 |
HP OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
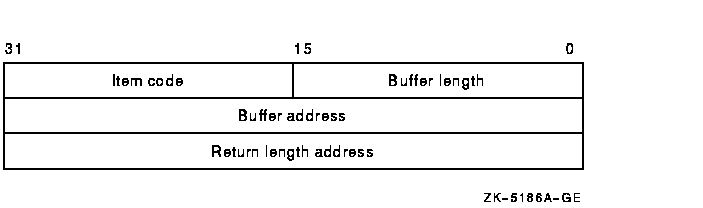
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
Buffer length
|
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length
is too small, $GETJPI truncates the data.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of
information that $GETJPI is to return. The $JPIDEF macro defines these
codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of the buffer in
which $GETJPI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of a word in
which $GETJPI writes the length (in bytes) of the information it
actually returned.
|
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item
descriptor:
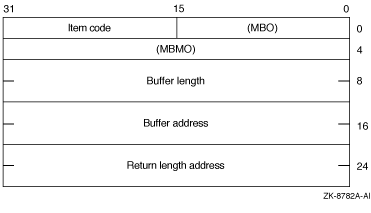
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item
list entries:
| Descriptor Field |
Definition |
|
MBO
|
The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Item code
|
A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the
buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by
the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes
section.
|
|
MBMO
|
The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to
distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries.
|
|
Buffer length
|
A quadword containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. The
length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the
item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length
is too small, $GETJPI truncates the data.
|
|
Buffer address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of the buffer in
which $GETJPI is to write the information.
|
|
Return length address
|
A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of a word in
which $GETJPI writes the length (in bytes) of the information it
actually returned.
|
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: |
io_status_block |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The
iosb argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and I64 systems) of the quadword
I/O status block.
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETJPI sets the
quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a
condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword
is reserved for future use.
Though this argument is optional, HP strongly recommends that you
specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the
service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be
sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service
completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of
the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned
in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of
the call to the $GETJPI service. The condition value returned in R0
gives you information about the success or failure of the service call
itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you
information about the success or failure of the service operation.
Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to
$GETJPI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and
the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: |
ast_procedure |
| type: |
procedure value |
| access: |
call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: |
by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64) |
| mechanism: |
by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETJPI completes. The
astadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems)
or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and I64 systems) of this routine.
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the
same access mode as the caller of the $GETJPI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: |
user_arg |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the
astadr argument. The astprm argument
is the longword parameter.
Item Codes
JPI$_ACCOUNT
Returns the account name of the process, which is an 8-byte string,
filled with trailing blanks if necessary.
JPI$_APTCNT
Returns, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64
systems), the active page table count of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_ASTACT
Returns the names of the access modes having active ASTs. This
information is returned in a longword bit vector. When bit 0 is set, an
active kernel mode AST exists; bit 1, an executive mode AST; bit 2, a
supervisor mode AST; and bit 3, a user mode AST.
JPI$_ASTCNT
Returns a count of the remaining AST quota, which is a longword integer
value.
JPI$_ASTEN
Returns a longword bit vector that indicates for each access mode
whether ASTs are enabled for that mode. When bit 0 is set, Kernel mode
has ASTs enabled; bit 1, Executive mode; bit 2, Supervisor mode; and
bit 3, User mode.
JPI$_ASTLM
Returns the AST limit quota of the process, which is a longword integer
value.
JPI$_AUTHPRI
Returns the authorized base priority of the process, which is a
longword integer value. The authorized base priority is the highest
priority a process without ALTPRI privilege can attain by means of the
$SETPRI service.
JPI$_AUTHPRIV
Returns the privileges that the process is authorized to enable. These
privileges are returned in a quadword privilege mask and are defined by
the $PRVDEF macro.
JPI$_BIOCNT
Returns a count of the remaining buffered I/O quota, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_BIOLM
Returns the buffered I/O limit quota of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_BUFIO
Returns a count of the buffered I/O operations of the process, which is
a longword integer value.
JPI$_BYTCNT
Returns the remaining buffered I/O byte count quota of the process,
which is a longword integer value.
JPI$_BYTLM
Returns the buffered I/O byte count limit quota of the process, which
is a longword integer value.
JPI$_CASE_LOOKUP_PERM
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns information about the file name
lookup case sensitivity of a specified process. This value is set for
the life of the process unless the style is set again. Values are 0
(PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND) and 1 (PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE).
For additional information, see the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications.
JPI$_CASE_LOOKUP_TEMP
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns information about the file name
lookup case sensitivity of a specified process. This value is set only
for the life of the image. Values are 0 (PPROP$K_CASE_BLIND) and 1
(PPROP$K_CASE_SENSITIVE).
For additional information, see the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications.
JPI$_CHAIN
Processes another item list immediately after processing the current
one. The buffer address field in the item descriptor specifies the
address of the next item list to be processed. You must specify the
JPI$_CHAIN item code last in the item list.
You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
JPI$_CLASSIFICATION
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns, as a 20-byte padded string, the
current MAC classification stored in the PSB.
JPI$_CLINAME
Returns the name of the command language interpreter that the process
is currently using. Because the CLI name can include up to 39
characters, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should
specify 39 bytes.
JPI$_CPU_ID
Returns, as a longword integer, the ID of the CPU on which the process
is running or on which it last ran. This value is returned as --1 if
the system is not a multiprocessor.
JPI$_CPULIM
Returns the CPU time limit of the process, which is a longword integer
value.
JPI$_CPUTIM
Returns the process's accumulated CPU time in 10-millisecond ticks,
which is a longword integer value.
JPI$_CREPRC_FLAGS
Returns the flags specified by the stsflg argument in
the $CREPRC call that created the process. The flags are returned as a
longword bit vector.
JPI$_CURPRIV
Returns the current privileges of the process. These privileges are
returned in a quadword privilege mask and are defined by the $PRVDEF
macro.
JPI$_CURRENT_AFFINITY_MASK
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the current explicit affinity mask
for the associated kernel thread.
JPI$_CURRENT_USERCAP_MASK
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the current user capability mask for
the associated kernel thread.
JPI$_DEADLOCK_WAIT
Returns the per-process deadlock wait ticks. This value is in 100-nsec
units.
JPI$_DFMBC
Returns the default multibuffer count for a process as a longword
integer value.
JPI$_DFPFC
Returns the default page fault cluster size of the process, which is a
longword integer value measured in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets
(on Alpha and I64 systems).
JPI$_DFWSCNT
Returns, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64
systems), the default working set size of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_DIOCNT
Returns the remaining direct I/O quota of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_DIOLM
Returns the direct I/O quota limit of the process, which is a longword
integer value.
JPI$_DIRIO
Returns a count of the direct I/O operations of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_EFCS
Returns the state of the process's local event flags 0 through 31 as a
longword bit vector.
JPI$_EFCU
Returns the state of the process's local event flags 32 through 63 as a
longword bit vector.
JPI$_EFWM
Returns the event flag wait mask of the process, which is a longword
bit vector.
JPI$_ENQCNT
Returns the remaining lock request quota of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_ENQLM
Returns the lock request quota of the process, which is a longword
integer value.
JPI$_EXCVEC
Returns the address of a list of exception vectors for the process.
Each exception vector in the list is a longword. There are eight
vectors in the list: these are, in order, a primary and a secondary
vector for kernel mode access, for executive mode access, for
supervisor mode access, and for user mode access.
The $GETJPI service cannot return this information for any process
other than the calling process; if you specify this item code and the
process is not the calling process, $GETJPI returns the value 0 in the
buffer.
JPI$_FAST_VP_SWITCH
On VAX systems, returns an unsigned longword containing the number of
times this process has issued a vector instruction that resulted in an
inactive vector processor being enabled without the expense of a vector
context switch. In other words, this count reflects those instances
where the process has reenabled a vector processor on which the
process's vector context has remained intact.
JPI$_FILCNT
Returns the remaining open file quota of the process, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_FILLM
Returns the open file limit quota of the process, which is a longword
value.
JPI$_FINALEXC
Returns the address of a list of final exception vectors for the
process. Each exception vector in the list is a longword. There are
four vectors in the list, one for each access mode, in this order:
kernel, executive, supervisor, and user.
The $GETJPI service cannot return this information for any process
other than the calling process; if you specify this item code and the
process is not the calling process, $GETJPI returns the value 0 in the
buffer.
JPI$_FREP0VA
Returns the address of the first free page at the end of the program
region (P0 space) of the process.
JPI$_FREP1VA
Returns the address of the first free page at the end of the control
region (P1 space) of the process.
JPI$_FREPTECNT
Returns the number of pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and
I64 systems) that the process has available for virtual memory
expansion.
On VAX systems, the value returned is a longword integer. On Alpha and
I64 systems, the value returned requires a quadword of storage. If the
buffer size supplied is not equal to 8 bytes, and the number of free
pagelets exceeds the maximum value that can be represented in a
longword, $GETJPI returns the largest positive 32-bit integer:
2147483647.
JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS
The JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS item code, which is specified in the
$GETJPI item list, provides additional control over $GETJPI; therefore,
$GETJPI might be unable to retrieve all the data requested in an item
list because JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS requests that $GETJPI not
perform certain actions that might be necessary to collect the data.
For example, a $GETJPI control flag might instruct the calling program
not to retrieve a process that has been swapped out of the balance set.
If $GETJPI is unable to retrieve any data item because of the
restrictions imposed by the control flags, it returns the data length
as 0. To verify that $GETJPI received a data item, examine the data
length to be sure that it is not 0. To ensure the verification, be sure
to specify the return length for each item in the $GETJPI item list
when any of the JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS flags is used.
Unlike other $GETJPI item codes, the JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS item is
an input item. The item list entry should specify a longword buffer.
The desired control flags should be set in this buffer.
Because the JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS item code tells $GETJPI how to
interpret the item list, it must be the first entry in the $GETJPI item
list. The error code SS$_BADPARAM is returned if it is not the first
item in the list.
The JPI$_GETJPI_CONTROL_FLAGS item code includes the following flags:
| Flag |
Description |
|
JPI$M_NO_TARGET_INSWAP
|
Does not retrieve a process that has been swapped out of the balance
set. This control flag is used to avoid adding the load of swapping
processes into a system. By using this control flag and requesting
information from a process that has been swapped out, the following
occurs:
- Any data stored in the virtual address space of the process is not
accessible.
- Any data stored in the process header (PHD) might not be accessible.
- Any data stored in resident data structures, such as the process
control block (PCB) or the job information block (JIB), is accessible.
You must examine the return length of an item to verify that the
item was retrieved.
|
|
JPI$M_NO_TARGET_AST
|
Does not deliver a kernel mode AST to the target process. This control
flag is used to avoid executing a target process to retrieve
information. By using this control flag and not delivering an AST to a
target process, the following occurs:
- Any data stored in the virtual address space of the process is not
accessible.
- Any data stored in system data structures, such as the process
header (PHD), the process control block (PCB), or the job information
block (JIB), is accessible.
You must examine the return length of an item to verify that the
item was retrieved.
The use of this control flag also implies that $GETJPI does not
swap in a process, because $GETJPI would only bring a process into
memory to deliver an AST to that process.
|
|
JPI$M_IGNORE_TARGET_STATUS
|
Attempts to retrieve as much information as possible, even though the
process might be suspended or is being deleted. This control flag is
used to retrieve all possible information from a process.
|
|
JPI$M_THREAD
|
Sets the wildcard mode to return information on all of the process's
kernel threads beginning with the initial kernel thread.
|
JPI$_GPGCNT
Returns, in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets (on Alpha and I64
systems), the process's global page count in the working set, which is
a longword integer value.
JPI$_GRP
Returns, as a longword integer value, the group number of the process's
UIC.
JPI$_HOME_RAD
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the home resource affinity domain
(RAD).
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, see the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
JPI$_IMAGECOUNT
Returns, as a longword integer value, the number of images that have
been run down for the process.
JPI$_IMAGE_AUTHPRIV
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the authorized privilege mask of the
installed image.
These privileges are returned in a quadword privilege mask and are
defined by the $PRVDEF macro.
JPI$_IMAGE_PERMPRIV
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the permanent (default) privilege
mask of the installed image.
These privileges are returned in a quadword privilege mask and are
defined by the $PRVDEF macro.
JPI$_IMAGE_RIGHTS
Returns the binary content of the image rights list as an array of
quadword identifiers. Each entry consists of a longword identifier
value and longword identifier attributes, as shown in Table SYS-43.
The image rights list is a set of identifiers associated with a
protected subsystem image. When a process runs a protected subsystem,
the subsystem rights are automatically added to the process's image
rights list. These identifiers are subsequently removed during image
rundown. Allocate a buffer that is sufficient to hold the image rights
list, because $GETJPI returns only as much of the list as will fit in
the buffer.
Table SYS-43 Attributes of an Identifier
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
KGB$M_DYNAMIC
|
Identifier can be enabled or disabled.
|
|
+KGB$M_NOACCESS
|
Rights of the identifier are null and void.
|
|
KGB$M_RESOURCE
|
Resources can be charged to the identifier.
|
|
+KGB$M_SUBSYSTEM
|
Identifier can be used to create protected subsystems.
|
+VAX specific
JPI$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the working (active) privilege mask
of the installed image.
These privileges are returned in a quadword privilege mask and are
defined by the $PRVDEF macro.
JPI$_IMAGNAME
Returns, as a character string, the directory specification and the
image file name.
JPI$_IMAGPRIV
Returns a quadword mask of the privileges with which the current image
was installed. If the current image was not installed, $GETJPI returns
the value 0 in the buffer.
JPI$_INITIAL_THREAD_PID
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the PID of the initial thread for the
target process. The PID is a longword hexadecimal value.
JPI$_INSTALL_RIGHTS
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the binary content of the install
rights list as an array of quadword identifiers. Each entry consists of
a longword identifier value and longword identifier attributes, as
shown in Table SYS-43. The install rights list is a set of identifiers
associated with an installed image.
JPI$_INSTALL_RIGHTS_SIZE
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns a longword integer containing the
number of bytes needed to store the install rights.
JPI$_JOBPRCCNT
Returns the total number of subprocesses owned by the job, which is a
longword integer value.
JPI$_JOBTYPE
Returns the execution mode of the process at the root of the job tree,
which is a longword integer value. The symbolic name and value for each
execution mode are listed in the following table. The $JPIDEF macro
defines the symbolic names.
| Mode Name |
Value |
|
JPI$K_DETACHED
|
0
|
|
JPI$K_NETWORK
|
1
|
|
JPI$K_BATCH
|
2
|
|
JPI$K_LOCAL
|
3
|
|
JPI$K_DIALUP
|
4
|
|
JPI$K_REMOTE
|
5
|
JPI$_KT_COUNT
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the current count of kernel threads
for the target process, which is a longword integer value.
JPI$_LAST_LOGIN_I
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last
successful interactive login prior to the current session. It returns a
quadword of 0 when processes have not executed the LOGINOUT image.
JPI$_LAST_LOGIN_N
Returns, as a quadword absolute time value, the date of the last
successful noninteractive login prior to the current session. It
returns a quadword of 0 when processes have not executed the LOGINOUT
image.
JPI$_LOGIN_FAILURES
Returns the number of login failures that occurred prior to the current
session. It returns a longword of 0 when processes have not executed
the LOGINOUT image.
JPI$_LOGIN_FLAGS
Returns a longword bit mask containing information related to the login
sequence. It returns a longword of 0 when processes have not executed
the LOGINOUT image. The following bits are defined:
| Symbolic Name |
Description |
|
JPI$M_NEW_MAIL_AT_LOGIN
|
User had new mail messages waiting at login.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD_CHANGED
|
User changed the primary password during login.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD_EXPIRED
|
User's primary password expired during login.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD_WARNING
|
System gave the user a warning at login that the account's primary
password would expire within 5 days.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD2_CHANGED
|
Account's secondary password was changed during login.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD2_EXPIRED
|
Account's secondary password expired during login.
|
|
JPI$M_PASSWORD2_WARNING
|
System gave the user a warning at login that the account's secondary
password would expire within 5 days.
|
JPI$_LOGINTIM
Returns the time at which the process was created, which is a standard
64-bit absolute time.
JPI$_MASTER_PID
Returns the process identification (PID) of the master process in the
job. The PID is a longword hexadecimal value.
JPI$_MAXDETACH
Returns the maximum number of detached processes allowed for the user
who owns the process specified in the call to $GETJPI. This limit is
set in the UAF record of the user. The number is returned as a word
decimal value. A value of 0 means that there is no limit on the number
of detached processes for that user name.
JPI$_MAXJOBS
Returns the maximum number of active processes allowed for the user who
owns the process specified in the call to $GETJPI. This limit is set in
the UAF record of the user. The number is returned as a word decimal
value. A value of 0 means that there is no limit on the number of
active processes for that user name.
JPI$_MEM
Returns the member number of the process's UIC, which is a longword
integer value.
JPI$_MODE
Returns the mode of the process, which is a longword integer value. The
symbolic name and value for each mode are listed in the following
table. The $JPIDEF macro defines the symbolic names.
| Mode Name |
Value |
|
JPI$K_OTHER
|
0
|
|
JPI$K_NETWORK
|
1
|
|
JPI$K_BATCH
|
2
|
|
JPI$K_INTERACTIVE
|
3
|
JPI$_MSGMASK
Returns the default message mask of the process, which is a longword
bit mask.
JPI$_MULTITHREAD
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the maximum kernel thread count
allowed for the target process, which is a longword integer value.
JPI$_NODENAME
Returns, as a character string, the name of the OpenVMS Cluster node on
which the process is running.
JPI$_NODE_CSID
Returns, as a longword hexadecimal integer, the cluster ID of the
OpenVMS Cluster node on which the process is running.
JPI$_NODE_VERSION
Returns, as a character string, the operating system version number of
the OpenVMS Cluster node on which the process is running.
JPI$_OWNER
Returns the process identification (PID) of the process that created
the specified process. The PID is a longword hexadecimal value.
JPI$_PAGEFLTS
Returns the total number of page faults incurred by the process. This
is a longword integer value.
JPI$_PAGFILCNT
Returns the remaining paging file quota of the process, which is a
longword integer value, measured in pages (on VAX systems) or pagelets
(on Alpha and I64 systems).
JPI$_PAGFILLOC
Returns the current paging file assignment of the process. The fourth
byte of the returned longword value is the index of the system page
file to which the process is currently assigned.
JPI$_PARSE_STYLE_IMAGE
On Alpha and I64 systems, set by $SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW, and can be
either PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL or PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED (located in
PPROPDEF). The return length is one byte.
JPI$_PARSE_STYLE_PERM
On Alpha and I64 systems, set by $SET_PROCESS_PROPERTIESW, and can be
either PARSE_STYLE$C_TRADITIONAL or PARSE_STYLE$C_EXTENDED (located in
PPROPDEF). The return length is one byte.
JPI$_PERMANENT_AFFINITY_MASK
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the permanent explicit affinity mask
for the associated kernel thread.
JPI$_PERMANENT_USERCAP_MASK
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the permanent user capability mask
for the associated kernel thread.
JPI$_PERSONA_AUTHPRIV
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns the authorized privilege mask of the
persona.
|

