 |
OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$DGBLSC
Marks an existing permanent global section for deletion. The actual
deletion of the global section takes place when all processes that have
mapped the global section have deleted the mapped pages.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$DGBLSC [flags] ,gsdnam ,[ident]
C Prototype
int sys$dgblsc (unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, struct _secid *ident);
Arguments
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Mask indicating global section characteristics. The
flags argument is a longword value. A value of 0 (the
default) specifies a group global section; a value of SEC$M_SYSGBL
specifies a system global section; a value of SEC$M_SHMGS on an OpenVMS
Galaxy system creates a shared-memory global section.
gsdnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
(VAX) |
Name of the global section to be deleted. The gsdnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
this name string.
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the group
UIC as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global
sections are unique to UIC groups.
You can specify any name from 1 to 43 characters. All processes mapping
to the same global section must specify the same name. Note that the
name is case sensitive.
Use of characters valid in logical names is strongly encouraged. Valid
values include alphanumeric characters, the dollar sign ($), and the
underscore (_). If the name string begins with an underscore (_), the
underscore is stripped and the resultant string is considered to be the
actual name. Use of the colon (:) is not permitted.
Names are first subject to a logical name translation, after the
application of the prefix GBL$ to the name. If the result translates,
it is used as the name of the section. If the resulting name does not
translate, the name specified by the caller is used as the name of the
section.
Additional information on logical name translations and on section name
processing is available in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
ident
| OpenVMS usage: |
section_id |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
Identification value specifying the version number of the global
section to be deleted and the matching criteria to be applied. The
ident argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha
systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a quadword structure
containing three fields.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number
contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits
and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. Values for these
fields can be assigned by installation convention to differentiate
versions of global sections. If you specify no version number when
creating a section, processes that specify a version number when
mapping cannot access the global section.
The first longword specifies, in its low-order 3 bits, the matching
criteria. The valid values, the symbolic names by which they can be
specified, and their meanings are listed in the following table:
| Value |
Name |
Match Criteria |
|
0
|
SEC$K_MATALL
|
Match all versions of the section.
|
|
1
|
SEC$K_MATEQU
|
Match only if major and minor identifications match.
|
|
2
|
SEC$K_MATLEQ
|
Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor
identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor
identification of the global section.
|
If you specify no address or specify it as 0 (the default), the version
number and match control fields default to 0.
Description
The Delete Global Section service marks an existing permanent global
section for deletion. The actual deletion of the global section takes
place when all processes that have mapped the global section have
deleted the mapped pages.
After a global section has been marked for deletion, any process that
attempts to map it receives the warning return status code
SS$_NOSUCHSEC.
Temporary global sections are automatically deleted when the count of
processes using the section goes to 0.
On VAX systems, a section located in memory that is shared by multiple
processors can be marked for deletion only by a process running on the
same processor that created the section.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one or more
of the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to delete a system global section
- PRMGBL privilege to delete a permanent global section
- PFNMAP privilege to delete a page frame section
- SHMEM privilege to delete a global section located in memory shared
by multiple processors
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET,
$MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC,
$UPDSECW
The $DGBLSC service does not unmap a global section from a process's
virtual address space. To do this, the process should call the Delete
Virtual Address Space ($DELTVA or $DELTVA_64) service, which deletes
the pages to which the section is mapped.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The global section name or name descriptor or the section
identification field cannot be read by the caller.
|
|
SS$_INTERLOCK
|
The bit map lock for allocating global sections from the specified
shared memory is locked by another process.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 15
characters.
|
|
SS$_IVSECFLG
|
You set an invalid flag, reserved flag, or flag requiring a user
privilege.
|
|
SS$_IVSECIDCTL
|
The section identification match control field is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
The caller does not have the privilege to delete a system global
section, does not have read/write access to a group global section, or
does not have the privilege to delete a global section located in
memory that is shared by multiple processors.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHSEC
|
The specified global section does not exist, or the identifications do
not match.
|
|
SS$_NOTCREATOR
|
The section is in memory shared by multiple processors and was created
by a process on another processor.
|
|
+SS$_SHMNOTCNCT
|
The shared memory named in the
name argument is not known to the system. This error
can be caused by a spelling error in the string, an improperly assigned
logical name, or the failure to identify the multiport memory as shared
at system generation time.
|
|
SS$_TOOMANYLNAM
|
The logical name translation of the
gsdnam string exceeded the allowed depth of 10.
|
+VAX specific
$DISMOU
Dismounts a mounted volume or volume sets.
Format
SYS$DISMOU devnam ,[flags]
C Prototype
int sys$dismou (void *devnam, unsigned int flags);
Arguments
devnam
| OpenVMS usage: |
device_name |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Device name of the device to be dismounted. The devnam
argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to
the device name string. The string can be either a physical device name
or a logical name. If it is a logical name, it must translate to a
physical device name.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
A longword bit vector specifying options for the dismount operation.
The flags argument is a longword bit vector wherein a
bit, when set, selects the corresponding option. Each bit has a
symbolic name; these names are defined by the $DMTDEF macro.
The flags and their meanings are listed in the following table:
| Flag |
Meaning |
|
DMT$M_ABORT
|
The volume is to be dismounted even if the caller did not mount the
volume. If the volume was mounted with MNT$M_SHARE specified, $DISMOU
dismounts the volume for all of the users who mounted it.
To specify DMT$M_ABORT, the caller must: (1) have GRPNAM privilege
for a group volume, (2) have SYSNAM privilege for a system volume, or
(3) either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
|
|
DMT$M_CLUSTER
|
The volume is to be dismounted clusterwide, that is, from all nodes in
the OpenVMS Cluster system. $DISMOU dismounts the volume from the
caller's node first and then from every other node in the existing
cluster.
DMT$M_CLUSTER dismounts only system or group volumes. To dismount a
group volume clusterwide, the caller must have GRPNAM privilege. To
dismount a system volume clusterwide, the caller must have SYSNAM
privilege.
DMT$M_CLUSTER has no effect if the system is not a member of a
cluster. DMT$M_CLUSTER applies only to disks.
|
|
DMT$M_FORCE
|
If connectivity to a device has been lost and the shadow set is in
mount verification, this flag causes a named shadow set member to be
immediately expelled from the shadow set.
|
|
DMT$M_MINICOPY_OPTIONAL
|
$DISMOU takes place, regardless of whether minicopy is enabled on the
disk.
|
|
DMT$M_MINICOPY_REQUIRED
|
$DISMOU fails if minicopy has not been enabled on the disk.
|
|
DMT$M_NOUNLOAD
|
Specifies that the volume is not to be physically unloaded after the
dismount. If both the DMT$M_UNLOAD and DMT$M_NOUNLOAD flags are
specified, the DMT$M_NOUNLOAD flag is ignored. If neither flag is
specified, the volume is physically unloaded, unless the DMT$M_NOUNLOAD
flag was specified on the $MOUNT system service or the /NOUNLOAD
qualifier was specified on the MOUNT command when the volume was
mounted.
|
|
DMT$M_OVR_CHECKS
|
Specifies that the volume should be dismounted without checking for
open files, spooled devices, installed images, or installed swap and
page files.
|
|
DMT$M_UNIT
|
The specified device, rather than the entire volume set, is dismounted.
|
|
DMT$M_UNLOAD
|
Specifies that the volume is to be physically unloaded after the
dismount. If both the DMT$M_UNLOAD and DMT$M_NOUNLOAD flags are
specified, the DMT$M_NOUNLOAD flag is ignored. If neither flag is
specified, the volume is physically unloaded, unless the DMT$M_NOUNLOAD
flag was specified on the $MOUNT system service or the /NOUNLOAD
qualifier was specified on the MOUNT command when the volume was
mounted.
|
Description
The Dismount Volume service dismounts a mounted volume or volume sets.
To dismount a private volume, the caller must own the volume.
When you issue the $DISMOU service, $DISMOU removes the volume from
your list of mounted volumes, deletes the logical name (if any)
associated with the volume, and decrements the mount count.
If the mount count does not equal 0 after being decremented, $DISMOU
does not mark the volume for dismounting (because the volume must have
been mounted shared). In this case, the total effect for the issuing
process is that the process is denied access to the volume and a
logical name entry is deleted.
If the mount count equals 0 after being decremented, $DISMOU marks the
volume for dismounting. After marking the volume for dismounting,
$DISMOU waits until the volume is idle before dismounting it. A native
volume is idle when no user has an open file to the volume, and a
foreign volume is idle when no channels are assigned to the volume.
Native volumes are Files-11 structured disks or ANSI-structured tapes.
Foreign volumes are not Files-11 or ANSI structured media.
After a volume is dismounted, nonpaged pool is returned to the system.
Paged pool is also returned if you mounted the volume using the /GROUP
or /SYSTEM qualifier.
If a volume is part of a Files-11 volume set and the flag bit
DMT$V_UNIT is not set, the entire volume set is dismounted.
When a Files-11 volume has been marked for dismount, new channels can
be assigned to the volume, but no new files can be opened.
Note that the SS$_NORMAL status code indicates only that $DISMOU has
successfully performed one or more of the actions just described:
decremented the mount count, marked the volume for dismount, or
dismounted the volume. The only way to determine that the dismount has
actually occurred is to check the device characteristics using the Get
Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) service.
By specifying the DVI$_DEVCHAR item code in a call to $GETDVI, you can
learn whether a volume is mounted (it is if the DEV$V_MNT bit is set)
or whether it is marked for dismounting (it is if the DEV$M_DMT bit is
set). If DEV$V_MNT is clear or if DEV$M_DMT is set, the mount count is
0.
Required Access or Privileges
Depending on the operation, the calling process might need one of the
following privileges to use $DISMOU:
- GRPNAM privilege to dismount a volume mounted with the /GROUP
qualifier
- SYSNAM privilege to dismount a volume mounted with the /SYSTEM
qualifier
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI,
$GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC,
$SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The device name descriptor cannot be read or does not describe a
readable device name.
|
|
SS$_DEVALLOC
|
The device is allocated to another process and cannot be dismounted by
the caller.
|
|
SS$_DEVOFFLINE
|
The specified device is not available.
|
|
SS$_DEVNOTMOUNT
|
The specified device is not mounted.
|
|
SS$_IVDEVNAM
|
The device name string is not valid.
|
|
SS$_IVLOGNAM
|
The device logical name has a length of 0 or is longer than the
allowable logical name length.
|
|
SS$_NOGRPNAM
|
GRPNAM privilege is required to dismount a volume mounted for groupwide
access.
|
|
SS$_NOIOCHAN
|
No I/O channel is available. To use $DISMOU, a channel must be assigned
to the volume.
|
|
SS$_NONLOCAL
|
The device is on a remote node.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHDEV
|
The specified device does not exist.
|
|
SS$_NOSYSNAM
|
SYSNAM privilege is required to dismount a volume mounted for
systemwide access.
|
|
SS$_NOTFILEDEV
|
The specified device is not file structured.
|
$DISPLAY_PROXY
Returns information about one or more existing proxies.
Format
SYS$DISPLAY_PROXY rem_node ,rem_user ,buffer_sizes ,proxy_node
,proxy_user ,default_user ,local_users ,flags ,[context]
C Prototype
int sys$display_proxy (void *rem_node, void *rem_user, unsigned short
int buffer_sizes [4], void *proxy_node, void *proxy_user, void
*default_user, unsigned int *local_users, unsigned int flags, unsigned
int *context);
Arguments
rem_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote node name of the proxy about which information is being
requested. The rem_node argument is the address of a
character-string descriptor pointing to the remote node name string.
A remote node name consists of 1 to 1024 characters. No specific
characters, format, or case are required for a remote node name string.
All node names are converted to their DECnet full name unless the
PRX$M_BYPASS_EXPAND flag is set with the flags
argument.
Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remote
node specification. If you specify wildcards for the
rem_node argument, the server searches the entire
proxy database for matches to the remote node and remote user you
specified. If a match is found, information about the matched proxy is
returned. See the Description section for additional details on
retrieving information about multiple proxies.
rem_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Remote user name of the proxy about which information is being
requested. The rem_user argument is the address of a
character-string descriptor pointing to the user name string.
A remote user name consists of 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters,
including dollar signs ($), underscores (_), and brackets ([ ]). Any
lowercase characters specified are automatically converted to uppercase.
The rem_user argument can be specified in user
identification code (UIC) format ([group, member]).
Brackets are allowed only if the remote user name string specifies a
UIC. Group and member are character-string representations of octal
numbers with no leading zeros.
Asterisk (*) and percent sign (%) wildcards are allowed for the remote
user specification. If you specify wildcards for the
rem_user argument, the server searches the entire
proxy database for matches to the remote node and remote user you
specified. If a match is found, information about the matched proxy is
returned. See the Description section for information about retrieving
information about multiple proxies.
buffer_sizes
| OpenVMS usage: |
return length block |
| type: |
array of 4 words (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Array of return lengths for various input buffers. The
buffer_sizes argument is the address of an array of
four words with the following format:
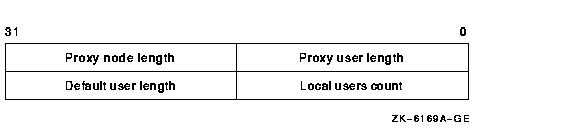
The following table defines the buffer_sizes fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Proxy user length
|
Return length (in bytes) of the
rem_user argument. The proxy user length field
contains a value in the range of 0 to 32. A value of 0 in this field
indicates that the service has failed or that there was no match for
the user specified by the
rem_user argument.
|
|
Proxy node length
|
Return length (in bytes) of the
rem_node argument. A value of 0 in this field
indicates that the service has failed or that there was no match for
the node specified by the
rem_node argument. The proxy node length field
contains values in the range of 0 to 1024.
|
|
Local users count
|
Number of local users associated with the matched proxy. The local
users count field contains a value in the range of 0 to 16. A value of
0 indicates that the matched proxy had no local users.
|
|
Default user length
|
Return length (in bytes) of the
default_user argument. The default user length field
contains a value in the range of 0 to 32. A value of 0 in this field
indicates that the matched proxy did not have a default user.
|
proxy_node
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Node name of a proxy matching the remote node name specified by the
rem_node argument and the remote user name specified
by the rem_user argument. The
proxy_node argument is the address of a
character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer to receive the proxy
node name.
The descriptor's buffer must be 1024 bytes long to receive a node name.
The length of the returned node name is specified by the proxy node
length field returned in the buffer specified by the
buffer_sizes argument.
proxy_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
User name of a proxy matching the remote node name specified by the
rem_node argument and the remote user name specified
by the rem_user argument. The
proxy_user argument is a character-string descriptor
pointing to a buffer to receive the remote user name of a proxy.
The descriptor's buffer must be 32 bytes long to receive a user name.
The length of the returned user name is specified by the proxy user
length field returned in the buffer specified by the
buffer_sizes argument.
default_user
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
Default user of a proxy matching the node name specified by the
rem_node argument and the remote user name specified
by the rem_user argument. The
default_user argument is the address of a
character-string descriptor pointing to a buffer to receive the default
user name.
The descriptor's buffer must be 32 bytes long to receive a user name.
The length of the returned user name is specified in the default user
length field in the buffer specified by the
buffer_sizes argument.
local_users
| OpenVMS usage: |
buffer |
| type: |
array of 0 to 16 user name buffers |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Array of local user names associated with a proxy matching the remote
node name specified by the rem_node argument and the
remote user name specified by the rem_user argument.
The local_users argument is the address of a buffer to
receive an array of local user names.
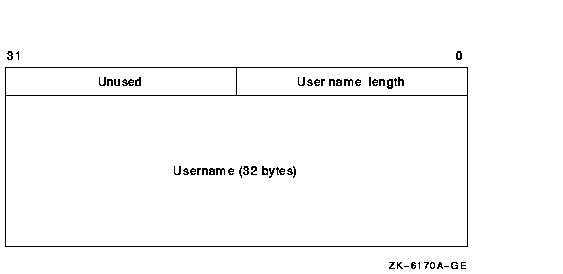
Each element in the array is a 36-byte block with the following format:
The following table defines the local_users fields:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
User name length
|
Length (in bytes) of the associated user name string. The length can be
in the range of 1 to 32 bytes.
|
|
Username
|
A fixed 32-byte blank padded character string containing a local user
name associated with the matched proxy.
|
|

