 |
HP COBOL
Reference Manual
Additional References
5.3.51 UNDERLINE
Function
The UNDERLINE clause specifies that each character of the field is
underlined when it is displayed on the screen.

Syntax Rule
The UNDERLINE clause may be specified only for elementary screen items.
5.3.52 USAGE
Function
The USAGE clause specifies the internal format of a data item or screen
item.
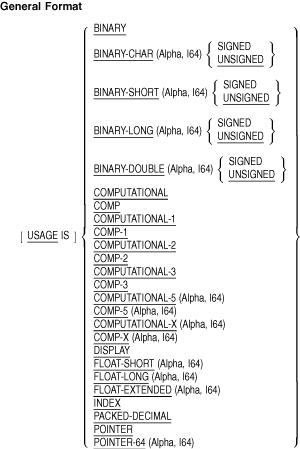
Syntax Rules
- BINARY is a synonym for COMPUTATIONAL and COMP.
On Alpha and
I64 systems, except for restrictions on the PICTURE clause,
COMPUTATIONAL-5 and COMPUTATIONAL-X are synonyms for COMPUTATIONAL and
COMP. <>
- COMP is an abbreviation for COMPUTATIONAL.
- COMP-1 is an abbreviation for COMPUTATIONAL-1.
- COMP-2 is an abbreviation for COMPUTATIONAL-2.
- COMP-3 is an abbreviation for COMPUTATIONAL-3.
- PACKED-DECIMAL is a synonym for COMPUTATIONAL-3 and COMP-3.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, COMP-5 is an abbreviation for
COMPUTATIONAL-5.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, COMP-X is an abbreviation for
COMPUTATIONAL-X.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, FLOAT-SHORT is a synonym for
COMPUTATIONAL-1.
- On Alpha and I64 systems, FLOAT-LONG and FLOAT-EXTENDED are
synonyms for COMPUTATIONAL-2. <>
- You can use the USAGE clause in any data description entry with a
level-number other than 66 or 88.
- If the USAGE clause is in the data description for a group item, it
can also be in data description entries for subordinate elementary and
group items. However, the usage of a subordinate item must be the same
as that in the group item data description entry.
- The PICTURE character-string of a COMP or COMP-3 item can contain
only the following symbols:
- On Alpha and I64 systems, the PICTURE character-string of a COMP-5
or COMP-X item can contain only the following symbols:
- 9
- S
- X (but not in combination with 9 or S) <>
- An index data item reference can appear in only:
- A SEARCH or SET statement
- A relation condition
- The USING phrase of the Procedure Division header
- The USING phrase of the CALL statement
- A report description entry or a screen description entry can only
specify USAGE IS DISPLAY.
- The data description entry for a USAGE IS INDEX data item cannot
contain any of the following clauses:
- BLANK WHEN ZERO
- JUSTIFIED
- PICTURE
- VALUE IS
- An elementary item with the USAGE IS INDEX clause cannot be a
conditional variable; that is, the elementary item's value cannot be
specified by level 88 items.
- The data description entry of a BINARY-CHAR, BINARY-SHORT,
BINARY-LONG, BINARY-DOUBLE, COMP-1, COMP-2, POINTER, or POINTER-64 item
cannot have a PICTURE clause. However, they are numeric and signed.
- The subject of a data description entry containing the USAGE IS
POINTER clause must not include any of the following clauses:
- BLANK WHEN ZERO
- JUSTIFIED
- PICTURE
General Rules
- You can specify the USAGE clause in the data description entry for
a group item. In this case, it applies to each elementary item in the
group. However, you cannot reference the group item in any operations
that do not permit alphanumeric operands. See rules 4 and 8 for more
information.
- The USAGE clause specifies the representation of an elementary data
item in storage. It does not affect the way that the program uses the
item. However, the rules for some Procedure Division statements
restrict the USAGE clause of statement operands.
- A BINARY-CHAR, BINARY-SHORT, BINARY-LONG, BINARY-DOUBLE, COMP,
COMP-1, COMP-2, COMP-3, COMP-5, COMP-X, FLOAT-SHORT, FLOAT-LONG, or
FLOAT-EXTENDED item can represent a value used in computations. The
PICTURE clauses for COMP and COMP-3 items must be numeric. The PICTURE
clauses for COMP-5 and COMP-X items may be numeric or X.
- A POINTER data item can represent an address value used in
computations. The compiler internally treats this item as a binary
integer. References to a POINTER item are allowed in the same context
as references to a COMP integer.
- If the data description entry for a group item specifies
BINARY-CHAR, BINARY-SHORT, BINARY-LONG, BINARY-DOUBLE, COMP, COMP-1,
COMP-2, COMP-3, COMP-5, COMP-X, FLOAT-SHORT, FLOAT-LONG,
FLOAT-EXTENDED, POINTER, or POINTER-64 usage, the usage applies to
elementary items in the group. It does not apply to the group itself;
and the program cannot use the group item in computations.
- The USAGE IS DISPLAY clause specifies that the data item is in
Standard Data Format.
- If no USAGE clause applies to an elementary item, its usage is
DISPLAY.
- If the USAGE IS INDEX clause applies to an elementary item, the
elementary item is called an index data item.
It contains a value that must correspond to an occurrence number of a
table element.
- If the data description entry for a group item specifies USAGE IS
INDEX, all elementary items in the group are index data items. However,
the group itself is not an index data item.
- When a MOVE or input-output statement refers to a group that
contains an index data item, the index data item is not converted to
another format during the operation. Conversion will occur when the
CONVERSION option is specified on ACCEPT or DISPLAY.
- The USAGE IS POINTER clause can be used only in a File,
Working-Storage, or Linkage Section data description entry.
- On OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems, the USAGE IS POINTER-64 clause
is provided for limited use in interfacing with applications in
languages requiring a 64-bit pointer. See Technical Notes. <>
Technical Notes
- The way a data item is represented in the Data Division of a
COBOL program determines whether it will be stored as an
integer, floating-point, packed decimal, display numeric, or character
string (text) data type. Tables 5-12 and 5-13 show
the following:
- COBOL data description entries and their corresponding data types
- The allocated storage in bytes for each entry; allocated storage is
the same on Tru64 UNIX and OpenVMS Alpha and I64 (except for POINTER)
Table 5-12 gives the corresponding data types for unscaled data
items, and Table 5-13 gives the data types for scaled data items.
For example, a data item described as PIC S9(4) USAGE IS DISPLAY
SIGN IS TRAILING is stored in 4 bytes of storage as a right overpunch
value.
Note
The default USAGE for a data item is DISPLAY. Therefore, you do not
need to specify the USAGE clause for display numeric, alphabetic, and
alphanumeric data items.
|
Table 5-12 Unscaled Data Items, Allocated Storage, and Corresponding Data Types
PICTURE
Clause |
USAGE Clause |
SIGN Clause |
Allocated Storage
in Bytes |
Standard
Data Type |
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n
|
Right (trailing) overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
TRAILING
|
n
|
Right (trailing) overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
LEADING
|
n
|
Left (leading) overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
TRAILING
SEPARATE
|
n+1
|
Right (trailing) separate
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
LEADING
SEPARATE
|
n+1
|
Left (leading) separate
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n
|
Unsigned numeric
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[n <= 4]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[5 <= n <= 9]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[10 <= n <= 18]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[19 <= n <= 31] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP
COMP-5
COMP-X
|
|
16
|
Octaword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 4]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[5 <= n <= 9]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[10 <= n <= 18]
|
COMP
COMP-5 (Alpha, I64)
COMP-X (Alpha, I64)
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[19 <= n <= 31] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP
COMP-5
COMP-X
|
|
16
|
Octaword integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC X(n)
[n <= 2] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP-5
COMP-X
|
|
2
|
Word integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC X(n)
[3 <= n <= 4] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP-5
COMP-X
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC X(n)
[5 <= n <= 8] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP-5
COMP-X
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
INDEX
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
POINTER
|
|
4
|
Longword integer (OpenVMS)
|
|
|
POINTER
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer (Tru64 UNIX)
|
|
|
POINTER-64 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer (OpenVMS Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-CHAR UNSIGNED (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-SHORT UNSIGNED (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-LONG UNSIGNED (Alpha, I64)
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-DOUBLE UNSIGNED (Alpha, I64)
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-CHAR SIGNED (Alpha, I64)
BINARY-CHAR (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-SHORT SIGNED (Alpha, I64)
BINARY-SHORT (Alpha, I64)
|
|
2
|
Word integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-LONG SIGNED (Alpha, I64)
BINARY-LONG (Alpha, I64)
|
|
4
|
Longword integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
BINARY-DOUBLE SIGNED (Alpha, I64)
BINARY-DOUBLE (Alpha, I64)
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
COMP-1
|
|
4
|
F_floating
S_format
2 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
|
Not applicable
|
COMP-2
|
|
8
|
D_floating
G_floating (Alpha, I64)
T_format
2 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
COMP-3
|
|
(n+1)/2
rounded up
|
Packed decimal
1
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)
[n <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
COMP-3
|
|
(n+1)/2
rounded up
|
Packed decimal
|
|
|
PIC X(n)
[n <= 268,435,455]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n
|
ASCII text
|
|
|
PIC A(n)
[n <= 268,435,455]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n
|
ASCII text
|
1The generated code treats this data type as a positive
value in all contexts except when it is a receiving-field operand. In
this case, the compiler stores the absolute value of the source data
item.
2On OpenVMS Alpha and I64 systems, the data type depends on
the /FLOAT qualifier. On Tru64 UNIX systems, it is always S format
for COMP-1, and always T format for COMP-2. Refer to the HP COBOL User Manual
Appendix B, describing compatibility with HP COBOL for OpenVMS VAX for information
on the /FLOAT=IEEE qualifier.
Table 5-13 Scaled Data Items, Allocated Storage, and Data Types
PICTURE
Clause |
USAGE Clause |
SIGN Clause |
Allocated Storage
in Bytes |
Standard
Data Type |
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n+s
|
Right (trailing)
overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
TRAILING
|
n+s
|
Right (trailing)
overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
LEADING
|
n+s
|
Left (leading)
overpunch
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
TRAILING
SEPARATE
|
n+s+1
|
Right (trailing)
separate
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
LEADING
SEPARATE
|
n+s+1
|
Left (leading)
separate
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
DISPLAY
|
|
n+s
|
Unsigned numeric
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 4]
|
COMP
|
|
2
|
Word integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[5 <= (n+s) <= 9]
|
COMP
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[10 <= (n+s) <= 18]
|
COMP
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
1
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[19<= (n+s) <= 31] (Alpha, I64)
|
COMP
|
|
16
|
Octaword integer
1 (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 4]
|
COMP
|
|
2
|
Word integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[5 <= (n+s) <= 9]
|
COMP
|
|
4
|
Longword integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[10 <= (n+s) <= 18]
|
COMP
|
|
8
|
Quadword integer
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[19 <= (n+s) <= 31]
|
COMP
|
|
16
|
Octaword integer (Alpha, I64)
|
|
|
PIC 9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
COMP-3
|
|
(n+s+1)/2
rounded up
|
Packed decimal
1
|
|
|
PIC S9(n)V9(s)
[(n+s) <= 31
(Alpha, I64) or
18 (VAX)]
|
COMP-3
|
|
(n+s+1)/2
rounded up
|
Packed decimal
|
1The generated code treats this data type as a positive
operand in all contexts except when it is a receiving-field operand. In
this case, the compiler stores the absolute value of the data type.
-
The OpenVMS Alpha operating system (as of Version 7.0) and OpenVMS I64
can dynamically allocate data in 64-bit address space. HP COBOL does
not support data in 64-bit address space, but limited use of it may be
made with the USAGE IS POINTER-64 clause on OpenVMS Alpha and I64. You
might need to describe a data item as USAGE IS POINTER-64 if your
program interfaces with an application in another language that
requires a 64-bit pointer. Then you would use the SET statement or a
VALUE clause to assign the address of a static COBOL variable to the
pointer variable. The pointer variable can be passed to a routine whose
interface definition requires a 64-bit pointer.
You can also use an
appropriate system service or the Run-Time Library routine
LIB$GET_VM_64 to allocate data and store the address in the pointer
variable. Because COBOL does not support dynamic allocation, there is
no way to dereference the pointer and access the allocated data.
However, you can pass the pointer to other languages that require a
64-bit pointer in 64-bit address space. <>
|

