 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the mask
indicating the access mode granted in the system, owner, group, and
world fields:
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
ACE$V_READ
|
Read access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_WRITE
|
Write access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_EXECUTE
|
Execute access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_DELETE
|
Delete access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_CONTROL
|
Modification of the access field is granted.
|
You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit
set by using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V.
Subsystem ACE
The Subsystem ACE maintains protected subsystems. Its format is as
follows:
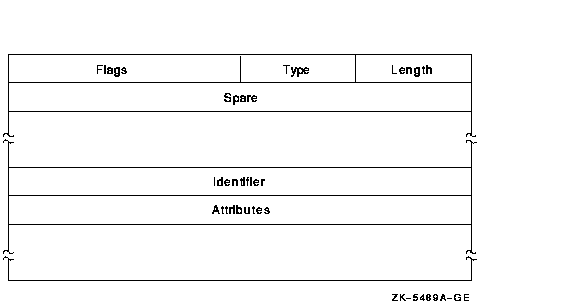
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name
for each:
| Field |
Symbol Name |
Description |
|
Length
|
ACE$B_SIZE
|
Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer.
|
|
Type
|
ACE$B_TYPE
|
Byte containing the type value ACE$C_SUBSYSTEM_IDS.
|
|
Flags
|
ACE$W_FLAGS
|
Word containing Subsystem ACE information and ACE type-independent
information.
|
|
Spare
|
ACE$L_SPARE1
|
Longword that is reserved for future use and must be 0.
|
|
Identifier/Attributes
|
ACE$Q_IMAGE_IDS
|
Longword identifier value and its associated longword attributes.
|
A Subsystem ACE can contain multiple identifier/attribute pairs. In
this case, the Subsystem ACE is an array of identifiers and attributes
starting at ACE$Q_IMAGE_IDS. Beginning at this offset, KGB$L_IDENTIFIER
and KGB$L_ATTRIBUTES are used to address each of the separate longwords.
The number of identifier/attribute pairs is computed by subtracting
ACE$C_LENGTH from ACE$W_SIZE and dividing by KGB$S_IDENTIFIER.
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is
independent of ACE type:
| Bit |
Meaning When Set |
|
ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE
|
This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file.
|
|
ACE$V_PROTECTED
|
This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must
delete this ACE explicitly.
|
The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the mask
indicating the access mode granted in the system, owner, group, and
world fields:
| Bit Position |
Meaning When Set |
|
ACE$V_READ
|
Read access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_WRITE
|
Write access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_EXECUTE
|
Execute access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_DELETE
|
Delete access is granted.
|
|
ACE$V_CONTROL
|
Modification of the access field is granted.
|
You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit
set by using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $CREATE_USER_PROFILE,
$FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY,
$GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT,
$REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_RESOURCE_DOMAIN, $SET_SECURITY
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The service completed successfully. The output string has overflowed
the buffer and has been truncated.
|
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The ACL entry or its descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the
string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the length word or
the string buffer cannot be written by the caller.
|
$FORMAT_AUDIT
Converts a security auditing event message from binary format to ASCII
text.
Format
SYS$FORMAT_AUDIT fmttyp ,audmsg ,[outlen] ,outbuf ,[width] ,[trmdsc]
,[routin] ,[fmtflg]
C Prototype
int sys$format_audit (unsigned int fmttyp, void *audmsg, unsigned short
int *outlen, void *outbuf, unsigned short int *width, void *trmdsc, int
(*routin)(__unknown_params), unsigned int fmtflg);
Arguments
fmttyp
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Format for the message. The fmttyp argument is a value
indicating whether the security audit message should be in brief
format, which is one line of information, or full format. The default
is full format. Refer to the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual for examples of formatted
output.
The following table defines the brief and full formats:
| Value |
Meaning |
|
NSA$C_FORMAT_STYLE_BRIEF
|
Use a brief format for the message.
|
|
NSA$C_FORMAT_STYLE_FULL
|
Use a full format for the message.
|
audmsg
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
byte stream (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Security auditing message to format. The audmsg
argument is the address of a buffer containing the message that
requires formatting.
outlen
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length of the formatted security audit message. The
outlen argument is the address of the word receiving
the final length of the ASCII message.
outbuf
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Buffer holding the formatted message. The outbuf
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to the buffer
receiving the message.
width
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Maximum width of the formatted message. The width
argument is the address of a word containing the line width value. The
default is 80 columns.
The width argument does not work consistently. In most
cases, if you specify both the width argument and the
full format style (NSA$C_FORMAT_STYLE_FULL), $FORMAT_AUDIT ignores the
width argument. The minimum width is 80 columns; lower
values do not limit the width to less than 80. If you specify a width
greater than 80 columns, most lines are not joined to use the full
width.
In most cases, you should avoid using the width
argument.
trmdsc
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Line termination characters used in a full format message. The
trmdsc argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to the line termination characters to insert within a line
segment whenever the width is reached.
routin
| OpenVMS usage: |
procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Routine that writes a formatted line to the output buffer. The
routin argument is the address of a routine called
each time a line segment is formatted. The argument passed to the
routine is the address of a character string descriptor for the line
segment.
When an application wants event messages in the brief format,
$FORMAT_AUDIT calls the routine twice to format the first event
message. The first time it is called, the routine passes a string
containing the column titles for the message. The second and subsequent
calls to the routine pass the formatted event message. By using this
routine argument, a caller can gain control at various points in the
processing of an audit event message.
fmtflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword (unsigned) |
| type: |
mask_longword |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Determines the formatting of certain kinds of audit messages. The
fmtflg argument is a mask specifying whether sensitive
information should be displayed or column titles built for messages in
brief format. For example, the operating system uses bit 0 to suppress
plain-text passwords from security alarm messages.
The following table describes the significant bits:
| Bit |
Value |
Description |
|
0
|
1
|
Do not format sensitive information.
|
|
|
0
|
Format sensitive information.
|
|
1
|
1
|
Build a column title for messages in brief format. (You must specify a
fmttyp of brief and a
routin argument.)
|
|
|
0
|
Do not build column titles.
|
Description
The Format Security Audit Event Message service converts a security
auditing event message from binary format to ASCII text and can filter
sensitive information. $FORMAT_AUDIT allows the caller to format a
message in a multiple-line format or a single-line format and tailor
the information for a display device of a specific width.
$FORMAT_AUDIT is intended for utilities that need to format the
security auditing event messages received from the audit server
listener mailbox or the system security audit log file.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
$FORMAT_AUDIT can cause a process to exceed its page-file quota
(PGFLQUOTA) if it has to format a long auditing event message. The
caller of $FORMAT_AUDIT can also receive quota violations from services
that $FORMAT_AUDIT uses, such as $IDTOASC, $FAO, and $GETMSG.
Related Services
$AUDIT_EVENT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_MSGNOTFND
|
The service completed successfully; however, the message code cannot be
found and a default message has been returned.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer length or
buffer cannot be written by the caller.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The item list contains an invalid identifier.
|
|
SS$_BUFFEROVF
|
The service completed successfully; however, the formatted output
string overflowed the output buffer and has been truncated.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights
database.
|
|
SS$_IVCHAN
|
The format of the specified identifier is not valid. This condition
value returned is not directly returned by $FORMAT_AUDIT. It is
indirectly returned when $FORMAT_AUDIT in turn calls another service,
such as an identifier translation or binary time translation service.
|
|
SS$_IVIDENT
|
The format of the specified identifier is invalid.
|
|
SS$_NOSUCHID
|
The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database.
This condition value returned is not directly returned by
$FORMAT_AUDIT. It is indirectly returned when $FORMAT_AUDIT in turn
calls another service, such as an identifier translation or binary time
translation service.
|
$FREE
The Free service unlocks all records that were previously locked for
the record stream.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY (Alpha and I64)
On Alpha and I64 systems, releases a user capability, indicating to
other processes that the resource is now available.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
Format
SYS$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY cap_num [,prev_num] [,flags]
C Prototype
int sys$free_user_capability (int *cap_num, struct _generic_64
*prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);
Arguments
cap_num
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Capability number to be released by the calling Kernel thread. This
number can range from 1 to 16. The cap_num argument is
the 32- or 64-bit address of the longword containing the user
capability number.
prev_mask
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The previous user capability reservation mask before execution of this
service call. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or
64-bit address of a quadword into which the service writes a quadword
bit mask specifying the previously reserved user capabilities.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_quadword |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference |
Options selected for the user capability reservation. The
flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit
corresponds to an option.
Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines.
The flags argument is constructed by performing a
logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
At this time, all bits are reserved to HP and must be 0.
Description
The Release a Reserved User Capability service releases a user
capability back to the global pool, making it available for subsequent
calls to $GET_USER_CAPABILITY. The state of all user capabilities in
the system are kept in SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS; this service clears
the bit position in that cell reflecting the capability number
specified in cap_num.
This service can also return the state of the global reservation bit
mask prior to a release operation.
Required Privileges
The caller must have both ALTPRI and WORLD privileges to call
$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY to release a user capability. No privileges are
required if $FREE_USER_CAPABILITY is called only to retrieve the
current user capability reservation mask.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$GET_USER_CAPABILITY, $CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more
arguments.
|
|
SS$_INSFARG
|
Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified, or no
operation was specified.
|
|
SS$_NOPRIV
|
Insufficient privilege for the attempted operation.
|
|
SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS
|
Too many arguments were presented to the system service.
|
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The requested user capability was already released.
|
$GET
The Get service retrieves a record from a file.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$GETDTI
Returns information about the state of transactions.
Format
SYS$GETDTI [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[log_id] ,[contxt]
,search ,itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$getdti (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
log_id [4], unsigned int *contxt, void *search, void *itmlst);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for these option
flags described in Table SYS-41. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-41 $GETDTI Option Flags
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_FULL_STATE
|
Indicates that the $GETDTI call for a specified TID is not to complete
until the ABORTED or COMMITTED state can be returned. Thus, if another
node or coordinating resource manager must be contacted and it is
currently unreachable, this service does not return until the node can
be contacted. Indicates on a wildcard search that only transactions
known to be in the ABORTED or COMMITTED states are to be returned.
|
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
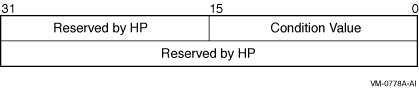
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of
the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same
access mode as that of the caller of the $GETDTI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
log_id
| OpenVMS usage: |
uid |
| type: |
octaword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The log id of the transaction manager that is coordinating the
transaction, returned as the log_id argument on a
$DECLARE_RM operation. The log_id argument verifies
that the recovery log returning transaction information is the same one
used to record transaction state information.
If you do not specify the same log id used by the transaction manager
to write transaction information, then $GETDTI will return an error.
If the log_id argument is specified as a zero UID,
then $GETDTI will use the current active log for this node. If the
specified transaction cannot be found in this log, then the returned
state will be aborted. The log identifier can only be specified as zero
when the DTI$_SEARCH_AS_NODE item is absent or results in a search that
specifies the local node. Note that the log_id
argument cannot be specified as a zero address.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to the
chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
contxt |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The address of a longword used to maintain a context between sequential
calls to $GETDTI. A call to $GETDTI will start a new search if the
context value is zero or continue the existing search if the context is
valid.
The search context is valid only after a successful call to $GETDTI and
is invalidated by a subsequent call to $GETDTI.
The context is also used as input to $SETDTI after a successful call to
$GETDTI. Calls to $SETDTI do not modify or invalidate the context.
search
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
descriptor list |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying how the search for transaction information is to
be bounded.
The search argument is the address of a list of item
descriptors, each of which describes a search item. The list of item
descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0. Each item descriptor in
the search item list acts as an input argument to $GETDTI and as such
is only required to be read only.
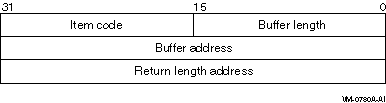
The following diagram shows the format of a single item descriptor:
The following table describes the search item
descriptor fields:
| Field |
Description |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of a buffer from which $GETDTI is to read the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code field of the
search item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small,
$GETDTI will return an error status.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the search
item that $GETDTI is to use. The $DTIDEF macro defines these codes.
Each item code is described in the Search Item Codes section below.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from
which $GETDTI reads the search information.
|
|
Return length address
|
This longword is not used in the search item list, because all search
items are read-only.
|
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
descriptor list |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying the transaction information that $GETDTI is to
return. The itmlst argument is the address of a list
of item descriptors, containing a single entry that describes an item
of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a
longword of 0. The item descriptor in the item list acts as an output
argument to $GETDTI and as such is required to be writeable in caller's
mode.
|


