 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
$SEARCH
The Search service scans a directory file and fills in various NAM
block fields. This service should be preceded by the Parse service, in
order to initialize the NAM block appropriately.
Refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual for additional information about this
service.
$SETAST
Enables or disables the delivery of asynchronous system traps (ASTs)
for the access mode from which the service call was issued.
Format
SYS$SETAST enbflg
C Prototype
int sys$setast (char enbflg);
Argument
enbflg
| OpenVMS usage: |
boolean |
| type: |
byte (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Value specifying whether ASTs are to be enabled. The
enbflg argument is a byte containing this value. The
value 1 enables AST delivery for the calling access mode; the value 0
disables AST delivery.
Description
The Set AST Enable service enables or disables the delivery of ASTs for
the access mode from which the service call was issued.
Required Access or Privileges
When an image is executing in user mode, ASTs are always enabled for
more privileged access modes. If ASTs are disabled for a more
privileged access mode, the operating system cannot deliver ASTs for
less privileged access modes until ASTs are enabled once again for the
more privileged access mode. Therefore, a process that has disabled
ASTs for a more privileged access mode must reenable ASTs for that mode
before returning to a less privileged access mode.
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$DCLAST, $SETPRA
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_WASCLR
|
The service completed successfully. AST delivery was previously
disabled for the calling access mode.
|
|
SS$_WASSET
|
The service completed successfully. AST delivery was previously enabled
for the calling access mode.
|
$SETCLUEVT
Establishes a request for notification when an OpenVMS Cluster
configuration event occurs.
Format
SYS$SETCLUEVT event ,astadr ,[astprm] ,[acmode] ,[handle]
C Prototype
int sys$setcluevt (unsigned int event, void
(*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int acmode, struct
_generic_64 *handle);
Arguments
event
| OpenVMS usage: |
event_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Event code indicating the type of cluster configuration event for which
an AST is to be delivered. The event argument is a
value indicating which type of event is of interest.
Each event type has a symbolic name. The $CLUEVTDEF macro defines the
following symbolic names:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
CLUEVT$C_ADD
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system.
|
|
CLUEVT$C_REMOVE
|
One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster
system.
|
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Notification AST routine to receive control after a change in OpenVMS
Cluster configuration occurs.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Optional AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine. The
astprm argument is a longword value containing the AST
parameter.
acmode
| OpenVMS usage: |
access_mode |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Optional access mode at which the configuration event AST is to
execute. The acmode argument is a longword containing
the access mode.
Each access mode has a symbolic name. The $PSLDEF macro defines the
following symbols for the four access modes:
| Symbol |
Access Mode |
|
PSL$C_KERNEL
|
Kernel
|
|
PSL$C_EXEC
|
Executive
|
|
PSL$C_SUPER
|
Supervisor
|
|
PSL$C_USER
|
User
|
The value of the access mode must not be more privileged than the
access mode of the caller.
handle
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Optional identifier to receive a value that uniquely identifies this
AST request. $SETCLUEVT sets this handle to a unique value so that it
can later be used to identify the request in the $CLRCLUEVT and
$TSTCLUEVT services.
Description
The Set Cluster Event service establishes a request for notification
when a cluster configuration event occurs. The service establishes only
one AST notification for a configuration event. To receive AST
notification for all cluster configuration events, the $SETCLUEVT
service must be reissued within the notification AST routine.
The service will verify that the input parameters specify a valid
request, allocate appropriate data structures to hold the request, and
enqueue the request for notification.
You must specify an event type and an AST address. You can specify an
AST parameter, the access mode, and an address into which to place the
handle of this request.
Errors will be returned in the following cases:
- If quotas are exceeded, an error identifying the specific quota
will be returned. It is important to note that this routine will return
an error and will not retry an attempt to get quota if quota is
exhausted on the first attempt. See the Condition Values Returned
section for types of errors that can be returned.
- If the astadr argument is omitted, SS$_BADPARAM
will be returned.
- If the event argument is omitted or incorrectly
specified, SS$_BADPARAM will be returned.
- If the access mode parameter is more privileged than the mode of
the caller, the mode of the caller will be used.
- If specified, the handle argument must be readable
and writable from the mode of the caller. SS$_ACCVIO is returned if
this is not the case.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$CLRCLUEVT, $TSTCLUEVT
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
SS$_ACCVIO
|
Unable to process parameters for improper use.
|
|
SS$_BADPARAM
|
The event was improperly specified.
|
|
SS$_EXASTLM
|
The process exceeded its quota for outstanding AST requests.
|
|
SS$_INSFMEM
|
The system dynamic memory is insufficient to complete the service.
|
$SETDDIR
Allows you to read and change the default directory string for the
process.
Format
SYS$SETDDIR [new-dir-addr] ,[length-addr] ,[cur-dir-addr]
C Prototype
int sys$setddir (void *newdiraddr, unsigned short int *lengthaddr, void
*curdiraddr);
Arguments
new-dir-addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
A descriptor of the new default directory. The
new-dir-addr argument is the address of the descriptor
that points to the buffer containing the new directory specification
that RMS will use to set the new process-default directory. If the
default directory is not to be changed, the value of the
new-dir-addr argument should be 0.
length-addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
A word that is to receive the length of the current default directory.
The length-addr argument is the address of the word
that will receive the length. If you do not want this value returned,
specify the value 0.
cur-dir-addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character-coded text string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
A descriptor of a buffer that is to receive the current default
directory string. The cur-dir-addr argument is the
address of the descriptor that points to the buffer area that is to
receive the current directory string.
Description
The Set Default Directory service allows you to read and change the
default directory string for the process. You should restore the
previous default directory string to its original state unless you want
the changed default directory string to last beyond the exit of your
image. The new directory name string is checked for correct syntax.
There is no predefined macro of the form $SETDDIR_G or $SETDDIR_S to
call this service.
On Alpha and I64 systems, the Set Default Directory service attempts to
replace the default directory string with a DID abbreviation if the
length of the resulting default directory exceeds 255 characters. If
this happens, then in addition to the normal syntax check, the entire
path to that specification, including the device, is verified and must
exist for the call to succeed.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR,
$SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
RMS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
RMS$_DIR
|
The directory name contains an error.
|
|
RMS$_IAL
|
The argument list is invalid.
|
$SETDFPROT
Allows you to read and write the default file protection for the
process.
Format
SYS$SETDFPROT [new-def-prot-addr] ,[cur-def-prot-addr]
C Prototype
int sys$setdfprot (unsigned short int *newdefprotaddr, unsigned short
int *curdefprotaddr);
Arguments
new-def-prot-addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
A word that specifies the new default file protection specification.
The new-def-prot-addr argument is the address of the
word that specifies the desired protection. If you do not want the
process-default file protection to be changed, specify the value 0.
cur-def-prot-addr
| OpenVMS usage: |
file_protection |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
A word that is to receive the current default file protection
specification. The cur-def-prot-addr argument is the
address of the word that receives the current process-default
protection. If you do not want the current default file protection,
specify the value 0.
Description
The Set Default File Protection service allows you to read and write
the default file protection for the process. You should restore the old
default file protection specification unless you want the changed
default to last beyond the exit of your image.
There is no predefined macro of the form $SETDEFPROT_G or $SETDEFPROT_S
to call this service.
Required Access or Privileges
None
Required Quota
None
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC,
$DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG,
$GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $GET_SECURITY, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO,
$QIOW, $SET_SECURITY, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
Condition Values Returned
|
RMS$_NORMAL
|
The service completed successfully.
|
|
RMS$_IAL
|
The argument list is invalid.
|
$SETDTI
The Set Distributed Transaction Information service removes resource
managers from transactions. It can also be used to modify transaction
states.
Format
SYS$SETDTI [efn], [flags], iosb, [astadr], [astprm], [contxt], func,
itmlst
C Prototype
int sys$setdti (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb
*iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int
*contxt, unsigned short int *func, void *itmlst);
Arguments
efn
| OpenVMS usage: |
ef_number |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If
this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.
flags
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags
argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an
option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for the option
flag described in Table SYS-52. All undefined bits must be 0. If this
argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-52 $SETDTI Operation Flag
| Flag Name |
Description |
|
DDTM$M_SYNC
|
Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH.
When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event
flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
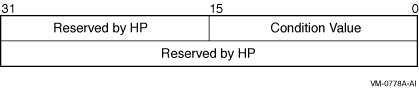
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is
returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned
section.
The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure entry mask |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The AST routine executed when the service completes, if SS$_NORMAL is
returned in R0. The astadr argument is the address of
the entry mask of this routine. The routine is executed in the same
access mode as that of the caller of the $SETDTI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
The AST parameter passed to the AST routine specified by the
astadr argument.
contxt
| OpenVMS usage: |
contxt |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
modify |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Context value obtained from a call to $GETDTI. It implicitly specifies
a node and transaction manager log identifier.
func
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Function modifier that specifies the set operation to be performed. The
func argument is a longword value containing the
function code.
Table SYS-53 lists the available function codes:
Table SYS-53 $SETDTI Function Codes
| Function |
Description |
|
DTI$K_DELETE_RM_NAME
|
Deletes the resource manager specified in
itmlst item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION,
DTI$T_PART_NAME from the transaction specified by
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID.
|
|
DTI$K_DELETE_TRANSACTION
|
Deletes the transaction specified by
itmlst item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID.
|
|
DTI$K_MODIFY STATE
|
Modifies the transaction specified by
itmlst item DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, DTI$T_TID,
using the transaction state specified in DTI$_B_STATE.
|
itmlst
| OpenVMS usage: |
item_list_3 |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Item list specifying the transaction information that $SETDTI is to
use. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of
item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The
list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0. Each item
descriptor in the item list acts as an input argument to $SETDTI and as
such is only required to be read only.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
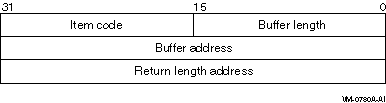
The following table describes the itmlst item
descriptor fields:
| Field |
Description |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of a buffer from which $SETDTI is to read the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length
is too small, $SETDTI will return an error status.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the search
item that $SETDTI is to use. The $DTIDEF macro defines these codes.
Each item code is described in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from
which $SETDTI reads the item information.
|
|
Return length address
|
This longword that is not used in the item list as all items are
read-only.
|
Item Codes
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION
When you specify DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION, $SETDTI uses the fields
in the following table to perform the $SETDTI call. Each function
requires a specific set of fields from the transaction record to
perform its operation. If one or more of these fields is not present or
valid, then the $SETDTI call will fail. The fields required by each
function are listed in the func argument description.
| Item |
Description |
|
DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN
|
A byte containing the length of the participant name field
DTI$T_PART_NAME.
|
|
DTI$B_STATE
|
A byte containing the state of the transaction. Two states are valid:
DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_NAME
|
A character field containing DTI$B_PART_NAME_LEN characters that
specifies a resource manager name.
To ensure smooth operation in a mixed-network environment, refer to
the chapter entitled Managing DECdtm Services in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, for
information on defining node names.
|
|
DTI$T_PART_LOG_ID
|
Reserved by HP.
|
|
DTI$T_TID
|
A 16-byte field containing the transaction identifier.
|
Description
The $SETDTI service can be used either to remove resource managers from
transactions, or to modify transaction states.
The $SETDTI service removes resource managers from a single transaction
or from all transactions when they no longer have any further interest
in a transaction. A call to $SETDTI typically follows a call to $GETDTI
that established a search context and returned the state of an
unresolved transaction.
When a resource manager is recovering from a system failure it will use
$GETDTI to return the state of all unresolved transactions. If the
resource manager can recover the transaction, then it needs to be
removed from the transaction in the same way it would have been removed
had it been able to call $ACK_EVENT with the forget status before the
system failure.
To remove a resource manager, $SETDTI uses the following fields from
the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor in the
itmlst argument:
- Transaction Identifier (TID)
- Resource Manager name
- Resource Manager log identifier
This information, along with the search context, is used to remove the
resource manager from the transaction. If the TID field is zero in the
DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor, then the resource manager
will be removed from all committed transactions in which it was
involved.
When searching for a resource manager, a comparison is made of the
leftmost bytes in the transaction manager's log records. This feature
enables multiple instances of resource manager classes to be removed
from the transaction manager's log after performing a recovery.
The $SETDTI service can also be used to modify transaction states. It
can perform two state transitions: from prepared to committed, or from
prepared to aborted. To modify transaction states, $SETDTI uses the
following fields from the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor
in the itmlst argument:
- Transaction Identifier (TID)
- Transaction state
To modify a transaction state, first modify the DTI$B_STATE field in
the DTI$_TRANSACTION_INFORMATION item descriptor to either
DTI$K_COMMITTED and DTI$K_ABORTED. Then specify the function code
DTI$K_MODIFY_TRANSACTION to instruct $SETDTI to perform the state
transition.
|

