 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
4.2 INPUT-OUTPUT Section
The INPUT-OUTPUT Section can contain two paragraphs:
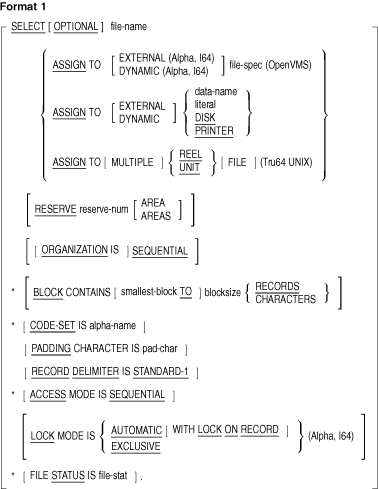
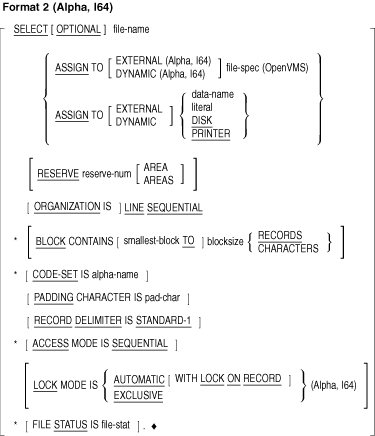
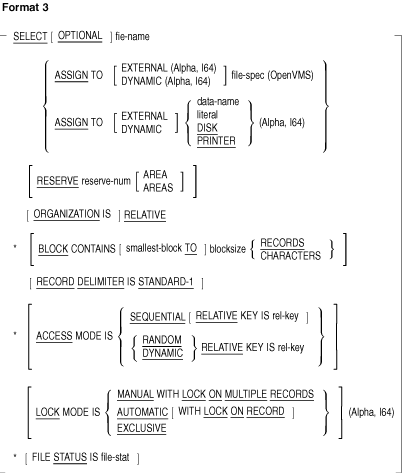
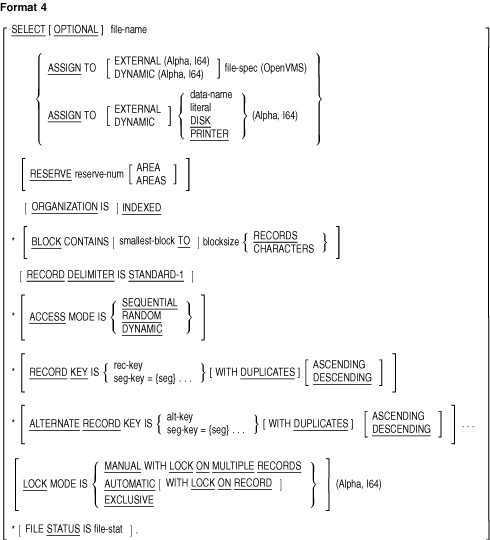
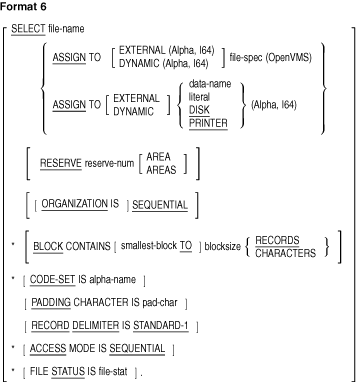
The FILE-CONTROL paragraph can contain the following clauses:
- ACCESS MODE clause
- ASSIGN clause
- BLOCK CONTAINS clause
- CODE-SET clause
- LOCK MODE clause (Alpha, I64)
- ORGANIZATION clause
- PADDING CHARACTER clause
- RECORD DELIMITER clause
- RESERVE clause
The I-O-CONTROL paragraph can contain the following clauses:
- APPLY clause
- SAME AREA clause
- RERUN clause
- MULTIPLE FILE clause
This section first describes the FILE-CONTROL paragraph and its
clauses, then it describes the I-O-CONTROL paragraph.
4.2.1 FILE_CONTROL
Function
The FILE-CONTROL paragraph declares the program's data
files.

Note
*Clauses marked with an asterisk (*) can be in either the SELECT clause
of the Environment Division or the file description entry of the Data
Division. They cannot be in both places for the same file.
|
file-name
is the internal name of a file connector.
Each file-name must have a file description (or Sort-Merge
File Description) entry in the Data Division. The same
file-name cannot appear more than once in the FILE-CONTROL
paragraph.
Syntax Rules
All Formats
- SELECT is optional in the FILE-CONTROL paragraph.
- If SELECT is used in the FILE-CONTROL paragraph, it must be the
first clause. Other clauses may follow it in any order.
- Each file described in the Data Division must be specified only
once in the FILE-CONTROL paragraph.
- On OpenVMS for every format, the first form of ASSIGN TO (marked
"OpenVMS ONLY") is available only on the OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS I64
operating systems and only if the default /STANDARD=NOXOPEN qualifier
is in effect.
The second form of ASSIGN TO is available on the
OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS I64 systems if the /STANDARD=XOPEN qualifier
is in effect. <>
Format 6---Report Files
- Each SELECT clause specifying a Report File must have a file
description entry containing a REPORT clause in the Data Division of
the same program.
General Rules
Formats 1, 2, 3, and 4---Sequential, Line Sequential, Relative, or Indexed Files
- You must specify an OPTIONAL phrase for files opened in INPUT, I-O,
or EXTEND mode that need not be present when the program runs.
- The rules for the OPEN statement describe the effects of the
OPTIONAL phrase.
- If the file connector referenced by file-name is an
external file connector, all file control entries in the run unit that
reference this file connector must have the following characteristics:
- The same specification for the OPTIONAL phrase
- A consistent full-file-name
- The same values for reserve-num, smallest-block,
and blocksize
- The same organization
Format 6---Report Files
- If the file connector referenced by file-name is an
external file connector, all file control entries in the run unit that
reference this file connector must have the following characteristics:
- A consistent full-file-name
- The same value for reserve-num
- Sequential organization
- The same CODE-SET clause
Additional References
Examples
The following examples assume that the VALUE OF ID clause is not in any
associated file description entry.
- Sequential file:
SELECT FILE-A
ASSIGN TO "INFILE".
|
This example refers to a file with sequential organization. The
word INFILE is equivalent to the nonnumeric literal "INFILE".
If there is no VALUE OF ID clause, the program accesses a file named
INFILE.DAT on OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems, or a file named INFILE on
Tru64 UNIX systems.
- Indexed file:
SELECT OPTIONAL FILE-A
ASSIGN TO "INFILE"
ORGANIZATION INDEXED.
|
In this example, the SELECT clause specifies that the indexed file
need not be present when the program opens it for INPUT, I-O, or EXTEND.
- Sort or merge file:
SELECT SORT-FILE
ASSIGN TO "SDFILE".
|
- Report file:
SELECT SUMMARY-REPORT
ASSIGN TO "OUTFIL"
FILE STATUS IS REPORT-ERRORS.
|
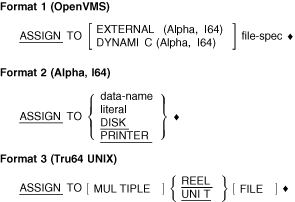
4.2.2 ASSIGN
Function
The ASSIGN clause associates a file with a partial or complete file
specification.
file-spec
on OpenVMS is either a nonnumeric literal or a COBOL word formed
according to the rules for user-defined names. It represents a partial
or complete file specification. It must conform to the rules for file
specifications as defined by RMS. <>
data-name
is the name of a COBOL data item that contains a partial or complete
file specification.
literal
is a nonnumeric literal containing a partial or complete file
specification.
DISK (Alpha, I64)
uses the file specification declared in the optional VALUE OF ID clause
as the file name. If the VALUE OF ID clause is not present, file-name-1
is used as the file name in the current directory.
PRINTER (Alpha, I64)
creates a print file as if the PRINT-CONTROL phrase of the APPLY clause
were specified in the I-O CONTROL paragraph. A print file should
contain only printable characters and line and page advancing
information written using the ADVANCING clause of the WRITE verb.
REEL or UNIT (Tru64 UNIX)
creates the file on a magnetic tape using the ANSI standard format as
defined by American National Standard X3.27-1978 (Level 3), Magnetic
Tape Labels and File Structure for Information Interchange. <>
Syntax Rules
- data-name cannot be DISK or PRINTER.
- EXTERNAL and DYNAMIC are allowed for syntax compatibility with
other COBOL vendors. They are treated as documentation only.
- Format 1 is available only on the OpenVMS operating system and only
if the default /STANDARD=NOXOPEN qualifier is in effect. <>
Format 2 is available on Alpha and I64 if the /STANDARD=XOPEN
qualifier is in effect. <>
On Tru64 UNIX, format 2 is the
default. <>
General Rules
- If there is no VALUE OF ID clause in the file description entry,
or that clause contains no file specification, the file specification
in the ASSIGN clause is the file specification.
- If there is a file specification in an associated VALUE OF ID
clause, the ASSIGN clause contains the default file specification. File
specification components in the VALUE OF ID clause override those in
the ASSIGN clause.
- On OpenVMS, if file-spec is not a literal, the compiler:
- Translates hyphens in the COBOL word to underline characters
- Treats the word as if it were enclosed in quotation marks
- file-spec may contain a logical name. <>
-
If you specify ASSIGN TO unquoted string, you need not specify this
name in the WORKING-STORAGE section. For example:
This assignment would use "TEST1.DAT" on OpenVMS Alpha and I64.
<>
On Tru64 UNIX systems, you would specify:
or:
ASSIGN TO TEST1
...
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 TEST1 PIC X(9) VALUE IS "TEST1.DAT".
|
- The file specification derived from one or both of the ASSIGN and
VALUE OF ID clauses might refer to an environment variable.
- On Tru64 UNIX systems, "" is not a valid file specification.
<>
- On all platforms, file-spec must conform to the rules of
the operating system where the run-time I-O occurs.
For indexed
files, file-spec must conform to the rules of the ISAM package
being used. Some older versions of ISAM on Tru64 UNIX may have a
10-character maximum for file-spec length. <>
Format 3
For files assigned to magnetic tape using ASSIGN TO REEL clause:
- If the length of the file name exceeds 17 characters, it is
truncated. Any lowercase characters in a file name are uppercased and
others outside the ANSI-"a" character set are converted to 'Z'.
An
"a" character is one of the set of the digits 0,1..9, the uppercase
letters A,B..Z, and the following special characters:
SP ! " % & ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = > ?
- Magnetic tape files must be ORGANIZATION SEQUENTIAL and either
fixed or variable length record format.
|






