where execute access applies. Protection is taken from the system or group global section templatefor page file or PFN global sections if the protargument is not specified. pfc
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Page fault cluster size indicating how many pages (on VAX systems) orpagelets (on Alpha systems) are to be brought into memory when a pagefault occurs for a single page.On Alpha systems, this argument is not used for page file sections orphysical page frame sections. The pfc argument isrounded up to CPU-specific pages. That is, at least 16 pagelets (on anAlpha system with an 8KB page size) will be mapped for each physicalpage. The system cannot map less than one physical page. On VAX systems, this argument is not used for page file sections orphysical page frame sections.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Section service allows a process to associate (map)a section of its address space with (1) a specified section of a file(a disk file section) or (2) specified physical addresses representedby page frame numbers (a page frame section). This service also allowsthe process to create either type of section and to specify that thesection be available only to the creating process (private section) orto all processes that map to it (global section).Creating a disk file section involves defining all or part of a diskfile as a section. Mapping a disk file section involves making acorrespondence between virtual blocks in the file and pages (on VAXsystems) or pagelets (on Alpha systems) in the caller's virtual addressspace. If the $CRMPSC service specifies a global section that alreadyexists, the service maps it. Any section created is created as entire pages. Refer to the memorymanagement section in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual. Depending on the actual operation requested, certain arguments arerequired or optional. Table SYS-21 summarizes how the $CRMPSC serviceinterprets the arguments passed to it and under what circumstances itrequires or ignores arguments. The $CRMPSC service returns the virtual addresses of the virtualaddress space created in the retadr argument, ifspecified. The section is mapped from a low address to a high address,whether the section is mapped in the program or control region. If an error occurs during the mapping of a global section, theretadr argument, if specified, indicates the pagesthat were successfully mapped when the error occurred. If no pages weremapped, the value of the longwords is indeterminate. In this case,either both longwords of the retadr argument willcontain the value --1, or the value of the longwords will be unaltered. The SEC$M_PFNMAP flag setting identifies the memory for the section asstarting at the page frame number specified in the vbnargument and extending for the number of CPU-specific pages specifiedin the pagcnt argument. Setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP flagplaces restrictions on the following arguments: | Argument | Restriction | | chan | Must be 0 | | pagcnt | Must be specified; cannot be 0 | | vbn | Specifies first page frame to be mapped | | pfc | Does not apply | | SEC$M_CRF | Must be 0 | | SEC$M_DZRO | Must be 0 | | SEC$M_PERM | Must be 1 if the flags SEC$M_GBL or SEC$M_SYSGBL are set | Setting the SEC$M_PAGFIL flag places the following restrictions on thefollowing flags: | Flag | Restriction | | SEC$M_CRF | Must be 0 | | SEC$M_DZRO | Assumed to be 0 | | SEC$M_GBL | Must be 1 | | SEC$M_PFNMAP | Must be 0 | | SEC$M_WRT | Assumed to be 0 | The flags argument bits 4 through 13 and 18 through 31must be 0. If the global section is mapped to a file (neither SEC$M_PAGFIL norSEC$M_PFNMAP is set), the security profile of the file is used todetermine access to the global section. On VAX systems, by default, the initial security profile created for apage file or PFN global section is taken from the group global sectiontemplate. If the SEC$M_SYSGBL flag is set, the profile is taken fromthe system global section template. The owner is then set to theprocess UIC. If the prot argument is nonzero, itreplaces the protection mask from the template. On Alpha and VAX systems, the flag bit SEC$M_WRT applies only to theway in which the newly created section is mapped. For a file to be madewritable, the channel used to open the file must allow write access tothe file. If the flag bit SEC$M_SYSGBL is set, the flag bit SEC$M_GBL must be setalso. Required Access or Privileges
If $CRMPSC specifies a global section and the SS$_NOPRIV conditionvalue is returned, the process does not have the required privilege tocreate that section. To create global sections, the process must havethe following privileges: - SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
- SHMEM privilege to create a global section in memory shared by multiple processors (VAX only)
Note that you do not need PFNMAP privilege to map an existing pageframe section. Required Quota
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must havesufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). The systemwide number ofglobal page file pages is limited by the system parameter GBLPAGFIL. Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,$UPDSECW
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. | | SS$_CREATED | The service completed successfully. The specified global section did not previously exist and has been created. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The inadr argument, gsdnam argument, or name descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the inadr argument was omitted; or the retadr argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_ENDOFFILE | The starting virtual block number specified is beyond the logical end-of-file, or the value in the relpag argument is greater than or equal to the actual size of the global section. | | SS$_EXBYTLM | The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to map the requested file. | | SS$_EXGBLPAGFIL | The process has exceeded the systemwide limit on global page file pages; no part of the section was mapped. | | SS$_EXQUOTA | The process exceeded its paging file quota while creating copy-on-reference or page file backing store pages. | | SS$_GPTFULL | There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the section. | | SS$_GSDFULL | There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. | | SS$_ILLPAGCNT | The page count value is negative or is 0 for a physical page frame section. | | SS$_INSFMEM | Not enough pages are available in the specified shared memory to create the section. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased size of the address space. | | SS$_IVCHAN | An invalid channel number was specified, that is, a channel number of 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available. | | SS$_IVCHNLSEC | The channel number specified is currently active. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVLVEC | The specified section was not installed using the /PROTECT qualifier. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, a flag requiring a privilege you lack, or an invalid combination of flags was specified. | | SS$_IVSECIDCTL | The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The process does not have the privileges to create a system global section (SYSGBL) or a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). The process does not have the privilege to create a section starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP). The process does not have the privilege to create a global section in memory shared by multiple processors (SHMEM). A page in the input address range is in the system address space. The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_NOSHPTS | A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_NOTFILEDEV | The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device. | | SS$_NOWRT | The section cannot be written to because the flag bit SEC$M_WRT is set, the file is read only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_SECREFOVF | The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647). | | SS$_SECTBLFUL | There are no entries available in the system global section table or in the process section table. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the gsdnam argument exceeded the allowed depth. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped, and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VASFULL | The process's virtual address space is full; no space is available in the page tables for the pages created to contain the mapped global section. |
$CRMPSC_FILE_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to map a section of its addressspace to a specified portion of a file. This service creates and maps aprivate disk file section.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_FILE_64 region_id_64 ,file_offset_64 ,length_64 ,chan,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,fault_cluster[,start_va_64]]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_file_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned__int64 file_offset_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned short intchan, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)),unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Argumentsregion_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the private disk filesection. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space.The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. file_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Byte offset into the file that marks the beginning of the section. Thefile_offset_64 argument is a quadword containing thisnumber. If you specify the file_offset_64 argument as0, the section is created beginning with the first byte in the file.The file_offset_64 argument must be a multiple ofvirtual disk blocks. length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | value |
Length, in bytes, of the private disk file section to be created andmapped to. The length specified must be 0 or a multiple of virtual diskblocks. If the length specified is 0 or extends beyond end-of-file(EOF), the disk file is mapped up to and including the virtual blocknumber that contains EOF.chan
| OpenVMS usage: | longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. Thechan argument is a longword containing this number.The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to orless privileged than the access mode of the caller.Use the OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) macro $OPEN to accessa file; the file options parameter in the file access block mustindicate a user file open (UFO) keyword. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned byan access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of thecalling process. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the private section to becreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and theSECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for the$CRMPSC_FILE_64 service: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_CRF | Pages are copy-on-reference. | | SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when copied. Note that SEC$M_DZRO and SEC$M_CRF cannot both be set and that SEC$M_DZRO set and SEC$M_WRT clear is an invalid combination. | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegalcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the private disk filesection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the usable virtual addressrange mapped in bytes. This length might differ from the total amountmapped. If the section being mapped does not completely fill the lastpage used to map the section, the return_va_64 andreturn_length_64 arguments indicate the highestaddress that actually maps the section.fault_cluster
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Page fault cluster in byte units indicating how many pages are to bebrought into memory when a page fault occurs for a single page. Thefault cluster specified will be rounded up to a multiple ofCPU-specific pages.If this argument is specified as 0, the process default page faultcluster will be used. If this argument is specified as more than themaximum allowed for the system, no condition value will be returned.The systemwide maximum will be used. start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the private disk file section. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. IfSEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument isnonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Private Disk File Section service allows a processto create a map to a private disk file section. Creating a private diskfile section involves mapping all or part of a disk file as a section.The section is mapped from a low address to a high address whether thesection is mapped in a region that grows from low to high addresses orfrom high to low addresses.The flag SEC$M_WRT applies only to the way in which the newly createdsection is mapped. For a file to be made writable, the channel used toopen the file must allow write access to the file. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
None Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased length of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space. The process must have sufficient byte count quota to satisfy therequest. If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must havesufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,$CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,$LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64,$UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The return_va_64 argument or the return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_CHANVIO | The specified channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_ENDOFFILE | The file_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. | | SS$_EXBYTLM | The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to map the requested file. | | SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA | The process exceeded its paging file quota. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_IVCHAN | An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified was 0 or a channel that is unassigned. | | SS$_IVCHNLSEC | The channel number specified is currently active, or there are no files opened on the specified channel. | | SS$_IVIDENT | An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified is larger than the number of channels available. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT | The length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk blocks. | | SS$_NOSHPTS | A virtual address within a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_NOTFILEDEV | The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device. | | SS$_OFF_NOTBLKALGN | The file_offset_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk blocks. | | SS$_NOWRT | The file is read-only, the flag bit SEC$M_WRT was set, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified range already exists and cannot be deleted because it is owned by a more privileged access mode than that of the caller. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. |
$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a memory-resident globaldemand-zero section and to map a section of its address space to theglobal section. Shared page table sections can also be created.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64 ,region_id_64,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64[[[[,start_va_64] ,map_length_64] ,reserved_length_64] ,rad_mask]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_gdzro_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, struct _generic_64*region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode,unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64*return_length_64,...);
Argumentsgs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bitstring descriptor pointing to this name string.ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing threefields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bitvirtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains theidentification value.The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,and their meanings are as follows: | Value | Symbolic Name | Match Criteria | | 0 | SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. | | 1 | SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. | | 2 | SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. | When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field isignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,the version number and match control fields default to 0. The version number is in the second longword. The version numbercontains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bitsand a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assignvalues for these fields by installation convention to differentiateversions of global sections. If no version number is specified when asection is created, processes that specify a version number whenmapping cannot access the global section. prot
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Protection to be applied to the global demand-zero section. The maskcontains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in eachfield. The following diagram depicts the mask:
 Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, inthat order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Deleteaccess bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access forthose situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,read access and write access are granted to all users. length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global demand-zero section to be created. Thelength_64 must be specified as a multiple of theCPU-specific page size. A length of 0 cannot be specified. Note
Creating a memory-resident global section with shared page table doesnot imply that the global section must have an even multiple ofCPU-specific page table pages. The global section might not fully usethe last page table page. |
region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page filesection.The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space. The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process'svirtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple of aCPU-specific page size.If a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64 argument,section_offset_64 must be an even multiple of thenumber of bytes that can be mapped by a CPU-specific page table page. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. This access mode is also the read access mode and the writeaccess mode. The acmode argument is a longwordcontaining the access mode.If the memory-resident global section is created with shared pagetables, this is the access mode that is stored in the owner, read, andwrite fields of the corresponding shared page table entries (PTEs). The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned byan access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of thecalling process. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the type of the global section to be created aswell as its characteristics. The flags argument is alongword bit vector in which each bit corresponds to a flag. The$SECDEF macro and the SECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for eachflag. You construct the flags argument by performing alogical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for the$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, virtually aligned addresses after the first available space are chosen for the mapping. | | SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. | | SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. | | SEC$M_RAD_HINT | When set, the argument rad_mask is used as a mask of RADs from which to allocate memory. See the rad_mask argument description for more information. | | SEC$M_READ_ONLY_SHPT | Create shared table pages for the section that allow read access only. | | SEC$M_SHMGS | Create a shared-memory global section. | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. | | SEC$M_MRES | Pages form a memory-resident section. By default, this page is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalidcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global demand-zerosection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address.If a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64 argument and the SEC$M_EXPREG flag isset, the returned virtual address is aligned to a CPU-specific pagetable page boundary. return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the virtual address rangemapped in bytes.start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the memory-resident global section.The specified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page alignedaddress. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, thestart_va_64 argument must not be specified or must bespecified as 0. If SEC$M_EXPREG is set and thestart_va_64 argument is nonzero, the condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned.If SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, start_va_64 is nonzero, anda shared page table region is specified, the specified starting addressmust be aligned to a natural page table page boundary; otherwise, thecondition value SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN is returned. If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the memory-residentglobal section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry andstart_va_64 is aligned to a multiple of CPU-specificpages appropriate for taking advantage of granularity hints (8, 64, or512 pages), then granularity hints are used to map to the globalsection. map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the memory-resident global section to be mapped. The lengthspecified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. If this argument isnot specified or is specified as zero, the global file section ismapped up to and including the last page in that section.If a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64 argument, map_length_64must be an even multiple of the number of bytes that can be mapped by aCPU-specific page table page or must include the last page within theglobal section. reserved_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | 32- or 64-bit reference |
Length, in bytes, of the global section as currently registered in theReserved Memory Registry. The reserved_length_64argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally alignedquadword into which the service returns the reserved length.If reserved_length_64 is not specified or is specifiedas 0, no reserved length is returned to the caller. If the memory-resident global section is not registered,reserved_length_64 is written with the value 0. rad_mask
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_quadword | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Use the rad_mask argument to specify from which RADsto allocate memory. Currently only one bit may be set. The specifiedRAD must contain memory. This argument is only a hint. Memory may beobtained from other RADs if no free memory is available at the time ofallocation.The rad_mask argument is considered only if theSEC$M_RAD_HINT flag is specified. Otherwise, this argument is ignored. On a system that does not support resource affinity domains (RADs),specifying 1 for the rad_mask argument is allowed. Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
DescriptionThe Create and Map to Global Demand-Zero Section service allows aprocess to create and map to a memory-resident global demand-zerosection. If you set the SEC$M_SHMGS flag, the section is created as aGalaxy-wide global demand-zero section in shared memory.You must call either the $CREATE_GDZRO service or the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64service on each instance where the Galaxy shared memory will beaccessed. Memory-resident or Galaxy-wide global sections contain demand-zeroallocation pages that are writable and memory resident. All pages inthese types of global section are shared by all processes that map tothe global section. If the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service specifies a global section that alreadyexists, the service maps to it only if it is a memory-resident globalsection. All pages in the memory-resident global section are shared byall processes that map to the global section. The global demand-zero pages are always resident in memory and are notbacked up by any file on any disk. The global pages are not chargedagainst any page file quota. The process must have the rightsidentifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER to create a memory-resident globalsection; otherwise, the error status SS$_NOMEMRESID is returned. The pages are always resident in memory and are not backed up by anyfile on any disk. The pages are not placed into the process's workingset list when the process maps to the global section and the virtualmemory is referenced by the process. The pages are also not chargedagainst the process's working set quota or against any page-file quota. Only memory-resident sections can be registered with the ReservedMemory Registry in the SYSMAN facility. Memory for Galaxy-wide sharedsections is reserved through appropriate settings of the consoleenvironment parameters. If the memory-resident global section is either not registered in theReserved Memory Registry or if the /NOALLOCATE qualifier was specifiedwhen the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,invalid global PTEs are written to the global page table and invalidPTEs are placed in the process page table. Physical memory is notallocated until the virtual memory is referenced. If the global section is registered in the Reserved Memory Registry,the size of the global section need not match the reserved size. If theglobal section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or ifthe reserved size is smaller than the size of the global section, theerror status SS$_INSFLPGS is returned if there are not enough fluidpages in the system to satisfy the request. If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section wasregistered in the Reserved Memory Registry, contiguous, alignedphysical pages are preallocated during system initialization for thisglobal section. Valid page table entries are placed in the global pagetable and in the process page table. If the reserved preallocatedmemory is smaller than the size of the global section, the errorSS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the global section is not created. If the memory-resident global section is not registered in the ReservedMemory Registry or if the /PAGE_TABLES qualifier was specified when theglobal section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, sharedpage tables are created for the global section. For more information about using the SYSMAN utility to create entriesto the Reserved Memory Registry, refer to the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual. Shared page tables consume the same internal OpenVMS data structures asa global section. The system parameters GBLPAGES and GBLSECTIONS mustaccount for the additional global pages and the additional globalsection. To use the shared page tables associated with a memory-resident globalsection, you must first create a shared page-table region (with$CREATE_REGION_64). To map to the memory-resident global section usingthe shared page tables, you must do the following: - Specify a shared page-table region in the region_id_64 argument.
- Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG or provide a CPU-specific page table page aligned virtual address in the start_va_64 argument.
- Specify a value for the section_offset_64 argument that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table page or zero.
- Specify a value for the map_length_64 argument that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table page or zero, or include the last page of the section.
See the description of the $CREATE_REGION_64 service for informationabout calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specificpage table page boundary. The memory-resident global section can be mapped with shared pagetables or private page tables. The following table lists the factorsassociated with determining whether the mapping occurs with shared pagetables or with private page tables: | Global Section Created with Shared Page Tables | Shared Page Table Region Specified by region_id_64 | Type of Page Tables Used in Mapping | | No | No | Private | | No | Yes | Private | | Yes | No | Private | | Yes | Yes | Shared | In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtualaddress within the specified region is used to map to the globalsection. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the region_id_64argument indicates a shared page table region, the first free virtualaddress within the specified region is rounded up to a CPU-specificpage table page boundary and used to map to the global section. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and if the /ALLOCATE qualifier wasspecified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for thememory-resident global section, the first free virtual address withinthe specified region is rounded up to the same virtual alignment as thephysical alignment of the preallocated pages and used to map to theglobal section. Granularity hints are set appropriately for eachprocess private PTE. In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the virtual address inthe start_va_64 argument is used to map to the globalsection. If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the value specified in thestart_va_64 argument can determine if the mapping ispossible and if granularity hints are used in the private page tables.If a shared page table region is specified by theregion_id_64 argument, the virtual address specifiedby the start_va_64 argument must be on an evenCPU-specific page table page boundary or an error is returned by thisservice. If the region_id_64 argument does not specifya shared page table region and /ALLOCATE was specified with the SYSMANcommand RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for this global section, granularity hintsare used only if the virtual alignment of start_va_64is appropriate for the use of granularity hints (either 8-page,64-page, or 512-page alignment). Whenever granularity hints are being used within the mapping of amemory-resident global section, if the length_64argument is not an exact multiple of the alignment factor, lowergranularity hints factors are used as appropriate at the higheraddressed portion of the global section. If thesection_offset_64 argument is specified, a lowergranularity hint factor can be used throughout the mapping of theglobal section to match the physical alignment of the first page mapped. When you map a Galaxy shared section or a memory resident section thathas an associated shared page table section, you have the followingoptions for accessing data: Table SYS-22 Shared Page Tables | Shared Page Tables | Read Only | Read and Write | | None created | Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. Private page tables will always be used, even if you are specifying a shared page table region into which to map the section. | Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. Private page tables will always be used, even if you are specifying a shared page table region into which to map the section. | | Write access | Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. Ensure that private page tables will be used. Do not specify a shared page table region into which to map the section. If you do, the error status SS$_IVSECFLG is returned. | Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. The shared page table section will be used for mapping if you specify a shared page table region into which to map the section. | | Read access | Do not set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. The shared page table section will be used for mapping if you specify a shared page table region into which to map the section. | Set the SEC$M_WRT flag in the map request. Ensure that private page tables will be used. Do not specify a shared page table region into which to map the section. If you do, the error status SS$_IVSECFLG is returned. | Notes
Shared page tables for Galaxy shared sections are also implemented asGalaxy shared sections. This implies that they allow either read accessonly on all OpenVMS instances connected to this section or read andwrite access on all instances. The setting of the SEC$M_READ_ONLY_SHPTflag as requested by the first instance to create the section is usedon all instances.Using the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service always implies that the SEC$M_WRTflag is set and that you want to map the section for writing. If youwant to use this service to create a section with shared page tablesfor read only access, you must use private page tables and you cannotspecify a shared page table region into which to map the section. |
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments and, if specified as a nonzero value, thereserved_length_64 argument. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument contains the value --1. If the service returns an error status value other than SS$_INSFLPGS orSS$_MRES_PFNSMALL, a value is not returned in thereserved_length_64 argument. If the service returns a successful condition value or if SS$_INSFLPGSor SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and thereserved_length_64 argument is specified as a nonzeroaddress, the length in bytes of the global section as registered in theReserved Memory Registry is returned in thereserved_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the followingprivileges: - SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER rights identifier to create a memory-resident section
- SHMEM privilege on OpenVMS Galaxy systems to create an object in Galaxy shared memory
Required Quota
If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident globalsection, the working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must besufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tablesrequired by the increase in virtual address space. If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident globalsection, the page file quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must besufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tablesrequired by the increase in virtual address space. Related Services
$CREATE_GDZRO, $CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC,$CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64,$DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64,$MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64,$UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. | | SS$_CREATED | The service completed successfully. The global section has been created. | | SS$_CREATED_SHPT | Global section has been created with shared page tables. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or the return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_BADRAD | The specified RAD contains no memory, or if the specified RAD is greater than or equal to the maximum number of RADs on the system. | | SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA | The process's page file quota is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH | Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it is not a memory-resident section. | | SS$_GPTFULL | There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the global section or for the shared page tables. | | SS$_GSDFULL | There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. | | SS$_INSFLPGS | Insufficient fluid pages available. | | SS$_INSFRPGS | Insufficient free shared pages or private pages. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_INV_SHMEM | Shared memory is not valid. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The specified access mode is greater than PSL$_USER, or the caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVPROTECT | The protection argument format is invalid. | | SS$_IVREGID | An invalid region ID was specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags was specified. | | SS$_IVSECIDCTL | The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. | | SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT | The length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specified pages. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the map_length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific page table pages. | | SS$_LOCK_TIMEOUT | An OpenVMS Galaxy lock timed out. | | SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL | Preallocated, contiguous, aligned physical memory specified in the Reserved Memory Registry is smaller than the length specified for the memory-resident global section by the length_64 argument. | | SS$_NOBREAK | An OpenVMS Galaxy lock is held by another node and was not broken. | | SS$_NOMEMRESID | The process attempted to create a memory-resident section, but was not holding the right identifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER. | | SS$_NOPRMGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). | | SS$_NOSYSGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system global section (SYSGBL). | | SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN | The section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table page aligned. | | SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG | The section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified input address range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_SECREFOVF | The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647). | | SS$_SECTBLFUL | There are no entries available in the system global section table for the global section or for the shared page tables. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or a page in the specified input address range is in another region, in system space, or inaccessible; or, the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table page aligned. |
$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a global disk file sectionand to map a section of its address space to the global section.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,file_offset_64 ,length_64,chan ,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64,return_length_64 [,fault_cluster
[,start_va_64 [,map_length_64]]]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_gfile_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,unsigned __int64 file_offset_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsignedshort int chan, struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned __int64section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void*(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Argumentsgs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bitstring descriptor pointing to this name string.ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing threefields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bitvirtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains theidentification value.The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,and their meanings are as follows: | Value | Symbolic Name | Match Criteria | | 0 | SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. | | 1 | SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. | | 2 | SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. | When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field isignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,the version number and match control fields default to 0. The version number is in the second longword. The version numbercontains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bitsand a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assignvalues for these fields by installation convention to differentiateversions of global sections. If no version number is specified when asection is created, processes that specify a version number whenmapping cannot access the global section. file_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Byte offset into the file that marks the beginning of the section. Thefile_offset_64 argument is a quadword containing thisnumber. If you specify the file_offset_64 argument as0, the section is created beginning with the first byte in the file.The file offset specified must be a multiple of virtual disk blocks. length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global disk file section to be created. Thelength specified must be 0 or a multiple of virtual disk blocks. If thelength specified is 0 or extends beyond the end-of-file (EOF), theglobal disk file section is created up to and including the virtualblock number that contains EOF.chan
| OpenVMS usage: | longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the channel on which the file has been accessed. Thechan argument is a longword containing this number.The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to orless privileged than the access mode of the caller.You can use the OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) macro $OPEN toaccess a file; the file options parameter in the file access block mustindicate a user file open (UFO) keyword. region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 64 bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region in which to map the globaldisk file section. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEFmacro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the threedefault regions in P0, P1, and P2 space.The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process'svirtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple ofvirtual disk blocks.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to becreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and theSECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for the$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 service: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_CRF | Pages are copy-on-reference. | | SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. | | SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when copied. Note that SEC$M_DZRO and SEC$M_CRF cannot both be set and that SEC$M_DZRO set and SEC$M_WRT clear is an invalid combination. | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. | | SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary. | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegalcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global disk filesection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address.Upon successful completion of this service, if thesection_offset_64 argument was specified, the virtualaddress returned in return_va_64 reflects the offsetinto the global section mapped such that the virtual address returnedcannot be aligned on a CPU-specific page boundary. The virtual addressreturned will always be on an even virtual disk block boundary. return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the virtual address rangemapped in bytes.Upon successful completion of this service, the value in thereturn_length_64 argument indicates the amount ofcreated address space backed by the section file. If the number of disk blocks mapped does not represent an exactmultiple of CPU-specific pages, the last page in the mapped addressspace will not be completely mapped by the section file. In this case,modifying memory beyond the amount indicated byreturn_length_64 can result in the loss of this data. Unlike the return_length_64 argument for the$CREATE_GFILE service, upon successful completion of this service, thereturn_length_64 argument does not represent the totallength of the global section created if thesection_offset_64 argument was specified as nonzero.The value in the section_offset_64 argument plus thevalue in the return_length_64 argument is the totallength of the global disk file section created. fault_cluster
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Page fault cluster in byte units indicating how many pages are to bebrought into memory when a page fault occurs for a single page. Thefault cluster specified will be rounded up to a multiple ofCPU-specific pages.If this argument is specified as 0, the system default page faultcluster will be used. If this argument is specified as more than themaximum allowed for the system, no error will be returned. Thesystemwide maximum will be used. start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global disk file section. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, this argument will not be used.If SEC$M_EXPREG is clear and the start_va_64 argumentis not specified or is specified as 0, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLGwill be returned.Always refer to the return_va_64 andreturn_length_64 arguments to determine the usablerange of virtual addresses mapped. map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword unsigned | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the global disk file section to be mapped. The lengthspecified must be a multiple of virtual disk blocks. If this argumentis not specified as zero, the global disk section is mapped up to andincluding the last disk block in the section.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Global Disk File Section service allows a process tocreate and map to a global disk file section.Creating a global disk file section involves defining all or part of adisk file as a section. The section is mapped from a low address to ahigh address whether the section is mapped in a region that grows fromlow to high addresses or from high to low addresses. If the$CRMPSC_GFILE_64 service specifies a global disk file section thatalready exists, the service maps it. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. The flag SEC$M_WRT applies only to the way in which the newly createdsection is mapped. For a file to be made writable, the channel used toopen the file must allow write access to the file. Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the followingprivileges: - SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
If the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must havesufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased length of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space. Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64,$CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64,$DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64,$ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. | | SS$_CREATED | The service completed successfully. The specified global section did not previously exist and has been created. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or the return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_CHANVIO | The specified channel was assigned from a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_ENDOFFILE | The file_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. | | SS$_EXBYTLM | The process has exceeded the byte count quota; the system was unable to map the requested file. | | SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA | The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference pages. | | SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH | Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it was not a global disk file section. | | SS$_GPTFULL | There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the section. | | SS$_GSDFULL | There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVCHAN | An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified was 0 or a channel that is unassigned. | | SS$_IVCHNLSEC | The channel number specified is currently active or there are no files opened on the specified channel. | | SS$_IVIDENT | An invalid channel number was specified; the channel number specified is larger than the number of channels available. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_IVSECIDCTL | The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. | | SS$_LEN_NOTBLKMULT | The length_64 or the map_length_64 argument is not a multiple of virtual disk blocks. | | SS$_NOPRMGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). | | SS$_NOSHPTS | The region ID of a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_NOSYSGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system global section (SYSGBL). | | SS$_NOTFILEDEV | The device is not a file-oriented, random-access, or directory device. | | SS$_NOWRT | The file is read-only, and the flag bit SEC$M_CRF is not set. | | SS$_OFF_NOTBLKALGN | The file_offset_64 or section_offset_64 argument is not virtual disk block aligned. | | SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG | The section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_SECREFOVF | The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647). | | SS$_SECTBLFUL | There are no entries available in the system global section table. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. |
$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a global page file sectionand to map a section of its address space to the global section.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64,return_length_64 [,start_va_64 [,map_length_64]]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_gpfile_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, struct _generic_64*region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode,unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64*return_length_64,...);
Argumentsgs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bitstring descriptor pointing to this name string.ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing threefields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bitvirtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains theidentification value.The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,and their meanings are as follows: | Value | Symbolic Name | Match Criteria | | 0 | SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. | | 1 | SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. | | 2 | SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. | When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field isignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,the version number and match control fields default to 0. The version number is in the second longword. The version numbercontains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bitsand a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assignvalues for these fields by installation convention to differentiateversions of global sections. If no version number is specified when asection is created, processes that specify a version number whenmapping cannot access the global section. prot
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file section. The maskcontains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in eachfield. The following diagram depicts the mask:
 Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, inthat order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Deleteaccess bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access forthose situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,read access and write access are granted to all users. length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length, in bytes, of the global page file section to be created. Thelength specified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. A length of0 cannot be specified.region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page filesection.The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space. The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. section_offset_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Offset into the global section to start mapping into the process'svirtual address space. The offset specified must be a multiple ofvirtual disk blocks.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned byan access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of thecalling process. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to becreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and theSECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for the$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64 service: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. SEC$M_EXPREG cannot be specified with the SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP flag. | | SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP cannot be specified with the SEC$M_EXPREG flag. | | SEC$M_PAGFIL | Pages form a global page file section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary. | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalidcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page filesection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the virtual address rangemapped in bytes.start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global page file section. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. IfSEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument isnonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.Always refer to the return_va_64 andreturn_length_64 arguments to determine the range ofvirtual addresses mapped. map_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the global page file section to be mapped. The lengthspecified must be a multiple of CPU-specific pages. If this argument isnot specified or is specified as zero, the global file section ismapped up to and including the last page in that section.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Global Page File Section service allows a process tocreate a map to global page file section. Creating a global page filesection involves defining a global section backed up by the system pagefile. The section is mapped from a low address to a high addresswhether the section is mapped in a region that grows from low to highaddresses or from high to low addresses. If the $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64service specifies a global section that already exists, the servicemaps it.If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
To create a global section, the process must have the followingprivileges: - SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
Required Quota
Because the section pages are copy-on-reference, the process must havesufficient paging file quota (PGFLQUOTA). The working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficientto accommodate the increased size of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space when the section is mapped. Related Services
$CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64,$CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,$DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS,$SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. | | SS$_CREATED | The service completed successfully. The specified global section did not previously exist and has been created. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or the return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_EXBYTLM | The process has exceeded the byte count quota. | | SS$_EXGBLPAGFIL | The process has exceeded the systemwide limit on global page file pages; no part of the section was mapped. | | SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA | The process exceeded its paging file quota, creating copy-on-reference pages. | | SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH | Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it is not a global disk or page file section. | | SS$_GPTFULL | There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the section. | | SS$_GSDFULL | There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_IVSECIDCTL | The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. | | SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT | The length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specified pages or was specified as 0. | | SS$_NOPRMGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). | | SS$_NOSHPTS | The region ID of a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_NOSYSGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system global section (SYSGBL). | | SS$_NOWRTACC | The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not allow write access. | | SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN | The section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned if a map to a global page file section was requested (SEC$M_PAGFIL is set in the flags argument). | | SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG | The section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_SECREFOVF | The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647). | | SS$_SECTBLFUL | There are no entries available in the system global section table. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. |
$CRMPSC_GPFN_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a permanent global pageframe section and to map a section of its address space to the globalpage frame section.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_GPFN_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,start_pfn ,page_count,region_id_64 ,relative_page ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64,return_length_64 [,start_va_64 [,map_page_count]]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_gpfn_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64,unsigned int prot, unsigned int start_pfn, unsigned int page_count,struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned int relative_page, unsignedint acmode, unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned__int64 *return_length_64,...);
Argumentsgs_name_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bitstring descriptor pointing to this name string.ident_64
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section.The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing threefields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bitvirtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains theidentification value.The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified,and their meanings are as follows: | Value | Symbolic Name | Match Criteria | | 0 | SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. | | 1 | SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. | | 2 | SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. | When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field isignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0,the version number and match control fields default to 0. The version number is in the second longword. The version numbercontains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bitsand a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assignvalues for these fields by installation convention to differentiateversions of global sections. If no version number is specified when asection is created, processes that specify a version number whenmapping cannot access the global section. prot
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Protection to be applied to the global page file section.The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to leftin each field. The following diagram depicts the mask:
 Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, inthat order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read,write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Deleteaccess bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access forthose situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified,read access and write access are granted to all users. start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: | page frame number | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins.page_count
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page count | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.region_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the global page framesection. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space.The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. relative_page
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page number | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Relative CPU-specific page number within the global section to startmapping.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the global section to becreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and theSECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for$CRMPSC_GPFN_64: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. | | SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_PFNMAP | Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. | | SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an illegalcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the global page framesection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit address of a naturally aligned quadword into which theservice returns the virtual address.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the virtual address rangemapped in bytes.start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the global page frame section. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page-aligned address.If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. IfSEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument isnonzero, the condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned.Always refer to the return_va_64 andreturn_length_64 arguments to determine the range ofvirtual addresses mapped. map_page_count
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page count | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the global page frame section to be mapped in CPU-specificpages.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Global Page Frame Section service allows a processto create and map to a global page frame section. Creating a globalpage frame section involves defining certain physical page framenumbers (PFNs) as a section.All global page frame sections are permanent. Pages mapped to a globalpage frame section are not included in or charged against the process'sworking set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in theworking set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a machine check ifthey are in I/O space. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
To create a global page frame section, the process must have thefollowing privileges: - SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section (if flag SEC$M_PERM is set)
- PFNMAP privilege to create a page frame section
Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased length of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space. Related Services
$CREATE_GPFN, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64,$CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64,$DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. | | SS$_CREATED | The service completed successfully. The specified global section did not previously exist and has been created. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or the return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_EXBYTLM | The process has exceeded the byte count quota. | | SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH | Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it was not a global disk file section. | | SS$_GPTFULL | There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the section. | | SS$_GSDFULL | There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. | | SS$_ILLRELPAG | The specified relative page argument is either larger than the highest page number within the section or is not a valid 32-bit physical page frame number. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_IVSECIDCTL | The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. | | SS$_NOPFNMAP | The process does not have the privilege to create or delete a section starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP). | | SS$_NOPRMGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). | | SS$_NOSHPTS | A virtual address within a shared page-table region was specified, or the region ID of a shared page-table region was specified. | | SS$_NOSYSGBL | The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system global section (SYSGBL). | | SS$_NOWRTACC | The specified global section is not copy-on-reference and does not allow write access. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page-aligned. |
$CRMPSC_PFN_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, allows a process to map a section of its addressspace to a specified physical address range represented by page framenumbers. This service creates and maps a private page frame section.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$CRMPSC_PFN_64 region_id_64 ,start_pfn ,page_count ,acmode ,flags,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64]
C Prototypeint sys$crmpsc_pfn_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned intstart_pfn, unsigned int page_count, unsigned int acmode, unsigned intflags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
Argumentsregion_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to map the private page framesection. The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro inSTARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three defaultregions in P0, P1, and P2 space.The following region IDs are defined: | Symbol | Region | | VA$C_P0 | Program region | | VA$C_P1 | Control region | | VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region | Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can bespecified. start_pfn
| OpenVMS usage: | page frame number | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins in memory.page_count
| OpenVMS usage: | CPU-specific page count | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Length of the page frame section in CPU-specific pages.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during themapping. The acmode argument is a longword containingthe access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned byan access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of thecalling process. Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create modeassociated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. Thecondition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is lessprivileged than the create mode for the region. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flag mask specifying the characteristics of the private section to becreated. The flags argument is a longword bit vectorin which each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro and theSECDEF.H file define a symbolic name for each flag. You construct theflags argument by performing a logical OR operation onthe symbol names for all desired flags.The following table describes each flag that is valid for the$CRMPSC_PFN_64 service: | Flag | Description | | SEC$M_EXPREG | Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of the specified region. | | SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. By default, pages can overmap existing address space. | | SEC$M_PFNMAP | Pages form a page frame section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. | | SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. | All other bits in the flags argument are reserved forfuture use by HP and should be specified as 0. The condition valueSS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalidcombination of flags is set. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address into which the private page framesection was mapped. The return_va_64 argument is the32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range mapped. Thereturn_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtualaddress of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returnsthe length of the virtual address range in bytes.start_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The starting virtual address to map the private page frame section. Thespecified virtual address must be a CPU-specific page aligned address.If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is specified, the start_va_64argument must not be specified or must be specified as 0. IfSEC$M_EXPREG is set and the start_va_64 argument isnonzero, the condition value SS$_IVESCFLG is returned.
DescriptionThe Create and Map Private Page Frame Section service allows a processto create a map to a private page frame section. Creating a privatepage frame section involves defining certain physical page numbers(PFNs) as a section. The section is mapped from a low address to a highaddress whether the section is mapped in a region that grows from lowto high addresses or from high to low addresses.All global page frame sections are permanent. Pages mapped bySEC$M_PFNMAP are not included in or charged against the process'sworking set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in theworking set by using $LKWSET_64; this can result in a machine check ifthey are in I/O space. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returnedaddress and returned length indicate the pages that were successfullymapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, thereturn_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, anda value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed toby the return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
PFNMAP privilege is required to create a page frame section. Required Quota
The working set quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient toaccommodate the increased length of the process page table required bythe increase in virtual address space. Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The return_va_64 argument or the return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_INSFWSL | The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. | | SS$_IVACMODE | The caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. | | SS$_IVSECFLG | An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags and arguments was specified. | | SS$_NOPFNMAP | The process does not have the privilege to create a section starting at a specific physical page frame number (PFNMAP). | | SS$_NOSHPTS | The region ID of a shared page table region was specified. | | SS$_PAGNOTINREG | A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_REGISFULL | The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. | | SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN | The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. |
$CVT_FILENAME (Alpha Only)Converts a string from RMS format to file-system (ACP-QIO) format orfrom file-system (ACP-QIO) format to RMS format.
FormatSYS$CVT_FILENAME cvttyp ,srcstr ,inflags ,outbuf ,outlen ,outflags
C Prototypeint sys$cvt_filename (unsigned int cvttyp, void *srcstr, unsigned intinflags, void *outbuf, unsigned short int *outlen, unsigned int*outflags);
Argumentscvttyp
| OpenVMS usage: | unsigned_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Longword value that indicates whether the conversion is from RMS formatto ACP-QIO format or vice versa.There are two legal values for this parameter, represented by thesymbols CVTFNM$C_ACPQIO_TO_RMS and CVTFNM$C_RMS_TO_ACPQIO, that aredefined by the $CVTFNMDEF macro. srcstr
| OpenVMS usage: | string of bytes or words | | type: | string of bytes or words | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
String to be converted by the service.If the conversion is from RMS format to ACP-QIO format,srcstr is an ISO-Latin-1 orVTF-7-encoded character string. If the conversion is from ACP-QIOformat to RMS format, srcstr is a string of byte-widthor word-width characters. The descriptor length field indicates the length of the input string inbytes, whether the characters are byte-width or word-width. The srcstr argument is the 32-bit address of adescriptor that points to this string. inflags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Longword flag mask indicating the characteristics of the input string.For conversion from RMS format to ACP-QIO format, only theCVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS flag is valid. For conversion from ACP-QIO format to RMS format, legal flags areCVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS and CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS (defined by the$CVTFNMDEF macro). | Flag | Description | | CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS | Input source string contains word-width UCS-2 characters (ACPQIO_TO_RMS conversion only). | | CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS | Input source string should be treated as an arbitrary string (such as a subdirectory name) rather than as a file name that contains (or should contain) dots or semicolons as type and version delimiters. | | CVTFNM$V_FORCE_UPCASE | Causes this system service to convert each character to uppercase. (ACPQIO_TO_RMS conversion only). | outbuf
| OpenVMS usage: | string of bytes or words | | type: | string of bytes or words | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The buffer into which the converted string is to be written.If the conversion is from RMS format to ACP-QIO format, the string mayconsist of byte-width ISO Latin-1 characters or word-width UCS-2characters, depending on the characters in the source string. (If anycharacter in the source string must be converted to UCS-2, then allcharacters in the output buffer will be converted to UCS-2.) If the conversion is from ACP-QIO format to RMS format, then the outputstring will consist of ISO Latin-1 and VTF-7 characters in RMS canonical form. (Refer to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications.) For ACPQIO_TO_RMS conversion, if the output string contains word-widthcharacters, the CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS flag in theoutflags flag mask will be set. The outbuf argument is the 32-bit address of adescriptor pointing to a buffer writable in the access mode of thecaller. outlen
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned | | type: | word (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32-bit reference |
The outlen argument is the 32-bit address of a(16-bit) word writable in the access mode of the caller.outflags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32-bit reference |
Longword flag mask in which the service sets or clears flags toindicate characteristics of the output string.For an RMS_TO_ACPQIO conversion, SYS$CVT_FILENAME sets the bitcorresponding to CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS (defined by the $CVTFNMDEF macro)if the characters of the converted string are one-word wide rather thanone-byte wide. If the characters of the converted string are one-bytewide, the service clears the CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS bit. All other bitsare cleared by an RMS_TO_ACPQIO conversion. The outflags argument is the 32-bit address of a32-bit flag mask writable in the access mode of the caller.
DescriptionThis service is intended to provide the conversion of a file name or asubdirectory name between the RMS format (as seen at the RMS interface)and the ACP-QIO format (as stored on disk). A file name consists of afile name, a file type, and a file version; and a subdirectory name isa string to which ".DIR;1" can be appended to form a directory filename, as stored on disk.Prior to Version 7.2, these representations were the same. This is notnecessarily the case for extended (ODS-5) file names. (Refer to theGuide to OpenVMS File Applications for details on ODS-5 file specifications.) Depending on the value of cvttyp, the service willperform a conversion of a string from RMS format to ACP-QIO format orfrom ACP-QIO format to RMS format. The source string is described by the argument srcstr,the output buffer is described by the argument outbuf,and the resultant string length is written to the argumentoutlen. If any of the source string falls within the address range of theoutput buffer, the output string is unpredictable. RMS-to-ACPQIO Conversion: A string described by the srcstr descriptor argumentis converted to an ISO Latin-1 or UCS-2 string with each characterrepresented in a form that can be passed to the ACP-QIO by the $QIOservice. If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is not set, the source stringwill be scanned and, if necessary, a dot and a semicolon will beinserted or appended as though a $PARSE were done with no default name,type, or version fields supplied. If the scan detects any delimitersindicating the presence of fields other than name (without FID), type,or version, a syntax error will be returned. If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is set, individual characterswill be validated and converted to their on-disk form; however, no scanwill be done to determine if the type and version delimiters arepresent, and no delimiters will be added. A percent sign (%) that is not preceded by the escape character (^) isconverted to a question mark. An ISO Latin-1 character that is precededby the escape character (^) is converted to the corresponding ISOLatin-1 character. AVTF-7 character (for example, ^U1234) that is preceded by the escapecharacter (^) is converted to a UCS-2 character (for example, 0x1234). If any character requires UCS-2 (word-width character) representation,all characters are represented in the output string with UCS-2. If nocharacter requires word-width character representation, all charactersare represented in the output string with ISO Latin-1 (byte-width)characters. Valid characters are those that are legal in an RMS file name (filename, file type, and file version) or in an RMS subdirectory name. Forexample, directory delimiters "[" and "]" are notlegal unless preceded by the escape character (^). ACPQIO-to-RMS Conversion: The string described by the srcstr descriptor argumentis converted to the RMS canonical form for that string. If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is clear, the source stringmust contain at least one semicolon and, to the left of the semicolon,at least one dot. If it does not, RMS$_SYN (syntax error) is returned.In the output string, all other dots and semicolons are preceded by theRMS escape character (^). If the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag is set, any dot or semicolonencountered is preceded in the output string by the RMS escapecharacter (^). The CVTFNM$V_WORD_CHARS flag of the inflags argumentindicates whether the input string is to be interpreted as havingbyte-width (ISO Latin-1) or word-width (UCS-2) characters. If theargument indicates word-width characters, but the input length value isan odd number, a syntax error is returned. Questions marks are converted to percent signs; percent signs arepreceded by the escape character (^). UCS-2 characters are converted to VTF-7 characters. All characters are represented in RMS canonical form. $CVT_FILENAME Usage: You can use this service to compare two file names using the sameconventions as RMS. For an example program, refer to: [SYSHLP.EXAMPLES]FILENAME_COMPARE.C. Required Access or Privileges
None. Required Quota
None. Related Services
None.
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_BADPARAM | Unrecognized conversion type, extraneous input flags set, or zero-length input string. | | SS$_INSFARG | Not enough arguments provided. | | SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS | Too many arguments provided. | | RMS$_SYN | The service could not translate one or more characters in the strings described by the srcstr argument. Either the input string has word-width characters but odd byte-length (ACPQIO_TO_RMS only), or the CVTFNM$V_NO_DELIMITERS input flag was clear, and the input string did not contain both type and version delimiters. | | SS$_BUFFEROVF | The output buffer was not large enough to accommodate the converted string. |
$DACEFCReleases the calling process's association with a common event flagcluster.
FormatSYS$DACEFC efn
C Prototypeint sys$dacefc (unsigned int efn);
Argumentefn
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of any event flag in the common cluster to be disassociated. Theefn argument is a longword containing this number;however, $DACEFC uses only the low-order byte. The number must be inthe range of 64 through 95 for cluster 2, and 96 through 127 forcluster 3.
DescriptionThe Disassociate Common Event Flag Cluster service disassociates thecalling process from a common event flag cluster and decreases thecount of processes associated with the cluster accordingly. When theimage associated with a cluster exits, the system disassociates thecluster. When the count of processes associated with a temporarycluster or with a permanent cluster that is marked for deletion reaches0, the cluster is automatically deleted.If a process issues this service specifying an event flag cluster withwhich it is not associated, the service completes successfully. Required Access or Privileges
A calling process must have PRMCEB privilege to delete a permanentcommon event flag cluster. Required Quota
None Related Services
$ASCEFC, $CLREF, $DLCEFC, $READEF, $SETEF, $WAITFR, $WFLAND, $WFLOR
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ILLEFC | You specified an illegal event flag number. The number must be in the range of event flags 64 through 127. | | SS$_INTERLOCK | The bit map lock for allocating common event flag clusters from the specified shared memory is locked by another process. |
$DALLOCDeallocates a previously allocated device.
FormatSYS$DALLOC [devnam] ,[acmode]
C Prototypeint sys$dalloc (void *devnam, unsigned int acmode);
Argumentsdevnam
| OpenVMS usage: | device_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Name of the device to be deallocated. The devnamargument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing tothe device name string. The string might be either a physical devicename or a logical name. If it is a logical name, it must translate to aphysical device name.If you do not specify a device name, all devices allocated by theprocess from access modes equal to or less privileged than thatspecified are deallocated. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode from which the deallocation is to be performed. Theacmode argument is a longword containing the accessmode.The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four accessmodes: | Symbol | Access Mode | | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
DescriptionThe Deallocate Device service deallocates a previously allocateddevice. The issuing process relinquishes exclusive use of the device,thus allowing other processes to assign or allocate that device. Youcan deallocate an allocated device only from access modes equal to ormore privileged than the access mode from which the original allocationwas made.This service does not deallocate a device if, at the time ofdeallocation, the issuing process has one or more I/O channels assignedto the device; in such a case, the device remains allocated. At image exit, the system automatically deallocates all devices thatare allocated at user mode. If you attempt to deallocate a mailbox, success is returned but nooperation is performed. Required Access or Privileges
None Required Quota
None Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DASSGN,$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The device name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller. | | SS$_DEVASSIGN | The device cannot be deallocated because the process still has channels assigned to it. | | SS$_DEVNOTALLOC | The device is not allocated to the requesting process. | | SS$_IVDEVNAM | You did not specify a device name string, or the device name string contains invalid characters. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The device name string has a length of 0 or has more than 63 characters. | | SS$_NONLOCAL | The device is on a remote node. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The device was allocated from a more privileged access mode. | | SS$_NOSUCHDEV | The specified device does not exist in the host system. |
$DASSGNDeassigns (releases) an I/O channel previously acquired using theAssign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN) service.
FormatSYS$DASSGN chan
C Prototypeint sys$dassgn (unsigned short int chan);
Argumentchan
| OpenVMS usage: | channel | | type: | word (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the I/O channel to be deassigned. The chanargument is a word containing this number.
DescriptionThe Deassign I/O Channel service deassigns (releases) an I/O channelthat it acquired using the Assign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN) service. Youcan deassign an I/O channel only from an access mode equal to or moreprivileged than the access mode from which the original channelassignment was made.When you deassign a channel, any outstanding I/O requests on thechannel are canceled. If a file is open on the specified channel, thefile is closed. If a mailbox was associated with the device when the channel wasassigned, the link to the mailbox is cleared. If the I/O channel was assigned for a network operation, the networklink is disconnected. If the specified channel is the last channel assigned to a device thathas been marked for dismounting, the device is dismounted. I/O channels assigned from user mode are automatically deassigned atimage exit. Required Access or Privileges
None. Note that you should use the SHARE privilege with caution.Applications, application protocols, and device drivers coded to expectonly exclusive access can encounter unexpected and errant behavior whenaccess to the device is unexpectedly shared. Unless the SHARE privilegeis explicitly supported by the application, the application protocol,and the device driver, its use is generally discouraged. Refer to theOpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual for additional information. Required Quota
None Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,$DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_IVCHAN | You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available. | | SS$_IVCHNLSEC | A process section file is currently accessed using the specified channel number. | | SS$_IVIDENT | On Alpha systems, you specified an invalid channel number that your process never assigned. | | SS$_NOICHAN | On Alpha systems, you specified a channel number outside of the set of channel numbers available for your process. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode. |
$DCLASTQueues an asynchronous system trap (AST) for the calling access mode orfor a less privileged access mode.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$DCLAST astadr ,[astprm] ,[acmode]
C Prototypeint sys$dclast (void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64astprm, unsigned int acmode);
Argumentsastadr
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure | | type: | procedure value | | access: | call without stack unwinding | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) | | mechanism: | by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
AST service routine to be executed. On Alpha systems, theastadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of thisroutine. On VAX systems, the astadr argument is the32-bit address of this routine.astprm
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 64-bit value (Alpha) | | mechanism: | by 32-bit value (VAX) |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST routine specified by theastadr argument. On Alpha sytems, theastprm argument is a quadword value containing thisparameter. On VAX systems, the astprm argument is alongword value containing this parameter.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode for which the AST is to be declared. The most privilegedaccess mode used is the access mode of the caller. The resultant modeis the access mode for which the AST is declared.
DescriptionThe Declare AST service queues an AST for the calling access mode orfor a less privileged access mode. For example, a routine executing insupervisor mode can declare an AST for either supervisor or user mode.The service does not validate the address of the AST service routine.If you specify an illegal address (such as 0), an access violationoccurs when the AST service routine is given control. Required Access or Privileges
None Required Quota
The $DCLAST service requires system dynamic memory and uses the ASTlimit (ASTLM) quota of the process. Related Services
$SETAST, $SETPRA
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_EXQUOTA | The process has exceeded its AST limit (ASTLM) quota. | | SS$_INSFMEM | The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the service. |
$DCLCMHOn Alpha systems, specifies the address of a routine to receive controlwhen a Change Mode to User or Change Mode to Supervisor instructiontrap occurs. On VAX systems, specifies the address of a routine to receive controlwhen a Change Mode to User or Change Mode to Supervisor instructiontrap occurs, or when a compatibility mode fault occurs.
FormatSYS$DCLCMH addres ,[prvhnd] ,[type]
C Prototypeint sys$dclcmh (int (*addres)(__unknown_params), void *(*(prvhnd)),char type);
Argumentsaddres
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Routine to receive control when a change mode trap or a compatibilitymode fault occurs. The addres argument is theexception handling code in the address space of the calling process.If you specify the addres argument as 0, $DCLCMHclears the previously declared handler. prvhnd
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Address of a previously declared handler. The prvhndargument is the address of a longword containing the address of thepreviously declared handler.type
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Handler type indicator. The type argument is alongword value. The value 0 (the default) indicates that a change modehandler is to be declared for the access mode at which the request isissued; the value 1 specifies that a compatibility mode handler is tobe declared.
DescriptionOn Alpha systems, the Declare Change Mode or Compatibility Mode Handlerservice calls the change mode handler as a normal procedure (that is,with a standard procedure call). The change mode handler must exit byperforming a standard procedure return to the change mode dispatcher. Arguments (for example, the change mode code) passed between theroutine that issued the change mode instruction and the change modehandler are strictly by agreement between the two procedures. The following MACRO code example shows a subroutine calling Change Modeto User. The example is written for Alpha users porting from VAXsystems.
CHG_MD: .CALL_ENTRY CHMU RET | Call this subroutine from any program that requires a Change Mode toUser instruction to be invoked. On VAX systems, the $DCLCMH service specifies the address of a routineto receive control when (1) a Change Mode to User or Change Mode toSupervisor instruction trap occurs, or (2) a compatibility mode faultoccurs. A change mode handler provides users with a dispatchingmechanism similar to that used for system service calls. It allows aroutine that executes in supervisor mode to be called from user mode.You declare the change mode handler from supervisor mode; then when theprocess executing in user mode issues a Change Mode to Supervisorinstruction, the change mode handler receives control and executes insupervisor mode. The top longword of the stack contains the zero-extended change modecode. The change mode handler must exit by removing the change modecode from the stack and issuing an REI instruction. The operating system uses compatibility mode handlers to bypass normalcondition handling procedures when an image executing in compatibilitymode causes a compatibility mode exception. Before transferring controlto the compatibility mode handler, the system saves the compatibilityexception code, the registers R0 through R6, and the PC and PSL in a10-longword array starting at the location CTL$AL_CMCNTX. Before thecompatibility mode handler exits, it must restore the saved registersR0 through R6, push the saved PC and PSL onto the stack, and exit byissuing an REI instruction. Required Access or Privileges
You can declare a change mode or compatibility mode handler only fromuser or supervisor mode. Required Quota
None Related Services
$SETEXV, $UNWIND
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The longword to receive the address of the previous change mode handler cannot be written by the caller. | | ++SS$_IVSSRQ | The call to the service is invalid because it attempted to declare a compatibility mode handler on Alpha systems. |
++Alpha specific
$DCLEXHDeclares an exit handling routine that receives control when an imageexits.
FormatSYS$DCLEXH desblk
C Prototypeint sys$dclexh (void *desblk);
Argumentdesblk
| OpenVMS usage: | exit_handler_block | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write | | mechanism: | by reference |
Exit handler control block. The desblk argument is theaddress of this control block. This control block, which describes theexit handler, is depicted in the following diagram:

DescriptionThe Declare Exit Handler service declares an exit handler routine thatreceives control when an image exits. Image exit normally occurs whenthe image currently executing in a process returns control to theoperating system. Image exit might also occur when you call the Exit($EXIT) or Force Exit ($FORCEX) service. Process exit handlers are notinvoked when a process is deleted (such as using a $DELPRC call, forexample).Exit handlers are described by exit control blocks. The operatingsystem maintains a separate list of these control blocks for user,supervisor, and executive modes, and the $DCLEXH service adds thedescription of an exit handler to the front of one of these lists. Theactual list to which the exit control block is added is determined bythe access mode of the $DCLEXH caller. At image exit, the image context, the image stack pointers, and thevalidity of any variables allocated on the stack are all indeterminate.Accordingly, the exit handler control block and any variables accessedby each exit handler must all be declared using non-volatile semantics.Examples of such non-volatile declarations include the BASIC and FortranCOMMON construct, and the Cstatic storage class. The declared exit handlers are called from the least-privilegedprocessor mode to the most-privileged mode, and the exit handler(s) foreach processor mode are called in the reverse order from which theywere originally declared. Each exit handler is executed only once; itmust be explicitly redeclared by the application if it is to beexecuted again. The exit handler routine is called as a normal procedure with theargument list specified in the third through nth longwords ofthe exit control block. The first argument is always the address of auser-allocated longword to receive the system status code indicatingthe reason for the exit; the system always fills in the referencedlongword before calling the exit handler. Accordingly, the exit handlerroutine receives a pointer to the status code as its first argument.Application programmers can append zero or more additionalapplication-specific longword arguments for use within the exit handlerroutine, with the total number of arguments controlled by the valuespecified in the argument count field. You can call this service only from user, supervisor, and executivemodes. Following is a BASIC programming example for this service. To view a Cexample, refer to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
program DCLEXH_EXAMPLE option type = explicit external long EXIT_HANDLER external long function SYS$DCLEXH external long function SYS$EXIT external long function LIB$STOP declare long RETURN_STATUS record EXIT_DESCRIPTOR long FORWARD_LINK long HANDLER_ADDR long ARG_COUNT long CONDITION_VALUE_PTR long RANDOM_EXAMPLE_VALUE ! borrow part of the record structure for data storage... long CONDITION_VALUE end record EXIT_DESCRIPTOR ! declare the exit handler block in non-volatile storage common (SaveBlock) EXIT_DESCRIPTOR EXHBLK PRINT PRINT "DCLEXH_EXAMPLE initializing..." PRINT EXHBLK::FORWARD_LINK = 0% EXHBLK::HANDLER_ADDR = loc(EXIT_HANDLER) EXHBLK::ARG_COUNT = 2% EXHBLK::CONDITION_VALUE_PTR = loc(EXHBLK::CONDITION_VALUE ) EXHBLK::RANDOM_EXAMPLE_VALUE = 303147% PRINT "Calling SYS$DCLEXH..." RETURN_STATUS = SYS$DCLEXH (EXHBLK by ref) call LIB$STOP (RETURN_STATUS by value) if (RETURN_STATUS and 1%) = 0% PRINT "SYS$DCLEXH called..." PRINT "Calling SYS$EXIT..." call SYS$EXIT(RETURN_STATUS by value)endfunction LONG EXIT_HANDLER(long CONDITION_VALUE, long RANDOM_VALUE by value) ! the exit handler gains control effectively after the main ! program module has exited. Direct access to (or otherwise ! sharing) variables used by the main routine requires explicit ! storage allocation control. option type = explicit print "EXIT_HANDLER invoked..." print "CONDITION_VALUE: ", CONDITION_VALUE print "RANDOM_VALUE: ", RANDOM_VALUE PRINT PRINT "DCLEXH_EXAMPLE done..." PRINTend function | Required Access or Privileges
None Required Quota
None Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,$WAKE The Cancel Exit Handler ($CANEXH) service removes an exit control blockfrom the list.
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The first longword of the exit control block cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_IVSSRQ | The call to the service is invalid because it was made from kernel mode. | | SS$_NOHANDLER | The exit handler control block address was not specified or was specified as 0. |
$DECLARE_RMCreates a new Resource Manager instance (RMI) in the calling process.
FormatSYS$DECLARE_RM [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id,event_handler ,[part_name] [,[rm_context] ,[acmode] ,[tm_log_id],[event_mask]]
C Prototypeint sys$declare_rm unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int*rm_id, void (*event_handler)(__unknown_params),...;
Argumentsefn
| OpenVMS usage: | ef_number | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. Ifthis argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flagsargument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to anoption flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these optionflags, described in Table SYS-23. All undefined bits must be 0. If thisargument is omitted, no flags are used. Table SYS-23 $DECLARE_RM Option Flags | Flag Name | Description | | DDTM$M_SYNC | Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. | | DDTM$M_VOLATILE | Set this flag for the new RMI to be volatile. With this flag set, the DECdtm transaction manager will not log information about any RM participants associated with the new RMI. Resource managers that never perform recovery should set this flag. If this flag is clear, the new RMI is not volatile. The DECdtm transaction manager will log the following information about each RM participant associated with the new RMI: - The name of the RM participant.
- The identifier (TID) of the transaction in which it is participating.
If this flag is clear and a recoverable failure occurs, such as a system crash, the resource manager can use the $GETDTI system service to query the transaction log to determine the outcome of the transactions in which it was participating before the failure occurred. | iosb
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service isreturned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returnedsection.The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
 astadr
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure | | type: | procedure entry mask | | access: | call without stack unwinding | | mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine that is executed when the service completes, ifSS$_NORMAL is returned in R0. The astadr argument isthe address of the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executedin the same access mode as that of the caller of the $DECLARE_RMservice.astprm
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The AST parameter that is passed to the AST routine specified by theastadr argument.rm_id
| OpenVMS usage: | identifier | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference |
Longword in which the identifier (RM_ID) of the new RMI is returned.This identifier is unique within the calling process at any time.event_handler
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure | | type: | procedure entry mask | | access: | call without stack unwinding | | mechanism: | by reference |
The new RMI's event handler. This routine is called to report an eventto the new RMI or one of its RM participants. Theevent_handler argument is the address of the entrymask of this routine. An event handler must be specified.This routine is called as an AST delivered by the DECdtm transactionmanager. The AST is executed in the access mode specified by theacmode argument. The AST parameter is the address of aDECdtm event report block that contains an event report. The DECdtm transaction manager reports events to an RMI and the RMparticipants associated with it using ASTs executed in the access modespecified in the call to $DECLARE_RM that created that RMI. The DECdtm transaction manager creates an event report block, andpasses its address to the AST routine in the parameter of the AST. Eachevent report block contains: - The identifier of the event report.
- A code that describes the event.
- The identifier (TID) of the transaction.
- The name of the RM participant or RMI.
- The context of the RM participant or RMI.
- Other data that depend on the type of the event.
Table SYS-24 describes the fields in an event report block, inalphabetical order: Table SYS-24 Fields in an Event Report Block | Symbol | Description | | DDTM$A_TID_PTR | Address of the identifier (TID) of the transaction. | | DDTM$L_ABORT_REASON | Abort reason code (longword). See the $ACK_EVENT service for a list of possible values. Present only in abort event reports. | | DDTM$L_EVENT_TYPE | A code that identifies the event (longword). The following table lists the possible values: | Symbol | Event | | DDTM$K_ABORT | Abort | | DDTM$K_COMMIT | Commit | | DDTM$K_PREPARE | Prepare | | DDTM$K_ONE_PHASE_COMMIT | One-phase commit | | DDTM$K_STARTED_DEFAULT | Default transaction started | | DDTM$K_STARTED_NONDEFAULT | Nondefault transaction started | | | DDTM$L_REPORT_ID | Event report identifier (unsigned longword). | | DDTM$L_RM_CONTEXT | The context of the RM participant or RMI to which the event report is being delivered (unsigned longword). | | DDTM$Q_PART_NAME | The name of the RM participant or RMI to which the event report is being delivered (descriptor). | | DDTM$Q_TX_CLASS | The transaction class of the transaction (descriptor). | Each event report must be acknowledged by calling $ACK_EVENT,specifying the identifier of the report. This acknowledgment need notcome from AST context. The DECdtm transaction manager delivers only one event report at a timeto each RM participant. For example, if a prepare event report has beendelivered to an RM participant, and the transaction is aborted whilethe RM participant is doing its prepare processing, then the DECdtmtransaction manager does not deliver an abort event report to that RMparticipant until it has acknowledged the prepare event report by acall to $ACK_EVENT. Note that the DECdtm transaction manager maydeliver multiple reports to an RMI. After acknowledging the event report, the RMI or RM participant shouldno longer access the event report block. part_name
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
The name of the new RMI. This is: - The default name of its RM participants, used when a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that adds one of these RM participants to a transaction does not specify the name of the new RM participant.
When an RM participant associated with the new RMI is added to a transaction by a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that has a zero part_name argument, then that RM participant inherits its name from the RMI. The name of that RM participant is the same as the name of the RMI. - The string passed in the participant name field of Transaction Started event reports delivered to the new RMI.
This string must be no longer than 32 characters. If this argument is omitted, the name of the new RMI is the null string. To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to thechapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, forinformation on defining node names. rm_context
| OpenVMS usage: | userarg | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The context of the new RMI. This is: - The default context of its RM participants, used when a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that adds one of these RM participants to a transaction does not specify the context of the new RM participant.
When an RM participant associated with the new RMI is added to a transaction by a call to $JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT that has a zero rm_context argument, then that RM participant inherits its context from the RMI. The context of that RM participant is the same as the context of the RMI. - The string passed in the context field of Transaction Started event reports delivered to the new RMI.
If this argument is omitted, the context of the new RMI is 0. acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The access mode of the new RMI. This is: - The access mode at which the ASTs delivered to its event handler are to be executed.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to call $ACK_EVENT to acknowledge an event report delivered to the new RMI or to its RM participants.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to delete the new RMI by calling $FORGET_RM.
- The least privileged access mode that the caller must be in to call $JOIN_RM to add a new RM participant associated with the new RMI.
- The most privileged access mode of new branches that this RMI is interested in, if the event_mask argument requests events of type Transaction Started.
The call to $START_TRANS or $START_BRANCH that adds a new branch to a transaction specifies the access mode of that transaction within this process. The DECdtm transaction manager reports a Transaction Started event to the new RMI only if the access mode of the transaction is the same as or less privileged than the access mode of the new RMI.
For example, if the access mode of the new RMI is supervisor, it will receive a Transaction Started event when a branch of the calling process is added to a transaction only if the access mode of that transaction is user or supervisor. The access mode of the new RMI is the least privileged of: - The access mode of the caller.
- The access mode specified by the acmode argument.
If this argument is omitted, the access mode of the new RMI is the sameas the access mode of the caller. tm_log_id
| OpenVMS usage: | DECnet_uid | | type: | octaword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by reference |
The globally unique identifier of the transaction log for the localnode. This identifier is used during resource manager recovery to checkthat the correct DECdtm transaction manager log is used. See $GETDTIfor more information.To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to thechapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, forinformation on defining node names. event_mask
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Requests the types of event to be reported to the new RMI and to its RMparticipants. The only type of event that can be reported to the newRMI is a Transaction Started event (a default or non-defaulttransaction started event). The following types of event can bereported to its RM participants: - Abort events
- Commit events
- One-phase commit events
- Prepare events
The event_mask argument is a longword bit mask that isthe logical OR of each bit set, where each bit corresponds to an event.The $DDTMDEF module defines a symbolic name for each flag bit.Table SYS-25 describes the flags. All undefined bits must be 0. If this argument is omitted, the following events are requested: - Abort events
- Commit events
- One-phase commit events
- Prepare events
Table SYS-25 $DECLARE_RM Event Selection Flags | Flag Name | Description | | DDTM$M_EV_ABORT | Specifies that abort events are to be reported to the RM participants associated with the new RMI. If this flag is set, when an abort event occurs for a transaction, the DECdtm transaction manager delivers an abort event report to each RM participant in the transaction that is associated with the new RMI. | | DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT | Specifies that commit events are to be reported to the RM participants associated with the new RMI. If this flag is set, when the DECdtm transaction manager decides that the outcome of a transaction is commit, it delivers a commit event report to each RM participant in the transaction that is associated with the new RMI. | | DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE | Specifies that prepare events are to be reported to the RM participants associated with the new RMI. If this flag is set, when the DECdtm transaction manager initiates the commit protocol (in response to a call to $END_TRANS) to determine the outcome of a transaction, it reports a prepare event to each RM participant in the transaction that is associated with the new RMI. The acknowledgment of a prepare event is a vote on the outcome of the transaction. See $ACK_EVENT for more information. | | DDTM$M_EV_TRANS_START | Specifies that events of type Transaction Started are to be reported to the new RMI. Events of type Transaction Started are: - Default transaction started events.
- Non-default transaction-started events.
If this flag is set, the DECdtm transaction manager will report one of these events to the new RMI whenever a new branch in the calling process is added to a transaction, provided that the access mode of the new branch is not more privileged than the access mode of the new RMI. The acknowledgment of that event report may add a new RM participant associated with the new RMI to that transaction. See the description of the acmode argument for a discussion of access modes. |
DescriptionThe $DECLARE_RM system service creates a new Resource Manager instance(RMI) in the calling process and returns its identifier.Preconditions for successful completion of $DECLARE_RM include: - The local node must have a DECdtm transaction log.
- The TP_SERVER process must be running on the local node.
When $DECLARE_RM completes successfully, a new RMI is created in thecalling process, and its identifier is returned. The new RMI has no RMparticipants. They are added to transactions by subsequent calls to$JOIN_RM or $ACK_EVENT. DECdtm events for the RMI and its RM participants, as specified byevent_mask, are reported to the specified eventhandler. If an RM does not specify DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE, its RM participants do nothave a vote on the outcome of their transactions. The DECdtmtransaction manager assumes that their votes are "yes". If an RM does not specify DDTM$M_EV_ABORT or DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT, DECdtmforgets the involvement of the RM participant associated with the RMIin the transaction when the corresponding event occurs. A one-phase commit event is reported to an RM participant if: - Both the DDTM$M_EV_PREPARE and DDTM$M_EV_COMMIT flags are set.
- It is the only RM participant in the transaction.
- It is running in the process that started the transaction (the process that called $START_TRANS).
The new RMI is deleted from the calling process: - On termination of the calling process.
- On termination of the current image, if the access mode of the RMI was user mode.
- On successful completion of a call to $FORGET_RM in the calling process that passes its identifier.
There is also a wait form of the service, $DECLARE_RMW. Required Privileges
None Required Quotas
BYTLM, ASTLM Related Services
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW,$CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS,$END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW,$GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW,$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW,$START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully. | | SS$_SYNCH | The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set). | | SS$_ACCVIO | An argument was not accessible to the caller. | | SS$_BADPARAM | Either the options flags were invalid or the event mask flags were invalid. | | SS$_EXASTLM | The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded. | | SS$_ILLEFC | The event flag number was invalid. | | SS$_INSFARGS | A required argument was missing. | | SS$_INSFMEM | There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation. | | SS$_INVBUFLEN | The string passed in the part_name argument was too long. | | SS$_NOLOG | The local node did not have a transaction log. | | SS$_TPDISABLED | The TP_SERVER process was not running on the local node. |
$DECLARE_RMWCreates a new Resource Manager instance (RMI) in the calling process.$DECLARE_RMW always waits for the request to complete before returningto the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $DECLARE_RM.
FormatSYS$DECLARE_RMW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id,event_handler ,[part_name] [,[rm_context] ,[acmode] ,[tm_log_id],[event_mask]]
C Prototypeint sys$declare_rmw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int*rm_id, void (*event_handler)(__unknown_params),...);
$DELETEThe Delete service removes an existing record from a relative orindexed file. You cannot use this service when processing sequentialfiles.Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this service.
$DELETE_BUFOBJ (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, deletes a buffer object previously created by the$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 system service.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$DELETE_BUFOBJ buffer_handle_64
C Prototypeint sys$delete_bufobj (struct _generic_64 *buffer_handle_64);
Argumentsbuffer_handle_64
| OpenVMS usage: | handle | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The buffer object to be deleted. The buffer_handle_64argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a 2-longword array previouslyreturned by a $CREATE_BUFOBJ_64 call.
DescriptionThe Delete Buffer Object system service deletes the buffer objectidentified by the buffer_handle_64 argument. Theassociated memory is made free to be paged, swapped, or deleted.Buffer objects are also automatically deleted at image rundown. Required Privileges
None Required Quota
None Related Services
$CREATE_BUFOBJ_64
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The buffer_handle_64 argument cannot be read by the caller. | | SS$_BADPARAM | The buffer_handle_64 argument is not a valid buffer handle. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The buffer object was created by a more privileged access mode than the caller's access mode. |
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK (Alpha Only)Invalidates an OpenVMS Galaxy lock and deletes it.Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS AlphaGalaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMS Galaxy systemservices, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
FormatSYS$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK handle
C Prototypeint sys$delete_galaxy_lock (unsigned __int64 lock_handle);
Argumentshandle
| OpenVMS usage: | galaxy lock handle | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read | | mechanism: | input by value |
The 64-bit lock handle that identifies the lock to be deleted. Thisvalue is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK.
DescriptionThis service invalidates the OpenVMS Galaxy lock and deletes it. Thememory for the lock is not truly deleted; however, it is put on a freelist for later use.Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL, SHMEM Required Quota
None Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE,$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO,$GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE, $RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | Normal completion. | | SS$_BADLCKTBL | Galaxy lock table is corrupt. | | SS$_IVLOCKID | Invalid lock id. | | SS$_IVLOCKTBL | Invalid lock table. | | SS$_LOCKINUSE | Invalid operation; lock is in use. | | SS$_NOCMKRNL | Operation requires CMKRNL privilege. | | SS$_NOSHMEN | Operation requires SHMEM privilege. |
$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE (Alpha Only)Deletes an OpenVMS Galaxy locktable.Note that this system service is supported only in an OpenVMS AlphaGalaxy environment. For more information about programming with OpenVMSGalaxy system services, refer to the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
FormatSYS$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE handle
C Prototypeint sys$delete_galaxy_lock_table (unsigned int *lcktbl_handle);
Argumentslcktbl_handle
| OpenVMS usage: | lock table handle | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read | | mechanism: | input by value |
The 32-bit lock table handle that identifies the table to be deleted.This value is returned by SYS$CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE.
DescriptionThis service deletes an OpenVMS Galaxy lock table. If there are nolonger any mappers of the locktable section, the table is deleted.Required Access or Privileges
CMKRNL, SHMEM Required Quota
None Related Services
$ACQUIRE_GALAXY_LOCK, $CREATE_GALAXY_LOCK_TABLE, $DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK,$DELETE_GALAXY_LOCK, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_INFO, $GET_GALAXY_LOCK_SIZE,$RELEASE_GALAXY_LOCK
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | Normal completion. | | SS$_BADPARAM | Bad parameter value. | | SS$_IVLOCKID | Invalid lock id. | | SS$_IVLOCKTBL | Invalid lock table. | | SS$_NOCMKRNL | Operation requires CMKRNL privilege. | | SS$_NOSHMEM | Operation requires SHMEM privilege. |
$DELETE_INTRUSIONSearches for and deletes all records in the intrusion database matchingthe caller's specifications.
FormatSYS$DELETE_INTRUSION user_criteria ,[flags]
C Prototypeint sys$delete_intrusion (void *user_criteria, unsigned int flags);
Argumentsuser_criteria
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string or item_list_3 | | type: | character-coded text string or longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor or by reference |
If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is FALSE:The user_criteria argument is the description ofintruder or suspect. This argument is the address of a character-stringdescriptor pointing to a buffer containing the user criteria to matchan intrusion record's user specification in the intrusion database. The user_criteria argument is a character string of 1to 1058 bytes containing characters to match the user specification onrecords in the intrusion database. A user specification is any combination of the suspect's or intruder'ssource node name, source user name, source DECnet-Plus address, localfailed user name, or local terminal. The user specification for anintrusion record is based on the input to the $SCAN_INTRUSION serviceand the settings of the LGI system parameter. For more information,refer to the HP OpenVMS Guide to System Security. Wildcards are allowed for the user_criteria argument.For example, if you specify an asterisk (*) for theuser_criteria argument, the service deletes allrecords in the intrusion database. If the CIA$M_ITEMLIST flag is TRUE: The user_criteria argument is now the address of a32-bit item list. If the item list is used, one item, theCIA$_USER_CRITERIAL item, must be present in the item list. TheITM$L_BUFADR should point to a buffer containing the specified usercriteria. The following table lists the valid item descriptions for theuser_criteria argument: | Item | Description | | CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST | Address of a list of 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which intrusions are to be deleted. | | CIA$_USER_CRITERIAL | Address of a buffer, 1-1058 bytes long, containing the intruder or suspect. | If the CIA$_SCSNODE_LIST item is present, it is the address of a listof 8-character null-padded SCS nodenames for which intrusions are to bedeleted. If this item is absent, the service deletes the specifiedintrusion records for all nodes in the cluster. MultipleCIA$_SCSNODE_LIST items are permitted. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Functional specification for the service. The flagsargument is a longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to anoption.Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $CIADEF macro defines thefollowing valid names for the $DELETE_INTRUSION service: | Symbolic Name | Description | | CIA$M_IGNORE_RETURN | The service should not wait for the return status from the security server. No return status from the server's function will be returned to the caller. | | CIA$M_ITEMLIST | If FALSE, the user_criteria argument is a character string. If TRUE, this argument is a 32-bit item list. |
DescriptionThe Delete Intrusion Records service deletes from the intrusiondatabase a set of records matching the criteria you specify in theuser_criteria argument. All records matching thecriteria you specify are deleted. You do not have to call the servicemore than once to delete a set of records.For example, if you specify an asterisk (*) for theuser_criteria argument, the service deletes allrecords in the intrusion database with one call. Required Access or Privileges
$DELETE_INTRUSION requires access to the intrusion database. You musthave SECURITY privilege to access the database. Required Quota
None Related Services
$SCAN_INTRUSION, $SHOW_INTRUSION
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The user_criteria argument cannot be read. | | SS$_BADBUFLEN | The length of the user_criteria argument is out of range. | | SS$_BADPARAM | An invalid flag was specified in the flags argument. | | SS$_NOSECURITY | The caller does not have SECURITY privilege. | | | | | This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server: | | | | | SECSRV$_CIADBEMPTY | No records in the intrusion database. | | SECSRV$_NOSUCHINTRUDER | No records matching the specified criteria were found in the intrusion database. | | SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE | The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later. |
$DELETE_PROXYDeletes an existing proxy or removes the default user or a local userfrom an existing proxy in the proxy database.
FormatSYS$DELETE_PROXY rem_node ,rem_user ,[local_user] ,[flags]
D Prototypeint sys$delete_proxy (void *rem_node, void *rem_user, void *local_user,unsigned int flags);
Argumentsrem_node
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote node name of the proxy to be deleted from or modified in theproxy database. The rem_node argument is the addressof a character-string descriptor pointing to the remote node namestring.A remote node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specificcharacters, format, or case are required for a remote node name string.All node names are converted to their DECnet for OpenVMS full nameunless the PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND flag is set with theflags argument. Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remotenode specification. If you specify wildcards for therem_node argument, the security server searches for anexact match to the specified remote node first. If it does not find anexact match, the server performs the requested operations on all of thematching proxies in the proxy database. rem_user
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote user name of the proxy to be deleted from or modified in theproxy database. The rem_user argument is the addressof a character-string descriptor pointing to the user name string.A remote user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters,including dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and brackets ([ ]). Anylowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase. The rem_user argument can be specified in useridentification code (UIC) format ([group, member]).Brackets are allowed only if the remote user name string specifies aUIC. Group and member are character-string representations of octalnumbers with no leading zeros. Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remoteuser specification. If you specify wildcards for therem_user argument, the server searches for an exactmatch to the specified remote user first. If it does not find an exactmatch, the server performs the requested operations on all of thematching proxies in the proxy database. local_user
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Local user name to delete from the proxy record specified by therem_node and rem_user arguments inthe proxy database. The local_user argument is theaddress of a character-string descriptor pointing to the local username.A local user name consists of 0 to 32 alphanumeric characters,including dollar signs ($) and underscores (_). If thelocal_user argument is not specified or has a lengthof 0, the server will delete the entire record or records specified bythe rem_node and rem_user argumentsfrom the proxy database. If the local_user argument is specified, the serverwill delete only the user name specified by thelocal_user argument from the record specified by therem_node and rem_user arguments. Thelocal_user argument can specify either the proxy'sdefault user or a user name in the proxy's local users list. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Functional specification for the service and type of user thelocal_user argument represents. Theflags argument is a longword bit mask wherein each bitcorresponds to an option.Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $PRXDEF macro defines thefollowing symbolic names: | Symbolic Name | Description | | PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND | The service should not convert the node name specified in the rem_node argument to its corresponding DECnet full name. If this flag is set, it is the caller's responsibility to ensure that the fully expanded node name is passed into the service. | | PRX$M_IGNORE_RETURN | The service should not wait for a return status from the security server. No return status from the server's function will be returned to the caller. | | PRX$M_EXACT | The service should match exactly the remote node and remote user and ignore wildcards. |
DescriptionThe Delete Proxy service deletes a proxy from, or modifies an existingproxy in, the proxy database.Required Access or Privileges
$DELETE_PROXY requires access to the proxy database. To achieve access,the caller must have either SYSPRV privilege or a UIC group less thanor equal to the MAXSYSGRP system parameter. Required Quota
None Related Services
$ADD_PROXY, $DISPLAY_PROXY, $VERIFY_PROXY
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The rem_node, rem_user, local_user, or flags argument cannot be read by the service. | | SS$_BADBUFLEN | The length of the rem_node, rem_user, or local_user argument was out of range. | | SS$_BADPARAM | An invalid flag was specified in the flags argument. | | SS$_NOSYSPRV | The caller does not have access to the proxy database. | | | | | This service can also return any of the following messages passed from the security server: | | | | | SECSRV$_BADNODENAMELEN | The node name length is out of range. | | SECSRV$_BADREMUSERLEN | The remote user name length is out of range. | | SECSRV$_INVALIDDELETE | You attempted to remove the last local user with no default user remaining, or you tried to remove the last default user with no local user remaining. You must have at least one local user or one default user. | | SECSRV$_NOSUCHPROXY | The proxy specified by the rem_node and rem_user arguments does not exist in the proxy database. | | SECSRV$_NOSUCHUSER | The specified local user does not exist in the proxy's local user list, or is not the proxy's default user. | | SECSRV$_PROXYNOTACTIVE | Proxy processing is currently stopped. Try the request again later. | | SECSRV$_SERVERNOTACTIVE | The security server is not currently active. Try the request again later. |
$DELETE_REGION_64 (Alpha Only)On Alpha systems, deletes a virtual region within the process's addressspace, including all created virtual addresses within the region.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$DELETE_REGION_64 region_id_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64,return_length_64
C Prototypent sys$delete_region_64 (struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned intacmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);
Argumentsregion_id_64
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The region ID associated with the region to be deleted. The region IDspecified must be one returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service. Youcannot specify VA$C_P0, VA$C_P1, or VA$C_P2.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Access mode associated with the call to $DELETE_REGION_64. Theacmode argument is a longword containing the accessmode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H inSYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for thefour access modes: | Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode | | 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel | | 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive | | 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor | | 3 | PSL$C_USER | User | The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.The caller can delete pages only if those pages are owned by an accessmode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller. Once all pages are deleted within the region, the region can be deletedonly if the region is owned by an access mode equal to or lessprivileged than the access mode of the caller. return_va_64
| OpenVMS usage: | address | | type: | quadword address | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The lowest process virtual address of the pages that $DELETE_REGION_64has successfully deleted. The return_va_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the virtual address of the first pagedeleted. Virtual addresses are deleted from low address to highaddress, regardless of the direction in which virtual addresses expandfor that region.return_length_64
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count | | type: | quadword (unsigned) | | access: | write only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The length of the virtual address range that $DELETE_REGION_64 hassuccessfully deleted. The return_length_64 argument isthe 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword intowhich the service returns the length of the deleted virtual addressrange in bytes.
DescriptionThe Delete a Virtual Region service is a kernel mode service that canbe called from any mode. This service deletes the user-defined regionspecified by the region_id_64 argument. You cannotdelete the program (P0), control (P1), or 64-bit program (P2) regions.The Delete a Virtual Region service also deletes all created virtualaddresses within the specified region before deleting the region itself. If a page within the region is owned by an access mode more privilegedthan the access mode of the caller, the condition value SS$_PAGOWNVIOis returned. The return_va_64 andreturn_length_64 arguments contain the virtual addressrange that was actually deleted by $DELETE_REGION_64. In this case, theregion is not deleted because there are still some pages mapped withinthe region. To delete a virtual region, the caller's access mode must be at leastas privileged as the access mode associated with the region. If thecaller is not privileged enough to delete the region, the conditionvalue SS$_REGOWNVIO is returned only if all pages were successfullydeleted from within the region. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a valuecannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by thereturn_va_64 and return_length_64arguments. If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned, no pages havebeen deleted, and the region has not been deleted. If an error other than SS$_ACCVIO occurs, the returned address andreturned length indicate the pages that were successfully deletedbefore the error occurred. If no pages were deleted, thereturn_va_64 argument contains the value --1 and avalue cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to bythe return_length_64 argument. Required Privileges
None Required Quota
None Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64,$CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELTVA_64,$EXPREG_64, $GET_REGION_INFO, $MGBLSC_64, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | Successful completion. All pages within the region have been deleted as well as the region itself. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The return_va_64 argument or the return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_IVREGID | Invalid region ID specified. This condition value is returned if P0, P1, or P2 space is specified because these regions cannot be deleted, or if no region exists for the specified ID. | | SS$_REGOWNVIO | The region is owned by a more privileged access mode than the access mode of the caller. All pages within the region have been deleted; however, the region has not been deleted. | | SS$_PAGOWNVIO | A page within the specified region is owned by a more privileged access mode than the access mode of the caller. | | SS$_VA_IN_USE | The existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. |
$DELLNMDeletes all logical names with the specified name at the specifiedaccess mode or outer access mode, or it deletes all the logical nameswith the specified access mode or outer access mode in a specifiedtable.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
FormatSYS$DELLNM tabnam ,[lognam] ,[acmode]
C Prototypeint sys$dellnm (void *tabnam, void *lognam, unsigned char *acmode);
Argumentstabnam
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) | | mechanism: | by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX) |
Name of a logical name table or a list of tables to be searched for thelogical name to be deleted. The tabnam argument is the32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alphasystems) of a descriptor that points to the table name. This argumentis required.If tabnam is not the name of a logical name table, itis assumed to be a logical name and is translated iteratively untileither the name of a logical name table is found or the number oftranslations allowed by the system has been performed. If tabnam translates to the name of a list of tables,$DELLNM does the following: - If you specify the lognam argument, $DELLNM searches (in order) each table in the list until it finds the first table that contains the specified logical name. If the logical name is at the specified access mode, $DELLNM then deletes occurrences of the logical name at the specified access mode and at outer access modes within the table.
- If you do not specify the lognam argument, $DELLNM deletes all of the logical names at the specified access mode or at outer access modes from the first table in the list whose access mode is equal to or less privileged than the caller's access mode.
lognam
| OpenVMS usage: | logical_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) | | mechanism: | by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX) |
Logical name to be deleted. The lognam argument is the32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alphasystems) of a descriptor that points to the logical name string.acmode
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode | | type: | byte (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) | | mechanism: | by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Access mode to be used in the delete operation. Theacmode argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a byte containingthis access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines symbolic names for the fouraccess modes.You determine the access mode actually used in the delete operation bymaximizing the access mode of the caller with the access modespecified by the acmode argument; that is, the lessprivileged of the two is used. However, if you have SYSNAM privilege, the delete operation is executedat the specified access mode regardless of the caller's access mode. If you omit this argument or specify it as 0, the access mode of thecaller is used in the delete operation. The access mode used in thedelete operation determines which tables are used and which names aredeleted.
DescriptionThe Delete Logical Name service deletes all logical names with thespecified name at the specified access mode or outer access mode, or itdeletes all the logical names with the specified access mode or outeraccess mode in a specified table. If any logical names being deletedare also the names of logical name tables, then all of the logicalnames contained within those tables and all of their subtables are alsodeleted.Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of thefollowing access or rights privileges to use $DELLNM: - Write and delete access to the logical name table to delete a logical name
- Write access to the directory table that contains the table name, or SYSPRV privilege, to delete a shareable logical name table
- SYSNAM privilege to delete a logical name or table at an inner access mode
- GRPNAM or SYSPRV privilege to delete a logical name from a group table
- SYSNAM or SYSPRV privilege to delete a logical name from a system table
Required Quota
None Related Services
$CRELNM, $CRELNT, $TRNLNM
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments. | | SS$_BADPARAM | One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table name was not specified. | | SS$_INSFMEM | There is insufficient dynamic memory to build a message describing the deletion of a clusterwide name. | | SS$_IVLOGNAM | The lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not in the required range of 1 through 255 characters. | | SS$_IVLOGTAB | The tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table. | | SS$_NOLOGNAM | The specified logical name table does not exist, or a logical name with an access mode equal to or less privileged than the caller's access mode does not exist in the logical name table. | | SS$_NOLOGTAB | The specified logical name table does not exist. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The caller lacks the necessary privilege to delete the logical name. | | SS$_TOOMANYLNAM | The logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth (10 translations). |
$DELMBXMarks a permanent mailbox for deletion.
FormatSYS$DELMBX chan
C Prototypeint sys$delmbx (unsigned short int chan);
Argumentchan
| OpenVMS usage: | channel | | type: | word (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
Number of the channel assigned to the mailbox that is to be deleted.The chan argument is a word containing this number.
DescriptionThe Delete Mailbox service marks a permanent mailbox for deletion. Theactual deletion of the mailbox and of its associated logical nameassignment occurs when no more I/O channels are assigned to the mailbox.You can delete a mailbox only from an access mode equal to or moreprivileged than the access mode from which the mailbox channel wasassigned. Temporary mailboxes are automatically deleted when theirreference count goes to 0. The $DELMBX service does not deassign the channel assigned by thecaller, if any. The caller must deassign the channel with the DeassignI/O Channel ($DASSGN) service. Required Access or Privileges
You need PRMMBX privilege to delete a permanent mailbox. Required Quota
None Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,$DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_DEVNOTMBX | The specified channel is not assigned to a mailbox. | | SS$_IVCHAN | You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number of 0 or a number larger than the number of channels available. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The specified channel is not assigned to a device; the process does not have the privilege to delete a permanent mailbox or a mailbox in memory shared by multiple processors; or the access mode of the caller is less privileged than the access mode from which the channel was assigned. |
$DELPRCAllows a process to delete itself or another process.
FormatSYS$DELPRC [pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,[flags]
C Prototypeint sys$delprc (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam);
Argumentspidadr
| OpenVMS usage: | process_id | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | modify | | mechanism: | by reference |
Process identification (PID) of the process to be deleted. Thepidadr argument is the address of a longword thatcontains the PID. The pidadr argument can refer to aprocess running on the local node or a process running on another nodein the OpenVMS Cluster system.You must specify the pidadr argument to deleteprocesses in other UIC groups. prcnam
| OpenVMS usage: | process_name | | type: | character-coded text string | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Process name of the process to be deleted. The prcnamis the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the processname string. A process running on the local node can be identified witha 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on a particular nodeon a cluster, specify the full process name, which includes the nodename as well as the process name. The full process name can contain upto 23 characters.You use the prcnam argument to delete only processesin the same UIC group as the calling process, because process names areunique to UIC groups, and the operating system uses the UIC groupnumber of the calling process to interpret the process name specifiedby the prcnam argument. You must use the pidadr argument to delete processesin other groups. flags
| OpenVMS usage: | mask | | type: | longword (unsigned) | | access: | read only | | mechanism: | by value |
The flags argument can be used to control whether exithandlers are called by $DELPRC. If the flags argumentis not specified or is specified with a zero, the system parameterDELPRC_EXIT controls what exit handlers, if any, are called by $DELPRC.The $DELPRCSYMDEF macro defines a symbolic name for EXIT and NOEXIT.The EXIT flag should be or'd with the access mode defined by the$PSLDEF macro for the initial exit handler. The following table describes each flag: | Flag | Description | | DELPRC$M_EXIT | When set, exit handlers as specified by DELPRC$M_MODE are called. This flag is ignored for a hard suspended process. | | DELPRC$M_MODE | 2 bit field: values psl$c_kernel, psl$c_exec, psl$c_super, psl$c_user (from the $PSLDEF macro) | | DELPRC$M_NOEXIT | Set to disable any exit handler execution | Note
Deleting the current process:When $DELPRC is used to delete the current process, execution cannotcontinue in the mode from which $DELPRC was called. The first exithandlers that are called will be in the next more privileged moderelative to the mode from which $DELPRC was called (subject to optionsdefined). For example: - $DELPRC called from user mode can call supervisor mode exit handlers.
- $DELPRC called from exec mode can only execute kernel mode exit handlers.
- $DELPRC called from kernel mode cannot call exit handlers.
|
DescriptionThe Delete Process service allows a process to delete itself or anotherprocess. If you specify neither the pidadr nor theprcnam argument, $DELPRC deletes the calling process;control is not returned. If the longword at addresspidadr is 0, the PID of the target process isreturned. This system service requires system dynamic memory.When you delete a process or subprocess, a termination message is sentto its creating process, provided the mailbox to receive the messagestill exists and the creating process has access to the mailbox. Thetermination message is sent before the final rundown is initiated;thus, the creating process might receive the message before the processdeletion is complete. Due to the complexity of the required rundown operations, a significanttime interval occurs between a delete request and the actual deletionof the process; however, the $DELPRC service returns to the callerimmediately after initiating the rundown operation. If you issue subsequent delete requests for a process currently beingdeleted, the requests return immediately with a successful completionstatus. Process exit handlers are not invoked when a process is deleted. Fordetails on exit handlers, see the $DCLEXH service. Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of thefollowing privileges to use $DELPRC: - GROUP privilege to delete processes in the same group that do not have the same UIC
- WORLD privilege to delete any process in the system
Required Quota
None. Deductible resource quotas granted to subprocesses are returnedto the creating process when the subprocesses are deleted. Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER,$PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND,$WAKE
Condition Values Returned | SS$_NORMAL | The service completed successfully. | | SS$_ACCVIO | The process name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the process identification cannot be written by the caller. | | SS$_INCOMPAT | The remote node is running an incompatible version of the operating system. | | SS$_INSFMEM | The system dynamic memory is insufficient for completing the operation. | | SS$_NONEXPR | The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified. | | SS$_NOPRIV | The caller does not have the privilege to delete the specified process. | | SS$_NOSUCHNODE | The process name refers to a node that is not currently recognized as part of the cluster. | | SS$_REMRSRC | The remote node has insufficient resources to respond to the request. (Bring this error to the attention of your system manager.) | | SS$_UNREACHABLE | The remote node is a member of the cluster but is not accepting requests. (This is normal for a brief period early in the system boot process.) |
|





