HP OpenVMS Systems Documentation |
OpenVMS System Manager's Manual
15.5.1.2 Specifying a Minimum Value with the MIN_ PrefixUse the MIN_ prefix if you do not want AUTOGEN to set a parameter below a specified value. MIN_ refers to the minimum value to which a parameter can be set by AUTOGEN. The following example sets the minimum value to 400,000:
15.5.1.3 Specifying a Maximum Value with the MAX_ PrefixUse the MAX_ prefix if you do not want AUTOGEN to set a parameter above a specified value. MAX_ refers to the maximum value to which a parameter can be set by AUTOGEN. The following example sets the maximum value to 400,000:
15.5.1.4 Specifying an Absolute ValueUse this method to specify a value for a parameter that AUTOGEN does not calculate. (Refer to the AUTOGEN section of the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for a table of the system parameters modified in AUTOGEN calculations.)
To specify an absolute parameter value, add an assignment statement in the following format to MODPARAMS.DAT:
For example, the following command assigns the node name BIGVAX to the SCSNODE parameter:
15.5.1.5 Defining the Number of VAXcluster Nodes (VAX Only)In a VAXcluster environment, use the NUM_NODES symbol to prevent temporary changes in VAXcluster membership from affecting AUTOGEN's calculation of VAXcluster-related parameter values. Define the NUM_NODES symbol in MODPARAMS.DAT to specify the number of nodes that are to run in the VAXcluster. AUTOGEN uses this value to set parameters that are affected by the number of VAXcluster nodes. For example, include the following line in MODPARAMS.DAT:
15.5.1.6 Defining the Number of Ethernet Adapters (VAX Only)In a VAXcluster environment, define the NUM_ETHERADAPT symbol in MODPARAMS.DAT to specify the total number of Ethernet adapters in the VAXcluster system. For example, include the following line in MODPARAMS.DAT:
15.5.1.7 Presetting Parameter Values Before Adding Memory (VAX Only)On VAX systems, if you plan to upgrade your system hardware by adding a large amount (512 MB or more) of memory, you might want to preset your system parameters to values appropriate for the additional memory. Presetting your system parameters minimizes the possibility of memory upgrade problems caused by inappropriate parameter values. Perform the following steps:
15.5.1.8 Overriding Parameters Related to DECnet
To override AUTOGEN's observations regarding the presence (or absence)
of DECnet, set the MODPARAMS.DAT parameter LOAD_DECNET_IMAGES to TRUE
(or FALSE). Controlling the setting is useful for sites that have no
synchronous network hardware but want to run asynchronous DECnet.
For the benefit of OpenVMS VAX systems with limited physical memory, AUTOGEN logs a warning message in its report if NPAGEDYN exceeds 10 percent of physical memory or if NPAGEVIR exceeds 33 percent of physical memory.
AUTOGEN also limits its own calculated value for NPAGEDYN to 20 percent
of physical memory, and limits NPAGEVIR to 50 percent of physical
memory. These calculated values are adequate for most workstations and
systems with 16 or fewer megabytes of physical memory. If your system
requires a larger value, you can override the AUTOGEN calculated values
by setting higher values in MODPARAMS.DAT.
On VAX systems, AUTOGEN feedback is useful only when a system has been running long enough to accurately reflect the system's normal work load. By default, AUTOGEN uses feedback if the data is older than 24 hours. On VAX systems, you can define the logical name AGEN$FEEDBACK_REQ_TIME to specify, in hours, a different minimum age required for feedback. AUTOGEN uses this value to determine whether the feedback is to be used. For example, you might define the logical name as follows, to indicate that AUTOGEN should use feedback if it is older than 19 hours:
To define this logical name each time the system starts up, add this
command to SYLOGICALS.COM.
You can include external parameter files in MODPARAMS.DAT. For example, you might want to set a system parameter to the same value on all nodes in a VAXcluster or an OpenVMS Cluster environment; you might also want to specify node-specific values for other system parameters. You could specify the cluster-common values in a separate cluster-common file and include this cluster-common file in the MODPARAMS.DAT file on each system in the cluster. To include a parameter file, place a command in the following format in MODPARAMS.DAT, or in any parameter file that is included in MODPARAMS.DAT:
To include a cluster-common parameter file named CLUSTERPARAMS.DAT, create a common parameter file with the following name: SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE]CLUSTERPARAMS.DAT Add the following line in the MODPARAMS.DAT file in the system-specific directory of each cluster:
15.5.4 Turning Off Logging of DCL StatementsThe contents of MODPARAMS.DAT are evaluated as DCL statements; you can make assignments to symbols with names that are not system parameters (for example, scratch variables or conditional assignments based on other values). Traditionally, every such assignment is logged in AGEN$PARAMS.REPORT, sometimes creating a large file with many logging statements that do not interest users.
You can prefix any assignments that you prefer not to log in
AGEN$PARAMS.REPORT with a dollar sign ($). When AUTOGEN encounters a
MODPARAMS.DAT record beginning with a dollar sign, it does not check
the list of known system parameters and does not log this record to
AGEN$PARAMS.REPORT.
Compaq recommends that you create a batch-oriented command procedure to automatically run AUTOGEN on a regular basis and send the resulting feedback reports to an appropriate Mail account. Example 15-2 provides a sample command procedure.
The command procedure in Example 15-2 runs two passes of AUTOGEN. On the first pass, AUTOGEN runs during peak workload times to collect data on realistic system work loads. This pass does not degrade system performance. On the second pass, AUTOGEN runs during off-peak hours to interpret the data collected in the first stage. The procedure sends the resulting report, contained in the file AGEN$PARAMS.REPORT, to the SYSTEM account. Review this report on a regular basis to see whether the load on the system has changed. Example 15-2 shows a sample command procedure. Use this procedure only as an example; create a similar command procedure as necessary to meet the needs of your configuration.
The commands in this procedure perform the following tasks:
15.6.1 Changing Parameter Values After Reviewing AUTOGEN ReportsIf the command procedure report described in Section 15.6 shows AUTOGEN's calculations are different from the current values, correct the tuning by executing AUTOGEN with one of the two following commands:
15.7 Managing System Parameters with SYSMAN
SYSMAN provides the ability to inspect and modify system parameters for an entire cluster or for any group of nodes, rather than just one system. The PARAMETERS commands available in SYSMAN duplicate the parameter functions of the System Generation utility (SYSGEN). You can use SYSMAN to manage system parameters as follows:
1Applies only to dynamic system parameters. SYSMAN provides the commands and functions shown in Table 15-3.
For more information about the temporary work area, see the next
section.
It helps to understand the different system parameter values explained in Section 15.1.1. Briefly, current values are stored in the default parameter file on disk. Active values are stored in memory and are used while the system is running. In addition to these values, SYSMAN writes a temporary copy into its own work area on disk. Figure 15-2 illustrates these different sets of values and how SYSMAN commands affect them. In this figure:
Figure 15-2 SYSMAN Temporary, Active, and Current Parameter Values 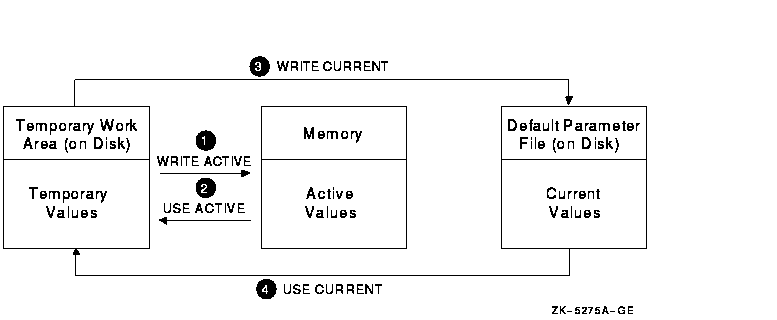
During a typical session, you can display and change values in the following sequence:
For a list of all the system parameters, refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Use the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS SHOW to display parameter values for all the nodes in a cluster.
15.7.3 Modifying a Parameter File with SYSMANUse the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS WRITE to write system parameter values and the name of the site-independent startup command procedure to your choice of parameter file or the current system parameter file on disk. The PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command sends a message to OPCOM to record the event, unless you have changed the system message format with the DCL command SET MESSAGE.
|