The number of elements returned in the buffer is specified in the local
users count field returned in the buffer specified by the
buffer_sizes argument.
Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $PRXDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
Contexts become invalid after one-half hour of non-use. This means that
if you call the $DISPLAY_PROXY service with a wildcard
rem_node or rem_user, and do not call
the service to get the next matching record within one-half hour, the
context becomes invalid. If the context has become invalid, you must
start your search of the proxy database over from its beginning by
resetting the context to 0.
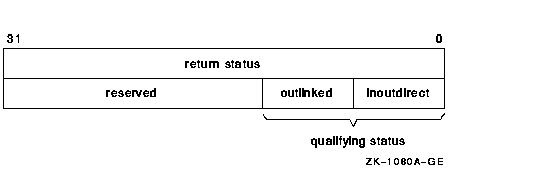
The two qualifying status flags, DNS$V_DNSB_INOUTDIRECT and
DNS$V_DNSB_OUTLINKED, are defined as follows:
Functions that access the DECdns server return a qualifying
status. Name conversion functions do not return qualifying status.
The AST routine executes in the access mode of the caller of $DNS.
DNS$_ADD_REPLICA
This request adds a directory replica in the specified clearinghouse.
Specify the item code DNS$_REPLICATYPE as either a secondary directory
(DNS$K_SECONDARY) or a read-only directory (DNS$K_READONLY).
You must have control access to the directory being replicated and
write access to the new replica's clearinghouse.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CLEARINGHOUSE
DNS$_DIRECTORY
DNS$_REPLICATYPE
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
$DNS returns the following qualifying status:
DNS$V_DNSB_OUTLINKED
DNS$_ALLOW_CH
This request permits a directory to store clearinghouse objects. This
request takes as input the name of a directory (DNS$_DIRECTORY).
You must have control access to the parent directory.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_DIRECTORY
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
DNS$_CREATE_DIRECTORY
This request creates a master directory in the specified clearinghouse.
You must have write or control access to the parent directory and write
access to the master replica's clearinghouse.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_DIRECTORY
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CLEARINGHOUSE
DNS$_WAIT
You can specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_OUTCTS
DNS$_CREATE_LINK
This request creates a soft link to a directory, object, soft link, or
clearinghouse in the namespace. Specify the target to which the soft
link points in the DNS$_TARGETNAME item code. Use the DNS$_RESOLVE_NAME
function code to check the existence of the target.
You must have write or control access to the directory in which the
soft link is being created.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_LINKNAME
DNS$_TARGETNAME
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_EXPIRETIME
DNS$_EXTENDTIME
DNS$_WAIT
You can specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_OUTCTS
DNS$_CREATE_OBJECT
This request creates an object in the namespace. Initially, the object
has the attributes of DNS$CTS, DNS$UTS, DNS$Class, DNS$ClassVersion,
and DNS$ACS. The name service creates the DNS$CTS, DNS$UTS, and DNS$ACS
attributes. The client application supplies the DNS$Class and
DNS$ClassVersion attributes. You can add attributes using the
DNS$_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE function.
The DECdns clerk cannot guarantee that an object has been
created. Another DNS$_CREATE_OBJECT request could supersede the object
created by your call. To verify an object creation, wait until the
directory is skulked and then check to see if the requested object is
present. If the value of the directory's DNS$ALLUPTO attribute is
greater than the DNS$CTS of the object, your object has been
successfully created.
If specified, DNS$_OUTCTS holds the creation timestamp of the newly
created object.
This function code returns the following:
SS$_NORMAL
DNS$_ENTRYEXISTS
DNS$_INVALID_OBJECTNAME
DNS$_INVALID_CLASSNAME
Any condition listed in the section Condition Values Returned
You must have write access to the directory where the object will
reside.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CLASS
DNS$_OBJECTNAME
DNS$_VERSION
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
You can specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_OUTCTS
DNS$_DELETE_DIRECTORY
This request removes a directory from the namespace.
You must have delete access to the directory being deleted and write,
control, or delete access to the parent directory.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_DIRECTORY
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
DNS$_DELETE_OBJECT
This request removes the specified object from the namespace.
This function code returns the following:
SS$_NORMAL
DNS$_INVALID_OBJECTNAME
Any condition listed in the section Condition Values Returned
You must have delete access to the object.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_OBJECTNAME
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
$DNS returns the following qualifying status:
DNS$V_DNSB_OUTLINKED
DNS$_DISALLOW_CH
This request prevents a directory from storing clearinghouse objects.
This request takes as input the name of a directory (DNS$_DIRECTORY).
You must have control access to the parent directory, and read or
control access to any child directories.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_DIRECTORY
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_WAIT
DNS$_ENUMERATE_ATTRIBUTES
This request returns a set of attribute names in DNS$_OUTATTRIBUTESET
that are associated with the directory, object, soft link, or
clearinghouse. Specify the entry type in the DNS$_LOOKINGFOR item code.
The function returns either DNS$K_SET or DNS$K_SINGLE along with the
set of attribute names.
To manipulate the attribute names returned by this call, you should use
the DNS$REMOVE_FIRST_SET_VALUE run-time library routine.
The DECdns clerk enumerates attributes in alphabetical order. A
return status of DNS$_MOREDATA implies that not all attributes have
been enumerated. You should make further calls, setting
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME to the last attribute in the set returned, until
the procedure returns SS$_NORMAL.
This function code returns the following:
SS$_NORMAL
DNS$_MOREDATA
DNS$_INVALID_ENTRYNAME
DNS$_INVALID_CONTEXTNAME
Any condition listed in the section Condition Values Returned
You must have read access to the directory, object, soft link, or
clearinghouse.
You must specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_ENTRY
DNS$_LOOKINGFOR
You must specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_OUTATTRIBUTESET
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME
DNS$_WAIT
You can specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME
$DNS returns the following qualifying status:
DNS$V_DNSB_OUTLINKED
DNS$_ENUMERATE_CHILDREN
This request takes as input a directory name with an optional simple
name that uses a wildcard. The DECdns clerk matches the input
against child directory entries in the specified directory.
The DECdns clerk returns a set of simple names of child
directories in the target directory that match the name with the
wildcard. A null set is returned when there is no match or the
directory has no child directories.
To manipulate the values returned by this call, you should use the
DNS$REMOVE_FIRST_SET_VALUE run-time routine. The value returned is a
simple name.
The clerk enumerates child directories in alphabetical order. If the
call returns DNS$_MOREDATA, not all child directories have been
enumerated and the client should make further calls, setting
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME to the last child directory in the set returned,
until the procedure returns SS$_NORMAL. Subsequent calls return the
child directories, starting with the directory specified in
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME and continuing in alphabetical order.
This function code returns the following:
SS$_NORMAL
DNS$_MOREDATA
DNS$_INVALID_DIRECTORYNAME
DNS$_INVALID_CONTEXTNAME
DNS$_INVALID_WILDCARDNAME
You must have read access to the parent directory.
You must specify the following input value item code:
DNS$_DIRECTORY
You must specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_OUTCHILDREN
You can specify the following input value item codes:
DNS$_CONF
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME
DNS$_WAIT
DNS$_WILDCARD
You can specify the following output value item code:
DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME
$DNS returns the following qualifying status:
DNS$V_DNSB_OUTLINKED
DNS$_ENUMERATE_OBJECTS
This request takes as input the directory name, a simple name that can
use a wildcard, and a class name that uses a wildcard. The DECdns
clerk matches these against objects in the directory. If a wildcard and
class filter are not specified, all objects in the directory are
returned.
The function returns (in DNS$_OUTOBJECTS) a set of simple names of
object entries in the directory that match the name with the wildcard.
The function also returns the class of the object entries, if specified
with DNS$_RETURNCLASS. If no object entries match the wildcard or the
directory contains no object entries, a null set is returned.
To manipulate the values returned by this call, you should use the
DNS$REMOVE_FIRST_SET_VALUE run-time routine. The value returned is a
simple name structure.
The clerk enumerates objects in alphabetical order. If the call returns
DNS$_MOREDATA, not all objects have been enumerated and the client
should make further calls, setting DNS$_CONTEXTVARNAME to the last
object in the set returned, until the procedure returns SS$_NORMAL. If
the class filter is specified, only those objects of the specified
classes are returned.
This function code returns the following:
SS$_NORMAL
DNS$_MOREDATA
DNS$_INVALID_DIRECTORYNAME
DNS$_INVALID_CONTEXTNAME
DNS$_INVALID_WILDCARDNAME
DNS$_INVALID_CLASSNAME